Abstract
Fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs) play key roles in proliferation, differentiation, and tumorigenesis. Previously, we demonstrated that FGFR1 expression is increased in urothelial carcinoma cell lines and tumors, which promotes proliferation and survival via activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. Here we examined splice variants of FGFR1 in both urothelial carcinoma cell lines and tumors. Two known FGFR1 IIIc splice variants (FGFR1α and FGFR1β) were expressed. FGFR1β lacks exon 3 of FGFR1α, removing the first Ig loop of the extracellular domain. Both isoforms were expressed at similar levels in normal urothelial cells, but FGFR1β was expressed at higher levels in most tumor cell lines. In tumor tissues, expression levels were higher than in controls, and the FGFR1β:FGFR1α ratio was significantly increased in association with tumor stage and grade. When FGFR1α and FGFR1β were expressed in urothelial cells, no differences in signaling were observed. FGFR1-induced proliferation paralleled MAPK pathway activation. The relative activation of FGFR1β and FGFR1α by all known mammalian FGFs was examined. Both isoforms were activated by the same FGFs, but the level of activation differed. FGFR1β showed higher affinity for low concentrations of FGF1, leading to enhanced signaling and increased proliferation. An FGFR1α-to-FGFR1β isoform switch and increased FGF1-induced activation of FGFR1β may result in a proliferative advantage that plays a key role during bladder tumor progression.
The fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family comprises 22 structurally related molecules that bind with high affinity to four FGF receptors (FGFRs1-4). Activation of receptor signaling and subsequent biological activity depends on spatial and temporal expression patterns and binding affinities of specific FGF:FGFR partners. Due to this complexity, FGFR activation can stimulate numerous downstream pathways and has been implicated in multiple biological processes.
FGFRs contain an extracellular ligand binding domain, a single transmembrane domain and an intracellular split tyrosine kinase domain. The extracellular domain contains two (FGFRβ) or three (FGFRα) immunoglobulin-like (Ig-like) domains1 and regulates ligand binding specificity and ligand-induced receptor dimerization.2,3 Specificity of FGF binding is conferred not only by the receptor family member but also by alternative splicing of the extracellular domain.3 The C-terminal half of Ig-like domain III may be encoded by either of two exons, resulting in IIIa, IIIb, or IIIc isoforms. The IIIa splice form contains normally intronic sequence upstream of exon 8 and 9 and terminates within the Ig domain III. This splice variant is a secreted FGF-binding protein with no known signaling ability.4 The IIIb and IIIc isoforms show different ligand binding specificity and signaling capabilities.1,5,6 Another RNA splicing event results in skipping of the exon encoding Ig-like domain I, resulting in a receptor containing only two Ig-like domains (FGFRβ)7 with a higher binding affinity for FGF1 and heparin.8,9 An increase in the FGFR1β:FGFR1α ratio has been associated with tumor progression, reduced relapse-free survival, and malignancy in astrocytomas,10 breast,11 and pancreatic12 cancers. However, little is known about the biological and functional consequences of increased expression of FGFR1β in cancer cells.
Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men in the United Kingdom and the United States13 (http://info.cancerresearchuk.org/cancerstats/types/bladder/?a=5441, last accessed September 7, 2010). The disease is characterized by a high proportion (∼70%) of noninvasive superficial papillary tumors at presentation, which frequently contain activating mutations in FGFR3.14 Recent studies have highlighted activated FGFR3 as a potential therapeutic target in noninvasive urothelial carcinoma (UC) of the bladder.15,16,17 FGFRs may also prove to be valid therapeutic targets in invasive disease. A high proportion of invasive tumors express high levels of FGFR1,18 and many show up-regulation of nonmutant FGFR3.19 Activation of FGFR1 led to increased proliferation and decreased apoptosis in normal urothelial cells and knockdown of FGFR1 in bladder cancer cell lines demonstrated that some lines depended on FGFR1 for survival and cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo.18
Little is known about the biological and functional consequences of increased expression of FGFR1β in cancer. Here, we have elucidated differences in FGFR1 splicing in UC cell lines and tumors and assessed the functional consequences of altered splicing. We examined the relative expression of FGFR1α and FGFR1β and determined the binding specificity of FGFR1α and FGFR1β for all known mammalian FGFs in normal urothelial cells. This is the first report of altered splicing of FGFR1 in bladder cancer and demonstrates that the splicing switch has a functional consequence.
Materials and Methods
Cell Lines, Tissues, and Materials
Thirty seven bladder lines were used: JMSU1, SW1710, TCCSUP, VMCUB-I, 253J, UM-UC3, T24, HT1197, 609BC, BFTC909, 97-24, HCV29, 5637, SV-HUC, VMCUB-III, 647V, SCaBER, BC-3C, J82, 96-1, 92-1, CAL29, LUCC1, VMCUB-II, 97-1, SD, RT112, 97-18, 97-6, HT1376, 97-7, JO’N, LUCC2, SW780, DSH1, 97-19, and 94-10. Cells were grown in standard media at 37°C in 5% CO2. Primary normal human urothelial cells (NHUC) or telomerase immortalized NHUC (TERT-NHUC)20 were derived from urothelium isolated from human ureter obtained at nephrectomy.21 These were maintained in PromoCell medium supplemented with keratinocyte growth medium 2 supplement pack (PromoCell, Heidelberg, Germany). Human recombinant FGF18 was from Invitrogen (Paisley, UK), FGFs 11, 13, and 14 were from Caltag-Med Systems (Little Balmer, UK), and other FGFs were from R&D Systems (Abingdon, UK).
