Abstract
The T84 human colonic epithelial cell line retains the ability to produce secretagogue-responsive monolayer cultures with high transepithelial resistance when grown and maintained on collagen-coated permeable supports in media supplemented with 5% newborn calf serum. The addition of highly purified insulin to the basolateral but not the apical membrane side of established monolayers caused the transepithelial resistance to decline more than eightfold over a 3-4-d period. By comparing the transepithelial flux of 22Na with that of the extracellular space marker, [3H]mannitol, the decline in electrical resistance was shown to be due solely to an effect on tight junction-mediated paracellular permeability. The effect of insulin was dose dependent with a half-maximal effect at 3.9 ng/ml (approximately 0.7 nM) and fully reversible over a 10-d time course. Simultaneous addition of 2 microM cycloheximide prevented the insulin-induced decline in resistance; in fact, this combination caused a significant increase in electrical resistance. There was no effect on the short-circuit current response of insulin-treated monolayers to secretagogues so long as media was changed daily. While no gross morphological changes were apparent, there did appear to be a subtle condensation of the perijunctional actin ring as visualized using rhodamine-labeled phalloidin. These results demonstrate that insulin modulates the permeability of the occluding junction in T84 cell monolayers through a receptor mediated process which probably involves changes in protein synthesis and cytoskeletal structure. Insulin was also shown to produce similar effects on two other intestinal epithelial cell lines.
Full text
PDF


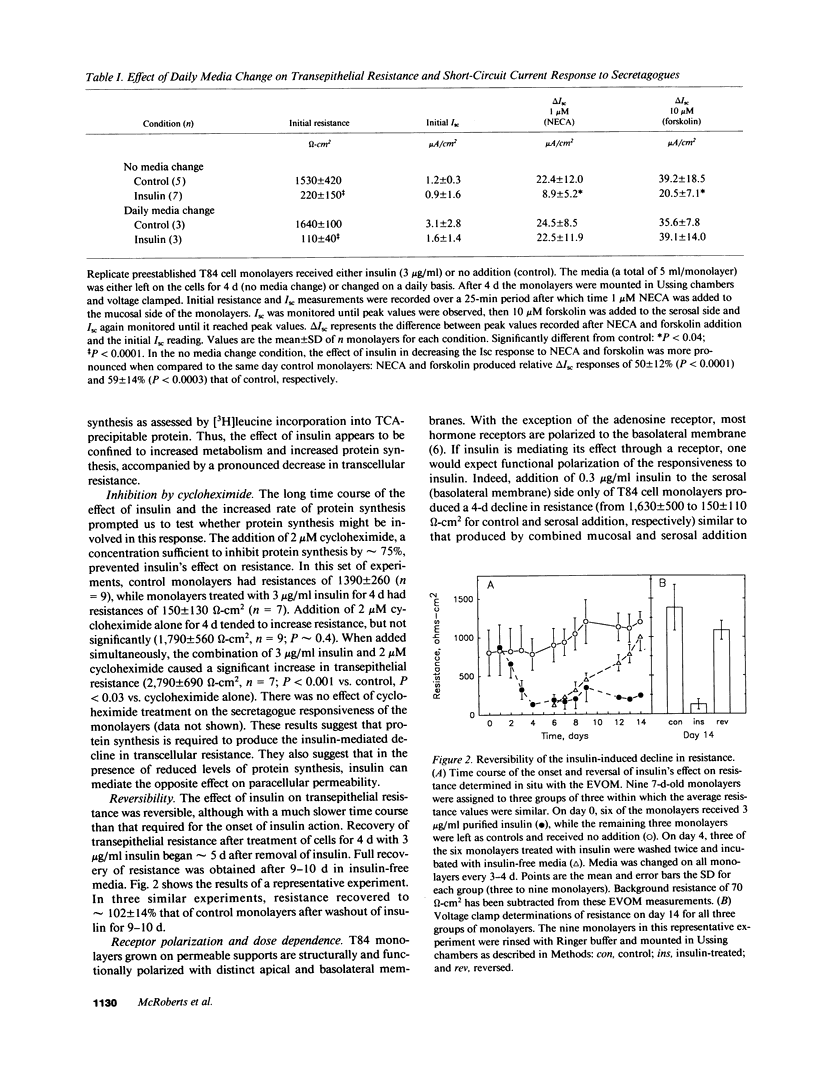



Images in this article
Selected References
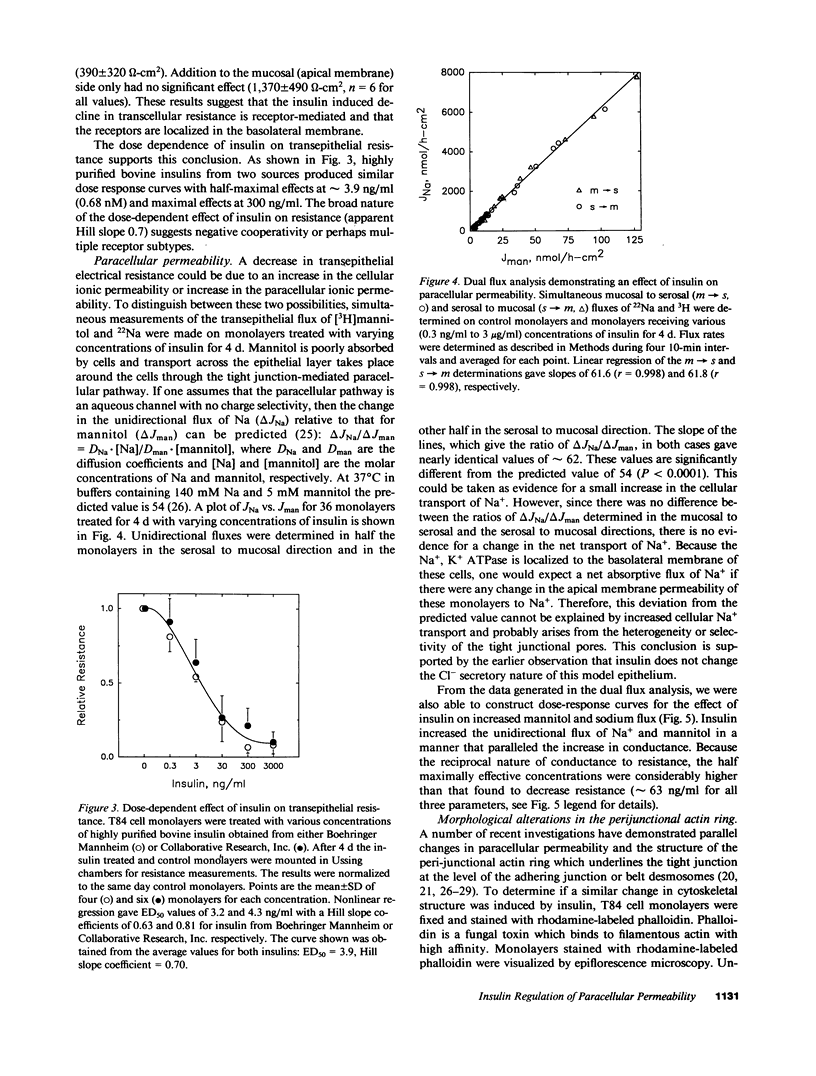
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar R. S., Boes M., Dake B. L., Booth B. A., Henley S. A., Sandra A. Insulin, insulin-like growth factors, and vascular endothelium. Am J Med. 1988 Nov 28;85(5A):59–70. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90398-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes D., Sato G. Serum-free cell culture: a unifying approach. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):649–655. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90540-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett K. E., Huott P. A., Shah S. S., Dharmsathaphorn K., Wasserman S. I. Differing effects of apical and basolateral adenosine on colonic epithelial cell line T84. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 1):C197–C203. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.1.C197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civan M. M., Peterson-Yantorno K., O'Brien T. G. Insulin and phorbol ester stimulate conductive Na+ transport through a common pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):963–967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M., Singer I. Insulin-mediated Na+ transport in the toad urinary bladder. Am J Physiol. 1977 Mar;232(3):F270–F277. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.232.3.F270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson D. C. Na and Cl transport across the isolated turtle colon: parallel pathways for transmural ion movement. J Membr Biol. 1977 Dec 15;37(3-4):213–233. doi: 10.1007/BF01940933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Cooke C. R., Andres R., Faloona G. R., Davis P. J. The effect of insulin on renal handling of sodium, potassium, calcium, and phosphate in man. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):845–855. doi: 10.1172/JCI107996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., Mandel K. G., Masui H., McRoberts J. A. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-induced chloride secretion by a colonic epithelial cell line. Direct participation of a basolaterally localized Na+,K+,Cl- cotransport system. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):462–471. doi: 10.1172/JCI111721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K., McRoberts J. A., Mandel K. G., Tisdale L. D., Masui H. A human colonic tumor cell line that maintains vectorial electrolyte transport. Am J Physiol. 1984 Feb;246(2 Pt 1):G204–G208. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.246.2.G204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffey M. E., Hainau B., Ho S., Bentzel C. J. Regulation of epithelial tight junction permeability by cyclic AMP. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):451–453. doi: 10.1038/294451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidelman M. L., May J. M., Biber T. U., Watlington C. O. Insulin stimulation of Na+ transport and glucose metabolism in cultured kidney cells. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jan;242(1):C121–C123. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.242.1.C121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidelman M. L., Watlington C. O. Effect of aldosterone and insulin on mannitol, Na+ and Cl- fluxes in cultured epithelia of renal origin (A6): evidence for increased permeability in the paracellular pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 12;931(2):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90208-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Usher P., Moses A. C. Monoclonal antibody to the type I insulin-like growth factor (IGF-I) receptor blocks IGF-I receptor-mediated DNA synthesis: clarification of the mitogenic mechanisms of IGF-I and insulin in human skin fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):664–668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R., Schmid C., Schwander J., Zapf J. Actions of insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:443–467. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo-Payet N., Hugon J. S. Insulin receptors in isolated adult mouse intestinal cells: studies in vivo and in organ culture. Endocrinology. 1984 May;114(5):1885–1892. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-5-1885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht G., Pothoulakis C., LaMont J. T., Madara J. L. Clostridium difficile toxin A perturbs cytoskeletal structure and tight junction permeability of cultured human intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Clin Invest. 1988 Nov;82(5):1516–1524. doi: 10.1172/JCI113760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill B. T., Whatley S. A simple, rapid microassay for DNA. FEBS Lett. 1975 Aug 1;56(1):20–23. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80102-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Barenberg D., Carlson S. Effects of cytochalasin D on occluding junctions of intestinal absorptive cells: further evidence that the cytoskeleton may influence paracellular permeability and junctional charge selectivity. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Dharmsathaphorn K. Occluding junction structure-function relationships in a cultured epithelial monolayer. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2124–2133. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Moore R., Carlson S. Alteration of intestinal tight junction structure and permeability by cytoskeletal contraction. Am J Physiol. 1987 Dec;253(6 Pt 1):C854–C861. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.6.C854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Stafford J., Barenberg D., Carlson S. Functional coupling of tight junctions and microfilaments in T84 monolayers. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 1):G416–G423. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.254.3.G416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Stafford J., Dharmsathaphorn K., Carlson S. Structural analysis of a human intestinal epithelial cell line. Gastroenterology. 1987 May;92(5 Pt 1):1133–1145. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(87)91069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Stafford J. Interferon-gamma directly affects barrier function of cultured intestinal epithelial monolayers. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):724–727. doi: 10.1172/JCI113938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
