Abstract
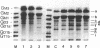
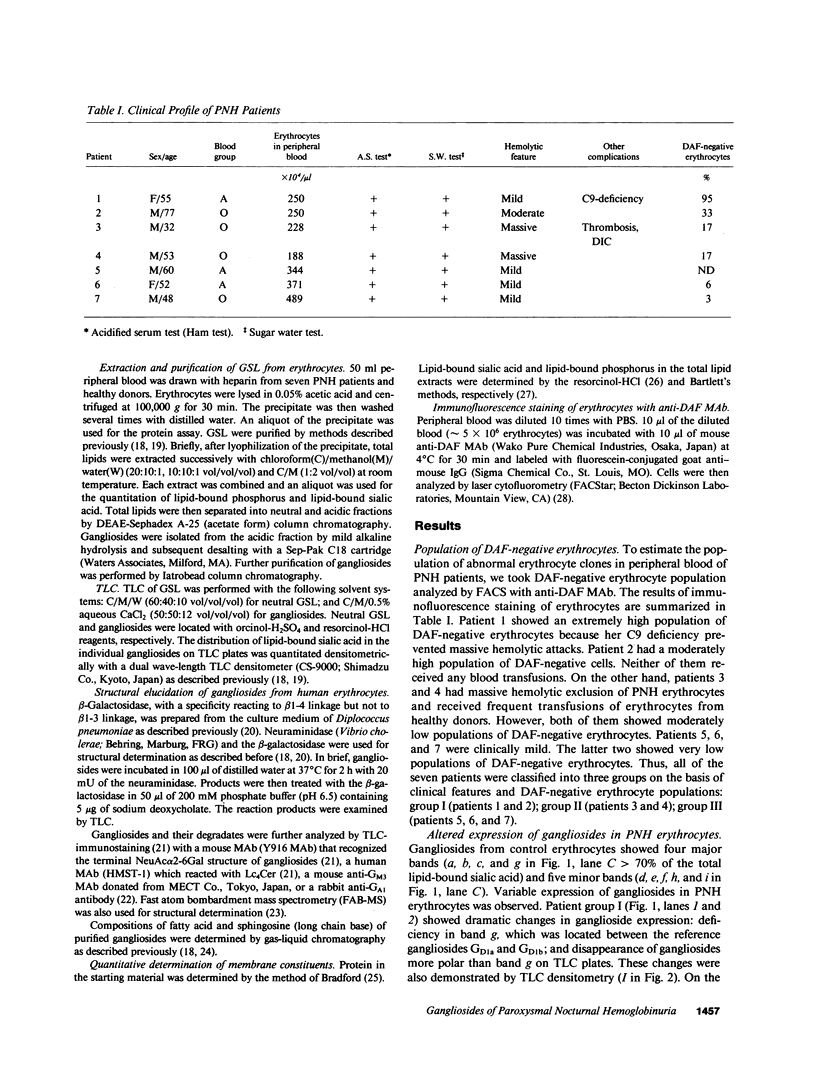
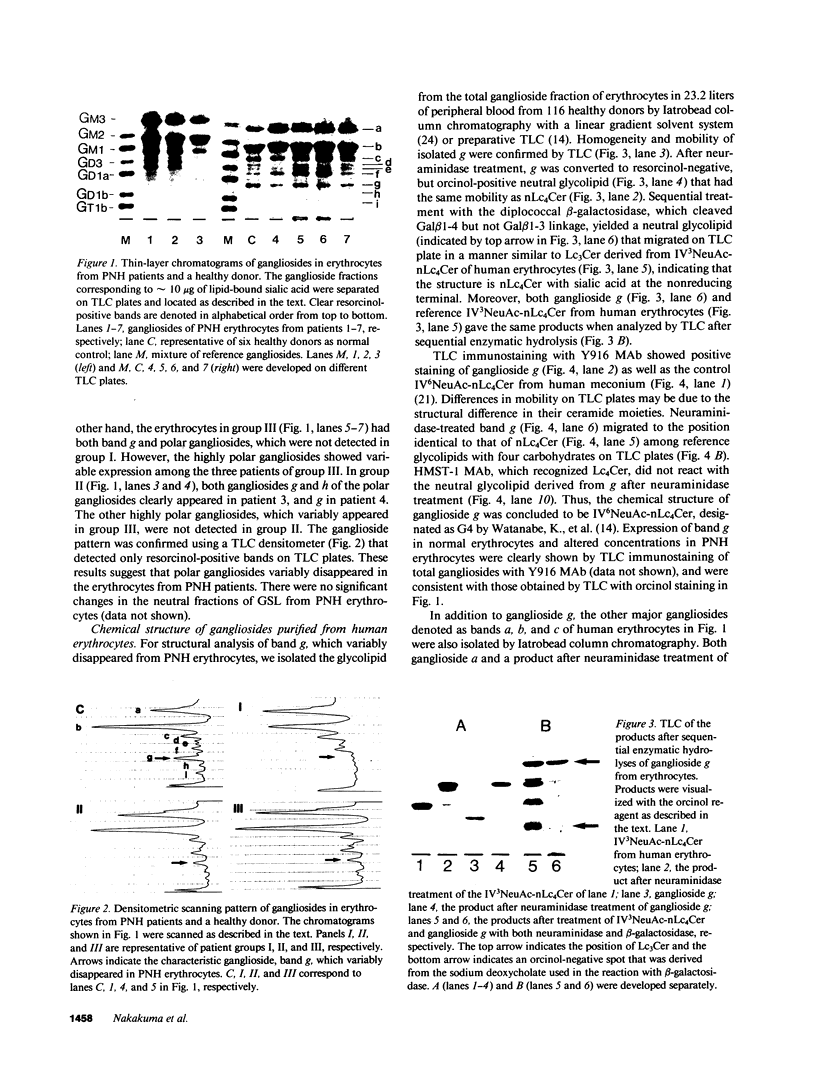
In paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), impaired glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (PI)-anchoring of membrane proteins such as decay-accelerating factor has been known to lead to increased susceptibility to complement. Moreover, abnormal expression of non-PI-anchoring glycoproteins such as C3b/C4b receptor (CR1) or glycophorin-alpha also has been shown in PNH. Therefore, we biochemically analyzed glycosphingolipids (GSL) as one of the membrane glycoconjugates of PNH erythrocytes. Erythrocytes of all seven PNH patients showed altered expression of sialosyl GSL (gangliosides) as compared with the control erythrocytes of healthy donors. Both a sialosylparagloboside (IV6NeuAc-nLc4Cer) among four major gangliosides and some minor gangliosides in normal erythrocytes variably disappeared in erythrocytes from the peripheral blood of PNH patients. As one of the possible mechanisms of altered expression of gangliosides in PNH erythrocytes, structural analysis suggested impaired sialylation of GSL. These results suggest not only the altered metabolism of gangliosides in PNH erythrocytes, but also a metabolic disorder of membrane glycoconjugates as a new feature of PNH.
