Abstract
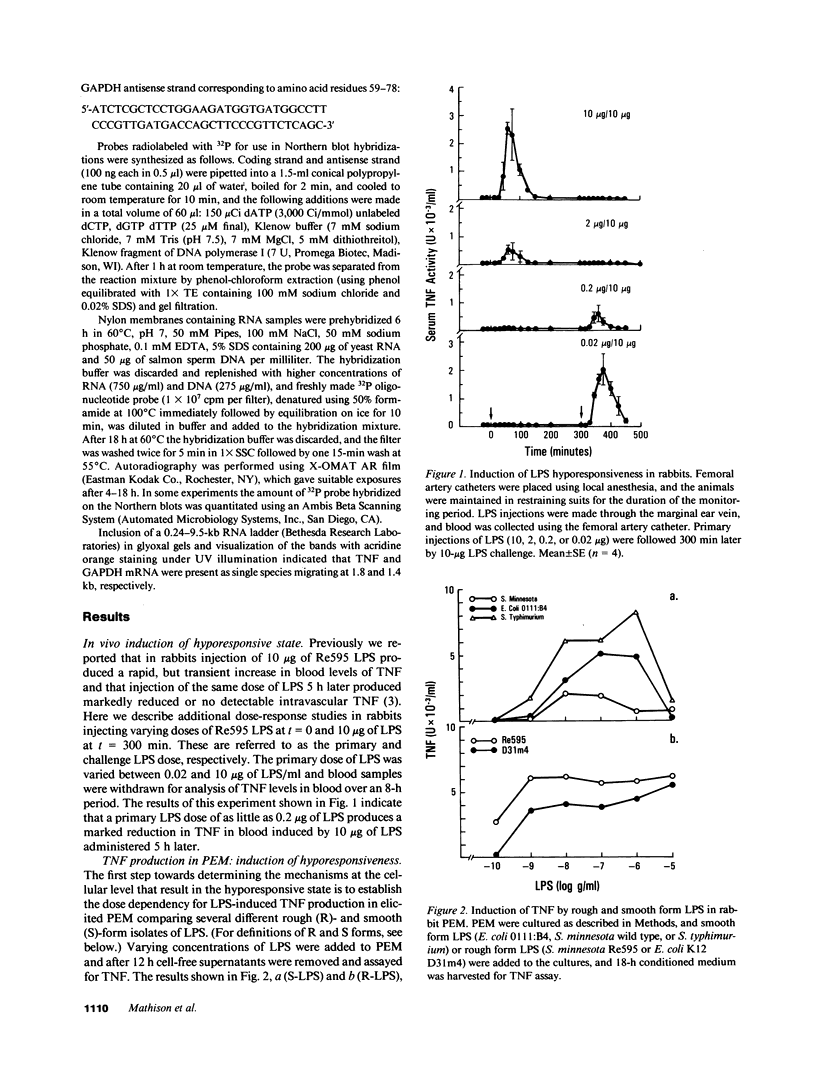
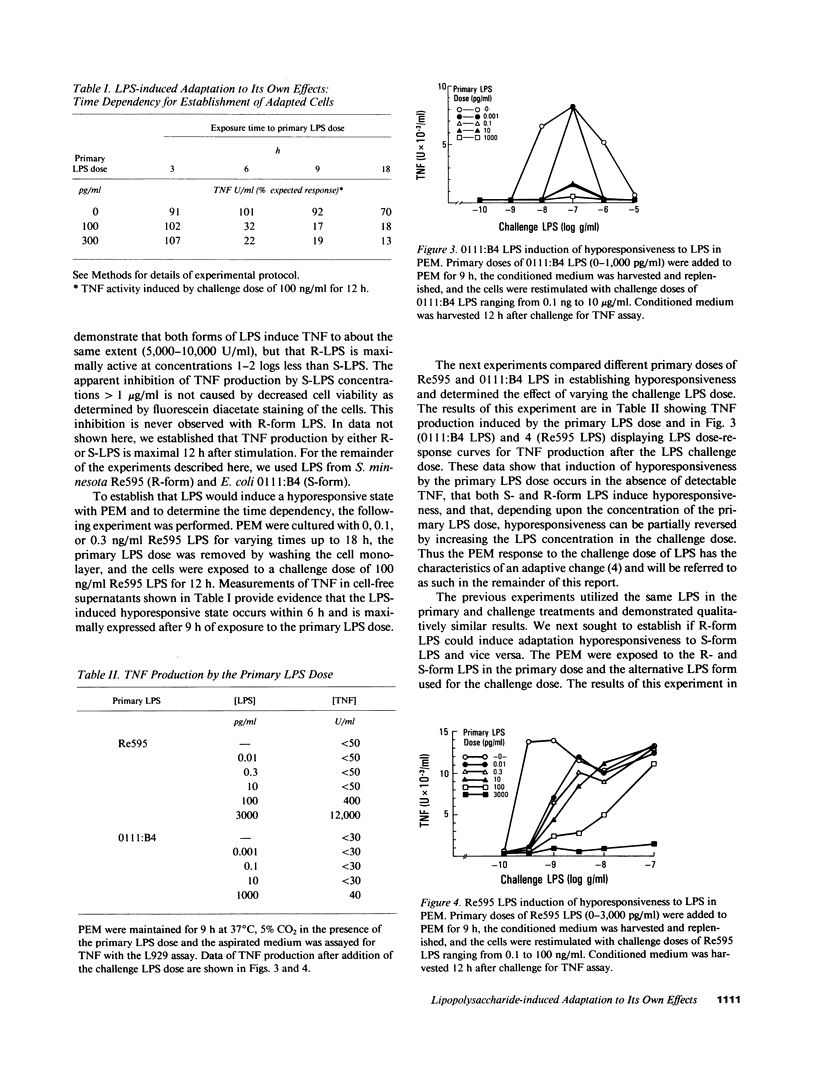
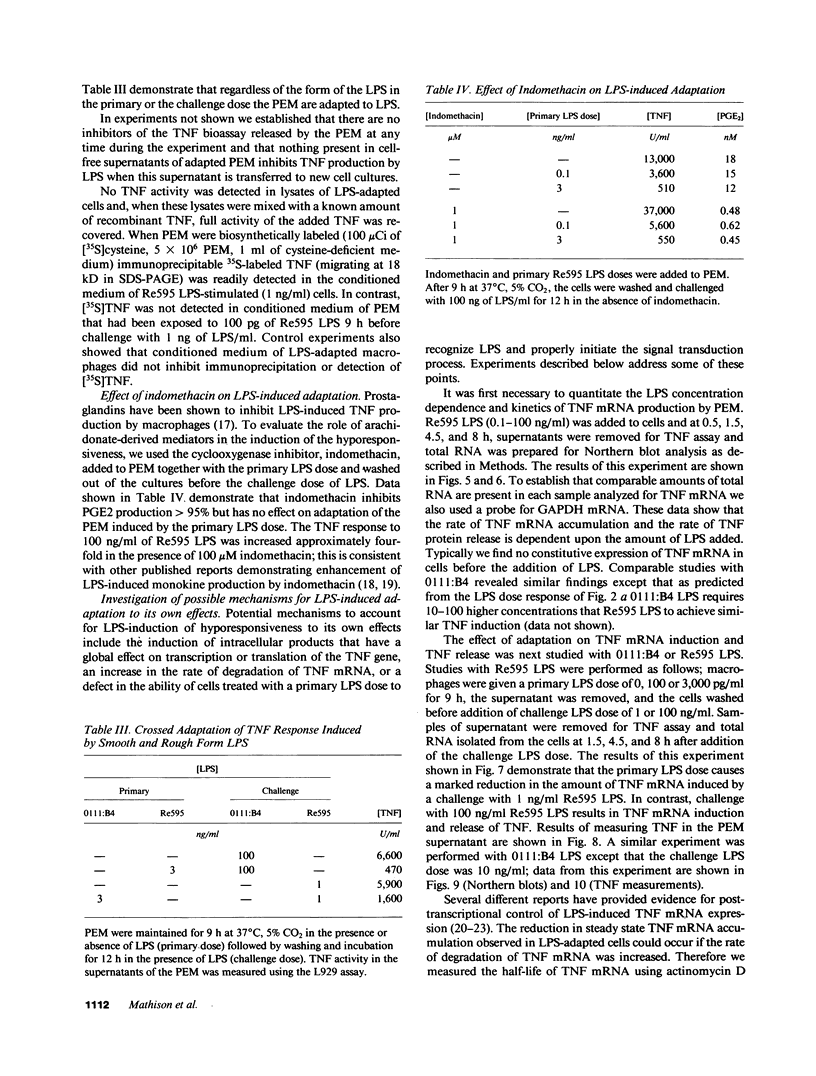
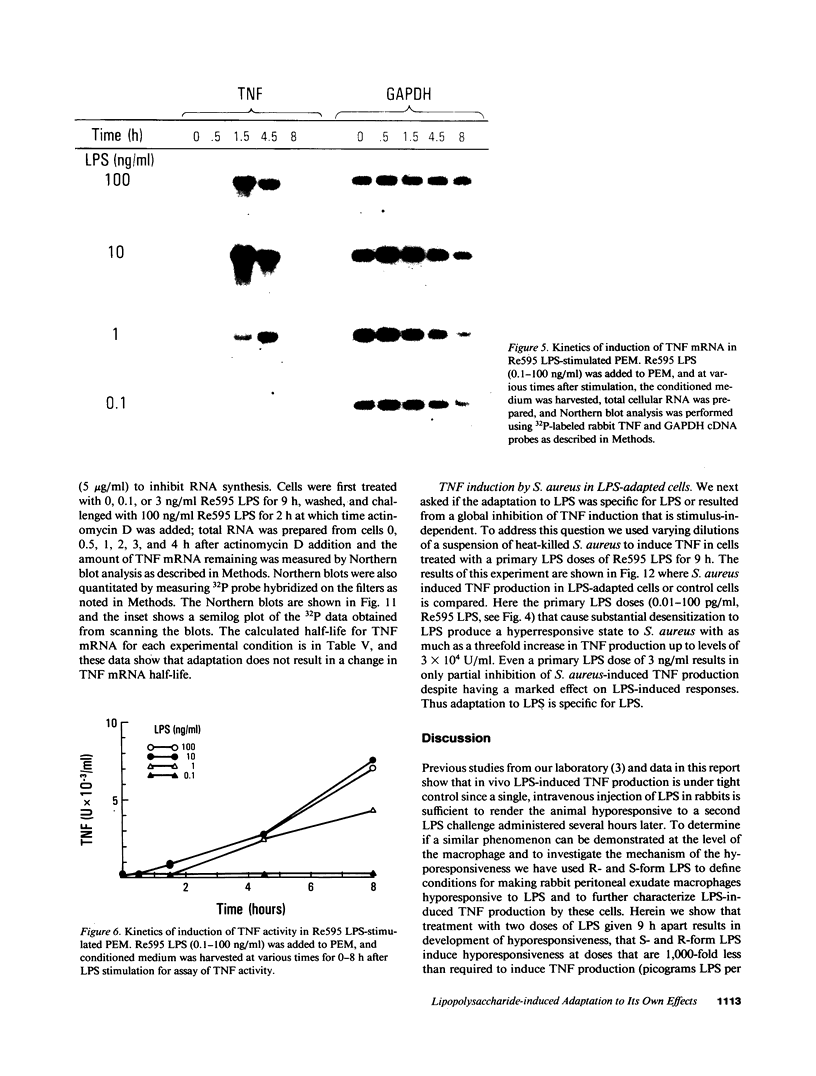
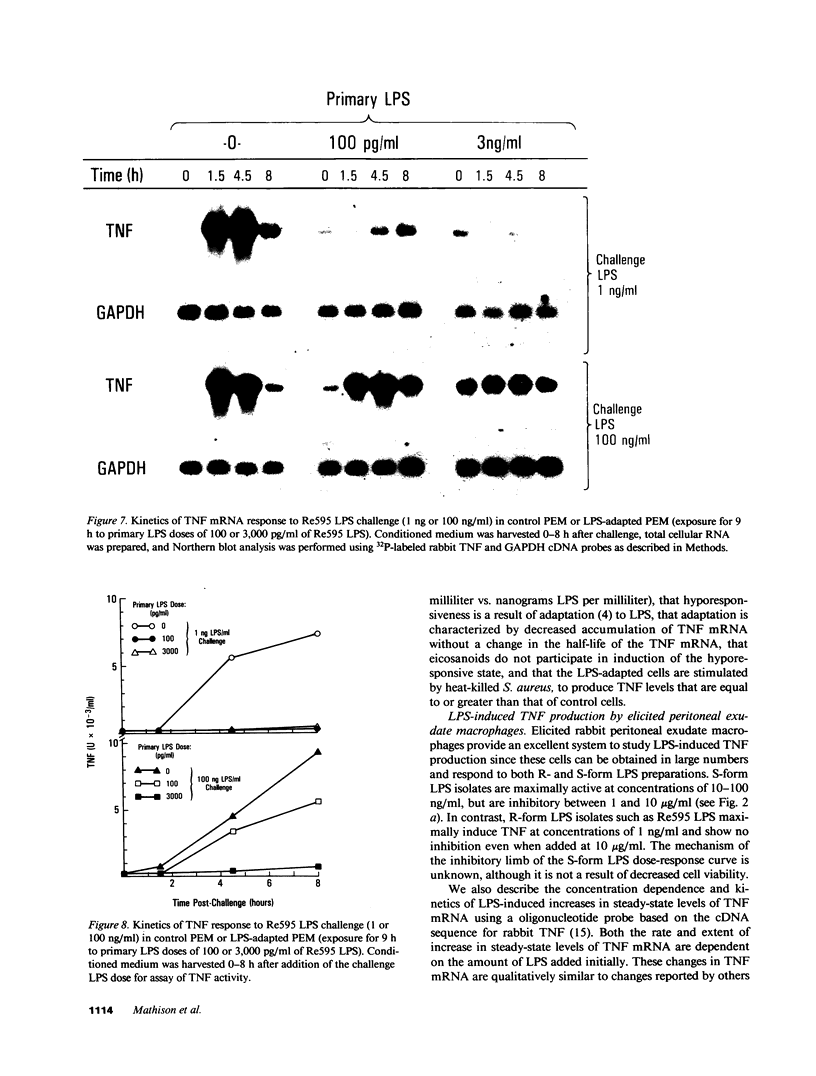
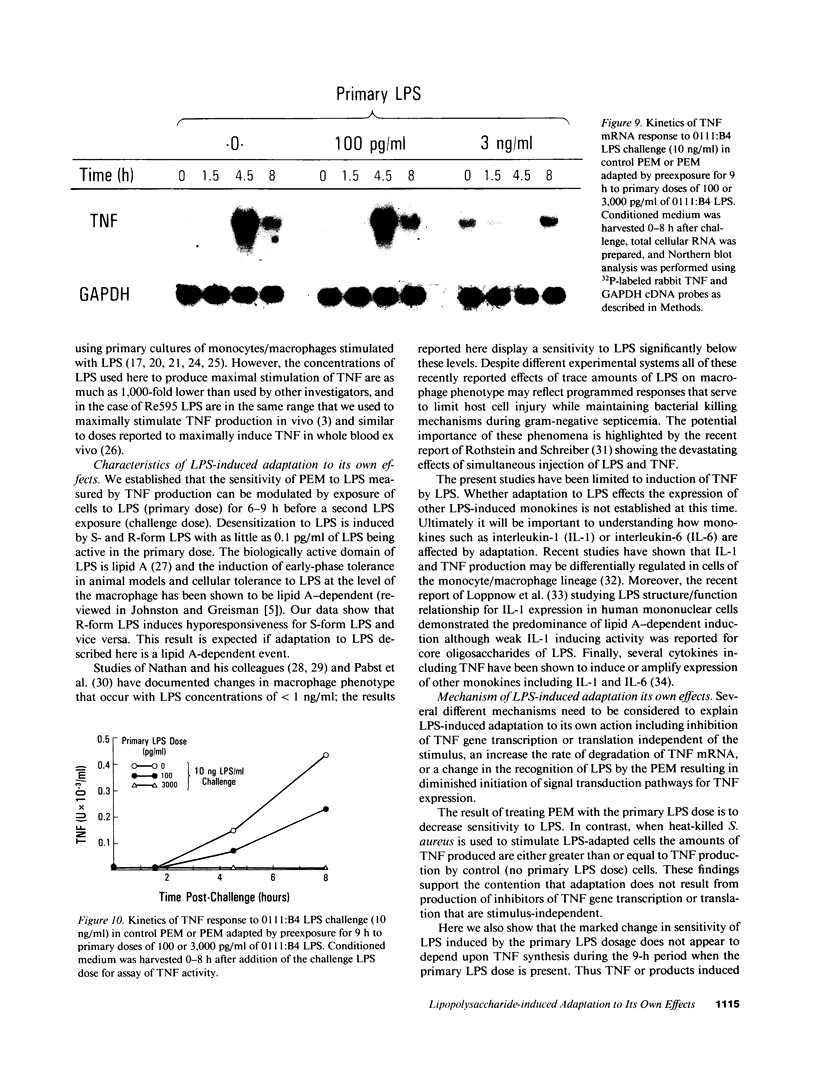
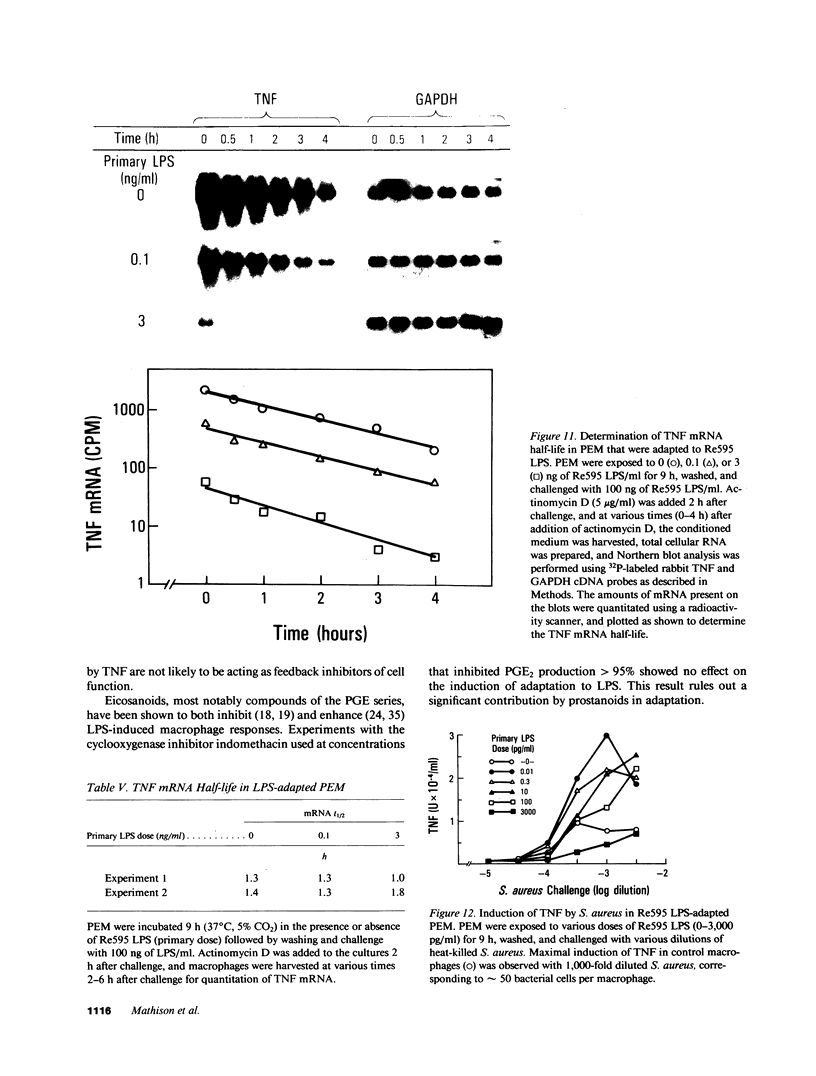
These experiments provide an explanation for the observation that two intravenous injections of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) spaced 5 h apart in rabbits cause tumor necrosis factor/cachectin (TNF) levels to rise in the blood only after the first LPS injection. Herein we show that treatment of elicited peritoneal exudate rabbit macrophages (PEM) with two doses of LPS given 9 h apart results in a marked reduction in TNF production by the second LPS exposure. This state of hyporesponsiveness is a result of adaptation to LPS, is induced by LPS concentrations that are 1,000-fold less than required to induce TNF production (picograms vs. nanograms), is characterized by a decrease in LPS-induced TNF mRNA without any change in TNF mRNA half-life, is not changed by including indomethacin in cultures, and is specific for LPS since LPS-adapted cells display a TNF response to heat-killed Staphylococcus aureus that is at least as good as that observed in control PEM.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler B., Krochin N., Milsark I. W., Luedke C., Cerami A. Control of cachectin (tumor necrosis factor) synthesis: mechanisms of endotoxin resistance. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3754653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Thompson P., Keyes J., Hagerty K., Crawford D. Assay of a ribonuclease that preferentially hydrolyses mRNAs containing cytokine-derived UA-rich instability sequences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 16;152(3):973–980. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80379-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Tkacenko V., Milsark I., Krochin N., Cerami A. Effect of gamma interferon on cachectin expression by mononuclear phagocytes. Reversal of the lpsd (endotoxin resistance) phenotype. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1791–1796. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchett S. K., Weaver W. M., Westall J. A., Larsen A., Kronheim S., Wilson C. B. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor/cachectin and IL-1 secretion in human mononuclear phagocytes. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3473–3481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael G. G., McMaster G. K. The analysis of nucleic acids in gels using glyoxal and acridine orange. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):380–391. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desch C. E., Kovach N. L., Present W., Broyles C., Harlan J. M. Production of human tumor necrosis factor from whole blood ex vivo. Lymphokine Res. 1989 Summer;8(2):141–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A. H., Nathan C. F. Trace levels of bacterial lipopolysaccharide prevent interferon-gamma or tumor necrosis factor-alpha from enhancing mouse peritoneal macrophage respiratory burst capacity. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):1971–1977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A. H., Sanchez E., Srimal S., Nathan C. F. Macrophages rapidly internalize their tumor necrosis factor receptors in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3924–3929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker D. L., Stovroff M. C., Merino M. J., Norton J. A. Tolerance to tumor necrosis factor in rats and the relationship to endotoxin tolerance and toxicity. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):95–105. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudenberg M. A., Galanos C. Induction of tolerance to lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-D-galactosamine lethality by pretreatment with LPS is mediated by macrophages. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1352–1357. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1352-1357.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas J. G., Thiel C., Blömer K., Weiss E. H., Riethmüller G., Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W. Downregulation of tumor necrosis factor expression in the human Mono-Mac-6 cell line by lipopolysaccharide. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Jul;46(1):11–14. doi: 10.1002/jlb.46.