Abstract
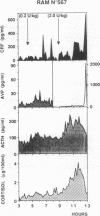
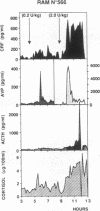
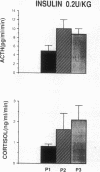
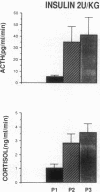
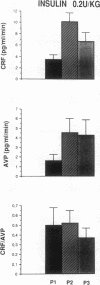
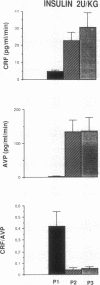
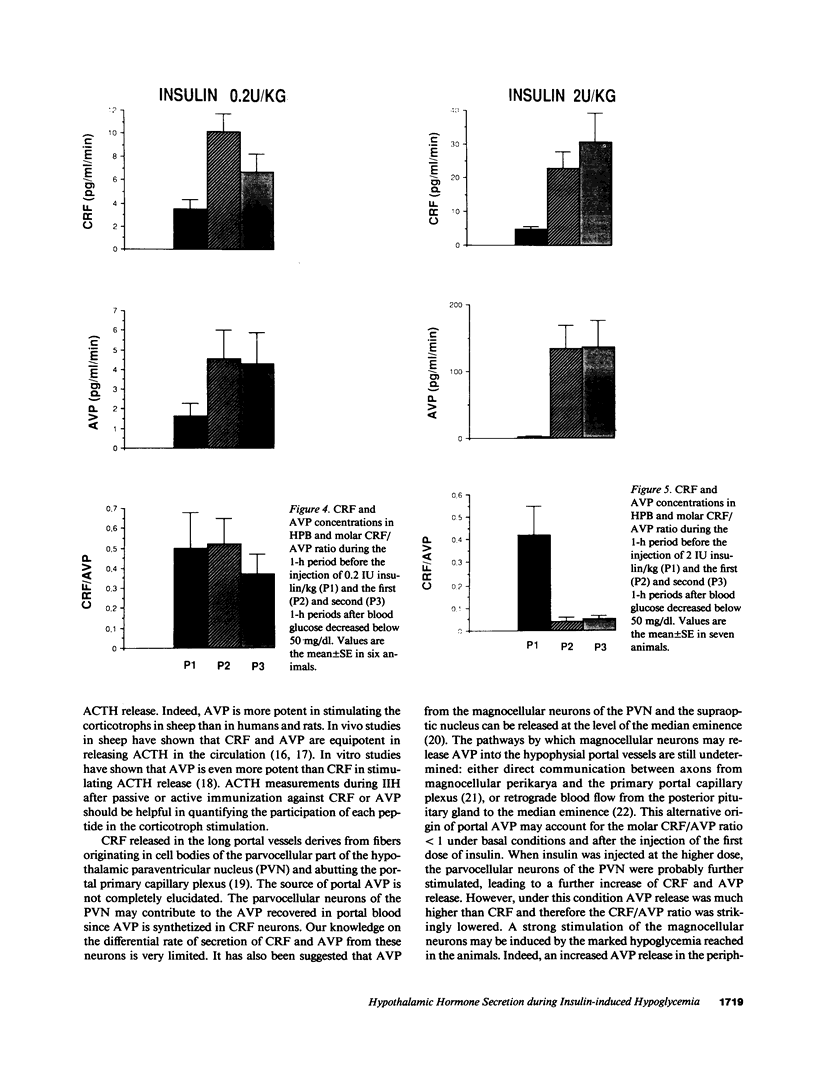
Insulin-induced hypoglycemia (IIH) is a strong stimulator of pituitary ACTH secretion. The mechanisms by which IIH activates the corticotrophs are still controversial. Indeed, in rats the variations of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) and arginine vasopressin (AVP) secretion in hypophysial portal blood (HPB) during IIH have been diversely appreciated. This may be due to the stressful conditions required for portal blood collection in rats. We studied the effects of IIH on the secretion of CRF and AVP in HPB and on the release of ACTH and cortisol in peripheral plasma in conscious, unrestrained, castrated rams. After the injection of a low (0.2 IU/kg) or high dose (2 IU/kg) of insulin, ACTH and cortisol levels in peripheral plasma increased in a dose-related manner. After injection of the low dose of insulin, CRF and AVP secretion in HPB were equally stimulated. After injection of the high dose of insulin, CRF secretion was further stimulated, while AVP release was dramatically increased. These results suggest that when the hypoglycemia is moderate, CRF is the main factor triggering ACTH release, and that the increased AVP secretion potentiates the stimulatory effect of CRF. When hypoglycemia is deeper, AVP secretion becomes predominant and may by itself stimulate ACTH release.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baertschi A. J. Portal vascular route from hypophysial stalk/neural lobe to adenohypophysis. Am J Physiol. 1980 Nov;239(5):R463–R469. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1980.239.5.R463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylis P. H., Robertson G. L. Rat vasopressin response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Endocrinology. 1980 Dec;107(6):1975–1979. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-6-1975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylis P. H., Zerbe R. L., Robertson G. L. Arginine vasopressin response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981 Nov;53(5):935–940. doi: 10.1210/jcem-53-5-935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caraty A., Grino M., Locatelli A., Oliver C. Secretion of corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) and vasopressin (AVP) into the hypophysial portal blood of conscious, unrestrained rams. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 15;155(2):841–849. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80572-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCherney G. S., DeBold C. R., Jackson R. V., Sheldon W. R., Jr, Kamilaris T. C., Island D. P., Orth D. N. Effect of ovine corticotropin-releasing hormone administered during insulin-induced hypoglycemia on plasma adrenocorticotropin and cortisol. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Jun;64(6):1211–1218. doi: 10.1210/jcem-64-6-1211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engler D., Pham T., Fullerton M. J., Ooi G., Funder J. W., Clarke I. J. Studies of the secretion of corticotropin-releasing factor and arginine vasopressin into the hypophysial-portal circulation of the conscious sheep. I. Effect of an audiovisual stimulus and insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Neuroendocrinology. 1989 Apr;49(4):367–381. doi: 10.1159/000125141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Familari M., Smith A. I., Smith R., Funder J. W. Arginine vasopressin is a much more potent stimulus to ACTH release from ovine anterior pituitary cells than ovine corticotropin-releasing factor. 1. In vitro studies. Neuroendocrinology. 1989 Aug;50(2):152–157. doi: 10.1159/000125214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
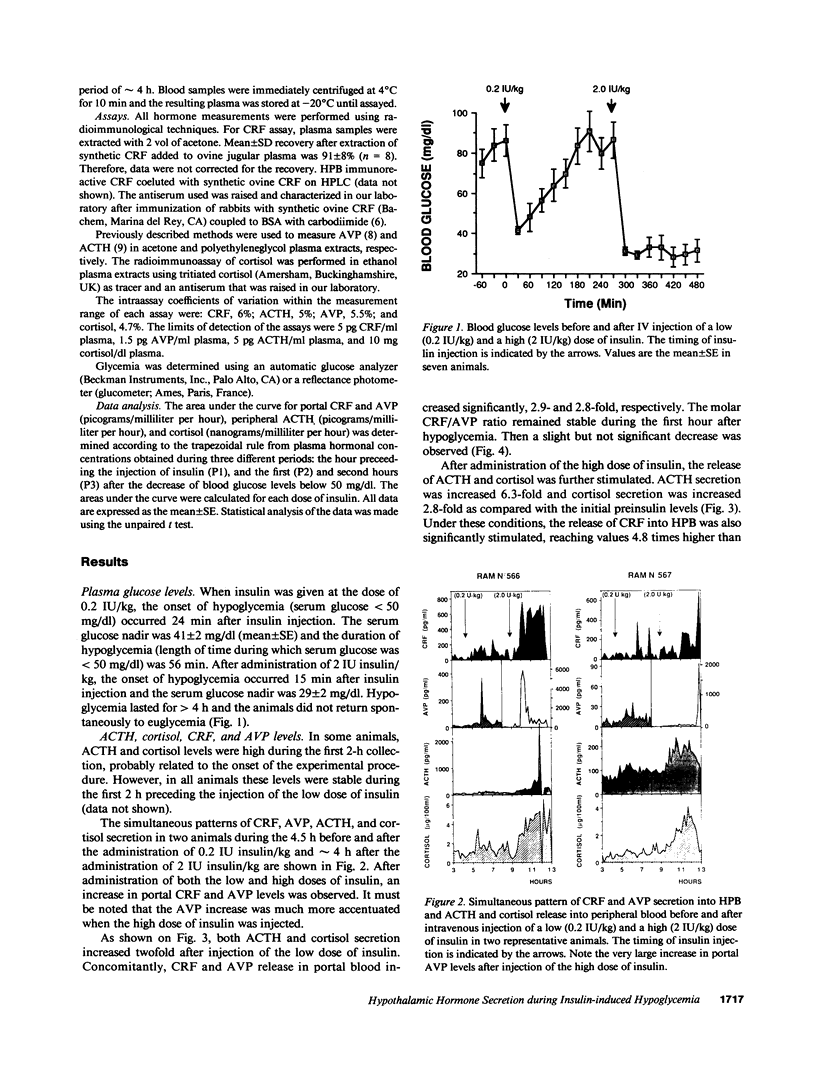
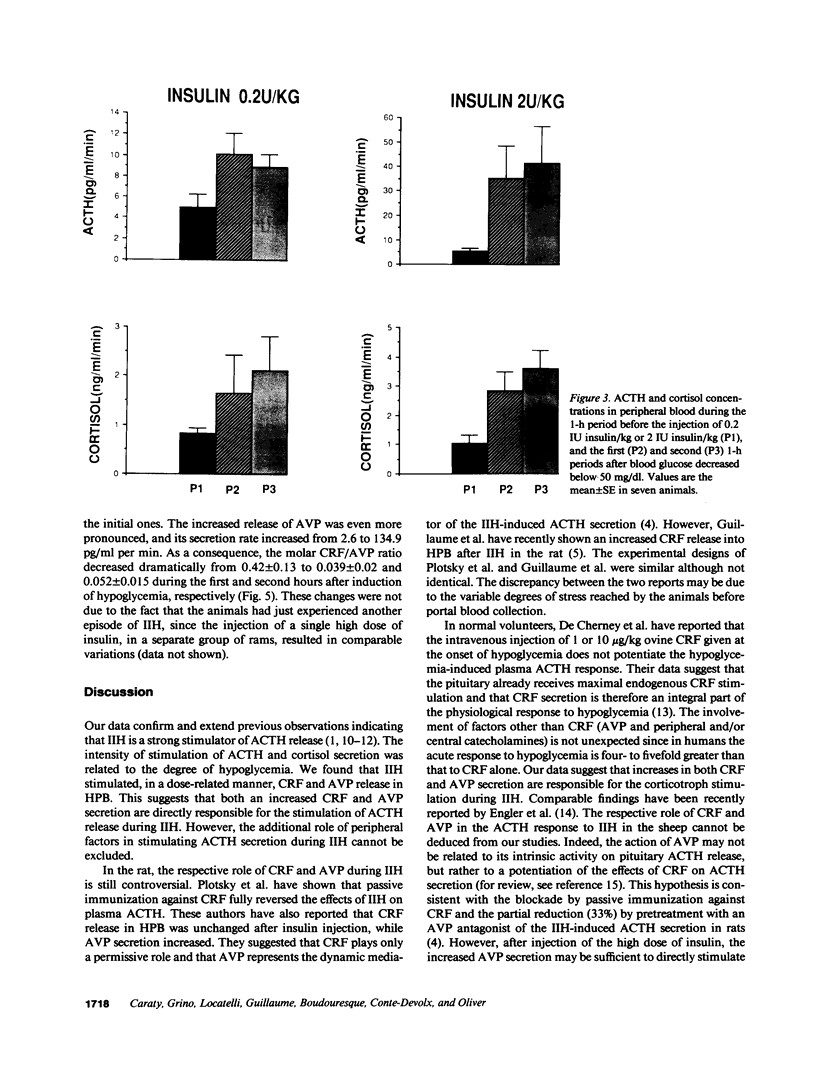
- Giaufre E., Conte-Devolx B., Morisson-Lacombe G., Boudouresque F., Grino M., Rousset-Rouviere B., Guillaume V., Oliver C. Anesthésie péridurale par voie caudale chez l'enfant. Etude des variations endocriniennes. Presse Med. 1985 Feb 2;14(4):201–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillaume V., Conte-Devolx B., Szafarczyk A., Malaval F., Pares-Herbute N., Grino M., Alonso G., Assenmacher I., Oliver C. The corticotropin-releasing factor release in rat hypophysial portal blood is mediated by brain catecholamines. Neuroendocrinology. 1987 Aug;46(2):143–146. doi: 10.1159/000124811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillaume V., Grino M., Conte-Devolx B., Boudouresque F., Oliver C. Corticotropin-releasing factor secretion increases in rat hypophysial portal blood during insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Neuroendocrinology. 1989 Jun;49(6):676–679. doi: 10.1159/000125187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes M. C., Antoni F. A., Aguilera G., Catt K. J. Magnocellular axons in passage through the median eminence release vasopressin. Nature. 