Abstract
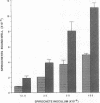
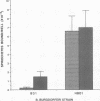
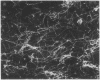
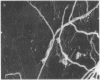
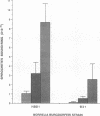
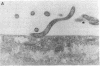
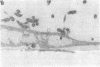
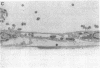
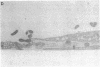
During the pathogenesis of Lyme disease, Borrelia burgdorferi spreads hematogenously from the site of a tick bite to several tissues throughout the body. The specific mechanism of spirochete emigration is presently unknown. Using cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells, we found that Borrelia burgdorferi bound to the endothelial cells and to the subendothelial matrix. Low passage isolates adhered 22-30-fold greater than a strain maintained in culture continuously. Spirochete binding to subendothelial matrix was inhibited 48-63% by pretreatment of the matrix with anti-fibronectin antiserum. Spirochete migration across endothelial monolayers cultured on amniotic membrane was increased when the monolayers were damaged by chemical or physical means. Electron microscopic examination of spirochete-endothelial interactions demonstrated the presence of spirochetes in the intercellular junctions between endothelial cells as well as beneath the monolayers. Scanning electron microscopy identified a mechanism of transendothelial migration whereby spirochetes pass between cells into the amniotic membrane at areas where subendothelium is exposed.
Full text
PDF

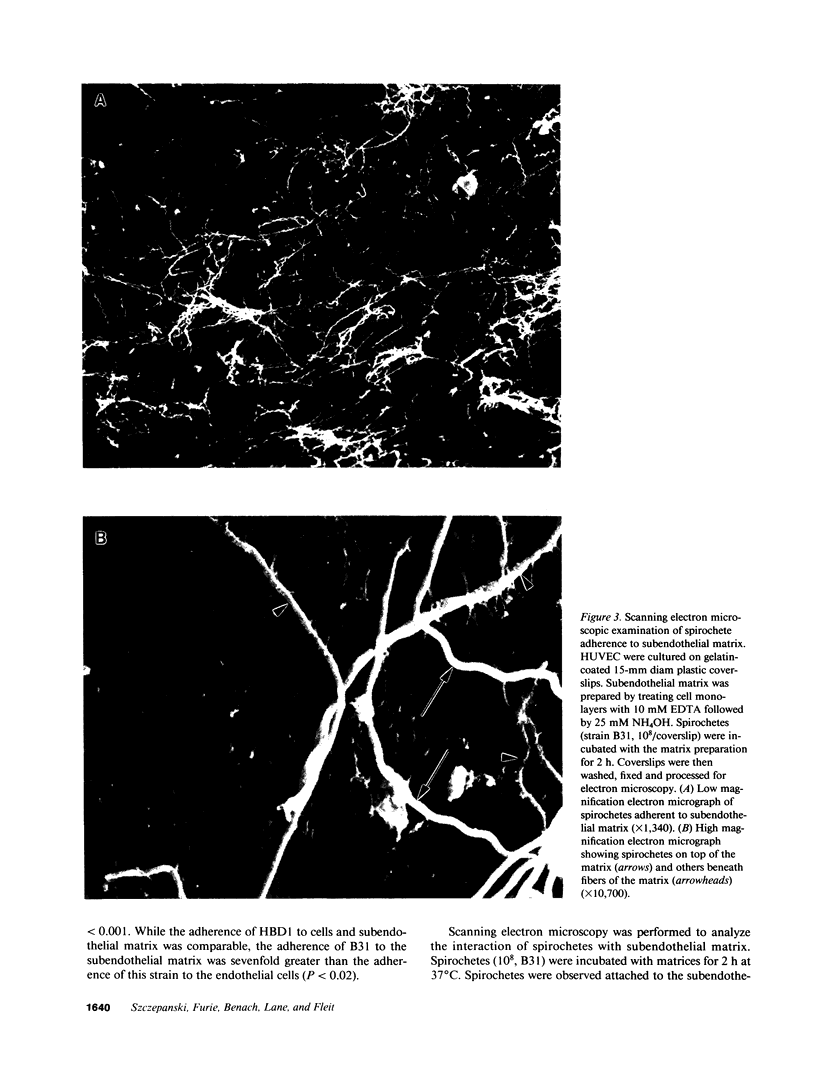


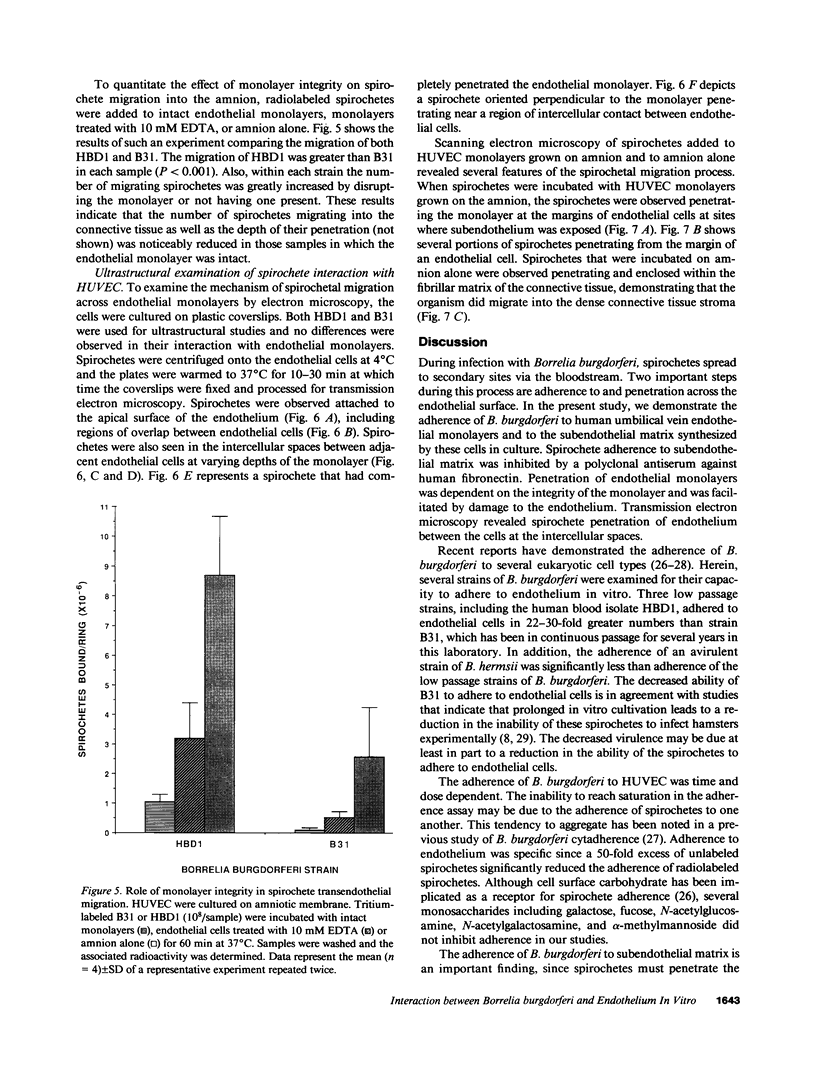

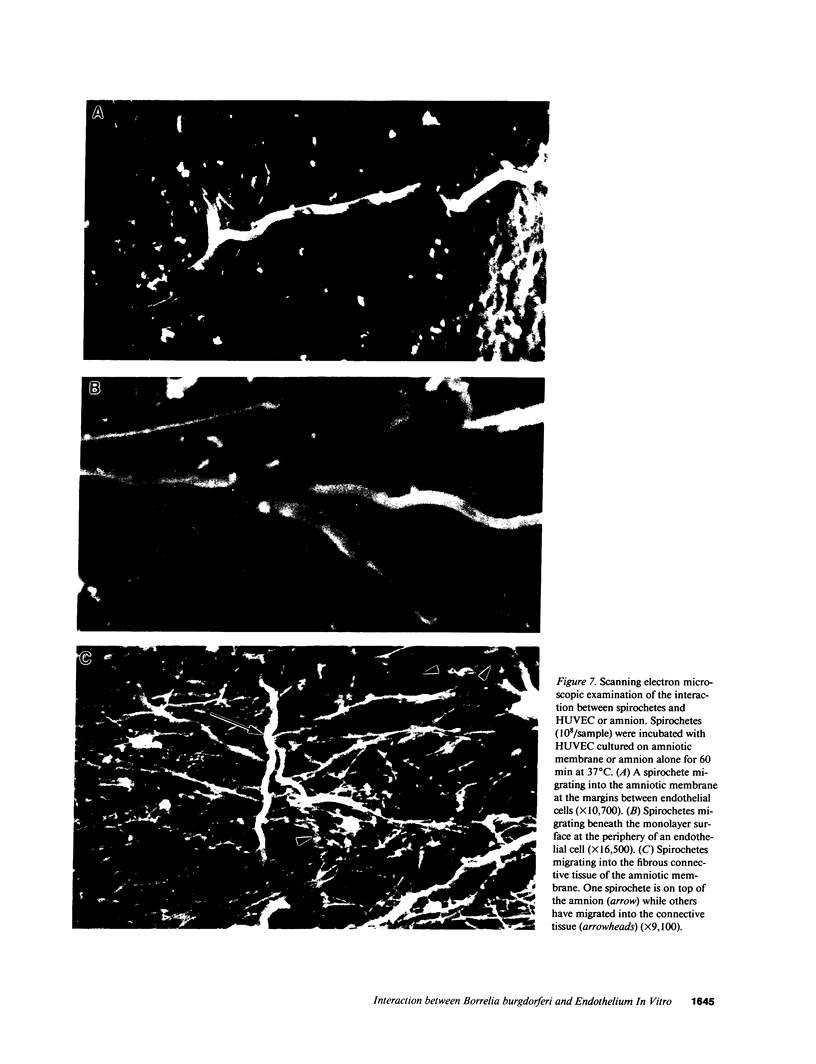


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benach J. L., Bosler E. M., Hanrahan J. P., Coleman J. L., Habicht G. S., Bast T. F., Cameron D. J., Ziegler J. L., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W. Spirochetes isolated from the blood of two patients with Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):740–742. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benach J. L., Coleman J. L., Garcia-Monco J. C., Deponte P. C. Biological activity of Borrelia burgdorferi antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:115–125. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benach J. L., Coleman J. L., Golightly M. G. A murine IgM monoclonal antibody binds an antigenic determinant in outer surface protein A, an immunodominant basic protein of the Lyme disease spirochete. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):265–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benach J. L., Fleit H. B., Habicht G. S., Coleman J. L., Bosler E. M., Lane B. P. Interactions of phagocytes with the Lyme disease spirochete: role of the Fc receptor. J Infect Dis. 1984 Oct;150(4):497–507. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.4.