The study was approved by the Local Research Ethics Committee and informed consent obtained from all patients. Cold cup biopsies of tumor tissues were snap-frozen and stored in liquid nitrogen. The remainder of the tumor was fixed in 10% formal saline for 24 hours, dehydrated, and embedded in paraffin for diagnostic assessment.22,23 All were transitional cell carcinoma.
Cloning of FGFR1, Production of Retroviruses, and Transductions
FGFR1 was amplified by RT-PCR as described previously.18 Individual isoform products were cloned into pGEM T-easy, sequenced, and subcloned into pFB-HYG.24 FGFR1 and shRNA constructs18 were transfected into Phoenix A packaging cells (ATCC, Manassas, VA), using siPORT XP-1 transfection agent (Ambion, Warrington, UK). After 48 hours, medium was harvested, 0.4 μm filtered, and mixed in equal amounts with fresh medium containing 8 μg/ml polybrene (Sigma, Poole, UK). Cells were incubated with retroviral supernatants for 8 hours. Forty-eight hours after transduction, cells expressing shRNA or FGFR1 isoforms were transferred into selection medium containing either puromycin or hygromycin respectively.
Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted from cell lines and from frozen tumor sections containing more than 90% tumor cells. RNA was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Crawley, UK), and 1 μg was reverse transcribed in the presence or absence of reverse transcriptase (Superscript II, Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Real-time RT-PCR analysis was performed using SYBR Green I as reporter and ROX as reference dye (Perkin-Elmer, Seer Green, UK), using SDHA as an internal control, as described previously.24 FGFR1 isoform levels were analyzed using the following primers: FGFR1αF, 5′-ctctaactgcagaacttgggatgt-3′; FGFR1αR, 5′-ccagggctgggcttgtt-3′; FGFR1βF, 5′-gaccttgcctgaacaagatgctc-3′; FGFR1βR, 5′-gcactgcatgcaatttcttttcc-3′.
Immunohistochemistry
For detection of FGFR1 protein, 5 μm deparaffinized and rehydrated sections were treated with 3% hydrogen peroxide (Sigma), pressure cooked for two minutes with citric acid buffer (pH 6), and blocked with an Avidin Biotin blocking kit (Vector Laboratories, Peterborough, UK). Primary antibody (FGFR1, 1:50, Epitomics, Wembley, UK) was applied overnight and detected with a biotinylated secondary antibody and 3,3-diaminobenzidine (DAB). Slides were counterstained with hematoxylin, dehydrated, and mounted. Antibody specificity was confirmed using sections from tumors with known high or low RNA expression levels of FGFR1 measured by real-time RT-PCR.
Western Blotting, Immunoprecipitation, and Phospho-Kinase Antibody Array
Cells were lysed in 1% Triton buffer [1% Triton-X 100, 2 mmol/L EDTA, and protease inhibitor cocktail (Sigma) in PBS] and lysates cleared by centrifugation at 10,000 rpm at 4°C for 10 minutes. Protein concentrations were determined using the Bradford assay (Biorad, Hemel Hempstead, UK). Antibodies used for Western blotting were anti-phospho-ERK (Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA), tubulin (Serotec, Kidlington, UK), FGFR1 (Santa Cruz), and 4G10 anti-phosphotyrosine (Cell Signaling, Hitchin, UK). Immunoprecipitation and Western blotting were carried out as described previously.18 Each Western blot was normalized to tubulin expression and quantified using Quantity One Software (Biorad). The Human Phospho-Kinase Antibody Array (R&D Systems) was used according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, the array was blocked then incubated with 200 μg of protein extracted from treated cells, before incubation with Detection Antibody Cocktail. The Arrays were imaged and quantified using Quantity One Software.
Phenotypic Assays
For proliferation assays 6 × 104 cells were plated per well in six-well dishes in duplicate. Cells were cultured with heparin and/or FGFs as described, and viable cells were counted after five days of culture using the Guava EasyCyte System (Millipore, Billerica, MA), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Each experiment was performed a minimum of three times.