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampton R. Y., Golenbock D. T., Raetz C. R. Lipid A binding sites in membranes of macrophage tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14802–14807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslberger A., Sayers T., Reiter H., Chung J., Schütze E. Reduced release of TNF and PCA from macrophages of tolerant mice. Circ Shock. 1988 Oct;26(2):185–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Yamamoto S., Kuroda S., Sakamoto H., Kajihara J., Kiyota T., Hayashi H., Kato M., Seko M. Molecular cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the cDNA coding for rabbit tumor necrosis factor. DNA. 1986 Apr;5(2):149–156. doi: 10.1089/dna.1986.5.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen P. J., Dinarello C. A., Strom T. B. Prostaglandins posttranscriptionally inhibit monocyte expression of interleukin 1 activity by increasing intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 15;137(10):3189–3194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr, Goldbeter A., Stock J. B. Amplification and adaptation in regulatory and sensory systems. Science. 1982 Jul 16;217(4556):220–225. doi: 10.1126/science.7089556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Chensue S. W., Phan S. H. Prostaglandins as endogenous mediators of interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):186–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Spengler M., May M. A., Spengler R., Larrick J., Remick D. Prostaglandin E2 regulates macrophage-derived tumor necrosis factor gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5380–5384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen N. E., Sullivan R. Interaction between endotoxin and human