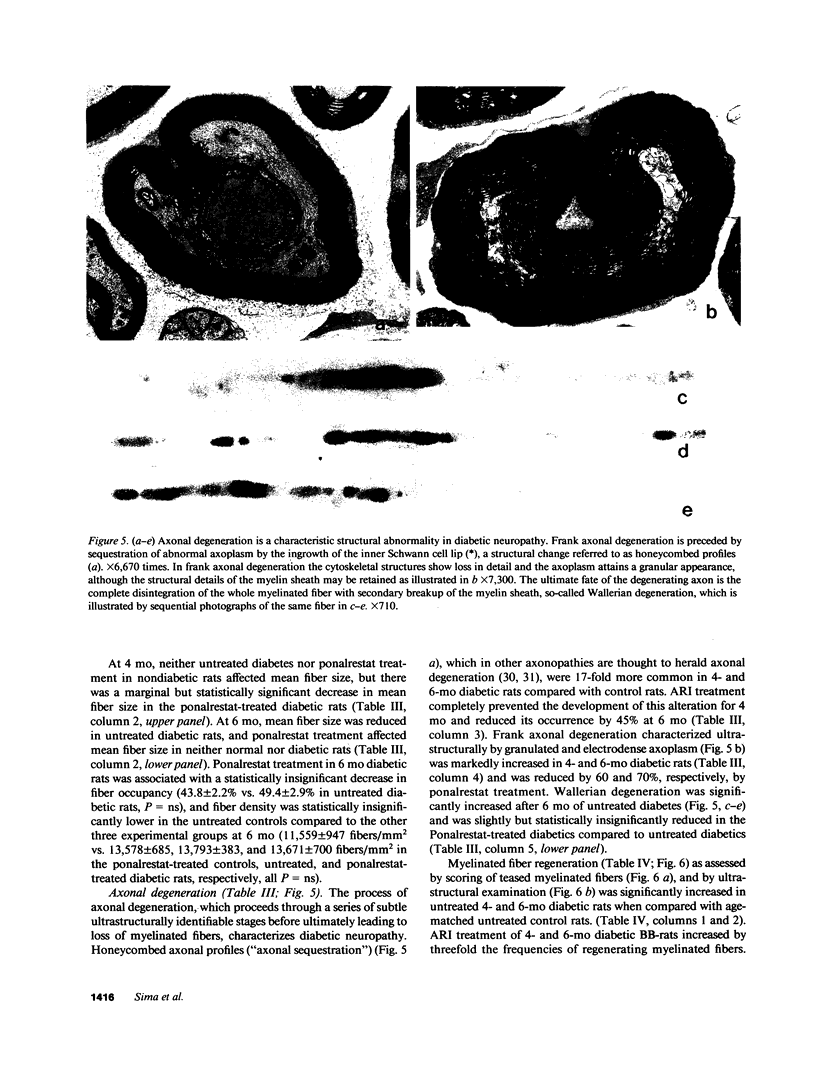
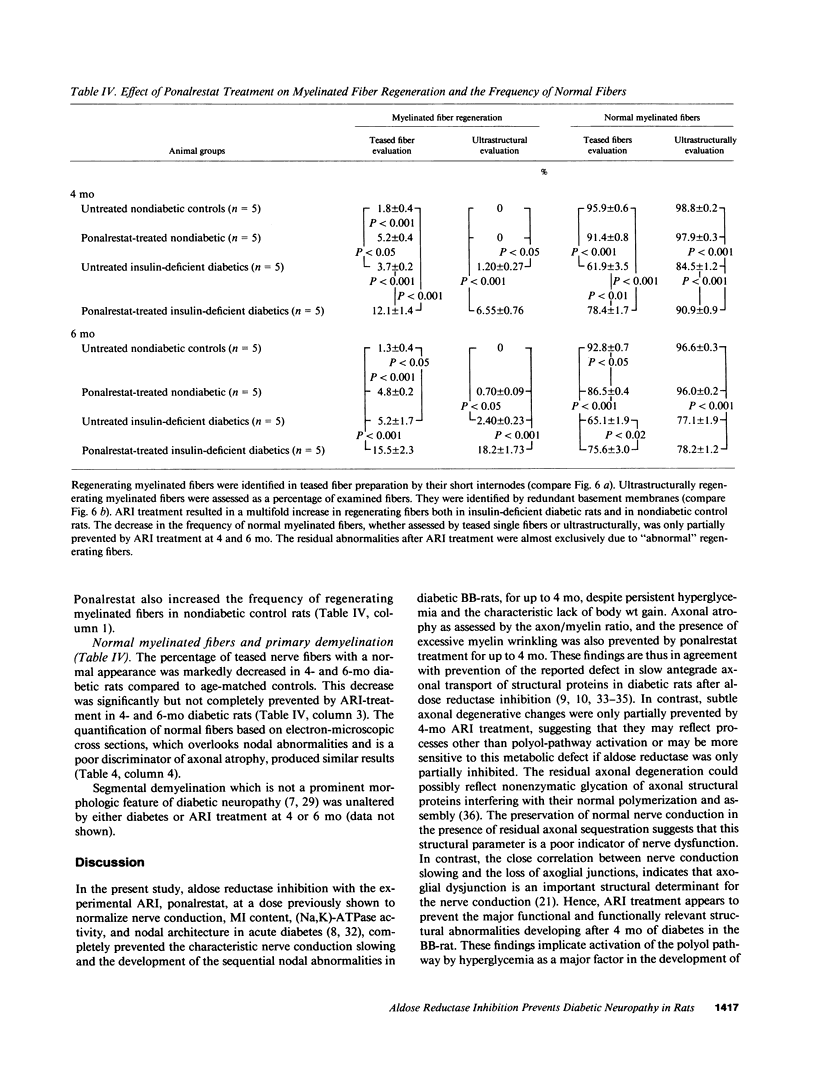
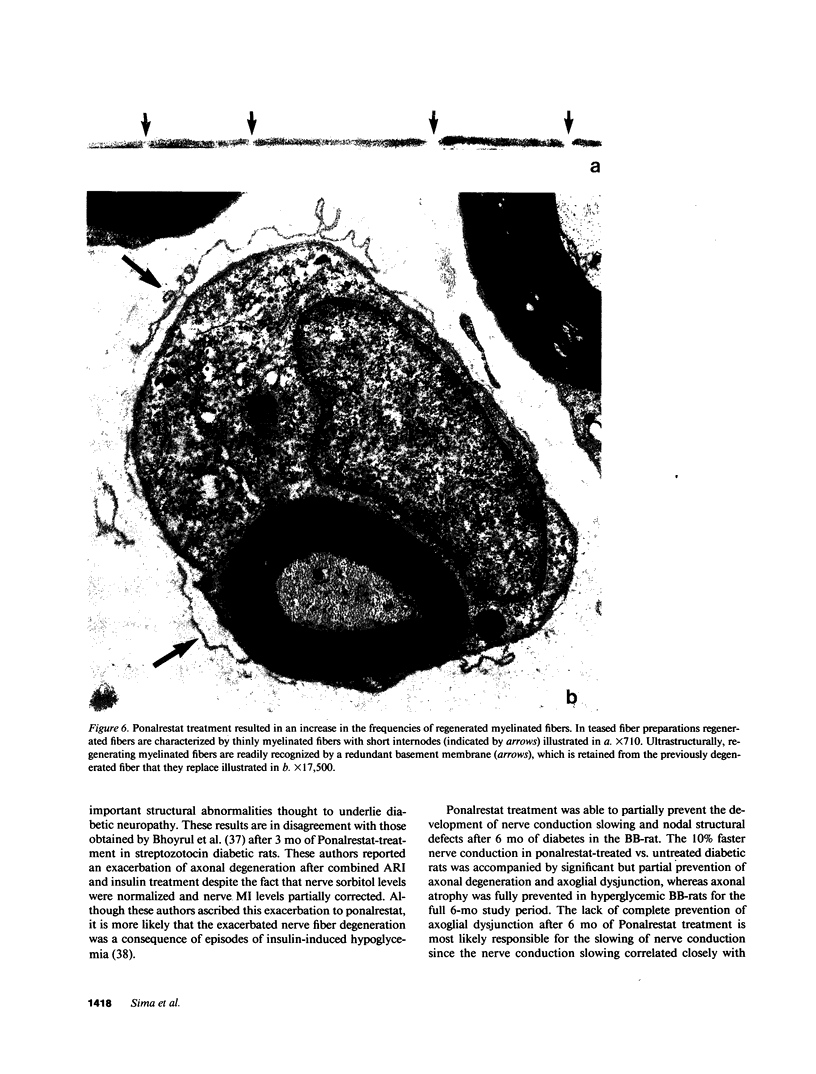
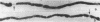Abstract
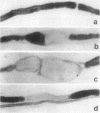
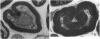
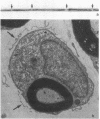
To test the hypothesis that aldose reductase inhibition may prevent or delay the development of functional and structural neuropathy in the insulin-deficient diabetic Bio-Breeding rat (BB-rat), hyperglycemic rats were begun on the aldose reductase inhibitor (ARI) ponalrestat 25 mg/kg body wt soon after the onset of diabetes and followed for 4 or 6 mo. Ponalrestat treatment completely prevented the characteristic nerve conduction slowing and structural abnormalities of the node of Ranvier for 4 mo despite only partial preservation of axonal integrity. Ponalrestat treatment for 6 mo achieved a partial but significant prevention of nerve conduction slowing, axoglial dysjunction, and axonal degenerative changes. This incomplete but significant prevention of neuropathy by ponalrestat suggests that additional mechanisms besides polyol-pathway activation may be of importance in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. Alternatively, the dosage used in the present study may not have been sufficient to achieve a complete prevention. Despite the only partial protective effect of ARI treatment on degenerative peripheral nerve changes in hyperglycemic BB-rats, 6 mo of treatment resulted in a more than threefold increase in regenerating nerve fibers. These data suggest that prophylactic ARI treatment may be efficacious in delaying the development of diabetic neuropathy.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhoyrul S., Sharma A. K., Stribling D., Mirrlees D. D., Peterson R. G., Farber M. O., Thomas P. K. Ultrastructural observations on myelinated fibres in experimental diabetes: effect of the aldose reductase inhibitor ponalrestat given alone or in conjunction with insulin therapy. J Neurol Sci. 1988 Jun;85(2):131–147. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(88)90151-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brismar T., Sima A. A. Changes in nodal function in nerve fibres of the spontaneously diabetic BB-Wistar rat: potential clamp analysis. Acta Physiol Scand. 1981 Dec;113(4):499–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1981.tb06928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brismar T., Sima A. A., Greene D. A. Reversible and irreversible nodal dysfunction in diabetic neuropathy. Ann Neurol. 1987 May;21(5):504–507. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyck P. J., Zimmerman B. R., Vilen T. H., Minnerath S. R., Karnes J. L., Yao J. K., Poduslo J. F. Nerve glucose, fructose, sorbitol, myo-inositol, and fiber degeneration and regeneration in diabetic neuropathy. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 1;319(9):542–548. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809013190904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. CAMs and Igs: cell adhesion and the evolutionary origins of immunity. Immunol Rev. 1987 Dec;100:11–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00526.