Results
FGFR1α and FGFR1β Expression in Bladder Cancer Cells
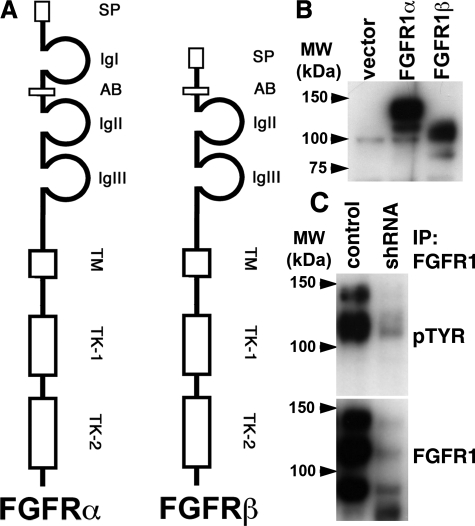
Alternative mRNA splicing and increased expression of FGFR1 has been described in numerous cancer types.10,11,12 To identify splice variants in bladder cancer cell lines, we performed RT-PCR for FGFR1 in JMSU1 and UMUC3, as these cell lines express high levels of FGFR1. PCR products were cloned and sequenced (data not shown). Only two isoforms were detected, FGFR1α and FGFR1β (Figure 1A). To study function, both isoforms were expressed using a retroviral system in TERT-NHUC and expression was confirmed by Western blotting (Figure 1B). We used immunoprecipitation of endogenous FGFR1 using lysates extracted from JMSU1 cells to demonstrate increased expression of FGFR1β and that FGFR1 is phosphorylated in response to FGF. JMSU1 expressed more FGFR1β protein, and both isoforms were phosphorylated in response to FGF activation (Figure 1C). Western blotting without immunoprecipitation showed a similar banding pattern (data not shown). To confirm that the detected proteins were FGFR1, we knocked down expression of FGFR1 in JMSU1 using a short hairpin RNA (shRNA) (Figure 1C). This reduced expression of the bands identified by immunoprecipitation, demonstrating that these bands were indeed FGFR1 isoforms. In addition, the proteins detected in UC cell lines were of similar size to FGFR1α and FGFR1β ectopically expressed in normal cells.
Figure 1.
Identification of FGFR1 splice variants in bladder cancer cell lines. A: Diagrammatic representation of the alternative mRNA splice variants of FGFR1 that were identified by RT-PCR. SP, signal peptide; Ig I-III, immunoglobulin-like domains I-III; TM, transmembrane domain; TK-1 and TK-2, tyrosine kinase domains. B: FGFR1α and FGFR1β were overexpressed in TERT-NHUC, and expression was confirmed by Western blotting MW, molecular weight. C: FGFR1 was immunoprecipitated from JMSU1 and JMSU1 expressing shRNA targeting FGFR1. Western blots were probed with an antiphosphotyrosine (4G10) antibody pTYR, stripped, and reprobed for FGFR1.
FGFR1β:FGFR1α Ratio Is Increased in Bladder Cancer
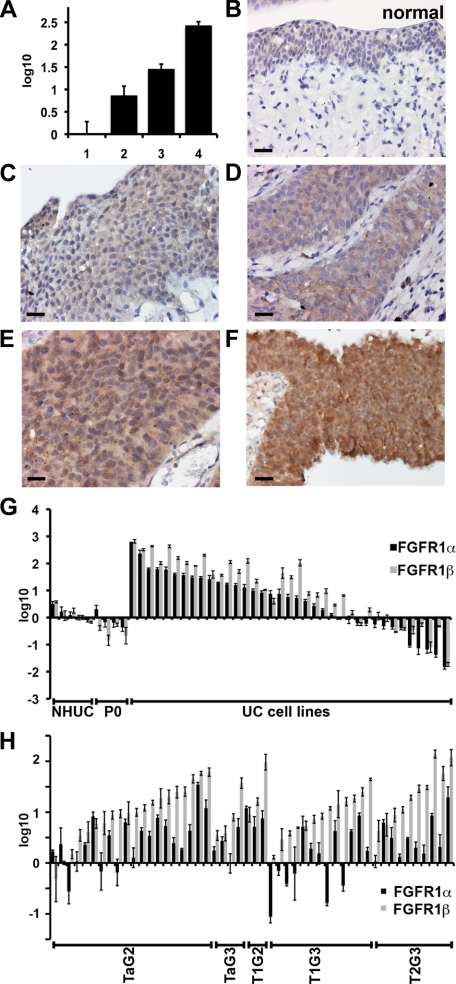
To measure expression levels of FGFRβ and FGFR1α in tumor samples we used real-time RT-PCR as current antibodies cannot distinguish the two isoforms. Initially we confirmed that mRNA expression levels correlate with protein levels. Expression levels of total FGFR1 were measured by real-time RT-PCR as described previously (Figure 2A).18 mRNA levels were then compared to FGFR1 protein detected by immunhistochemistry in the same samples (Figure 2B–F). This indicated a direct correlation between FGFR1 mRNA and protein expression. Antibody specificity was confirmed using cell pellets from a cell line that does not express FGFR1, and the same line with ectopic over-expression of FGFR1α or FGFR1β. The antibody detected both FGFR1 isoforms (data not shown).
Figure 2.
Expression levels of FGFR1α and FGFR1β in bladder cancer cell lines and tumors. A: Total FGFR1 levels were measured in four tumor samples by real-time RT-PCR (1, pTa grade 2; 2, pT1 grade 3; 3, pT2 grade 3; and 4 pT1 grade 3). Expression levels were normalized to normal bladder urothelium and are represented as log10. C–F: The same tumor samples were stained for FGFR1 by immunohistochemistry and compared to normal urothelium (B). Size bar is 20 μm; magnification, ×40. G: Expression of FGFR1α and FGFR1β in bladder cancer cell lines. H: Expression of FGFR1α and FGFR1β in tumor samples.
