Abstract
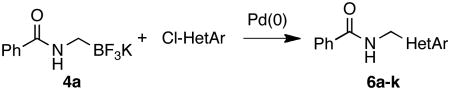
Amidomethyltrifluoroborates were successfully synthesized in a one-pot fashion and used in cross-coupling reactions with a wide variety of aryl and heteroaryl chlorides.
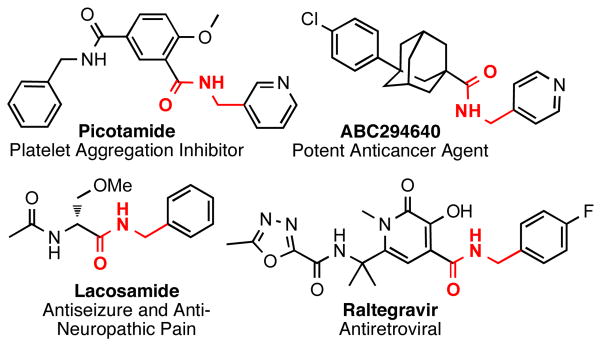
Amidomethylarenes are commonly found in a variety of biologically active compounds (Figure 1).1 Several strategies have been developed to obtain amidomethyl-containing products such as nucleophilic displacement,2 reductive N-alkylation,3 and more commonly amidation.4 These methods follow a consonant reactivity pattern based on the nucleophilicity of the nitrogen. Recently, cross-coupling reactions using N,N-dialkylaminomethyltrifluoroborates were described to access the analogous aminomethyl moiety.5 This approach provides access to amines using a C-C bond connection strategy complementary to existing C-N bond-forming approaches.
Figure 1.
Biologically Active Molecules Containing the Amidomethyl Moiety
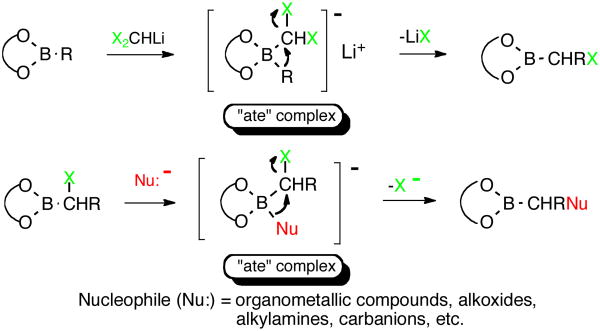
The N,N-dialkylaminomethyltrifluoroborates used in previous coupling efforts were obtained by a direct SN2 displacement of the halides of potassium halomethyltrifluoroborates. Unfortunately, amidomethyltrifluoroborates cannot be accessed in this manner, and thus it was necessary to develop a different approach to the trifluoroborate starting materials. The strategy chosen was based on previous work pioneered by Matteson,6 in which substituted boronate esters were obtained from halomethylboronate esters via intramolecular nucleophilic displacement and one carbon homologation of in situ generated LiCHX2 or LiCH2X species (X = Cl, Br, I).7 The “ate” complex resulting from initial attack of the nucleophile at the boron atom is followed by α-transfer to the neighboring carbon to form the elaborated boronate ester (Figure 2).8
Figure 2.
Reaction mechanism of the one-carbon homologation of boronate esters and the intramolecular nucleophilic displacement of α-halo boronate esters with various nucleophiles.
Amidomethylboronate esters have been synthesized following this strategy,9 but only a few examples were reported, and poor to moderate yields were observed for the formation of α-unsubstituted products in a process that required two to three steps.9f,10 Furthermore, apart from their biological evaluations, amidomethylborons have not been used with success as Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling partners.11 We disclose herein the formation of amidomethyltrifluoroborates synthesized in an original one-pot process from halomethylboronate esters. Additionally we report their palladium-catalyzed coupling with various aryl- and heteroaryl chlorides, which constitutes the first successful example of amidomethylation by a cross-coupling protocol. 12,13
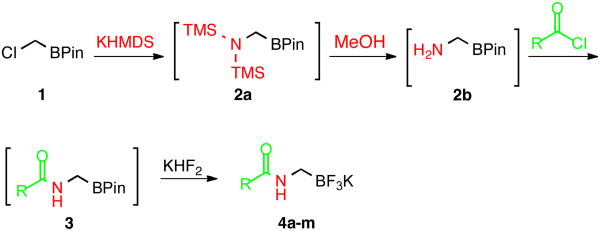
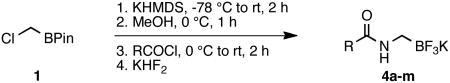
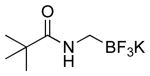
The current study began with the preparation of amidomethyltrifluoroborates 4a-m using an adaptation of the Matteson procedure (Scheme 1).9
Scheme 1.
