Abstract
We have studied rat vascular smooth muscle (VSM) cells in culture for the presence of key elements of the glandular kallikrein-kinin system. Direct radioimmunoassay (RIA) using antiserum against rat urinary kallikrein detected a glandular kallikrein-like enzyme (GKLE) in VSM cells and in media. VSM homogenates and culture media had kininogenase activity, generating kinins from dog kininogen. About half of the GKLE was enzymatically inactive which could be activated with trypsin. Kininogenase activity was inhibited completely by aprotinin but only 20% by soybean trypsin inhibitor (SBTI). Trypsin liberated kinins from homogenates and media, demonstrating that VSM cells contain kininogen. Homogenates and media rapidly degrade bradykinin. GKLE, kininogen, and bradykininase activity were all present in VSM cells grown in defined media that contain no serum, thus eliminating any contamination or artefacts from fetal calf serum in standard culture media. Blood vessels of the rat have been reported to contain GKLE. Our observations indicate that GKLE is synthesized by VSM cells, not deposited from plasma. Furthermore, VSM cells synthesize kininogen and bradykininase(s), the other key elements of the glandular kallikrein-kinin system. Thus it is possible that the system functions as an autocoid mechanism that regulates local vascular tone.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashley P. L., MacDonald R. J. Tissue-specific expression of kallikrein-related genes in the rat. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 13;24(17):4520–4527. doi: 10.1021/bi00338a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
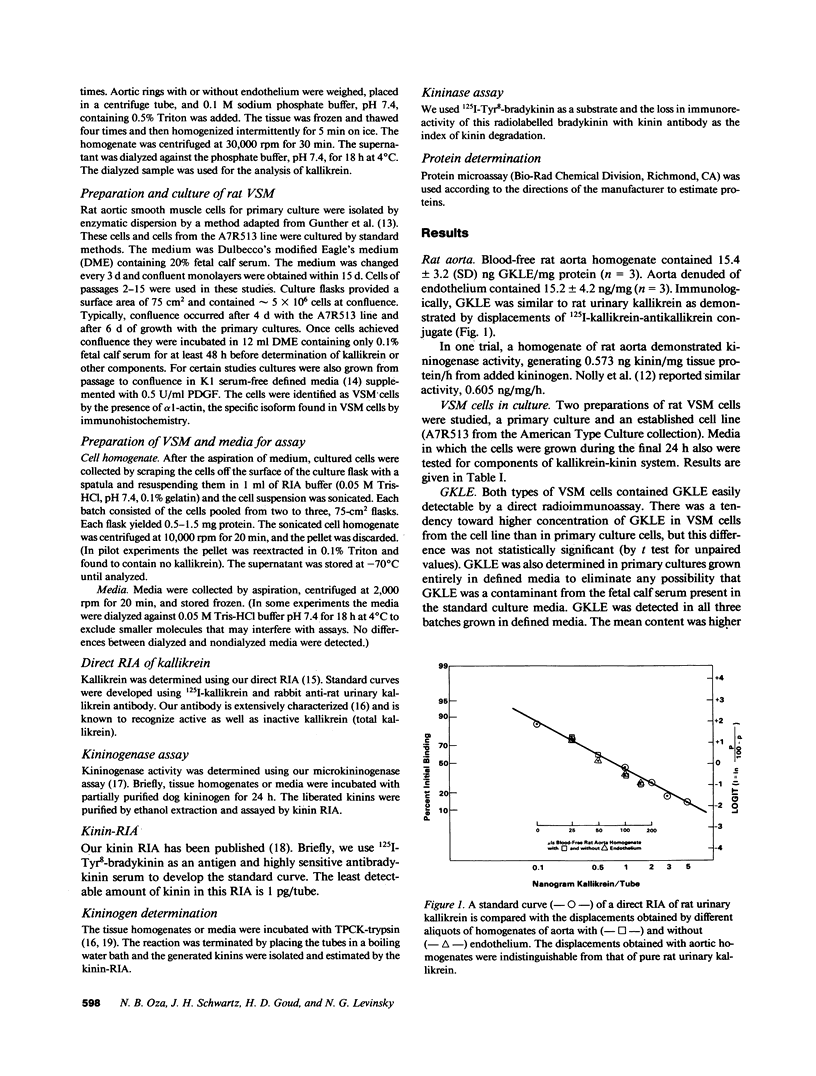
- Beasley D., Oza N. B., Levinsky N. G. Micropuncture localization of kallikrein secretion in the rat nephron. Kidney Int. 1987 Jul;32(1):26–30. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell M. A., Wilson W. H., Shooter E. M. The relationship between glandular kallikrein and growth factor-processing proteases of mouse submaxillary gland. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7287–7294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardin A. D., Witt K. R., Chao J., Margolius H. S., Donaldson V. H., Jackson R. L. Degradation of apolipoprotein B-100 of human plasma low density lipoproteins by tissue and plasma kallikreins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8522–8528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao J., Chao L., Margolius H. S. Identification of a kallikrein-like latent serine protease in human erythrocyte membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jun 15;121(2):722–729. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90241-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao J., Woodley C., Chao L., Margolius H. S. Identification of tissue kallikrein in brain and in the cell-free translation product encoded by brain mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15173–15178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currie M. G., Geller D. M., Chao J., Margolius H. S., Needleman P. Kallikrein activation of a high molecular weight atrial peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Apr 30;120(2):461–466. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91276-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunther S., Alexander R. W., Atkinson W. J., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Functional angiotensin II receptors in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):289–298. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hial V., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Peyton M. P., Wilcox G. M., Pisano J. J. Angiotensin metabolism by cultured human vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells. Microvasc Res. 1979 May;17(3 Pt 1):314–329. doi: 10.1016/s0026-2862(79)80007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Alles W. P. Urinary kallikrein: a physiological regulator of epithelial Na+ absorption. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5345–5348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberthal W., Oza N. B., Bernard D. B., Levinsky N. G. The effect of cations on the activity of human urinary kallikrein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10827–10830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald R. J., Margolius H. S., Erdös E. G. Molecular biology of tissue kallikrein. Biochem J. 1988 Jul 15;253(2):313–321. doi: 10.1042/bj2530313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolly H., Scicli A. G., Scicli G., Carretero O. A. Characterization of a kininogenase from rat vascular tissue resembling tissue kallikrein. Circ Res. 1985 Jun;56(6):816–821. doi: 10.1161/01.res.56.6.816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oza N. B. A new direct radioimmunoassay of rat urinary kininogen. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 May 15;37(10):1965–1969. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90543-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oza N. B. Development of a rat urinary kallikrein-binding radioimmunoassay and identification of homologous enzyme in plasma. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1981 Oct;19(10):1033–1038. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1981.19.10.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey J. E., Atlas S. A., Laragh J. H., Oza N. B., Ryan J. W. Human urinary kallikrein converts inactive to active renin and is a possible physiological activator of renin. Nature. 1978 Sep 14;275(5676):144–145. doi: 10.1038/275144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaggio A. M., Schwartz J. H., Bengele H. H., Gordon F. D., Alexander E. A. Mechanisms of H+ secretion by inner medullary collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 2):F391–F400. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.3.F391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimojo N., Chao J., Chao L., Margolius H. S., Mayfield R. K. Identification and characterization of a tissue kallikrein in rat skeletal muscles. Biochem J. 1987 May 1;243(3):773–778. doi: 10.1042/bj2430773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg M. S., Oza N. B., Levinsky N. G. Components of the kallikrein-kinin system in rat urine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Jun 1;33(11):1779–1782. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90349-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoi O. O., Seldin D. C., Spragg J., Pinkus G. S., Austen K. F. Sequential cleavage of proinsulin by human pancreatic kallikrein and a human pancreatic kininase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3612–3616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