Next, isoform-specific real-time RT-PCR primers were designed to amplify FGFR1α and FGFR1β. To evaluate specificity, FGFR1α and FGFR1β were expressed in RT4 (that expresses low levels of FGFR1) and each primer set tested with cDNA extracted from RT4-vector, RT4-FGFR1α or RT4-FGFR1β and normalized to the expression of succinate dehydrogenase subunit A (SDHA), an internal control. Primers targeting FGFR1α showed no specificity for FGFR1β and vice versa (data not shown). Levels of FGFR1 isoforms were then measured in UC cell lines and tumors (Figure 2). FGFR1α and FGFR1β expression was increased compared to NHUC and uncultured urothelium (P0) in most UC cell lines, as observed previously for total FGFR1.18 FGFR1β was expressed more than FGFR1α in 83% of cell lines (31/37) (Figure 2G). The average FGFR1β:FGFR1α ratio for P0 cells was 0.99, for NHUC, 1.85, and for UC cell lines the ratio was 8.1. The ratios were calculated by comparing the normalized expression of FGFR1β and FGFR1α to SDHA per sample and represent the fold difference between FGFR1β and FGFR1α.
We then examined 50 tumor samples; 20 TaG2, 4 TaG3, 3 T1G2, 13 T1G3, 10 ≥T2G3 (Figure 2H). The average fold increase for FGFR1β (22.0) was significantly greater than for FGFR1α (4.3) (P < 0.05), and 78% (39/50) of tumor samples expressed more FGFR1β than FGFR1α. No significant association was observed for expression of FGFR1α or FGFR1β with stage or grade. However, the increase in FGFR1β:FGFR1α ratio was significantly associated with both stage (P = 0.019) and grade (P = 0.039).
Alternative Splicing Does Not Alter FGFR1 Signaling
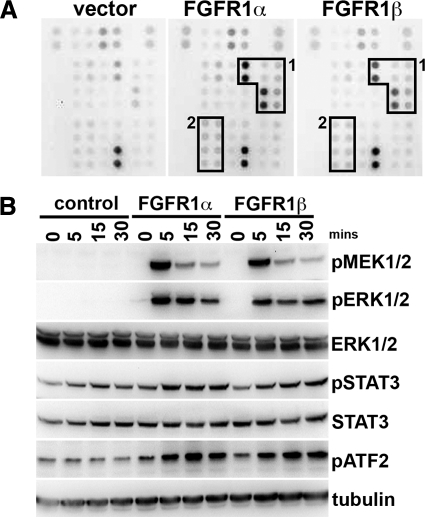
Next we examined the downstream signaling pathways activated by FGFR1α and FGFR1β in TERT-NHUC to determine whether splicing altered signal transduction (Figure 3). A phosphokinase-specific array was used to examine multiple signaling pathways. The major pathway activated was the MAPK pathway, with significant activation of p38, MSK1, MEK1/2, ERK, CREB, and JUN. No difference between FGFR1α and FGFR1β was observed (Figure 3A). Activation of the pathways was confirmed by Western blotting (Figure 3B).
Figure 3.
Signaling downstream of FGFR1α and FGFR1β. A: Human phospho-kinase array analysis to examine differences between FGFR1α and FGFR1β signaling. Boxes 1 and 2 represent activated proteins from the MAPK- and STAT-induced signaling cascades, respectively. B: Confirmation by Western blotting of phosphorylation of proteins identified in the array analysis. Samples were taken over a time course of FGF2 treatment from TERT-NHUC cells expressing FGFR1α FGFR1β and controls.
Multiple FGFs Activate FGFR1α and FGFR1β
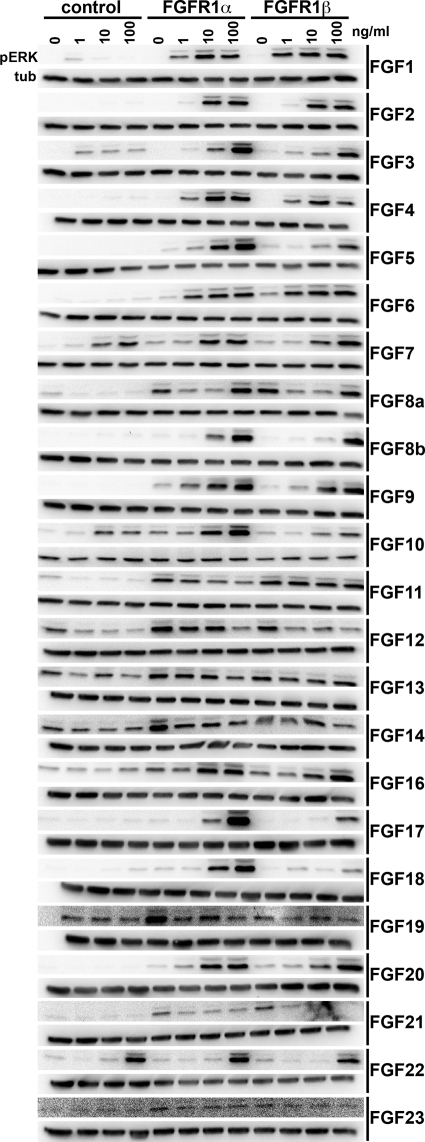
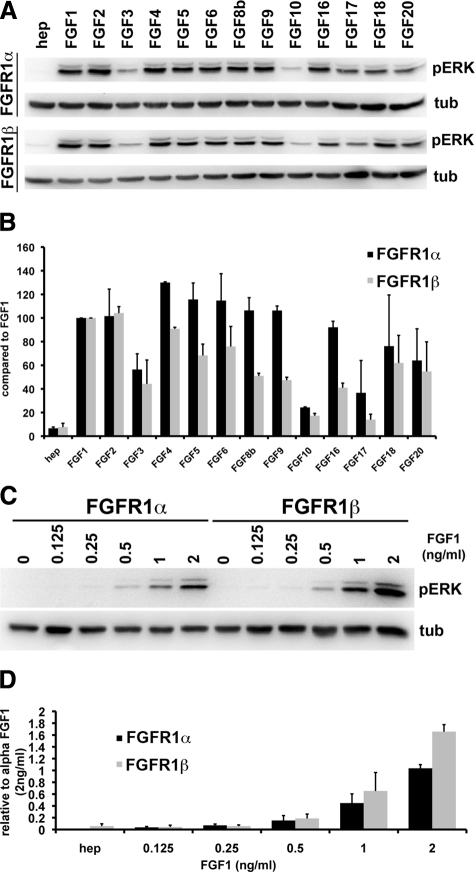
As the signaling cascades activated by FGFR1α and FGFR1β were similar, we hypothesized that splicing may alter ligand binding affinities. Previously we demonstrated that activation of FGFR1 in TERT-NHUC induced proliferation via activation of the MAPK pathway.18 Activation of ERK was therefore used as a read-out of FGFR1α and FGFR1β signaling. TERT-NHUC and TERT-NHUC expressing either FGFR1α or FGFR1β were cultured with FGFs for 15 minutes (Figure 4). FGFs 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8b, 9, 16, 17, 18, and 20 activated FGFR1α and FGFR1β at 100 ng/ml. FGFs10, 17 and 18 activated FGFR1α more than FGFR1β at this time point. FGFs 3, 7, 10, and 22 activated the MAPK pathway