One-pot process to synthesize 4a-m
Thus 2-(chloromethyl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane 1 in the presence of potassium hexamethyldisilazide gave the expected disilylated aminoboronate ester 2a, which was deprotected in situ by the addition of methanol. The revealed free amine 2b was then reacted with various acyl chlorides to form the corresponding amides. The crude boronate esters 3 obtained in this one-pot fashion were directly treated with a saturated solution of KHF2 to afford 4a-m in good to excellent overall yields (Table 1).
Table 1.
Preparation of Amidomethyltrifluoroborates
 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | RCOCl | product | % isolated yield | |
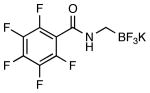
| 1 | 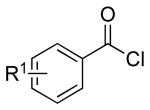 |
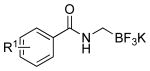 |
4a: R1 = H | 67 |
| 4b: R1 = p-F | 76 | |||
| 4c: R1 = p-CF3 | 71 | |||
| 4d: R1 = p-Ph | 77 | |||
| 4e: R1 = m-OMe | 69a | |||
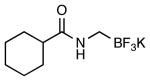
| 2 |  |
 |
4f | 62 |
| 3 | 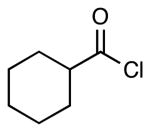 |
 |
4g | 59a |
| 4 | 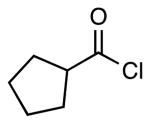 |
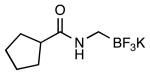 |
4h | 60a |
| 5 | 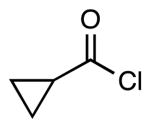 |
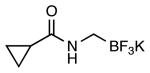 |
4i | 56 |
| 6 | 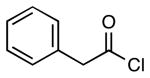 |
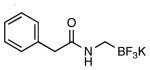 |
4j | 63 |
| 7 | 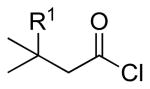 |
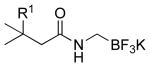 |
4k: R1 = H | 41 |
| 4l: R1 = Me | 41 | |||
| 8 | 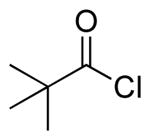 |
 |
4m | 54 |
Reaction for 12 h at rt in the presence of RCOCl
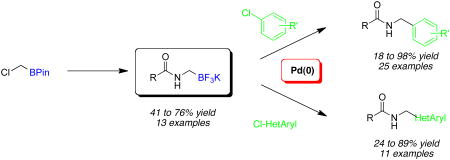
This method provided access to aromatic substituted carbamides 4a-f that contained electron withdrawing and electron donating groups (Table 1, entries 1 and 2). Saturated carbocycles (entries 3-5) as well as alkyl side chains (entries 6-8) could also be incorporated.
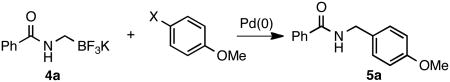
With these compounds in hand, the cross-coupling conditions were first optimized with 4a and p-chloroanisole as the electrophilic partner (Table 2, entry 6). The most effective coupling conditions were found to be 2.5 mol % of Pd(OAc)2, 5 mol % of XPhos and 3 equiv of Cs2CO3 in a 10:1 cyclopentyl methyl ether (CPME) and water mixture at 85 °C for 6 h with a stoichiometric amount of potassium trifluoroborate. On a larger scale reaction (1 g of product), the catalyst loading could be lowered to 1 mol % with similar results (entry 6). The generality of the method was then investigated by using structurally and electronically diverse aryl chlorides. Throughout the series of reaction partners studied, the expected coupling products were obtained in good to excellent yields, and a variety of functional groups including nitriles, ketones, aldehydes, esters, and alcohols were tolerated under these conditions. Sterically hindered electrophiles (Table 2, entries 2, 3, 7, 10) were found to couple in excellent yields, although an increase in the catalyst loading or in the reaction time was required.