1986 Jan 23;319(6051):326–329. doi: 10.1038/319326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jezová D., Kvetnanský R., Kovács K., Oprsalová Z., Vigas M., Makara G. B. Insulin-induced hypoglycemia activates the release of adrenocorticotropin predominantly via central and propranolol insensitive mechanisms. Endocrinology. 1987 Jan;120(1):409–415. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-1-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller-Wood M. E., Shinsako J., Keil L. C., Dallman M. F. Insulin-induced hypoglycemia in conscious dogs. I. Dose-related pituitary and adrenal responses. Endocrinology. 1981 Sep;109(3):818–824. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-3-818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller-Wood M. E., Wade C. E., Shinsako J., Keil L. C., van Loon G. R., Dallman M. F. Insulin-induced hypoglycemia in conscious dogs: effect of maintaining carotid arterial glucose levels on the adrenocorticotropin, epinephrine, and vasopressin responses. Endocrinology. 1983 Feb;112(2):624–632. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-2-624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss J. Z. Dynamism of chemoarchitecture in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. Brain Res Bull. 1988 Jun;20(6):699–708. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(88)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kárteszi M., Dallman M. F., Makara G. B., Stark E. Regulation of the adrenocortical response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Endocrinology. 1982 Aug;111(2):535–541. doi: 10.1210/endo-111-2-535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mezey E., Reisine T. D., Brownstein M. J., Palkovits M., Axelrod J. Beta-adrenergic mechanism of insulin-induced adrenocorticotropin release from the anterior pituitary. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1085–1087. doi: 10.1126/science.6093262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver C., Mical R. S., Porter J. C. Hypothalamic-pituitary vasculature: evidence for retrograde blood flow in the pituitary stalk. Endocrinology. 1977 Aug;101(2):598–604. doi: 10.1210/endo-101-2-598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oomura Y. Glucose as a regulator of neuronal activity. Adv Metab Disord. 1983;10:31–65. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-027310-2.50008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotsky P. M., Bruhn T. O., Vale W. Hypophysiotropic regulation of adrenocorticotropin secretion in response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Endocrinology. 1985 Jul;117(1):323–329. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-1-323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pradier P., Davicco M. J., Safwate A., Tournaire C., Dalle M., Barlet J. P., Delost P. Plasma adrenocorticotrophin, cortisol and aldosterone responses to ovine corticotrophin-releasing factor and vasopressin in sheep. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1986 Jan;111(1):93–100. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1110093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redekopp C., Livesey J. H., Toth A., Donald R. A. Effect of ovine corticotropin releasing factor and arginine vasopressin on ACTH and aldosterone secretion in sheep. Horm Metab Res. 1985 Aug;17(8):428–429. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1013566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe G. A., Bradshaw J. E., Nicholson M. V., Grunstein H. S., Storlien L. H. Rapid bidirectional effects of insulin on hypothalamic noradrenergic and serotoninergic neuronal activity in the rat: role in glucose homeostasis. Endocrinology. 1985 Oct;117(4):1590–1597. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-4-1590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun C. L., Thoa N. B., Kopin I. J. Comparison of the effects of 2-deoxyglucose and immobilization on plasma levels of catecholamines and corticosterone in awake rats. Endocrinology. 1979 Jul;105(1):306–311. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-1-306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szafarczyk A., Alonso G., Ixart G., Malaval F., Assenmacher I. Diurnal-stimulated and stress-induced ACTH release in rats is mediated by ventral noradrenergic bundle. Am J Physiol. 1985 Aug;249(2 Pt 1):E219–E226. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.249.2.E219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilders F. J., Berkenbosch F., Vermes I., Linton E. A., Smelik P. G. Role of epinephrine and vasopressin in the control of the pituitary-adrenal response to stress. Fed Proc. 1985 Jan;44(1 Pt 2):155–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usategui R., Oliver C., Vaudry H., Lombardi G., Rozenberg I., Mourre A. M. Immunoreactive alpha-MSH and ACTH levels in rat plasma and pituitary. Endocrinology. 1976 Jan;98(1):189–196. doi: 10.1210/endo-98-1-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watabe T., Tanaka K., Kumagae M., Itoh S., Takeda F., Morio K., Hasegawa M., Horiuchi T., Miyabe S., Shimizu N. Hormonal responses to insulin-induced hypoglycemia in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Dec;65(6):1187–1191. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-6-1187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]