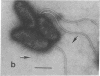
Abstract
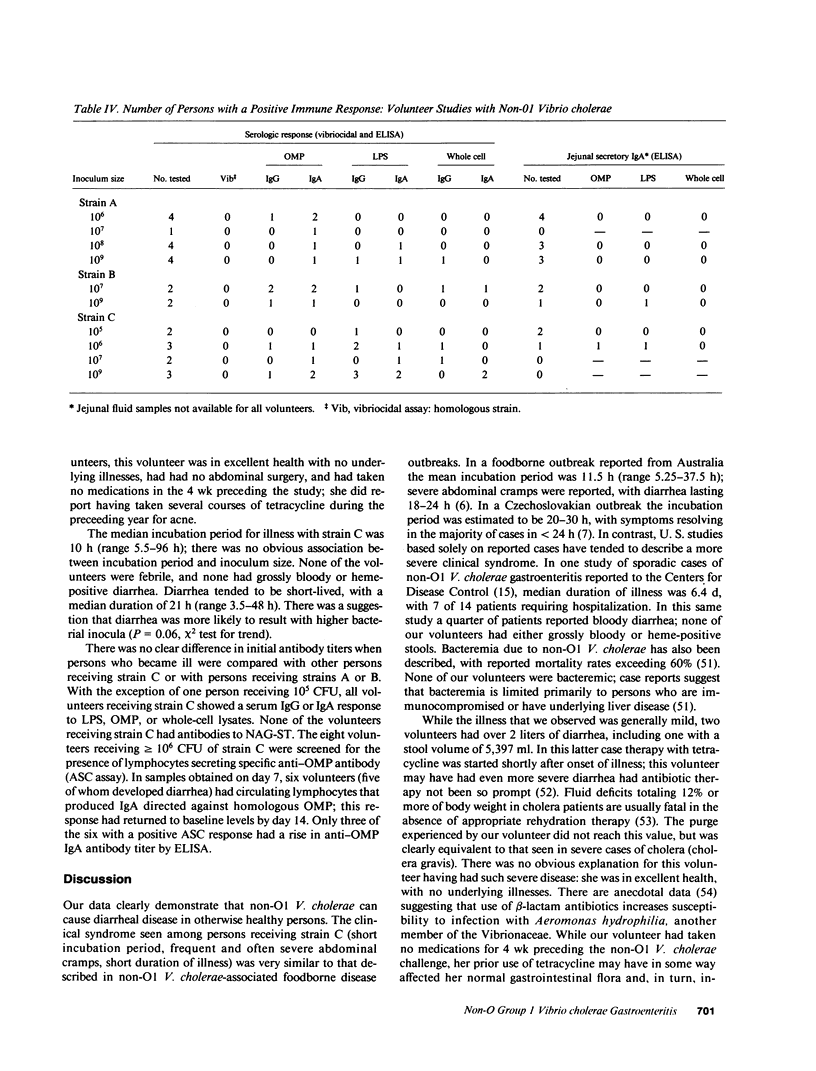
In this study, 27 volunteers received one of three non-O group 1 Vibrio cholerae strains in doses as high as 10(9) CFU. Only one strain (strain C) caused diarrhea: this strain was able to colonize the gastrointestinal tract, and produced a heat-stable enterotoxin (NAG-ST). Diarrhea was not seen with a strain (strain A) that colonized the intestine but did not produce NAG-ST, nor with a strain (strain B) that produced NAG-ST but did not colonize. Persons receiving strain C had diarrhea and abdominal cramps. Diarrheal stool volumes ranged from 154 to 5,397 ml; stool samples from the patient having 5,397 ml of diarrhea were tested and found to contain NAG-ST. The median incubation period for illness was 10 h. There was a suggestion that occurrence of diarrhea was dependent on inoculum size. Immune responses to homologous outer membrane proteins, lipopolysaccharide, and whole-cell lysates were demonstrable with all three strains. Our data demonstrate that V. cholerae of O groups other than 1 are able to cause severe diarrheal disease. However, not all strains are pathogenic for humans: virulence of strain C may be dependent on its ability both to colonize the intestine and to produce a toxin such as NAG-ST.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldová E., Láznicková K., Stepánková E., Lietava J. Isolation of nonagglutinable vibrios from an enteritis outbreak in Czechoslovakia. J Infect Dis. 1968 Feb;118(1):25–31. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arita M., Takeda T., Honda T., Miwatani T. Purification and characterization of Vibrio cholerae non-O1 heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):45–49. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.45-49.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benavente L., Gotuzzo E., Guerra J., Grados O., Guerra H., Bravo N. Diagnosis of typhoid fever using a string capsule device. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1984;78(3):404–406. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(84)90134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. E., Levine M. M., Clements M. L., Young C. R., Svennerholm A. M., Holmgren J. Protective efficacy in humans of killed whole-vibrio oral cholera vaccine with and without the B subunit of cholera toxin. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1116–1120. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1116-1120.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. E., Merson M. H., Rowe B., Taylor P. R., Abdul Alim A. R., Gross R. J., Sack D. A. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea: acquired immunity and transmission in an endemic area. Bull World Health Organ. 1981;59(2):263–268. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bäck E., Ljunggren A., Smith H., Jr Non-cholera Vibrios in Sweden. Lancet. 1974 Apr 20;1(7860):723–724. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92921-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens J. D., Sack D. A., Harris J. R., Chakraborty J., Khan M. R., Stanton B. F., Kay B. A., Khan M. U., Yunus M., Atkinson W. Field trial of oral cholera vaccines in Bangladesh. Lancet. 1986 Jul 19;2(8499):124–127. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91944-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements M. L., Levine M. M., Young C. R., Black R. E., Lim Y. L., Robins-Browne R. M., Craig J. P. Magnitude, kinetics, and duration of vibriocidal antibody responses in North Americans after ingestion of Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1982 Apr;145(4):465–473. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.4.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dakin W. P., Howell D. J., Sutton R. G., O'Keefe M. F., Thomas P. Gastroenteritis due to non-agglutinable (non-cholera) vibrios. Med J Aust. 1974 Sep 28;2(13):487–490. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1974.tb70935.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darfeuille-Michaud A., Forestier C., Joly B., Cluzel R. Identification of a nonfimbrial adhesive factor of an enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strain. Infect Immun. 1986 May;52(2):468–475. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.2.468-475.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta-Roy K., Banerjee K., De S. P., Ghose A. C. Comparative study of expression of hemagglutinins, hemolysins, and enterotoxins by clinical and environmental isolates of non-O1 Vibrio cholerae in relation to their enteropathogenicity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):875–879. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.875-879.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., Moon H. W., Whipp S. C. Detection of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin with the use of adrenal cells in tissue culture. Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):334–336. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutt A. K., Alwi S., Velauthan T. A shellfish-borne cholera outbreak in Malaysia. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1971;65(6):815–818. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(71)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkow S. Molecular Koch's postulates applied to microbial pathogenicity. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jul-Aug;10 (Suppl 2):S274–S276. doi: 10.1093/cid/10.supplement_2.s274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch M. J., Valdespino J. L., Wells J. G., Perez-Perez G., Arjona F., Sepulveda A., Bessudo D., Blake P. A. Non-01 Vibrio cholerae infections in Cancun, Mexico. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Mar;36(2):393–397. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1987.36.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest B. D. Identification of an intestinal immune response using peripheral blood lymphocytes. Lancet. 1988 Jan 16;1(8577):81–83. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90284-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Brunton L. L., Schnaitman T. C., Rebhun L. I., Gilman A. G. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate and alteration of Chinese hamster ovary cell morphology: a rapid, sensitive in vitro assay for the enterotoxins of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1974 Aug;10(2):320–327. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.2.320-327.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L., Stevens J. B., Craven J. A. A study of Escherichia coli strains isolated from pigs with gastro-intestinal disease. Can J Comp Med. 1971 Jul;35(3):258–266. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. H., Vial P. A., Kaper J. B., Mekalanos J. J., Levine M. M. Morphological studies on fimbriae expressed by Vibrio cholerae 01. Microb Pathog. 1988 Apr;4(4):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90086-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanchalay S., Seriwatana J., Echeverria P., Holmgren J., Tirapat C., Moseley S. L., Taylor D. N. Non-O1 Vibrio cholerae in Thailand: homology with cloned cholera toxin genes. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Feb;21(2):288–289. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.2.288-289.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington D. A., Hall R. H., Losonsky G., Mekalanos J. J., Taylor R. K., Levine M. M. Toxin, toxin-coregulated pili, and the toxR regulon are essential for Vibrio cholerae pathogenesis in humans. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1487–1492. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoge C. W., Watsky D., Peeler R. N., Libonati J. P., Israel E., Morris J. G., Jr Epidemiology and spectrum of Vibrio infections in a Chesapeake Bay community. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):985–993. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Schell W. L., Fanning G. R., Wachsmuth I. K., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Blake P. A., Brenner D. J., Farmer J. J., 3rd Aeromonas intestinal infections in the United States. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Nov;105(5):683–689. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-5-683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Arita M., Takeda T., Yoh M., Miwatani T. Non-O1 Vibrio cholerae produces two newly identified toxins related to Vibrio parahaemolyticus haemolysin and Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Lancet. 1985 Jul 20;2(8447):163–164. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90277-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Kasemsuksakul K., Oguchi T., Kohda M., Miwatani T. Production and partial characterization of pili on non-O1 Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):217–218. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose Y., Yamamoto K., Nakasone N., Tanabe M. J., Takeda T., Miwatani T., Iwanaga M. Enterotoxicity of El Tor-like hemolysin of non-O1 Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1090–1093. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1090-1093.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston K. H., Holmes K. K., Gotschlich E. C. The serological classification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. I. Isolation of the outer membrane complex responsible for serotypic specificity. J Exp Med. 1976 Apr 1;143(4):741–758. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.4.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantele A. M., Takanen R., Arvilommi H. Immune response to acute diarrhea seen as circulating antibody-secreting cells. J Infect Dis. 1988 Nov;158(5):1011–1016. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.5.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Nataro J. P., Roberts N. C., Siebeling R. J., Bradford H. B. Molecular epidemiology of non-O1 Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio mimicus in the U.S. Gulf Coast region. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):652–654. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.652-654.