Abstract
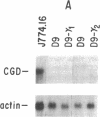
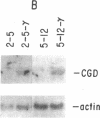
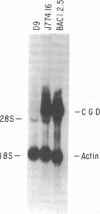
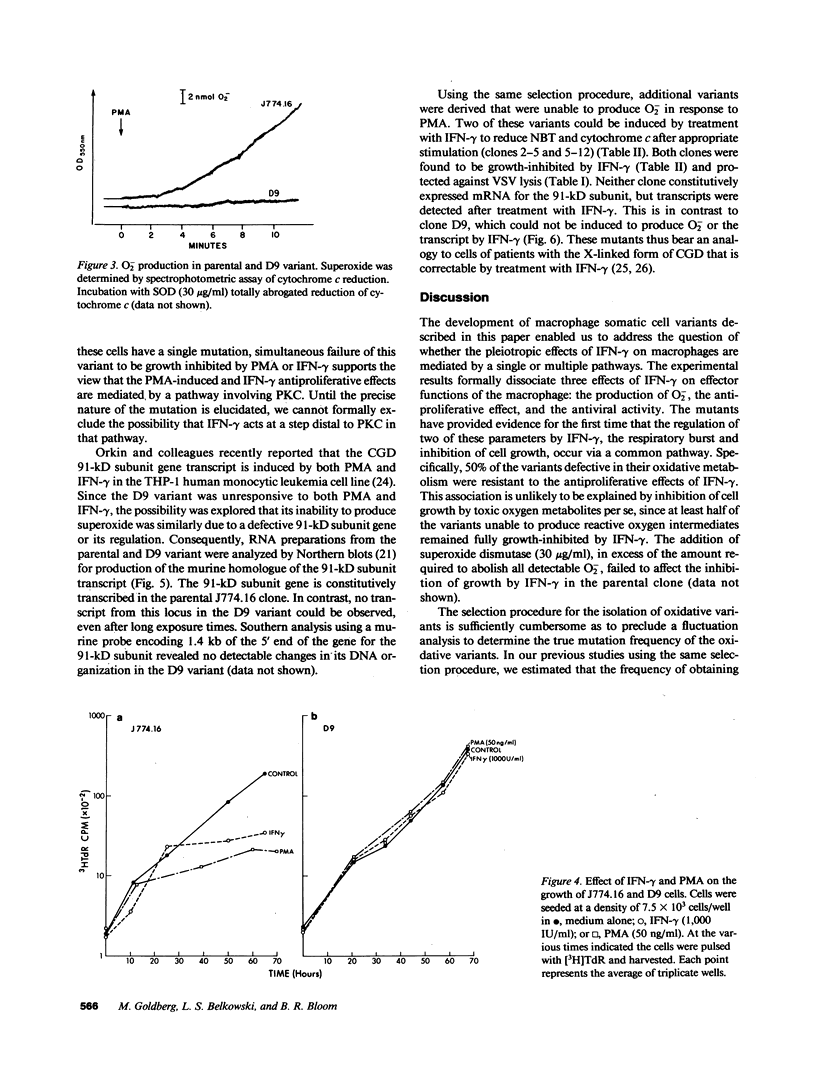
The importance of oxidative cytocidal mechanisms of phagocytic cells in immune protection against microbial pathogens is uniquely revealed by chronic granulomatous disease (CGD), a genetic deficiency disease of man. This cytocidal response in mononuclear phagocytes is principally regulated by IFN-gamma. A somatic cell genetic approach was taken to select oxidative variants from a cloned murine macrophage cell line, J774.16, which formally permitted us to dissociate three regulatory effects of IFN-gamma on these cells: the antiproliferative effect, the antiviral effect, and production of superoxide anion. Half of the variants defective in O-2 production after phorbol myristate acetate stimulation were also resistant to the antiproliferative effects of IFN-gamma. This result suggests that IFN-gamma-induced growth inhibition and production of cytocidal oxygen intermediates are mediated via a common pathway. The somatic cell genetic approach has allowed us to develop in vitro macrophage models for several forms of CGD. One variant characterized in detail, D9, was unable to produce superoxide after stimulation by phorbol esters. At the molecular level, Northern blot analysis revealed that the mRNA encoding the large subunit of the putative CGD gene product, cytochrome b558, was absent in this variant. Another class of variants constitutively unable to produce O-2 or the cytochrome b558 mRNA could be induced to do so by IFN-gamma. These somatic mutants may be useful models in clarifying the role of the CGD gene product and its regulation in the production of cytocidal oxygen intermediates.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bancroft G. J., Schreiber R. D., Bosma G. C., Bosma M. J., Unanue E. R. A T cell-independent mechanism of macrophage activation by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1104–1107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohler M. C., Seger R. A., Mouy R., Vilmer E., Fischer A., Griscelli C. A study of 25 patients with chronic granulomatous disease: a new classification by correlating respiratory burst, cytochrome b, and flavoprotein. J Clin Immunol. 1986 Mar;6(2):136–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00918746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Berkow R. L., Roberts R. L., Shurin S. B., Scott P. J. Chronic granulomatous disease due to a defect in the cytosolic factor required for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase activation. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):606–610. doi: 10.1172/JCI113360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T. Classification of chronic granulomatous disease. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1988 Jun;2(2):241–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damiani G., Kiyotaki C., Soeller W., Sasada M., Peisach J., Bloom B. R. Macrophage variants in oxygen metabolism. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):808–822. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekowitz R. A., Dinauer M. C., Jaffe H. S., Orkin S. H., Newburger P. E. Partial correction of the phagocyte defect in patients with X-linked chronic granulomatous disease by subcutaneous interferon gamma. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jul 21;319(3):146–151. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198807213190305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan X. D., Goldberg M., Bloom B. R. Interferon-gamma-induced transcriptional activation is mediated by protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5122–5125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M., Belkowski L. S., Bloom B. R. Regulation of macrophage growth and antiviral activity by interferon-gamma. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1331–1340. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyre P. M., Morganelli P. M., Miller R. Recombinant immune interferon increases immunoglobulin G Fc receptors on cultured human mononuclear phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):393–397. doi: 10.1172/JCI110980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamers M. N., de Boer M., Meerhof L. J., Weening R. S., Roos D. Complementation in monocyte hybrids revealing genetic heterogeneity in chronic granulomatous disease. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):553–555. doi: 10.1038/307553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. A., Becton D. L., Somers S. D., Gray P. W., Adams D. O. Interferon-gamma modulates protein kinase C activity in murine peritoneal macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1378–1381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes B., Page A. R., Good R. A. Studies of the metabolic activity of leukocytes from patients with a genetic abnormality of phagocytic function. J Clin Invest. 