independent of ectopic FGFR1 expression. As the level of MAPK activation may influence the phenotypic outcome,18 we measured the level of activation after 5 minutes to compare the level of activation induced by each FGF (Figure 5A). Tubulin was used as a loading control and for normalization when quantifying the levels of pERK. Interestingly, the level of FGFR1β activation by numerous FGFs was lower than that of FGFR1α. Only FGF1 and FGF2 consistently activated FGFR1α and FGFR1β to similar high levels (Figure 5B).
Figure 4.
Activation of the MAPK pathway by FGFs. TERT-NHUC and TERT-NHUC expressing FGFR1α and FGFR1β were cultured with heparin (10 μg/ml) or heparin with 1, 10, or 100 ng/ml FGF for 15 minutes. The top and bottom blots represent pERK and tubulin, respectively.
Figure 5.
FGFR1β is activated more than FGFR1α at lower concentrations of FGF1. A: TERT-NHUC expressing FGFR1α or FGFRβ were cultured with heparin and 100 ng/ml FGF for 5 minutes. Western blots were performed for pERK, stripped, and reprobed for tubulin. B: Levels of pERK were normalized to tubulin and quantified with Quantity One Software (BioRad). C: FGFR1α and FGFR1β were cultured with 0, 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 1, and 2 ng/ml FGF1, and lysates were probed for pERK and tubulin. D: Quantitation of pERK levels normalized to tubulin.
FGFR1β Shows a Higher Sensitivity to Low Concentrations of FGF1
Previous reports indicate that FGFR1β has a higher affinity for FGF1 and FGF2 than FGFR1α.8,9 We demonstrated that low concentrations of FGF1 activated FGFR1β signaling more than FGFR1α signaling (Figure 5, C and D). FGF2 and FGF6 induced similar levels of activation in cells expressing FGFR1α or FGFR1β, while the other FGFs that show bioactivity appeared to have a reduced binding affinity for FGFR1β (data not shown). This demonstrates that expression of FGFR1β specifically increases the sensitivity for FGF1 and not other FGFs in urothelial cells.
Low Levels of FGF1 Promote FGFR1β-Induced Proliferation
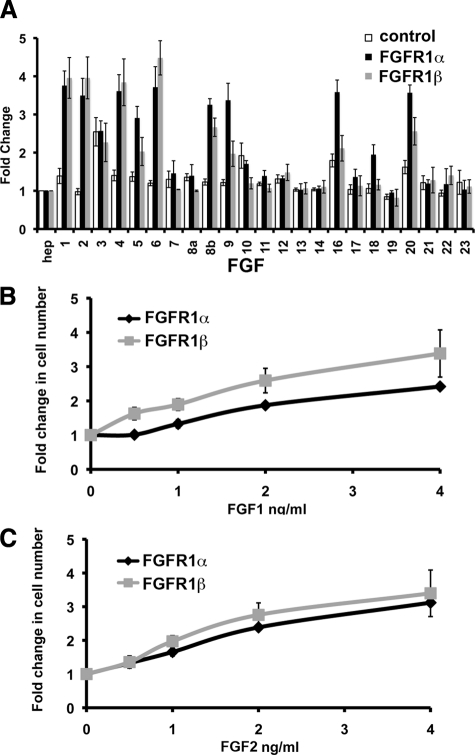
To determine whether activation of FGFR1 correlated with increased proliferation, TERT-NHUC expressing FGFR1α or FGFR1β and controls were cultured with FGFs for 96 hours (Figure 6A). FGFR1α expressing cells cultured with FGF1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8b, 9, 16, 18, and 20 and FGFR1β expressing cells cultured with FGF1, 2, 4, 6, 8b, and 20 showed a significant increase (P < 0.05) in cell number compared to the vector control cells. In the majority of cases, the level of MAPK activation shown in Figure 4 correlated with the increase in cell number shown in Figure 6A. Lower levels of MAPK activation (as shown previously18) resulted in no increase or lower numbers of cells compared to those with higher levels of MAPK activation. For example FGFs 3, 10, and 17 resulted in no significant change in cell number compared to cells not expressing FGFR1. FGF3 stimulated an increase in cell number independent of FGFR1. In addition, cells expressing FGFR1β showed a significantly (P < 0.05) smaller increase in cell number when cultured with FGFs 9, 16, 18, and 20 compared to cells expressing FGFR1α. This is comparable to the decreased level of MAPK activation observed in these cells (Figure 5B). In contrast, cells expressing FGFR1β showed a lower level of activation than FGFR1α when cultured with FGFs 4, 6, and 8b but showed no difference in cell number.