Table 2.
Cross-Coupling of 4a with Diverse Aryl Chlorides
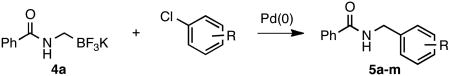 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | chloride | product | % isolated yield | |
| 1 |  |
 |
5a | 87 |
| 2 | 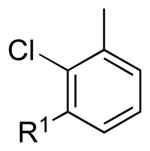 |
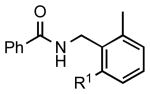 |
5b: R1 = H | 83 (91)a |
| 5c: R1 = Me | 88b | |||
| 3 | 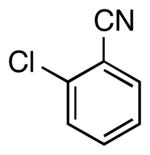 |
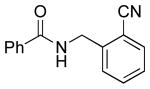 |
5d | 65a |
| 4 | 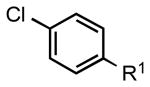 |
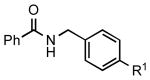 |
5e: R1 = CN | 87 |
| 5f: R1 = CHO | 88 | |||
| 5g: R1 = Ac | 88 | |||
| 5 | 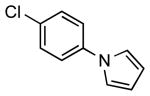 |
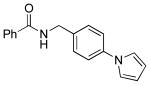 |
5h | 98 |
| 6 | 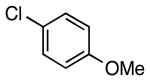 |
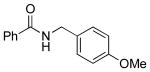 |
5i | 95 (91)c |
| 7 | 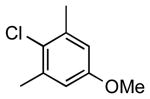 |
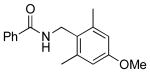 |
5j | 74 |
| 8 | 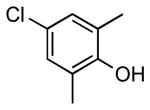 |
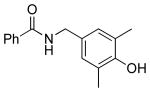 |
5k | 87 |
| 9 | 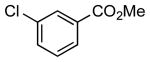 |
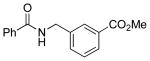 |
5l | 89 |
| 10 |  |
 |
5m | 76 |
All reactions were carried out using 0.3 mmol of 4a and aryl chloride, 2.5 mol % Pd(OAc)2, 5 mol % XPhos, 0.9 mmol of Cs2CO3, 10:1 CPME/H2O (0.09 M), 85 °C, 6 h.
Used 5 mol % Pd(OAc)2, 10 mol % XPhos.
Heated reaction for 14 h.
Reaction performed on 4.1 mmol scale using 1 mol % Pd(OAc)2 and 2 mol % XPhos, 24 h at 85 °C.
To investigate the method further, the array of electrophiles was expanded to heteroaryl chlorides (Table 3). Chloropyridines bearing the halogen in the 3 or 4 position and other heteroaryl chlorides such as quinoline, thiophene or furan derivatives were successfully coupled with 4a under our previously described conditions in moderate to excellent yields. Unfortunately, despite attempting to increase the reaction temperature and increase or decrease the catalyst loading, 2-chloropyridine (6d) and 2-chloro-4-methoxypyrimidine (6g) gave rise to a significant amount of homocoupled product (entries 3, 6).
Table 3.
