Abstract
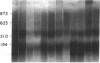
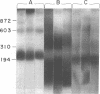
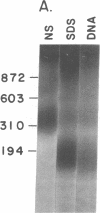
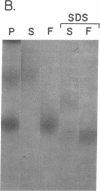
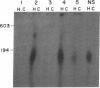
Little is known about endogenous systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) plasma DNA even though it is the presumed precursor of DNA-containing immune complexes, thought to play a central role in lupus glomerulonephritis. DNA purified from SLE plasma formed discrete bands, corresponding to sizes of about 150-200, 400, 600, and 800 bp, closely resembling the characteristic 200 bp "ladder" found with oligonucleosomal (ON) DNA. By radiolabeling DNA while in whole plasma, the very small amounts present could be further characterized. All of 24 such specimens formed two or more discrete bands on 6% PAGE. Detergent treatment of plasma resulted in a DNA migration pattern similar to that of purified DNA, suggesting disruption of DNA-protein complexes. DNA purified from authentic ON and detergent-treated ON behaved similarly. A significant portion of DNA, labeled in SLE plasma could be specifically immunoprecipitated with monoclonal antihistone antibody as was the case with ON. These immunoprecipitates, when redissolved, exhibited the expected size distribution upon PAGE. It is concluded that DNA in SLE plasma occurs as a series of multimeric complexes, at least a portion of which is noncovalently bound to histone. These results are consistent with an ON-like structure for SLE plasma DNA as had been suggested by theoretical considerations and may have important implications for its immunologic behavior in SLE and perhaps other disorders.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakayev V. V., Bakayeva T. G., Varshavsky A. J. Nucleosomes and subnucleosomes: heterogeneity and composition. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):619–629. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90079-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustin M. Immunological approaches to chromatin and chromosome structure and function. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1979;88:105–142. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67331-3_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J. E., Hardin J. A. Linked sets of antinuclear antibodies: what do they mean? J Rheumatol Suppl. 1987 Jun;14 (Suppl 13):106–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis G. L., Jr, Davis J. S., 4th Detection of circulating DNA by counterimmunoelectrophoresis (CIE). Arthritis Rheum. 1973 Jan-Feb;16(1):52–58. doi: 10.1002/art.1780160108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emlen W., Ansari R., Burdick G. DNA-anti-DNA immune complexes. Antibody protection of a discrete DNA fragment from DNase digestion in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jul;74(1):185–190. doi: 10.1172/JCI111400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournié G. J. Circulating DNA and lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 1988 Feb;33(2):487–497. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch S. O., McVey E. Purification and characterization of two major DNA-binding proteins in human serum. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1881–1887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung P. P., Mao J. C., Ling C. M., Overby L. R. Hybridisation of Dane particle DNA with the free plasma DNA of hepatitis carriers. Nature. 1975 Feb 13;253(5492):571–572. doi: 10.1038/253571a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Structure of chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:931–954. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. Z., Steinman C. R. Plasma DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Characterization of cloned base sequences. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Jun;32(6):726–733. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCoubrey-Hoyer A., Okarma T. B., Holman H. R. Partial purification and characterization of plasma DNA and its relation to disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Med. 1984 Jul;77(1):23–34. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90431-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Felsenfeld G. Nucleosome structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:1115–1156. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.005343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Sano H., Abe T., Homma M., Steinberg A. D. Correlation between clinical activity of systemic lupus erythematosus and the amounts of DNA in DNA/anti-DNA antibody immune complexes. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):1960–1965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raptis L., Menard H. A. Quantitation and characterization of plasma DNA in normals and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1391–1399. doi: 10.1172/JCI109992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieber M., Contreras C. E., Rieber M. S., Bianco N. E. Novel DNA-protein complex and a large DNA in SLE cryoprecipitates. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Oct;66(1):61–67. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano H., Morimoto C. Dna isolated from DNA/anti-DNA antibody immune complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus is rich in guanine-cytosine content. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1341–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollner-Webb B., Camerini-Otero R. D., Felsenfeld G. Chromatin structure as probed by nucleases and proteases: evidence for the central role of histones H3 and H4. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):179–193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman C. R. Circulating DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Association with central nervous system involvement and systemic vasculitis. Am J Med. 1979 Sep;67(3):429–435. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90789-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman C. R. Circulating DNA in systemic lupus erythematosus. Isolation and characterization. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):832–841. doi: 10.1172/JCI111278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman C. R., Deesomchok U., Spiera H. Detection of anti-DNA antibody using synthetic antigens. Characterization and clinical significance of binding of poly (deoxyadenylate-deoxythymidylate) by serum. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1330–1341. doi: 10.1172/JCI108401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman C. R. Detection and semiquantitation of DNA by counterimmunoelectrophoresis (CIE). Methods Enzymol. 1982;84:187–193. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)84016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Cohen A. S., Fries J. F., Masi A. T., McShane D. J., Rothfield N. F., Schaller J. G., Talal N., Winchester R. J. The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1271–1277. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H. Apoptosis: cell death in tissue regulation. J Pathol. 1987 Dec;153(4):313–316. doi: 10.1002/path.1711530404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]