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger B. W., Clemmensen O. J., Ackerman A. B. Lyme disease is a spirochetosis. A review of the disease and evidence for its cause. Am J Dermatopathol. 1983 Apr;5(2):111–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdwell C. R., Gospodarowicz D., Nicolson G. L. Identification, localization, and role of fibronectin in cultured bovine endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3273–3277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheresh D. A., Spiro R. C. Biosynthetic and functional properties of an Arg-Gly-Asp-directed receptor involved in human melanoma cell attachment to vitronectin, fibrinogen, and von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17703–17711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comstock L. E., Thomas D. D. Penetration of endothelial cell monolayers by Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1626–1628. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1626-1628.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtney H. S., Ofek I., Simpson W. A., Hasty D. L., Beachey E. H. Binding of Streptococcus pyogenes to soluble and insoluble fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):454–459. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.454-459.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duray P. H., Steere A. C. Clinical pathologic correlations of Lyme disease by stage. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:65–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleit H. B., Kuhnle M. Biochemical characterization of an Fc gamma receptor purified from human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3120–3125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleit H. B., Wright S. D., Durie C. J., Valinsky J. E., Unkeless J. C. Ontogeny of Fc receptors and complement receptor (CR3) during human myeloid differentiation. J Clin Invest. 1984 Feb;73(2):516–525. doi: 10.1172/JCI111238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Haudenschild C. C., Zetter B. R. Long-term culture of capillary endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5217–5221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie M. B., Cramer E. B., Naprstek B. L., Silverstein S. C. Cultured endothelial cell monolayers that restrict the transendothelial passage of macromolecules and electrical current. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):1033–1041. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Monco J. C., Fernandez-Villar B., Benach J. L. Adherence of the Lyme disease spirochete to glial cells and cells of glial origin. J Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;160(3):497–506. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.3.