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagius J., Brattberg A., Jameson S., Berne C. Limited benefit of treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy with an aldose reductase inhibitor: a 24-week controlled trial. Diabetologia. 1985 Jun;28(6):323–329. doi: 10.1007/BF00283137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene D. A., Chakrabarti S., Lattimer S. A., Sima A. A. Role of sorbitol accumulation and myo-inositol depletion in paranodal swelling of large myelinated nerve fibers in the insulin-deficient spontaneously diabetic bio-breeding rat. Reversal by insulin replacement, an aldose reductase inhibitor, and myo-inositol. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1479–1485. doi: 10.1172/JCI112977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene D. A., De Jesus P. V., Jr, Winegrad A. I. Effects of insulin and dietary myoinositol on impaired peripheral motor nerve conduction velocity in acute streptozotocin diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1326–1336. doi: 10.1172/JCI108052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene D. A., Lattimer S. A., Sima A. A. Are disturbances of sorbitol, phosphoinositide, and Na+-K+-ATPase regulation involved in pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy? Diabetes. 1988 Jun;37(6):688–693. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.6.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene D. A., Lattimer S. A., Sima A. A. Sorbitol, phosphoinositides, and sodium-potassium-ATPase in the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. N Engl J Med. 1987 Mar 5;316(10):599–606. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198703053161007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene D. A., Lattimer S., Ulbrecht J., Carroll P. Glucose-induced alterations in nerve metabolism: current perspective on the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy and future directions for research and therapy. Diabetes Care. 1985 May-Jun;8(3):290–299. doi: 10.2337/diacare.8.3.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene D. A., Yagihashi S., Lattimer S. A., Sima A. A. Nerve Na+-K+-ATPase, conduction, and myo-inositol in the insulin-deficient BB rat. Am J Physiol. 1984 Oct;247(4 Pt 1):E534–E539. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.4.E534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judzewitsch R. G., Jaspan J. B., Polonsky K. S., Weinberg C. R., Halter J. B., Halar E., Pfeifer M. A., Vukadinovic C., Bernstein L., Schneider M. Aldose reductase inhibition improves nerve conduction velocity in diabetic patients. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jan 20;308(3):119–125. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198301203080302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lattimer S. A., Sima A. A., Greene D. A. In vitro correction of impaired Na+-K+-ATPase in diabetic nerve by protein kinase C agonists. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 1):E264–E269. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.256.2.E264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. S., MacGregor L. C., Fluharty S. J., King G. L. Differential regulation of protein kinase C and (Na,K)-adenosine triphosphatase activities by elevated glucose levels in retinal capillary endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):90–94. doi: 10.1172/JCI113889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Medori R., Autilio-Gambetti L., Jenich H., Gambetti P. Changes in axon size and slow axonal transport are related in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Neurology. 1988 Apr;38(4):597–601. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.4.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medori R., Jenich H., Autilio-Gambetti L., Gambetti P. Experimental diabetic neuropathy: similar changes of slow axonal transport and axonal size in different animal models. J Neurosci. 1988 May;8(5):1814–1821. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-05-01814.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D. M., Sima A. A. Diabetic neuropathy in the mutant mouse [C57BL/ks(db/db)]: a morphometric study. Diabetes. 1980 Jan;29(1):60–67. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sima A. A., Bouchier M., Christensen H. Axonal atrophy in sensory nerves of the diabetic BB-Wistar rat: a possible early correlate of human diabetic neuropathy. Ann Neurol. 1983 Mar;13(3):264–272. doi: 10.1002/ana.410130307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sima A. A., Bril V., Nathaniel V., McEwen T. A., Brown M. B., Lattimer S. A., Greene D. A. Regeneration and repair of myelinated fibers in sural-nerve biopsy specimens from patients with diabetic neuropathy treated with sorbinil. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 1;319(9):548–555. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809013190905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sima A. A., Brismar T. Reversible diabetic nerve dysfunction: structural correlates to electrophysiological abnormalities. Ann Neurol. 1985 Jul;18(1):21–29. doi: 10.1002/ana.410180105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sima A. A. Can the BB-rat help to unravel diabetic neuropathy? Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1985 Jul-Aug;11(4):253–264. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1985.tb00023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sima A. A., Hay K. Functional aspects and pathogenetic considerations of the neuropathy in the spontaneously diabetic BB-Wistar rat. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1981 Sep-Oct;7(5):341–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1981.tb00237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sima A. A., Lattimer S. A., Yagihashi S., Greene D. A. Axo-glial dysjunction. A novel structural lesion that accounts for poorly reversible slowing of nerve conduction in the spontaneously diabetic bio-breeding rat. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):474–484. doi: 10.1172/JCI112326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sima A. A., Nathaniel V., Bril V., McEwen T. A., Greene D. A. Histopathological heterogeneity of neuropathy in insulin-dependent and non-insulin-dependent diabetes, and demonstration of axo-glial dysjunction in human diabetic neuropathy. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):349–364. doi: 10.1172/JCI113327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sima A. A., Zhang W. X., Greene D. A. Diabetic and hypoglycemic neuropathy--a comparison in the BB rat. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1989 May 15;6(4):279–296. doi: 10.1016/0168-8227(89)90068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terkildsen A. B., Christensen N. J. Reversible nervous abnormalities in juvenile diabetics with recently diagnosed diabetes. Diabetologia. 1971 Apr;7(2):113–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00443891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson D. R., Holmes P. R., Mayer J. H. Reversal, by treatment with an aldose reductase inhibitor, of impaired axonal transport and motor nerve conduction velocity in experimental diabetes mellitus. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Aug 16;31(2):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson D. R., Moriarty R. J., Mayer J. H. Prevention and reversal of defective axonal transport and motor nerve conduction velocity in rats with experimental diabetes by treatment with the aldose reductase inhibitor Sorbinil. Diabetes. 1984 May;33(5):470–476. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.5.470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson D. R., Townsend J., Fretten P. Prevention of defective axonal transport in streptozocin-diabetic rats by treatment with "Statil" (ICI 128436), an aldose reductase inhibitor. Diabetes. 1985 Oct;34(10):970–972. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.10.970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. D., Barnes C. G., Fisher D. J., Jessop J. D., Baker R. W. Improvement in nerve conduction following treatment in newly diagnosed diabetics. Lancet. 1971 Feb 27;1(7696):428–430. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92415-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. K., Howarth N. L., Devenny J. J., Bitensky M. W. Structural and functional consequences of increased tubulin glycosylation in diabetes mellitus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6546–6550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winegrad A. I. Banting lecture 1986. Does a common mechanism induce the diverse complications of diabetes? Diabetes. 1987 Mar;36(3):396–406. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.3.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winegrad A. I., Simmons D. A., Martin D. B. Has one diabetic complication been explained? N Engl J Med. 1983 Jan 20;308(3):152–154. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198301203080309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]