Figure 6.
FGF activation of FGFR1 induces an increase in cell number. A: TERT-NHUC (control) and TERT-NHUC expressing FGFR1α or FGFR1β were cultured with heparin and FGF (100 ng/ml) for 96 hours. FGFR1α and FGFR1β cells were cultured with low concentrations of FGF1 (B) or with FGF2 (C) for 96 hours. Measurements are viable cell numbers taken from an average of three experiments, and error bars represent SD.
In concert with increased MAPK activation (Figure 5C), low concentrations of FGF1 (0.5, 1, and 2 ng/ml) induced significantly (P < 0.05) greater proliferation of cells expressing FGFR1β than of cells expressing FGFR1α (Figure 6B). No significant difference was observed with low concentrations of FGF2 (Figure 6C) or FGF6 (data not shown), correlating with no difference in MAPK activation. Overall, this suggests that altered splicing of FGFR1 in bladder cancer specifically increases sensitivity to low levels of FGF1, giving these cells a proliferative advantage.
Discussion
FGFRs are important players in bladder tumorigenesis. FGFR3 is frequently activated by mutation,14 and FGFR3 expression is increased in both low- and high-stage tumors.19 Our recent studies demonstrate that many bladder tumors also express high levels of FGFR1.18 Increased expression of FGFR1 has been observed in numerous cancer types including breast,25 prostate,26 glioblastoma,27,28 and astrocytoma.29 In our previous study, no relationship of total FGFR1 mRNA and tumor stage or grade was observed in UC.18 In normal urothelium, FGFR1α is expressed at equivalent levels to FGFR1β, as in other normal tissues.10,11,30 We found that FGFR1β is the predominant form in UC and that an α to β switch is associated with increasing tumor stage and grade. Again this is similar to findings in other tumors.10,11,12 The presence of increased FGFR1 in low stage UC suggests that increased total FGFR1 expression may be an early event in the development of both superficial and muscle invasive UC. However, the α to β switch in tumors of high stage and grade indicates that alternative splicing is a critical event in the development of invasive UC. This switch may be a useful prognostic indicator for UC progression.
To recapitulate the increased levels of FGFR1 found in UC, we expressed FGFR1 in telomerase-immortalized normal human urothelial cells.20 The level of expressed FGFR1 was comparable to levels observed in tumor samples and UC cell lines, validating this system as a tool to study FGFR1 activation. Although high expression levels of some tyrosine kinase receptors can lead to autoactivation,31 in TERT-NHUC, FGFR1 activation remained ligand-dependent.
We demonstrated that many FGFs can activate FGFR1. Two previous studies have comprehensively examined receptor specificity of the fibroblast growth factor family and showed a similar increase in proliferation in response to FGFs 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, and 20.2,3 We also observed an increase in proliferation in response to FGFs 16 and 18. This may reflect a difference related to differences in biological context between urothelial cells and the murine pro-B cell line BaF3 used previously. Interestingly, not all FGFs that activated signal transduction induced proliferation. FGFs 3, 10, and 17 activated the MAPK pathway but did not promote cell division. These FGFs showed the lowest levels of MAPK activation. Our previous study demonstrated that the level of MAPK pathway activation by FGFR1 regulated the proliferative response in urothelial cells,18 suggesting that low levels of MAPK activation may result in a low level or no proliferation. Although FGF18-induced activation of the MAPK pathway was relatively high at 5 minutes, only a small increase or no increase in proliferation was observed with FGFR1α and FGFR1β, respectively. After 15 minutes, the FGF18-induced MAPK activation in FGFR1β cells was reduced significantly, suggesting that sustained activation is important for proliferation in these cells. Consistent with our observation that FGF8b but not FGF8a activates FGFR1, it has been demonstrated that FGF8b has a higher affinity for FGFRs and can bind directly to FGFR1.32 FGFs 11–14 showed no biological activity, consistent with a previous report.33
Only FGFR1α has been examined previously,2,3 and hence our study is the first to fully characterize the changes in FGF binding affinities of FGFR1β. Although previous studies have demonstrated the biochemical characteristics of FGFR1β,8,9 little is known about the biological function of FGFR1β in cancer cells. The second and third Ig-like domains are responsible for ligand binding,34 suggesting that the first domain, encoded by exon 3, does not regulate this process. In insect cells, FGFR1β has been shown to exhibit increased binding affinity for FGF1 and FGF2.8 In concordance with this finding, normal bladder cells expressing FGFR1β showed a higher level of activation and increased proliferation in the presence of low concentrations of FGF1 compared to cells expressing FGFR1α. This is the first study to confirm that increased sensitivity for FGF1 results in increased downstream signaling and proliferation. Although this was observed for FGF1, no difference was observed for FGF2. This may reflect the difference in biological systems between our study and those in insect cells and highlights the importance of performing similar studies in biologically relevant systems. Interestingly, sensitivity to many of the FGFs that activated FGFR1α was reduced in cells expressing FGFR1β. These included the FGF9 subfamily (FGFs 9, 16, and 20) and FGFs 5 and 18. The biological relevance of this finding is not understood, and more work is required to explain this phenomenon.