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J., Lockman H., Colwell R. R., Joseph S. W. Ecology, serology, and enterotoxin production of Vibrio cholerae in Chesapeake Bay. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jan;37(1):91–103. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.1.91-103.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay B. A., Sack R. B., Spira W. M., Guerra H. E., Guerrero C. E., Chaparro E., Yi A. E., Salazar-Lindo E., Chea E., Wachsmuth I. K. Vibrio cholerae non-O1 isolated from five people with diarrhoea in Lima. Lancet. 1984 Jan 28;1(8370):218–218. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92133-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Black R. E., Clements M. L., Lanata C., Sears S., Honda T., Young C. R., Finkelstein R. A. Evaluation in humans of attenuated Vibrio cholerae El Tor Ogawa strain Texas Star-SR as a live oral vaccine. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):515–522. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.515-522.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Caplan E. S., Waterman D., Cash R. A., Hornick R. B., Snyder M. J. Diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli that produce only heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Jul;17(1):78–82. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.1.78-82.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Escherichia coli infections. N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 15;313(7):445–447. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508153130710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea: enterotoxigenic, enteropathogenic, enteroinvasive, enterohemorrhagic, and enteroadherent. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):377–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Kaper J. B., Herrington D., Losonsky G., Morris J. G., Clements M. L., Black R. E., Tall B., Hall R. Volunteer studies of deletion mutants of Vibrio cholerae O1 prepared by recombinant techniques. Infect Immun. 1988 Jan;56(1):161–167. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.1.161-167.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Nalin D. R., Hoover D. L., Bergquist E. J., Hornick R. B., Young C. R. Immunity to enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):729–736. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.729-736.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M., Ristaino P., Marley G., Smyth C., Knutton S., Boedeker E., Black R., Young C., Clements M. L., Cheney C. Coli surface antigens 1 and 3 of colonization factor antigen II-positive enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: morphology, purification, and immune responses in humans. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):409–420. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.409-420.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCINTYRE O. R., FEELEY J. C., GREENOUGH W. B., 3rd, BENENSON A. S., HASSAN S. I., SAAD A. DIARRHEA CAUSED BY NON-CHOLERA VIBRIOS. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1965 May;14:412–418. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1965.14.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCardell B. A., Madden J. M., Shah D. B. Isolation and characterization of a cytolysin produced by Vibrio cholerae serogroup non-O1. Can J Microbiol. 1985 Aug;31(8):711–720. doi: 10.1139/m85-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr, Black R. E. Cholera and other vibrioses in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 7;312(6):343–350. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502073120604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr, Wilson R., Davis B. R., Wachsmuth I. K., Riddle C. F., Wathen H. G., Pollard R. A., Blake P. A. Non-O group 1 Vibrio cholerae gastroenteritis in the United States: clinical, epidemiologic, and laboratory characteristics of sporadic cases. Ann Intern Med. 1981 May;94(5):656–658. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-5-656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Ishibashi M., Takeda Y., Kaper J. B. Detection of the thermostable direct hemolysin gene and related DNA sequences in Vibrio parahaemolyticus and other vibrio species by the DNA colony hybridization test. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):481–486. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.481-486.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Chen M. E., Holmes R. K., Kaper J., Levine M. M. Environmental and human isolates of Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio parahaemolyticus produce a Shigella dysenteriae 1 (Shiga)-like cytotoxin. Lancet. 1984 Jan 14;1(8368):77–78. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson K., Parker C. D. Identification and characterization of Vibrio cholerae surface proteins by radioiodination. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):87–93. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.87-93.