Cross-Coupling of 4a with Various Heteroaryl Chlorides
 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | chloride | product | % isolated yield | |
| 1 | 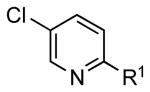 |
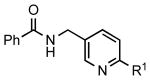 |
6a: R1 = H | 79 |
| 6b: R1 = OMe | 89 | |||
| 2 | 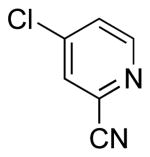 |
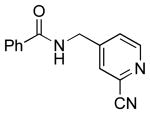 |
6c | 25 (49)a |
| 3 | 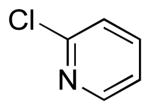 |
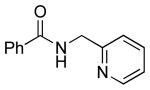 |
6d | 24 (33)a |
| 4 | 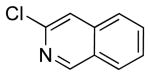 |
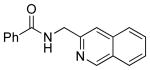 |
6e | 58b (66)a |
| 5 | 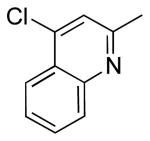 |
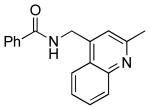 |
6f | 86 |
| 6 | 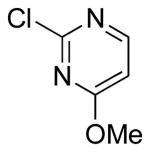 |
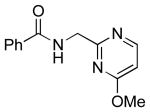 |
6g | 25 |
| 7 | 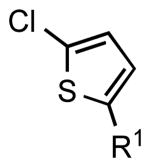 |
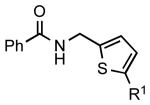 |
6h: R1 = H | 86 |
| 6i: R1 = Ac | 78 | |||
| 6j: R1 = CHO | 82 | |||
| 8 | 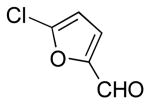 |
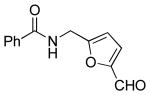 |
6k | 89 |
All reactions were carried out using 0.3 mmol of 4a and heteroaryl chloride, 2.5 mol % Pd(OAc)2, 5 mol % XPhos, 0.9 mmol of Cs2CO3, 10:1 CPME/H2O (0.09 M), 85 °C, 6 h.
Heated for 24 h with 5 mol % Pd(OAc)2, 10 mol % XPhos.
Heated reaction for 14 h.
We next examined the efficiency of the reaction with different amidomethyltrifluoroborates (Table 4). Both cyclic and acyclic carbamides gave the expected coupling product in good to excellent yields except for the biphenyl- and the pentafluorophenyl substrates (7d and 7f) (Table 4, entries 1 and 2), where degradation products were mostly recovered.
Table 4.
Cross-Coupling with Various Potassium Amidomethyltrifluoroborates
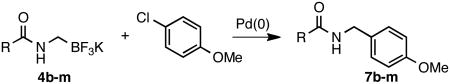 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | R | product | % isolated yield | ||
| 1 | 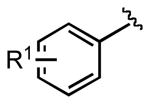 |
4b | 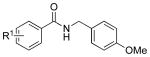 |
7b: R1 = p-F | 89 |
| 4c | 7c: R1 = p-CF3 | 88 | |||
| 4d | 7d: R1 = p-Ph | 18 | |||
| 4e | 7e: R1 = m-OMe | 81 | |||
| 2 | 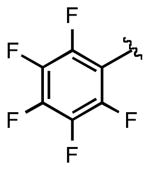 |
4f | 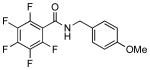 |
7f | 32 |
| 3 | 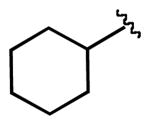 |
4g | 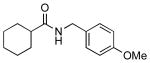 |
7g | 77 |
| 4 | 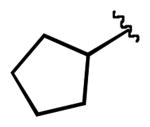 |
4h | 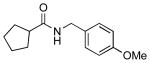 |
7h | 90 |
| 5 | 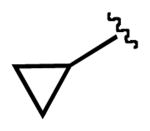 |
4i | 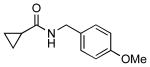 |
7i | 52 (83)a |
| 6 | 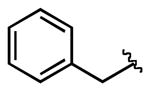 |
4j | 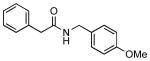 |
7j | 94 |
| 7 | 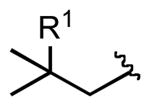 |
4k | 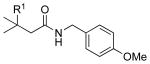 |
7k: R1 = H | 83 |
| 4l | 7l: R1 = Me | 93 | |||
| 8 | 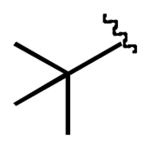 |
4m | 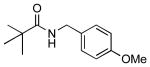 |
7m | 81 |
All reactions were carried out using 0.3 mmol of 1a and aryl chloride, 2.5 mol % Pd(OAc)2, 5 mol % XPhos, 0.9 mmol of Cs2CO3, 10:1 CPME/H2O (0.09 M), 85 °C, 6 h.