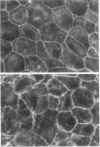
- Madara J. L. Tight junction dynamics: is paracellular transport regulated? Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):497–498. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90562-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather J. P., Sato G. H. The growth of mouse melanoma cells in hormone-supplemented, serum-free medium. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Apr;120(1):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90549-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin J. M., O'Brien T. G. Effects of tumor promoters on LLC-PK1 renal epithelial tight junctions and transepithelial fluxes. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):C597–C602. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.4.C597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami H., Masui H. Hormonal control of human colon carcinoma cell growth in serum-free medium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3464–3468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palant C. E., Duffey M. E., Mookerjee B. K., Ho S., Bentzel C. J. Ca2+ regulation of tight-junction permeability and structure in Necturus gallbladder. Am J Physiol. 1983 Sep;245(3):C203–C212. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.3.C203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petruson B., Hansson H. A., Petruson K. Insulin-like growth factor I is a possible pathogenic mechanism in nasal polyps. Acta Otolaryngol. 1988 Jul-Aug;106(1-2):156–160. doi: 10.3109/00016488809107384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser C. G., Sankaran L., Hennighausen L., Topper Y. J. Comparison of the roles of insulin and insulin-like growth factor I in casein gene expression and in the development of alpha-lactalbumin and glucose transport activities in the mouse mammary epithelial cell. Endocrinology. 1987 Apr;120(4):1411–1416. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-4-1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochat T., Casale J., Hunninghake G. W., Peterson M. W. Neutrophil cathepsin G increases permeability of cultured type II pneumocytes. Am J Physiol. 1988 Nov;255(5 Pt 1):C603–C611. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.5.C603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rom W. N., Basset P., Fells G. A., Nukiwa T., Trapnell B. C., Crysal R. G. Alveolar macrophages release an insulin-like growth factor I-type molecule. J Clin Invest. 1988 Nov;82(5):1685–1693. doi: 10.1172/JCI113781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Winter M., Shasby S. S. Oxidants and conductance of cultured epithelial cell monolayers: inositol phospholipid hydrolysis. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 1):C781–C788. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.6.C781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele-Perkins G., Turner J., Edman J. C., Hari J., Pierce S. B., Stover C., Rutter W. J., Roth R. A. Expression and characterization of a functional human insulin-like growth factor I receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11486–11492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verspohl E. J., Roth R. A., Vigneri R., Goldfine I. D. Dual regulation of glycogen metabolism by insulin and insulin-like growth factors in human hepatoma cells (HEP-G2). Analysis with an anti-receptor monoclonal antibody. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1436–1443. doi: 10.1172/JCI111555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M. J., Smith P. L., Fromm M., Frizzell R. A. Crypts are the site of intestinal fluid and electrolyte secretion. Science. 1982 Dec 17;218(4578):1219–1221. doi: 10.1126/science.6293054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]