1967 Sep;46(9):1422–1432. doi: 10.1172/JCI105634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Baehner R. L. Chronic granulomatous disease: correlation between pathogenesis and clinical findings. Pediatrics. 1971 Nov;48(5):730–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King D. P., Jones P. P. Induction of Ia and H-2 antigens on a macrophage cell line by immune interferon. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):315–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyotaki C., Bloom B. R. Activation of murine macrophage cell lines. Possible involvement of protein kinases in stimulation of superoxide production. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):923–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyotaki C., Peisach J., Bloom B. R. Oxygen metabolism in cloned macrophage cell lines: glucose dependence of superoxide production, metabolic and spectral analysis. J Immunol. 1984 Feb;132(2):857–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Byrne G. I., Rothermel C. D., Cartelli D. M. Lymphokine enhances oxygen-independent activity against intracellular pathogens. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):234–239. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata Y., Rosen O. M., Makman M. H., Bloom B. R. Biochemical analysis of mutants of a macrophage cell line resistant to the growth-inhibitory activity of interferon. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1342–1347. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Wiebe M. E., Rubin B. Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):670–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Prendergast T. J., Wiebe M. E., Stanley E. R., Platzer E., Remold H. G., Welte K., Rubin B. Y., Murray H. W. Activation of human macrophages. Comparison of other cytokines with interferon-gamma. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):600–605. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newburger P. E., Ezekowitz R. A., Whitney C., Wright J., Orkin S. H. Induction of phagocyte cytochrome b heavy chain gene expression by interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5215–5219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamura N., Curnutte J. T., Roberts R. L., Babior B. M. Relationship of protein phosphorylation to the activation of the respiratory burst in human neutrophils. Defects in the phosphorylation of a group of closely related 48-kDa proteins in two forms of chronic granulomatous disease. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6777–6782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H. Molecular genetics of chronic granulomatous disease. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:277–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkos C. A., Dinauer M. C., Walker L. E., Allen R. A., Jesaitis A. J., Orkin S. H. Primary structure and unique expression of the 22-kilodalton light chain of human neutrophil cytochrome b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3319–3323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sechler J. M., Malech H. L., White C. J., Gallin J. I. Recombinant human interferon-gamma reconstitutes defective phagocyte function in patients with chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4874–4878. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Cross A. R., Garcia R. C., Borregaard N., Valerius N. H., Soothill J. F., Jones O. T. Absence of cytochrome b-245 in chronic granulomatous disease. A multicenter European evaluation of its incidence and relevance. N Engl J Med. 1983 Feb 3;308(5):245–251. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198302033080503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeg P. S., Moore R. N., Johnson H. M., Oppenheim J. J. Regulation of murine macrophage Ia antigen expression by a lymphokine with immune interferon activity. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1780–1793. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Tanowitz H., Bloom B. R. Growth of Trypanosoma cruzi in a cloned macrophage cell line and in a variant defective in oxygen metabolism. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1322–1331. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1322-1331.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel S. N., Havell E. A., Spitalny G. L. Monoclonal antibody-mediated inhibition of interferon-gamma-induced macrophage antiviral resistance and surface antigen expression. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):2917–2923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkman D. J., Buescher E. S., Gallin J. I., Fauci A. S. B cell lines as models for inherited phagocytic diseases: abnormal superoxide generation in chronic granulomatous disease and giant granules in Chediak-Higashi syndrome. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3006–3009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]