Comprehensive information on the expression of FGFs in the normal urinary tract and UC is lacking. However, FGF1 and FGF2 levels are increased in the urine of patients with bladder cancer,35,36 and increased FGF1 expression has been observed in UC, with strongest expression in high-grade tumors.37 This supports the hypothesis that FGFR1 is ligand-dependent in bladder cancer and suggests that a coordinated increase in FGF1 and FGFR1β is an important step in bladder tumorigenesis. FGFR1/FGF1 interactions may prove to be an important therapeutic target in future drug design strategies.
Acknowledgments
We thank the staff and patients in the Pyrah Department of Urology (St James’s University Hospital Leeds) for provision of clinical samples, and Joanne Brown for excellent technical support.
Footnotes
Address reprint requests to Margaret A. Knowles, Ph.D., Cancer Research UK Clinical Centre, Leeds Institute of Molecular Medicine, St James’s University Hospital, Leeds, LS9 7TF, UK. E-mail: m.a.knowles@leeds.ac.uk.
Supported by Association for International Cancer Research grant 06-034.
References
- Johnson DE, Williams LT. Structural and functional diversity in the FGF receptor multigene family. Adv Cancer Res. 1993;60:1–41. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60821-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X, Ibrahimi OA, Olsen SK, Umemori H, Mohammadi M, Ornitz DM. Receptor specificity of the fibroblast growth factor family: the complete mammalian FGF family. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:15694–15700. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M601252200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornitz DM, Xu J, Colvin JS, McEwen DG, MacArthur CA, Coulier F, Gao G, Goldfarb M. Receptor specificity of the fibroblast growth factor family. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:15292–15297. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.25.15292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duan DS, Werner S, Williams LT. A naturally occurring secreted form of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor 1 binds basic FGF in preference over acidic FGF. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:16076–16080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chellaiah AT, McEwen DG, Werner S, Xu J, Ornitz DM. Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) 3. Alternative splicing in immunoglobulin-like domain III creates a receptor highly specific for acidic FGF/FGF-1. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:11620–11627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner S, Duan DS, de Vries C, Peters KG, Johnson DE, Williams LT. Differential splicing in the extracellular region of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 generates receptor variants with different ligand-binding specificities. Mol Cell Biol. 1992;12:82–88. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.82. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson DE, Lu J, Chen H, Werner S, Williams LT. The human fibroblast growth factor receptor genes: a common structural arrangement underlies the mechanisms for generating receptor forms that differ in their third immunoglobulin domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1991;11:4627–4634. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi E, Kan M, Xu J, Wang F, Hou J, McKeehan WL. Control of fibroblast growth factor receptor kinase signal transduction by heterodimerization of combinatorial splice variants. Mol Cell Biol. 1993;13:3907–3918. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F, Kan M, Yan G, Xu J, McKeehan WL. Alternately spliced NH2-terminal immunoglobulin-like Loop I in the ectodomain of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor 1 lowers affinity for both heparin and FGF-1. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:10231–10235. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.17.10231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi F, Saya H, Bruner JM, Morrison RS. Differential expression of two fibroblast growth factor-receptor genes is associated with malignant progression in human astrocytomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:484–488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luqmani YA, Mortimer C, Yiangou C, Johnston CL, Bansal GS, Sinnett D, Law M, Coombes RC. Expression of 2 variant forms of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 in human breast. Int J Cancer. 1995;64:274–279. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910640411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickers SM, Huang ZQ, MacMillan-Crow L, Greendorfer JS, Thompson JA. Ligand activation of alternatively spliced fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 modulates pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell malignancy. J Gastrointest Surg. 2002;6:546–553. doi: 10.1016/s1091-255x(02)00036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer. J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. doi: 10.3322/CA.2007.0010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappellen D, De Oliveira C, Ricol D, de Medina S, Bourdin J, Sastre-Garau X, Chopin D, Thiery JP, Radvanyi F. Frequent activating mutations of FGFR3 in human bladder and cervix carcinomas. Nat Genet. 1999;23:18–20. doi: 10.1038/12615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson DC, Hurst CD, Knowles MA. Knockdown by shRNA identifies S249C mutant FGFR3 as a potential therapeutic target in bladder cancer. Oncogene. 2007;26:5889–5899. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard-Pierrot I, Brams A, Dunois-Larde C, Caillault A, Diez de Medina SG, Cappellen D, Graff G, Thiery JP, Chopin D, Ricol D, Radvanyi F. Oncogenic properties of the mutated forms of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3b. Carcinogenesis. 2006;27:740–747. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgi290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qing J, Du X, Chen Y, Chan P, Li H, Wu P, Marsters S, Stawicki S, Tien J, Totpal K, Ross S, Stinson S, Dornan D, French D, Wang QR, Stephan JP, Wu Y, Wiesmann C, Ashkenazi A. Antibody-based targeting of FGFR3 in bladder carcinoma and t(4;14)-positive multiple myeloma in mice. J Clin Invest. 2009;119:1216–1229. doi: 10.1172/JCI38017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson DC, Lamont FR, Shnyder SD, Knowles MA. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 promotes proliferation and survival via activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 2009;69:4613–4620. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson DC, Baldo O, Harnden P, Knowles MA. FGFR3 protein expression and its relationship to mutation status and prognostic variables in bladder cancer. J Pathol. 2007;213:91–98. doi: 10.1002/path.2207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman EJ, Hurst CD, Pitt E, Chambers P, Aveyard JS, Knowles MA. Expression of hTERT immortalises normal human urothelial cells without inactivation of the p16/Rb pathway. Oncogene. 2006;25:5037–5045. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate J, Hutton KA, Thomas DF, Trejdosiewicz LK. Normal human urothelial cells in vitro: proliferation and induction of stratification. Lab Invest. 1994;71:583–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UICC Geneva: Union Internationale Contre le Cancer; Classification of malignant tumours, Bladder. 1978:pp 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- WHO Histological typing of urinary bladder tumours. International Histological Classification of Tumours. 1973:10. [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson DC, L'Hote CG, Kennedy W, Pitt E, Knowles MA. Alternative splicing of fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 produces a secreted isoform that inhibits fibroblast growth factor-induced proliferation and is repressed in urothelial carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 2005;65:10441–10449. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-1718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis-Filho JS, Simpson PT, Turner NC, Lambros MB, Jones C, Mackay A, Grigoriadis A, Sarrio D, Savage K, Dexter T, Iravani M, Fenwick K, Weber B, Hardisson D, Schmitt FC, Palacios J, Lakhani SR, Ashworth A. FGFR1 emerges as a potential therapeutic target for lobular breast carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:6652–6662. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng S, Wang F, Matsubara A, Kan M, McKeehan WL. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 limits and receptor 1 accelerates tumorigenicity of prostate epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 1997;57:5369–5378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison RS, Yamaguchi F, Bruner JM, Tang M, McKeehan W, Berger MS. Fibroblast growth factor receptor gene expression and immunoreactivity are elevated in human glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Res. 1994;54:2794–2799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allerstorfer S, Sonvilla G, Fischer H, Spiegl-Kreinecker S, Gauglhofer C, Setinek U, Czech T, Marosi C, Buchroithner J, Pichler J, Silye R, Mohr T, Holzmann K, Grasl-Kraupp B, Marian B, Grusch M, Fischer J, Micksche M, Berger W. FGF5 as an oncogenic factor in human glioblastoma multiforme: autocrine and paracrine activities. Oncogene. 2008;27:4180–4190. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison RS, Yamaguchi F, Saya H, Bruner JM, Yahanda AM, Donehower LA, Berger M. Basic fibroblast growth factor and fibroblast growth factor receptor I are implicated in the growth of human astrocytomas. J Neurooncol. 1994;18:207–216. doi: 10.1007/BF01328955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobrin MS, Yamanaka Y, Friess H, Lopez ME, Korc M. Aberrant expression of type I fibroblast growth factor receptor in human pancreatic adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 1993;53:4741–4744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway KL, 3rd, Sweeney C. EGF receptor activation by heterologous mechanisms. Cancer Cell. 2002;1:405–406. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(02)00076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen SK, Li JY, Bromleigh C, Eliseenkova AV, Ibrahimi OA, Lao Z, Zhang F, Linhardt RJ, Joyner AL, Mohammadi M. Structural basis by which alternative splicing modulates the organizer activity of FGF8 in the brain. Genes Dev. 2006;20:185–198. doi: 10.1101/gad.1365406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen SK, Garbi M, Zampieri N, Eliseenkova AV, Ornitz DM, Goldfarb M, Mohammadi M. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) homologous factors share structural but not functional homology with FGFs. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:34226–34236. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M303183200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson DE, Lee PL, Lu J, Williams LT. Diverse forms of a receptor for acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1990;10:4728–4736. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodak GW, Hospelhorn V, Judge SM, Mayforth R, Koeppen H, Sasse J. Increased levels of fibroblast growth factor-like activity in urine from patients with bladder or kidney cancer. Cancer Res. 1988;48:2083–2088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien TS, Smith K, Cranston D, Fuggle S, Bicknell R, Harris AL. Urinary basic fibroblast growth factor in patients with bladder cancer and benign prostatic hypertrophy. Br J Urol. 1995;76:311–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1995.tb07706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravery V, Jouanneau J, Gil Diez S, Abbou CC, Caruelle JP, Barritault D, Chopin DK. Immunohistochemical detection of acidic fibroblast growth factor in bladder transitional cell carcinoma. Urol Res. 1992;20:211–214. doi: 10.1007/BF00299719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]