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. J., Furie M. B., Nicholson S. C., Fischbarg J., Liebovitch L. S., Silverstein S. C. Effects of human neutrophil chemotaxis across human endothelial cell monolayers on the permeability of these monolayers to ions and macromolecules. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Jun;135(3):355–366. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041350302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Yamada K. M. Fibronectins: multifunctional modular glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):369–377. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Mosher D. F. Synthesis of fibronectin by cultured human endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1978 Jun 1;147(6):1779–1791. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.6.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Nogueira Araujo G. M. A simple method of reducing the fading of immunofluorescence during microscopy. J Immunol Methods. 1981;43(3):349–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Marek N., Kodner C. Infection of Syrian hamsters with Lyme disease spirochetes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1099–1101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1099-1101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klotz S. A., Maca R. D. Endothelial cell contraction increases Candida adherence to exposed extracellular matrix. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2495–2498. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2495-2498.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene C. I., Bartlet C. P., Heale G. Identification of the connective tissues synthesized by the venous and arterial endothelia of the human umbilical cord: a comparative study. Br J Exp Pathol. 1988 Apr;69(2):177–188. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrance J. H., Hasty D. L., Simpson W. A. Adherence of Streptococcus sanguis to conformationally specific determinants in fibronectin. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2279–2285. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2279-2285.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Proctor R. A. Binding and factor XIIIa-mediated cross-linking of a 27-kilodalton fragment of fibronectin to Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1980 Aug 22;209(4459):927–929. doi: 10.1126/science.7403857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa S. K., Yurberg E. R., Hatcher V. B., Levitt M. A., Lowy F. D. Bacterial adherence to human endothelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):218–224. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.218-224.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson K. M., Baseman J. B., Alderete J. F. Treponema pallidum receptor binding proteins interact with fibronectin. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1958–1970. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Edwards J. E., Jr, Gibson T. R., Moore J. C., Cohen A. H., Green I. Adherence of Candida to cultured vascular endothelial cells: mechanisms of attachment and endothelial cell penetration. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1264–1274. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidli J., Hunziker T., Moesli P., Schaad U. B. Cultivation of Borrelia burgdorferi from joint fluid three months after treatment of facial palsy due to Lyme borreliosis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):905–906. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwan T. G., Burgdorfer W., Garon C. F. Changes in infectivity and plasmid profile of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, as a result of in vitro cultivation. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1831–1836. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1831-1836.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz M. A., Juliano R. L. Surface activation of the cell adhesion fragment of fibronectin. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Aug;153(2):550–555. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90624-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenman S., Vaheri A. Distribution of a major connective tissue protein, fibronectin, in normal human tissues. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1054–1064. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Baseman J. B., Alderete J. F. Enhanced levels of attachment of fibronectin-primed Treponema pallidum to extracellular matrix. Infect Immun. 1986 Jun;52(3):736–741. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.3.736-741.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Baseman J. B., Alderete J. F. Fibronectin mediates Treponema pallidum cytadherence through recognition of fibronectin cell-binding domain. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):514–525. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Comstock L. E. Interaction of Lyme disease spirochetes with cultured eucaryotic cells. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1324–1326. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1324-1326.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Navab M., Haake D. A., Fogelman A. M., Miller J. N., Lovett M. A. Treponema pallidum invades intercellular junctions of endothelial cell monolayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3608–3612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vercellotti G. M., Lussenhop D., Peterson P. K., Furcht L. T., McCarthy J. B., Jacob H. S., Moldow C. F. Bacterial adherence to fibronectin and endothelial cells: a possible mechanism for bacterial tissue tropism. J Lab Clin Med. 1984 Jan;103(1):34–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]