Abstract
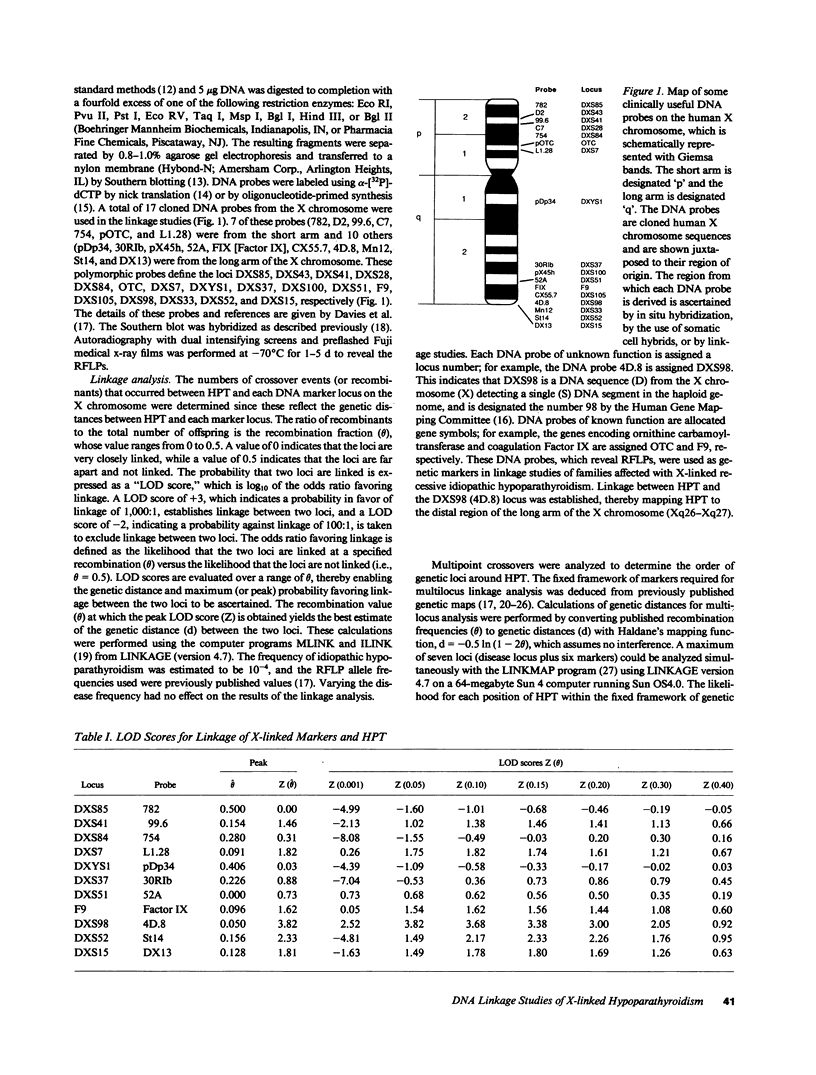
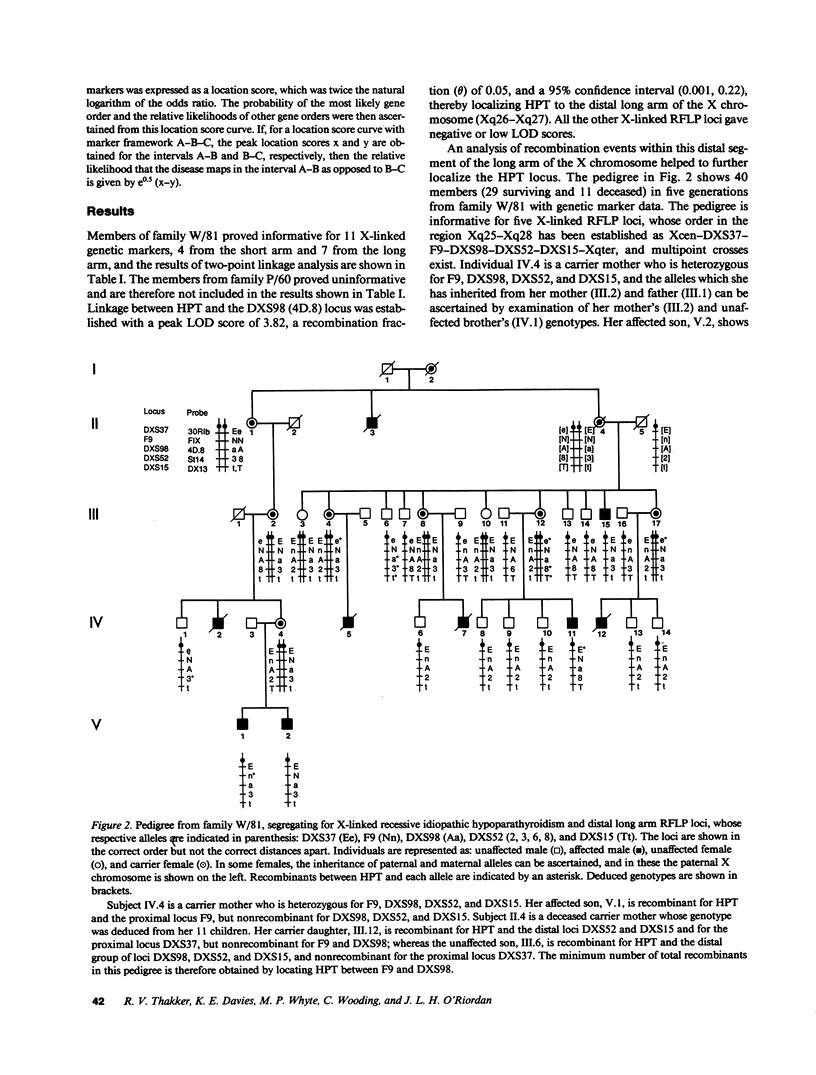
Idiopathic hypoparathyroidism has been reported to occur as an X-linked recessive disorder in two multigeneration kindreds. Affected individuals, who are males, suffer from infantile onset of epilepsy and hypocalcemia, which appears to be due to an isolated congenital defect of parathyroid gland development; females are not affected and are normocalcemic. We have performed linkage studies in these two kindreds (5 affected males, 11 obligate carrier females, and 44 unaffected members) and have used cloned human X chromosome sequences identifying restriction fragment length polymorphisms to localize the mutant gene causing this disorder. Our studies established linkage between the X-linked recessive idiopathic hypoparathyroid gene (HPT) and the DXS98 (4D.8) locus, peak LOD score = 3.82 (theta = 0.05), thereby mapping HPT to the distal long arm of the X chromosome (Xq26-Xq27). Multilocus analysis indicated that HPT is proximal to the DXS98 (4D.8) locus but distal to the F9 (Factor IX) locus, thereby revealing bridging markers for the disease. The results of this study will improve genetic counseling of affected families, and further characterization of this gene locus will open the way for elucidating the factors controlling the development and activity of the parathyroid glands.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn T. G., Antonarakis S. E., Kronenberg H. M., Igarashi T., Levine M. A. Familial isolated hypoparathyroidism: a molecular genetic analysis of 8 families with 23 affected persons. Medicine (Baltimore) 1986 Mar;65(2):73–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr D. G., Prader A., Esper U., Rampini S., Marrian V. J., Forfar J. O. Chronic hypoparathyroidism in two generations. Helv Paediatr Acta. 1971 Dec;26(5):507–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs B. A., Nussbaum R. L. Two anonymous X-specific human sequences detecting restriction fragment length polymorphisms in region Xq26----qter. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 Nov;10(6):607–613. doi: 10.1007/BF01535226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bronsky D., Kiamko R. T., Waldstein S. S. Familial idiopathic hypoparathyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Jan;28(1):61–65. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-1-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannizzaro L. A., Emanuel B. S. In situ hybridization and translocation breakpoint mapping. III. DiGeorge syndrome with partial monosomy of chromosome 22. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;39(3):179–183. doi: 10.1159/000132131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Mandel J. L., Weissenbach J., Fellous M. Report of the committee on the genetic constitution of the X and Y chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;46(1-4):277–315. doi: 10.1159/000132481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Pearson P. L., Harper P. S., Murray J. M., O'Brien T., Sarfarazi M., Williamson R. Linkage analysis of two cloned DNA sequences flanking the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus on the short arm of the human X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2303–2312. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley R. I., Zackai E. H., Emanuel B. S., Kistenmacher M., Greenberg F., Punnett H. H. The association of the DiGeorge anomalad with partial monosomy of chromosome 22. J Pediatr. 1982 Aug;101(2):197–200. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keutmann H. T., Sauer M. M., Hendy G. N., O'Riordan L. H., Potts J. T., Jr Complete amino acid sequence of human parathyroid hormone. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 26;17(26):5723–5729. doi: 10.1021/bi00619a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3443–3446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor S. L., Sakaguchi A. Y., Szoka P., Hendy G. N., Kronenberg H. M., Rich A., Shows T. B. Human parathyroid hormone gene (PTH) is on short arm of chromosome 11. Somatic Cell Genet. 1983 Sep;9(5):609–616. doi: 10.1007/BF01574261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEDEN V. H. True idiopathic hypoparathyroidism as a sexlinked recessive trait. Am J Hum Genet. 1960 Sep;12:323–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson M., Kenwrick S., Thibodeau S., Faulk K., Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F., Davies K. E. Mapping of DNA markers close to the fragile site on the human X chromosome at Xq27.3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2639–2651. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohn R. D., Leffell M. S., Leadem P., Johnson D., Rubio T., Emanuel B. S. Familial third-fourth pharyngeal pouch syndrome with apparent autosomal dominant transmission. J Pediatr. 1984 Jul;105(1):47–51. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80355-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidtke J., Kruse K., Pape B., Sippell G. Exclusion of close linkage between the parathyroid hormone gene and a mutant gene locus causing idiopathic hypoparathyroidism. J Med Genet. 1986 Jun;23(3):217–219. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.3.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B., McAlpine P. J., Boucheix C., Collins F. S., Conneally P. M., Frézal J., Gershowitz H., Goodfellow P. N., Hall J. G., Issitt P. Guidelines for human gene nomenclature. An international system for human gene nomenclature (ISGN, 1987). Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1987;46(1-4):11–28. doi: 10.1159/000132471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte M. P., Kim G. S., Kosanovich M. Absence of parathyroid tissue in sex-linked recessive hypoparathyroidism. J Pediatr. 1986 Nov;109(5):915–915. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80741-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte M. P., Weldon V. V. Idiopathic hypoparathyroidism presenting with seizures during infancy: X-linked recessive inheritance in a large Missouri kindred. J Pediatr. 1981 Oct;99(4):608–611. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Chapelle A., Herva R., Koivisto M., Aula P. A deletion in chromosome 22 can cause DiGeorge syndrome. Hum Genet. 1981;57(3):253–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00278938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