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder R. W., Wachsmuth I. K., Buxton A. E., Evans D. G., DuPont H. L., Mason E., Barrett F. F. Infantile diarrhea produced by heat-stable enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. N Engl J Med. 1976 Oct 14;295(16):849–853. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197610142951601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safrin S., Morris J. G., Jr, Adams M., Pons V., Jacobs R., Conte J. E., Jr Non-O:1 Vibrio cholerae bacteremia: case report and review. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Sep-Oct;10(5):1012–1017. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.5.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakazaki R., Shimada T. Serovars of Vibrio cholerae identified during 1970-1975. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1977 Oct;30(5):279–282. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.30.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears S. D., Richardson K., Young C., Parker C. D., Levine M. M. Evaluation of the human immune response to outer membrane proteins of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):439–444. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.439-444.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shehabi A. A., Drexler H., Richardson S. H. Virulence mechanisms associated with clinical isolates of non-O1 Vibrio cholerae. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Apr;261(2):232–239. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80040-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shehabi A. A., Richardson S. H. Enterotoxigenicity of clinical isolates of non-O1 Vibrio cholerae. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1985 Nov;260(3):311–318. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(85)80019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. L., Jr Serotyping of non-cholera vibrios. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jul;10(1):85–90. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.1.85-90.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spira W. M., Fedorka-Cray P. J., Pettebone P. Colonization of the rabbit small intestine by clinical and environmental isolates of non-O1 Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio mimicus. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1175–1183. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1175-1183.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao T., Shimonishi Y., Kobayashi M., Nishimura O., Arita M., Takeda T., Honda T., Miwatani T. Amino acid sequence of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Vibrio cholerae non-01. FEBS Lett. 1985 Dec 2;193(2):250–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80163-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao T., Tominaga N., Yoshimura S., Shimonishi Y., Hara S., Inoue T., Miyama A. Isolation, primary structure and synthesis of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Yersinia enterocolitica. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 1;152(1):199–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. K., Miller V. L., Furlong D. B., Mekalanos J. J. Use of phoA gene fusions to identify a pilus colonization factor coordinately regulated with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2833–2837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twedt R. M., Madden J. M., Hunt J. M., Francis D. W., Peeler J. T., Duran A. P., Hebert W. O., McCay S. G., Roderick C. N., Spite G. T. Characterization of Vibrio cholerae isolated from oysters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jun;41(6):1475–1478. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.6.1475-1478.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace C. K., Anderson P. N., Brown T. C., Khanra S. R., Lewis G. W., Pierce N. F., Sanyal S. N., Segre G. V., Waldman R. H. Optimal antibiotic therapy in cholera. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;39(2):239–245. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. C., Morris J. G., Jr, Maneval D. R., Jr, Richardson K., Kaper J. B. Cloning of the cytotoxin-hemolysin gene of Vibrio vulnificus. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):922–924. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.922-924.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Ichinose Y., Nakasone N., Tanabe M., Nagahama M., Sakurai J., Iwanaga M. Identity of hemolysins produced by Vibrio cholerae non-O1 and V. cholerae O1, biotype El Tor. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):927–931. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.927-931.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Takeda Y., Miwatani T., Craig J. P. Evidence that a non-O1 Vibrio cholerae produces enterotoxin that is similar but not identical to cholera enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):896–901. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.896-901.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Shawi N., Thewaini A. J. Non-agglutinable vibrios isolated in the 1966 epidemic of cholera in Irag. Bull World Health Organ. 1969;40(1):163–166. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]