Abstract
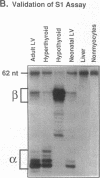
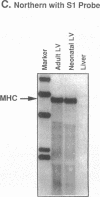
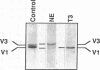
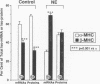
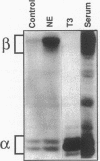
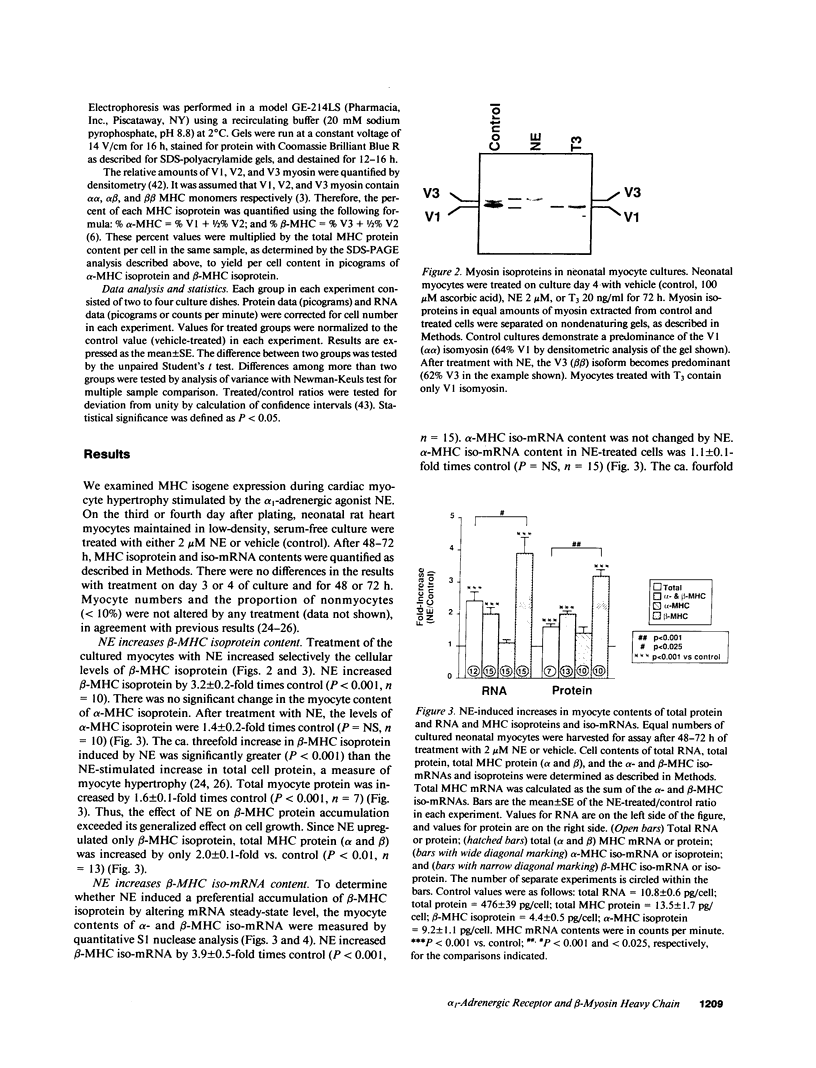
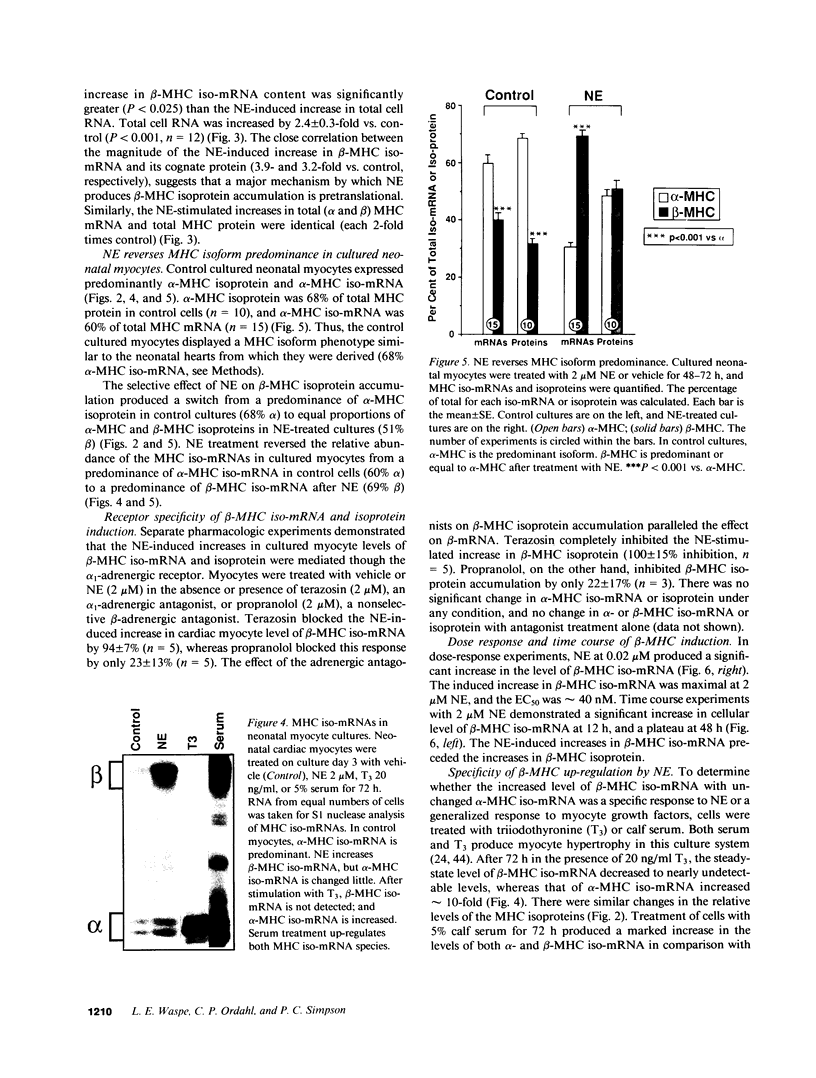
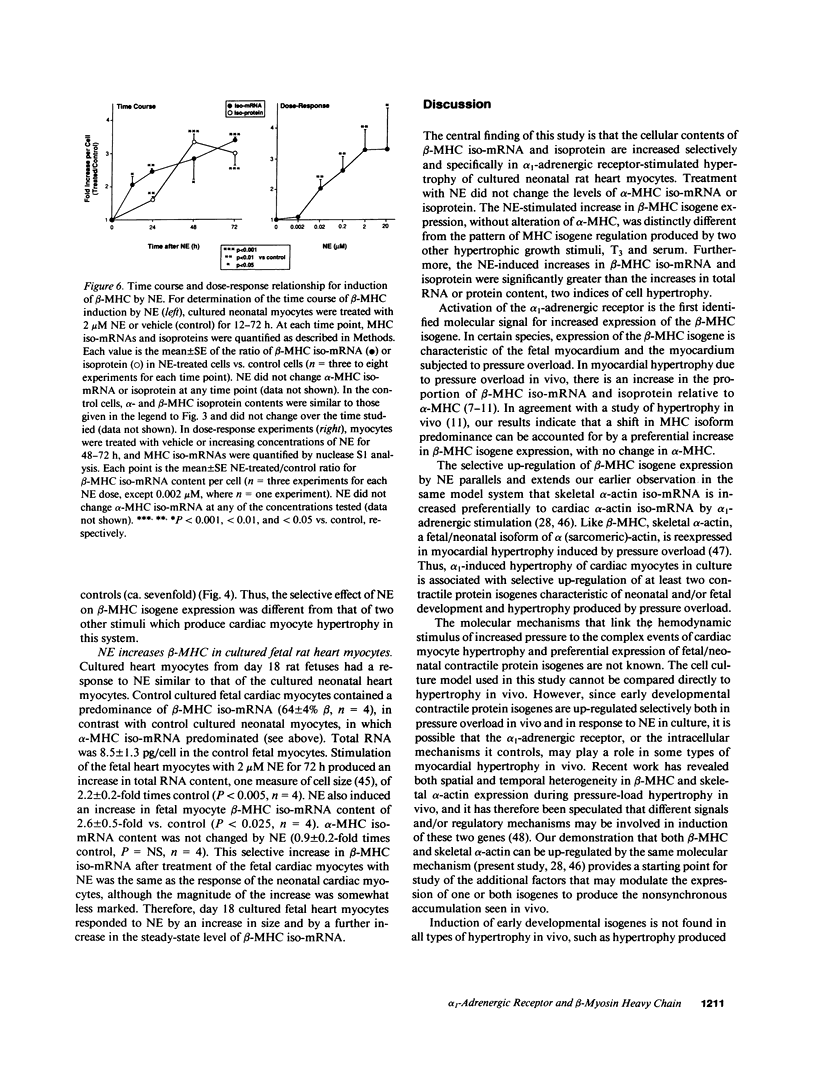
Cardiac hypertrophy produced in vivo by pressure overload is characterized by selective up-regulation of the fetal/neonatal beta-cardiac myosin heavy chain (MHC) isogene. However, a molecular signal for beta-MHC isogene induction has not been identified. We examined cardiac MHC isogene expression in a cell culture model for hypertrophy. alpha-MHC and beta-MHC iso-protein and iso-mRNA levels in cultured cardiac myocytes were quantified during hypertrophy stimulated by the alpha 1-adrenergic agonist, norepinephrine (NE). beta-MHC iso-protein content was increased 3.2-fold vs. control (P less than 0.001), whereas alpha-MHC isoprotein content was not changed significantly (1.4-fold vs. control, P = NS). MHC iso-mRNA levels were quantified by nuclease S1 analysis, using a single oligonucleotide probe. NE increased beta-MHC iso-mRNA content by 3.9-fold vs. control (P less than 0.001), but there was no change in alpha-MHC iso-mRNA (1.1-fold vs. control, P = NS). The NE-stimulated increase in beta-MHC iso-mRNA preceded in time the increase in beta-MHC isoprotein accumulation. The EC50 for NE induction of beta-MHC was 40 nM, and pharmacologic experiments indicated alpha 1-adrenergic receptor specificity. alpha-MHC isogene expression was predominant in control myocytes (68% alpha-isoprotein and 60% alpha-iso-mRNA). In contrast, beta-MHC expression was equal to alpha-MHC or predominant after treatment with NE (51% beta-isoprotein and 69% beta-iso-mRNA). Thus, alpha 1-adrenergic receptor stimulation increases the cellular contents of beta-MHC iso-mRNA and beta-MHC isoprotein during hypertrophy of cultured neonatal rat cardiac myocytes, but does not change the levels of alpha-MHC iso-mRNA or isoprotein. The effect on beta-MHC is mediated primarily at the level of mRNA steady-state level (pretranslational). Activation of the alpha 1-adrenergic receptor is the first identified molecular signal for increased beta-MHC isogene expression in a model of cardiac hypertrophy.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Nageotte R., Chambraud B., Rougeon F. Mouse immunoglobulin genes: a bacterial plasmid containing the entire coding sequence for a pre-gamma 2a heavy chain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1231–1241. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baserga R. Growth in size and cell DNA replication. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Mar;151(1):1–5. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67986-5_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besterman J. M., Duronio V., Cuatrecasas P. Rapid formation of diacylglycerol from phosphatidylcholine: a pathway for generation of a second messenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6785–6789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishopric N. H., Simpson P. C., Ordahl C. P. Induction of the skeletal alpha-actin gene in alpha 1-adrenoceptor-mediated hypertrophy of rat cardiac myocytes. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1194–1199. doi: 10.1172/JCI113179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Bos T. J., Admon A., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K., Tjian R. Human proto-oncogene c-jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2825349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Buxton I. L., Brunton L. L. Alpha 1-adrenergic and muscarinic cholinergic stimulation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis in adult rat cardiomyocytes. Circ Res. 1985 Oct;57(4):532–537. doi: 10.1161/01.res.57.4.532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chizzonite R. A., Zak R. Regulation of myosin isoenzyme composition in fetal and neonatal rat ventricle by endogenous thyroid hormones. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12628–12632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsholtz H. P., Mangalam H. J., Potter E., Albert V. R., Supowit S., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Two different cis-active elements transfer the transcriptional effects of both EGF and phorbol esters. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1552–1557. doi: 10.1126/science.3491428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett A. W., Sinha A. M., Umeda P. K., Jakovcic S., Rabinowitz M., Zak R. Regulation of myosin synthesis by thyroid hormone: relative change in the alpha- and beta-myosin heavy chain mRNA levels in rabbit heart. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 10;23(8):1596–1599. doi: 10.1021/bi00303a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin L. A., Moeller M. The mechanism of recovery of hepatic T4-5'-deiodinase during glucose-refeeding: role of glucagon and insulin. Metabolism. 1983 Jun;32(6):543–551. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(83)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Bahl J. J., Markham B. E., Roeske W. R., Morkin E. Hormonal regulation of myosin heavy chain and alpha-actin gene expression in cultured fetal rat heart myocytes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13316–13322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Markham B. E., Morkin E. Effects of thyroid hormone on alpha-actin and myosin heavy chain gene expression in cardiac and skeletal muscles of the rat: measurement of mRNA content using synthetic oligonucleotide probes. Circ Res. 1986 Aug;59(2):194–201. doi: 10.1161/01.res.59.2.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrich C. J., Simpson P. C. Differential acute and chronic response of protein kinase C in cultured neonatal rat heart myocytes to alpha 1-adrenergic and phorbol ester stimulation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1988 Dec;20(12):1081–1085. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(88)90588-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. F., McGrath P. A., Hale P. T. Electrophoretic analysis of multiple forms of rat cardiac myosin: effects of hypophysectomy and thyroxine replacement. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1978 Nov;10(11):1053–1076. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(78)90401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. Y., McGrath P. A., White R. I. Electrophoretic analysis of multiple forms of myosin in fast-twitch and slow-twitch muscles of the chick. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):87–95. doi: 10.1042/bj1570087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holubarsch C., Goulette R. P., Litten R. Z., Martin B. J., Mulieri L. A., Alpert N. R. The economy of isometric force development, myosin isoenzyme pattern and myofibrillar ATPase activity in normal and hypothyroid rat myocardium. Circ Res. 1985 Jan;56(1):78–86. doi: 10.1161/01.res.56.1.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Chiu R., Karin M. Transcription factor AP-2 mediates induction by two different signal-transduction pathways: protein kinase C and cAMP. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumo S., Lompré A. M., Matsuoka R., Koren G., Schwartz K., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Myosin heavy chain messenger RNA and protein isoform transitions during cardiac hypertrophy. Interaction between hemodynamic and thyroid hormone-induced signals. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):970–977. doi: 10.1172/JCI112908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumo S., Mahdavi V. Thyroid hormone receptor alpha isoforms generated by alternative splicing differentially activate myosin HC gene transcription. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):539–542. doi: 10.1038/334539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumo S., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. All members of the MHC multigene family respond to thyroid hormone in a highly tissue-specific manner. Science. 1986 Feb 7;231(4738):597–600. doi: 10.1126/science.3945800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumo S., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Protooncogene induction and reprogramming of cardiac gene expression produced by pressure overload. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):339–343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karliner J. S., Simpson P. C. Beta-adrenoceptor and adenylate cyclase regulation in cardiac myocyte growth. Basic Res Cardiol. 1988 Nov-Dec;83(6):655–663. doi: 10.1007/BF01906960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A. M., Katz P. B. Homogeneity out of heterogeneity. Circulation. 1989 Mar;79(3):712–717. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.79.3.