Used 5 mol % Pd(OAc)2, 10 mol % XPhos.
Finally, the electrophile compatibility was examined (Table 5). Surprisingly, the aryl iodide gave low yields, indicating that the oxidative addition is not the limiting step of the catalytic cycle under these conditions. Aryl triflates and -bromides coupled cleanly in high yields. Unfortunately, tosylate derivatives exhibited no reactivity.
Table 5.
Electrophile Compatibility
 | ||
|---|---|---|
| entry | aryl electrophile | % isolated yield |
| 1 | I | 31 |
| 2 | Br | 85 |
| 3 | OTf | 93 |
| 4 | OTs | traces |
All reactions were carried out using 0.3 mmol of 1a and aryl chloride, 2.5 mol % Pd(OAc)2, 5 mol %XPhos, 0.9 mmol of Cs2CO3, 10:1 CPME/H2O (0.09 M), 85 °C, 6 h.
In summary, an efficient one-pot synthetic protocol successfully delivered α-unsubstituted amidomethyltrifluoroborates. These trifluoroborates proved to be suitable reagents to introduce the amidomethyl functional group into substrates via a unique bond construction. Various electron-rich and electron-poor aryl and heteroaryl electrophiles were used, demonstrating the generality of this method.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a National Priorities Research Program (NPRP) grant from the Qatar National Research Fund (Grant no. 08-035-1-008) and the NIH (R01 GM-081376). We thank Frontier Scientific for a generous gift of Pd(OAc)2. Dr. Rakesh Kohli (University of Pennsylvania) is acknowledged for obtaining HRMS data.
Footnotes
Supporting Information Available Experimental procedures, spectral characterization, and copies of 1H, 13C, 19F, and 11B NMR spectra for all compounds. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http/pubs.acs.org.
References
- 1.(a) French KJ, Zhuang Y, Maines LW, Gao P, Wang W, Beljanski V, Upson JJ, Green CL, Keller SN, Smith CD. J Phamarcol Exp Ther. 2010;133:129. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.163444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Belyk KM, Morrison HG, Jones P, Summa V. WO Patent 60,730. 2007; (c) McIntyre JA, Castaner J. Drugs Future. 2004;29:992. [Google Scholar]; (d) Ratti S, Quarato P, Casagrande C, Fumagalli R, Corsini A. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998;355:77. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(98)00467-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gajda T, Zwierzak A. Biochemistry. 1981;1:1005. [Google Scholar]
- 3.(a) Dubé D, Scholte AA. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999;40:2295. [Google Scholar]; (b) Oaki Y, Kobayashi S. J Comb Chem. 1999;1:371. [Google Scholar]
- 4.(a) Han SY, Kim YA. Tetrahedron. 2004;60:2447. [Google Scholar]; (b) Montalbetti CAGN, Falque V. Tetrahedron. 2005;61:10827. [Google Scholar]; (c) Huang Z, Reilly JE, Buckle RN. Synlett. 2007:1026. [Google Scholar]; (d) NordstrØm LU, Vogt H, Madsen R. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:17672. doi: 10.1021/ja808129p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Terada Y, Ieda N, Komura K, Sugi Y. Synlett. 2008:2318. [Google Scholar]; (f) Burés J, Martín M, Urpí F, Vilarrasa J. J Org Chem. 2009;74:2203. doi: 10.1021/jo802825e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.(a) Molander GA, Ham J. Org Lett. 2006;8:2031. doi: 10.1021/ol060375a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Molander GA, Sandrock DL. Org Lett. 2007;9:1597. doi: 10.1021/ol070543e. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Molander GA, Gormisky PE, Sandrock DL. J Org Chem. 2008;73:2052. doi: 10.1021/jo800183q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.For reviews on α-halo boronate esters see: Matteson DS. Chem Rev. 1989;89:1535.Matteson DS. Tetrahedron. 1989;45:1859.Matteson DS. Tetrahedron. 1998;54:10555.