Full text
PDF
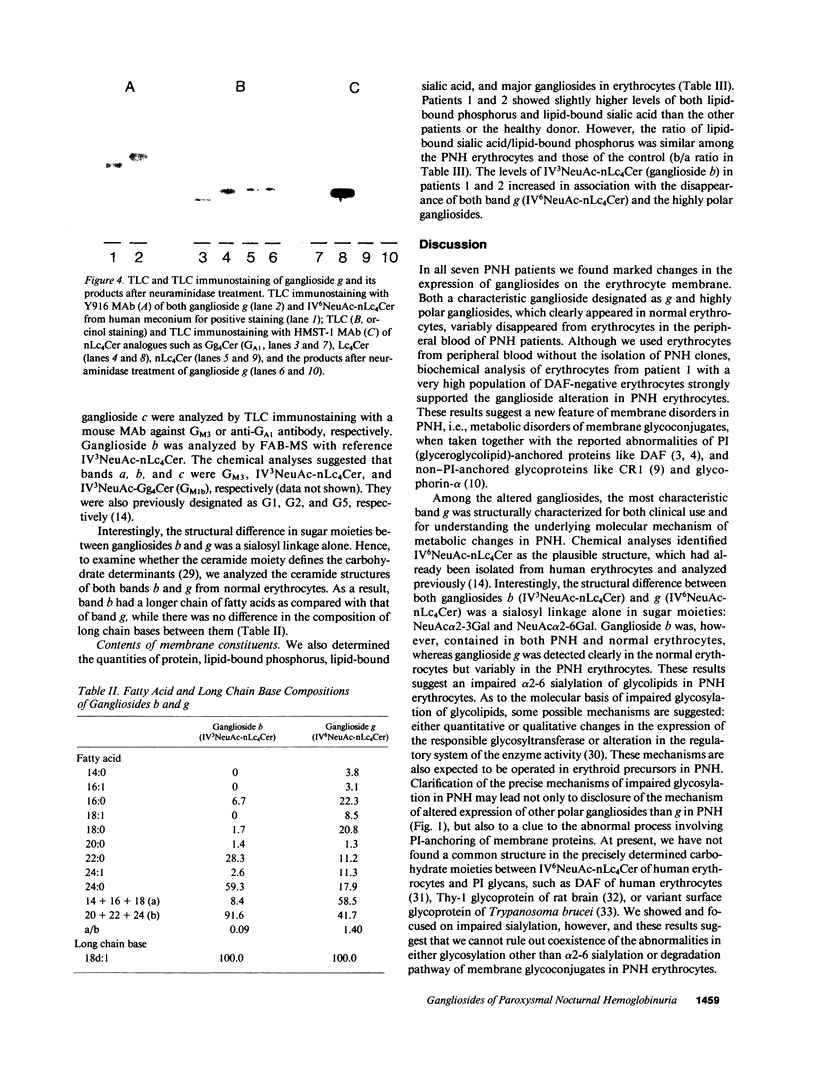
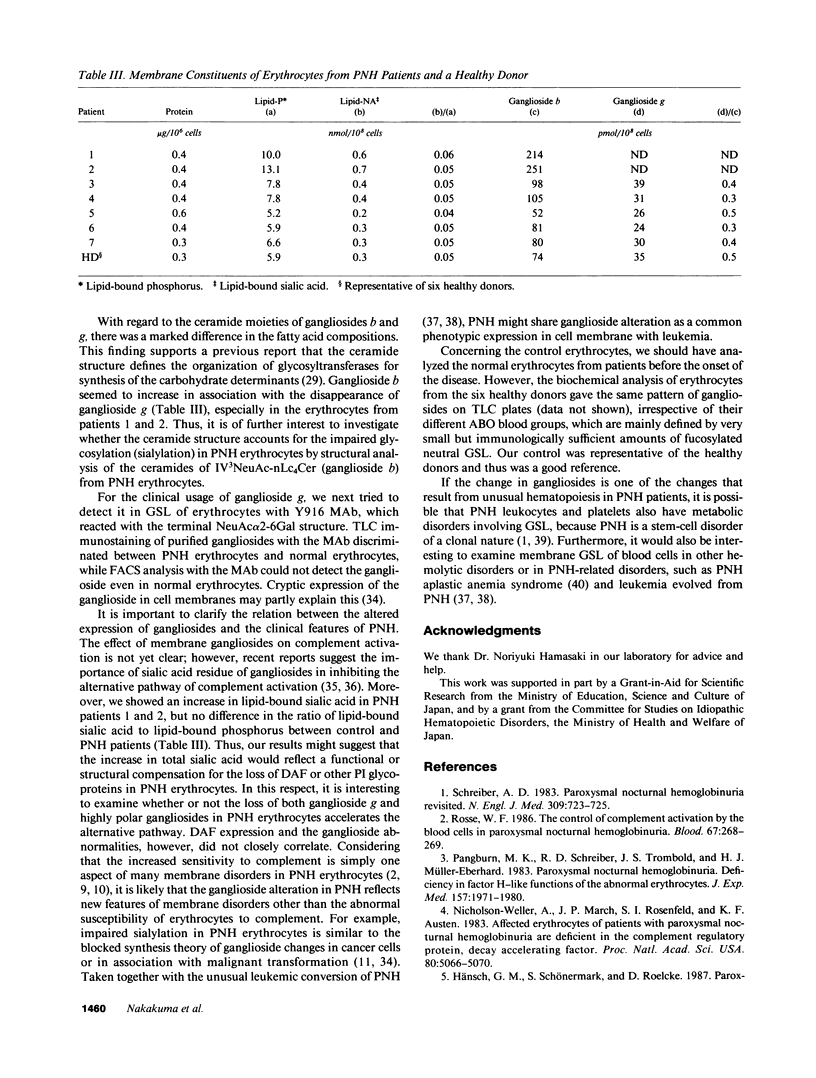

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando S., Isobe M., Nagai Y. High performance preparative column chromatography of lipids using a new porous silica, Iatrobeads. I. Separation of molecular species of sphingoglycolipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 22;424(1):98–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davitz M. A., Low M. G., Nussenzweig V. Release of decay-accelerating factor (DAF) from the cell membrane by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PIPLC). Selective modification of a complement regulatory protein. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1150–1161. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine D. V., Gluck W. L., Rosse W. F., Weinberg J. B. Acute myeloblastic leukemia in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Evidence of evolution from the abnormal paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria clone. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):314–317. doi: 10.1172/JCI112802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Homans S. W., Dwek R. A., Rademacher T. W. Glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol moiety that anchors Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein to the membrane. Science. 1988 Feb 12;239(4841 Pt 1):753–759. doi: 10.1126/science.3340856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakomori S. Glycosphingolipids in cellular interaction, differentiation, and oncogenesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:733–764. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakomori S., Kannagi R. Glycosphingolipids as tumor-associated and differentiation markers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Aug;71(2):231–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakomori S. Structures and organization of cell surface glycolipids dependency on cell growth and malignant transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 20;417(1):55–89. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(75)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Bell R. M. Functions of sphingolipids and sphingolipid breakdown products in cellular regulation. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):500–507. doi: 10.1126/science.2643164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homans S. W., Ferguson M. A., Dwek R. A., Rademacher T. W., Anand R., Williams A. F. Complete structure of the glycosyl phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor of rat brain Thy-1 glycoprotein. Nature. 1988 May 19;333(6170):269–272. doi: 10.1038/333269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänsch G. M., Schönermark S., Roelcke D. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria type III. Lack of an erythrocyte membrane protein restricting the lysis by C5b-9. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):7–12. doi: 10.1172/JCI113065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänsch G. M., Weller P. F., Nicholson-Weller A. Release of C8 binding protein (C8bp) from the cell membrane by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Blood. 1988 Sep;72(3):1089–1092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamori M., Nagai Y. Monosialogangliosides of rabbit skeletal muscle. Characterization of N-acetylneuraminosyl lacto-N-noroctaosyl ceramide. J Biochem. 1981 Apr;89(4):1253–1264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamori M., Noguchi M., Yamamoto T., Yago M., Nozawa S., Nagai Y. Selective terminal alpha 2-3 and alpha 2-6 sialylation of glycosphingolipids with lacto-series type 1 and 2 chains in human meconium. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jun 6;233(1):134–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81370-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamori M., Shimomura J., Tsuyuhara S., Mogi M., Ishizaki S., Nagai Y. Differential reactivities of fucosyl GM1 and GM1 gangliosides on rat erythrocyte membrane revealed by analysis with anti-fucosyl GM1 and GM1 antisera. J Biochem. 1983 Jul;94(1):1–10. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannagi R., Nudelman E., Hakomori S. Possible role of ceramide in defining structure and function of membrane glycolipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3470–3474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi T., Nakakuma H., Kagimoto T., Shirono K., Horikawa K., Hidaka M., Iwamori M., Nagai Y., Takatsuki K. Characteristic mode of action of gangliosides in selective modulation of CD4 on human T lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Feb 15;158(3):1050–1059. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92828-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi T., Takaoka T., Yoshida E., Iwamori M., Takatsuki K., Nagai Y. A new approach to the modification of cell membrane glycosphingolipids: ganglioside composition of JTC-12 P3 cells altered by feeding with galactose as a sole carbohydrate source in protein- and lipid-free synthetic medium. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Dec;179(2):507–516. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90288-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawano F., Chosa M., Matsuoka M., Oyamada N., Takatsuki K. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: termination in acute monocytic leukemia and reappearance after chemotherapy with N4-palmitoyl-1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine (PL-AC) and vincristine. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1987 Jun;17(2):123–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima K., Iwamori M., Takasaki S., Kubushiro K., Nozawa S., Iizuka R., Nagai Y. Diplococcal beta-galactosidase with a specificity reacting to beta 1-4 linkage but not to beta 1-3 linkage as a useful exoglycosidase for the structural elucidation of glycolipids. Anal Biochem. 1987 Sep;165(2):465–469. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90297-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. M., Dacie J. V. The aplastic anaemia--paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria syndrome. Br J Haematol. 1967 Mar;13(2):236–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1967.tb08736.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Saltiel A. R. Structural and functional roles of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol in membranes. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):268–275. doi: 10.1126/science.3276003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Gottlieb A., Kinoshita T., Hall S., Silber R., Nussenzweig V., Rosse W. F. Relationship between decay accelerating factor deficiency, diminished acetylcholinesterase activity, and defective terminal complement pathway restriction in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):165–174. doi: 10.1172/JCI113043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Walter E. I., Roberts W. L., Haas R., Rosenberry T. L. Decay accelerating factor of complement is anchored to cells by a C-terminal glycolipid. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):6740–6747. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek M. T., Bremer E. G., Mold C. Effect of gangliosides on activation of the alternative pathway of human complement. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1581–1587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek M. T., Mold C., Bremer E. G. Inhibition of the alternative pathway of human complement by structural analogues of sialic acid. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1588–1594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momoi T., Ando S., Magai Y. High resolution preparative column chromatographic system for gangliosides using DEAE-Sephadex and a new porus silica, Iatrobeads. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 27;441(3):488–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakakuma H., Sanai Y., Shiroki K., Nagai Y. Gene-regulated expression of glycolipids: appearance of GD3 ganglioside in rat cells on transfection with transforming gene E1 of human adenovirus type 12 DNA and its transcriptional subunits. J Biochem. 1984 Nov;96(5):1471–1480. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson-Weller A., March J. P., Rosenfeld S. I., Austen K. F. Affected erythrocytes of patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria are deficient in the complement regulatory protein, decay accelerating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5066–5070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi Y., Iwamori M., Ogawa T., Nagai Y. Analysis of long-chain bases in sphingolipids by positive ion fast atom bombardment or matrix-assisted secondary ion mass spectrometry. Biochemistry. 1987 Jun 30;26(13):3990–3995. doi: 10.1021/bi00387a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oni S. B., Osunkoya B. O., Luzzatto L. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: evidence for monoclonal origin of abnormal red cells. Blood. 1970 Aug;36(2):145–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pangburn M. K., Schreiber R. D., Trombold J. S., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: deficiency in factor H-like functions of the abnormal erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1971–1980. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. J., Soldato C. M., Rosse W. F. Abnormality of glycophorin-alpha on paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1130–1143. doi: 10.1172/JCI111299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F. The control of complement activation by the blood cells in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Blood. 1986 Feb;67(2):268–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. CHROMATOGRAPHIC SEPARATION OF HUMAN BRAIN GANGLIOSIDES. J Neurochem. 1963 Sep;10:613–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb08933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. D. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria revisited. N Engl J Med. 1983 Sep 22;309(12):723–725. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198309223091209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm L., Månsson J. E., Li Y. T. Isolation and structural determination of a novel ganglioside, a disialosylpentahexosylceramide from human brain. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 25;248(2):740–742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe K., Powell M. E., Hakomori S. I. Isolation and characterization of gangliosides with a new sialosyl linkage and core structures. II. Gangliosides of human erythrocyte membranes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8223–8229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]