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litten R. Z., 3rd, Martin B. J., Low R. B., Alpert N. R. Altered myosin isozyme patterns from pressure-overloaded and thyrotoxic hypertrophied rabbit hearts. Circ Res. 1982 Jun;50(6):856–864. doi: 10.1161/01.res.50.6.856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lompre A. M., Schwartz K., d'Albis A., Lacombe G., Van Thiem N., Swynghedauw B. Myosin isoenzyme redistribution in chronic heart overload. Nature. 1979 Nov 1;282(5734):105–107. doi: 10.1038/282105a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lompré A. M., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Expression of the cardiac ventricular alpha- and beta-myosin heavy chain genes is developmentally and hormonally regulated. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6437–6446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long C. S., Ordahl C. P., Simpson P. C. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor stimulation of sarcomeric actin isogene transcription in hypertrophy of cultured rat heart muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):1078–1082. doi: 10.1172/JCI113951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahdavi V., Chambers A. P., Nadal-Ginard B. Cardiac alpha- and beta-myosin heavy chain genes are organized in tandem. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2626–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahdavi V., Periasamy M., Nadal-Ginard B. Molecular characterization of two myosin heavy chain genes expressed in the adult heart. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):659–664. doi: 10.1038/297659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medford R. M., Wydro R. M., Nguyen H. T., Nadal-Ginard B. Cytoplasmic processing of myosin heavy chain messenger RNA: evidence provided by using a recombinant DNA plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5749–5753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercadier J. J., Lompré A. M., Wisnewsky C., Samuel J. L., Bercovici J., Swynghedauw B., Schwartz K. Myosin isoenzyme changes in several models of rat cardiac hypertrophy. Circ Res. 1981 Aug;49(2):525–532. doi: 10.1161/01.res.49.2.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morkin E., Flink I. L., Goldman S. Biochemical and physiologic effects of thyroid hormone on cardiac performance. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1983 Mar-Apr;25(5):435–464. doi: 10.1016/0033-0620(83)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nag A. C., Cheng M. Expression of myosin isoenzymes in cardiac-muscle cells in culture. Biochem J. 1984 Jul 1;221(1):21–26. doi: 10.1042/bj2210021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai R., Pritzl N., Low R. B., Stirewalt W. S., Zak R., Alpert N. R., Litten R. Z. Myosin isozyme synthesis and mRNA levels in pressure-overloaded rabbit hearts. Circ Res. 1987 May;60(5):692–699. doi: 10.1161/01.res.60.5.692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible T. F., Ciambrone G. J., Capasso J. M., Scheuer J. Cardiac conditioning ameliorates cardiac dysfunction associated with renal hypertension in rats. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1086–1094. doi: 10.1172/JCI111294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible T. F., Malhotra A., Ciambrone G. J., Scheuer J. Chronic swimming reverses cardiac dysfunction and myosin abnormalities in hypertensive rats. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Apr;60(4):1435–1441. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.4.1435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheuer J., Bhan A. K. Cardiac contractile proteins. Adenosine triphosphatase activity and physiological function. Circ Res. 1979 Jul;45(1):1–12. doi: 10.1161/01.res.45.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheuer J., Malhotra A., Hirsch C., Capasso J., Schaible T. F. Physiologic cardiac hypertrophy corrects contractile protein abnormalities associated with pathologic hypertrophy in rats. J Clin Invest. 1982 Dec;70(6):1300–1305. doi: 10.1172/JCI110729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiaffino S., Samuel J. L., Sassoon D., Lompré A. M., Garner I., Marotte F., Buckingham M., Rappaport L., Schwartz K. Nonsynchronous accumulation of alpha-skeletal actin and beta-myosin heavy chain mRNAs during early stages of pressure-overload--induced cardiac hypertrophy demonstrated by in situ hybridization. Circ Res. 1989 May;64(5):937–948. doi: 10.1161/01.res.64.5.937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz K., de la Bastie D., Bouveret P., Oliviéro P., Alonso S., Buckingham M. Alpha-skeletal muscle actin mRNA's accumulate in hypertrophied adult rat hearts. Circ Res. 1986 Nov;59(5):551–555. doi: 10.1161/01.res.59.5.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T. E., Rhodes C., Rigby P. W., Berg P. Biochemical method for mapping mutational alterations in DNA with S1 nuclease: the location of deletions and temperature-sensitive mutations in simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):989–993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P., McGrath A., Savion S. Myocyte hypertrophy in neonatal rat heart cultures and its regulation by serum and by catecholamines. Circ Res. 1982 Dec;51(6):787–801. doi: 10.1161/01.res.51.6.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P. Norepinephrine-stimulated hypertrophy of cultured rat myocardial cells is an alpha 1 adrenergic response. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):732–738. doi: 10.1172/JCI111023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P., Savion S. Differentiation of rat myocytes in single cell cultures with and without proliferating nonmyocardial cells. Cross-striations, ultrastructure, and chronotropic response to isoproterenol. Circ Res. 1982 Jan;50(1):101–116. doi: 10.1161/01.res.50.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P. Stimulation of hypertrophy of cultured neonatal rat heart cells through an alpha 1-adrenergic receptor and induction of beating through an alpha 1- and beta 1-adrenergic receptor interaction. Evidence for independent regulation of growth and beating. Circ Res. 1985 Jun;56(6):884–894. doi: 10.1161/01.res.56.6.884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]