- 7.(a) Brown HC, Rogic MM, Rathke MW, Kabalka GW. J Am Chem Soc. 1968;90:818. [Google Scholar]; (b) Matteson DS, Mah RWH. J Am Chem Soc. 1963;85:2599. [Google Scholar]; (c) Brown HC, De Lue NR, Yamamoto Y, Maruyama K, Kasahara T, Murahashi S, Sanoda A. J Org Chem. 1977;42:4088. [Google Scholar]
- 8.(a) Sadhu KM, Matteson DS. Organometallics. 1985;4:1687. [Google Scholar]; (b) Sadhu KM, Matteson DS. Tetrahedron Lett. 1986;27:795. [Google Scholar]; (c) Brown HC, Phadke AS, Rangaishenvi MV. J Am Chem Soc. 1998;110:6263. doi: 10.1021/ja00226a061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Brown HC, Singh SM. Organometallics. 1986;5:994. [Google Scholar]; (e) Brown HC, Singh SM, Rangaishenvi MV. J Org Chem. 1986;51:3150. [Google Scholar]; (f) Wallace RH, Zong KK. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992;33:6941. [Google Scholar]; (g) Soundararajan R, Li G, Brown HC. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994;35:8957. [Google Scholar]; (m) Davoli P, Fava R, Morandi S, Spaggiari A, Prati F. Tetrahedron. 1993;49:177. [Google Scholar]
- 9.(a) Matteson DS, Sadhu KM, Lienhard GE. J Am Chem Soc. 1981;103:5241. [Google Scholar]; (b) Matteson DS, Jesthi PK, Kizhakethil MS. Organometallics. 1984;3:1284. [Google Scholar]; (c) Matteson DS, Sadhu KM. Organometallics. 1984;3:614. [Google Scholar]; (d) Verleijen JPG, Faber PM, Bodewes HH, Braker AH, Van Leusen D, van Leusen AM. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995;36:2109. [Google Scholar]; (e) Matteson DS, Singh RP, Sutton CH, Verheyden JD, Lu JH. Heteroat Chem. 1997;8:487. [Google Scholar]; (f) Matteson DS. Pure Appl Chem. 2003;75:1249. [Google Scholar]; (g) Lai JH, Liu Y, Wu W, Zhou Y, Maw HH, Bachovchin WW, Bhat KL, Bock CW. J Org Chem. 2006;71:512. doi: 10.1021/jo051757h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (h) Inglis SR, Woon ECY, Thompson AL, Schofield CJ. J Org Chem. 2010;75:468. doi: 10.1021/jo901930v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.(a) Caselli E, Powers RA, Blasczcak LC, Wu CYE, Prati F, Shoicher BK. Chem Biol. 2001;8:17. doi: 10.1016/s1074-5521(00)00052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Kinder DH, Katzenellenbogen JA. J Med Chem. 1985;28:1917. doi: 10.1021/jm00150a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Pechenov A, Stefanova ME, Nicholas RA, Peddi S, Gutheil WG. Biochemistry. 2003;42:579. doi: 10.1021/bi026726k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tanaka K. US Patent 15,351. 2008:A1.
- 12.For reviews on organotrifluoroborate salts see: Molander GA, Figueroa R. Aldrichim Acta. 2005;38:49.Molander GA, Ellis N. Acc Chem Res. 2007;40:275. doi: 10.1021/ar050199q.Stefani HA, Cella R, Adriano S. Tetrahedron. 2007;63:3623.Darses S, Genêt JP. Chem Rev. 2008;108:288. doi: 10.1021/cr0509758.
- 13.(a) Molander GA, Biolatto B. J Org Chem. 2007;68:4302. doi: 10.1021/jo0342368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Molander GA, Canturk B, Kennedy LE. J Org Chem. 2009;74:973. doi: 10.1021/jo802590b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.