monocytes: characteristics of the binding of 3H-labeled lipopolysaccharide and 51Cr-labeled lipid A before and after the induction of endotoxin tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3491–3495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei M. G., Morrison D. C. Specific endotoxic lipopolysaccharide-binding proteins on murine splenocytes. I. Detection of lipopolysaccharide-binding sites on splenocytes and splenocyte subpopulations. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):996–1005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lister M. D., Glaser K. B., Ulevitch R. J., Dennis E. A. Inhibition studies on the membrane-associated phospholipase A2 in vitro and prostaglandin E2 production in vivo of the macrophage-like P388D1 cell. Effects of manoalide, 7,7-dimethyl-5,8-eicosadienoic acid, and p-bromophenacyl bromide. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8520–8528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loppnow H., Brade H., Dürrbaum I., Dinarello C. A., Kusumoto S., Rietschel E. T., Flad H. D. IL-1 induction-capacity of defined lipopolysaccharide partial structures. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3229–3238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Wolfson E., Ulevitch R. J. Participation of tumor necrosis factor in the mediation of gram negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced injury in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1925–1937. doi: 10.1172/JCI113540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh J. K., Jablons D. M., Mulé J. J., Nordan R. P., Rudikoff S., Lotze M. T., Rosenberg S. A. In vivo induction of IL-6 by administration of exogenous cytokines and detection of de novo serum levels of IL-6 in tumor-bearing mice. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):162–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Männel D. N., Falk W. Optimal induction of tumor necrosis factor production in human monocytes requires complete S-form lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):1953–1958. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.1953-1958.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabst M. J., Hedegaard H. B., Johnston R. B., Jr Cultured human monocytes require exposure to bacterial products to maintain an optimal oxygen radical response. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):123–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney S. D., Herlihy W. C., Schimmel P. A new troponin T and cDNA clones for 13 different muscle proteins, found by shotgun sequencing. Nature. 1983 Apr 21;302(5910):718–721. doi: 10.1038/302718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renz H., Gong J. H., Schmidt A., Nain M., Gemsa D. Release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha from macrophages. Enhancement and suppression are dose-dependently regulated by prostaglandin E2 and cyclic nucleotides. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2388–2393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein J. L., Schreiber H. Synergy between tumor necrosis factor and bacterial products causes hemorrhagic necrosis and lethal shock in normal mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):607–611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotman B., Papermaster B. W. Membrane properties of living mammalian cells as studied by enzymatic hydrolysis of fluorogenic esters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):134–141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sariban E., Imamura K., Luebbers R., Kufe D. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of tumor necrosis factor gene expression in human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1506–1510. doi: 10.1172/JCI113482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor exerts endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine control of inflammatory responses. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1269–1277. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spengler R. N., Spengler M. L., Strieter R. M., Remick D. G., Larrick J. W., Kunkel S. L. Modulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene expression. Desensitization of prostaglandin E2-induced suppression. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 15;142(12):4346–4350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virca G. D., Kim S. Y., Glaser K. B., Ulevitch R. J. Lipopolysaccharide induces hyporesponsiveness to its own action in RAW 264.7 cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21951–21956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]