Abstract
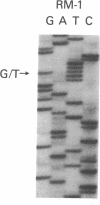
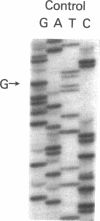
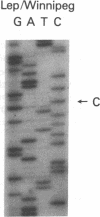
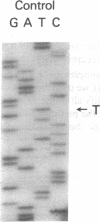
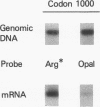
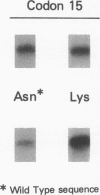
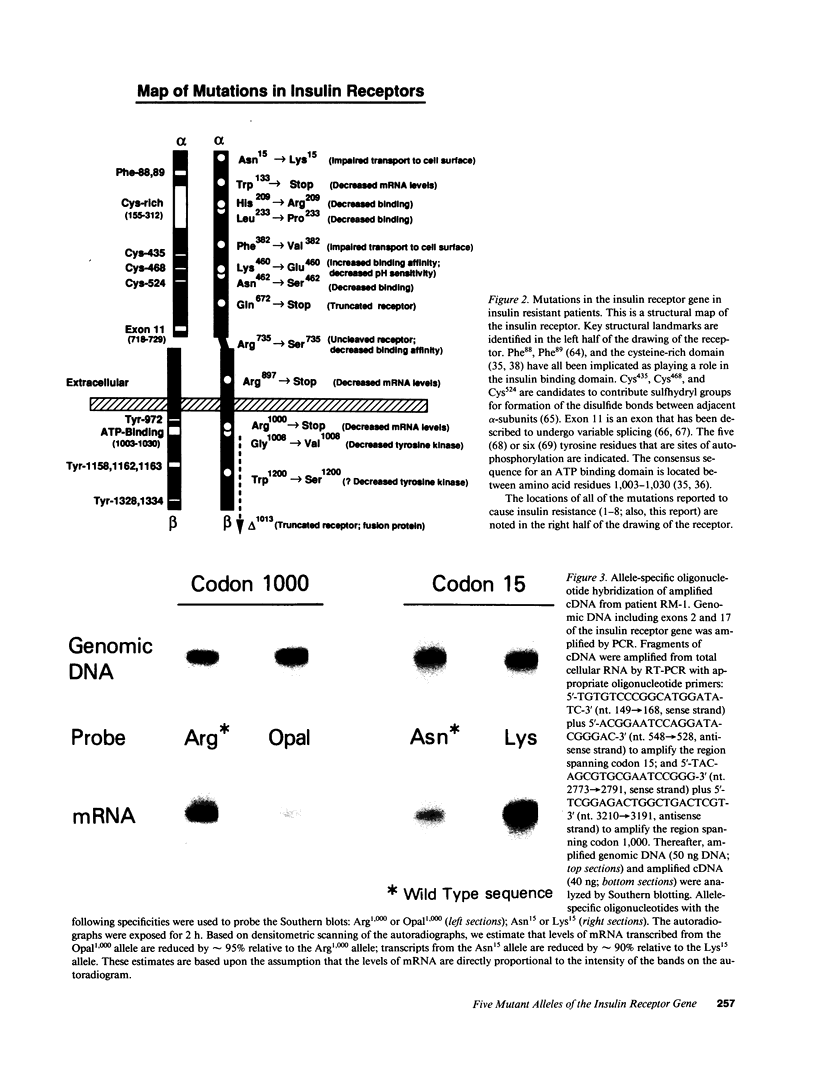
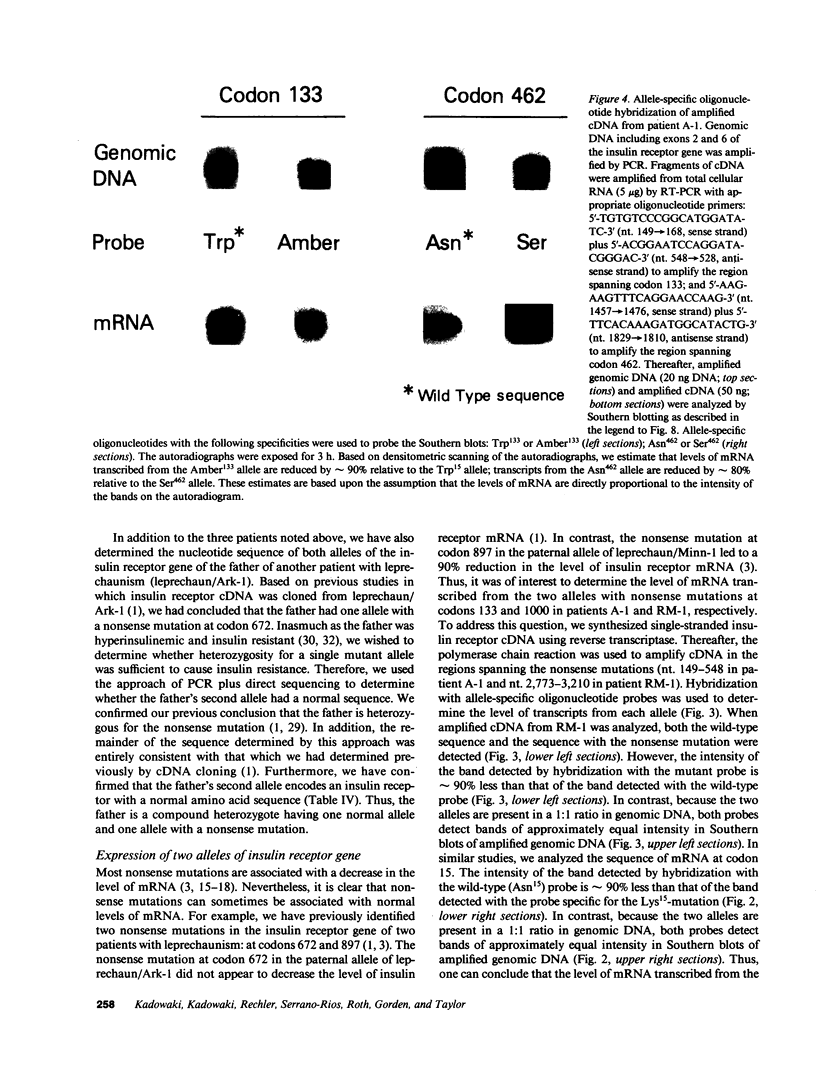
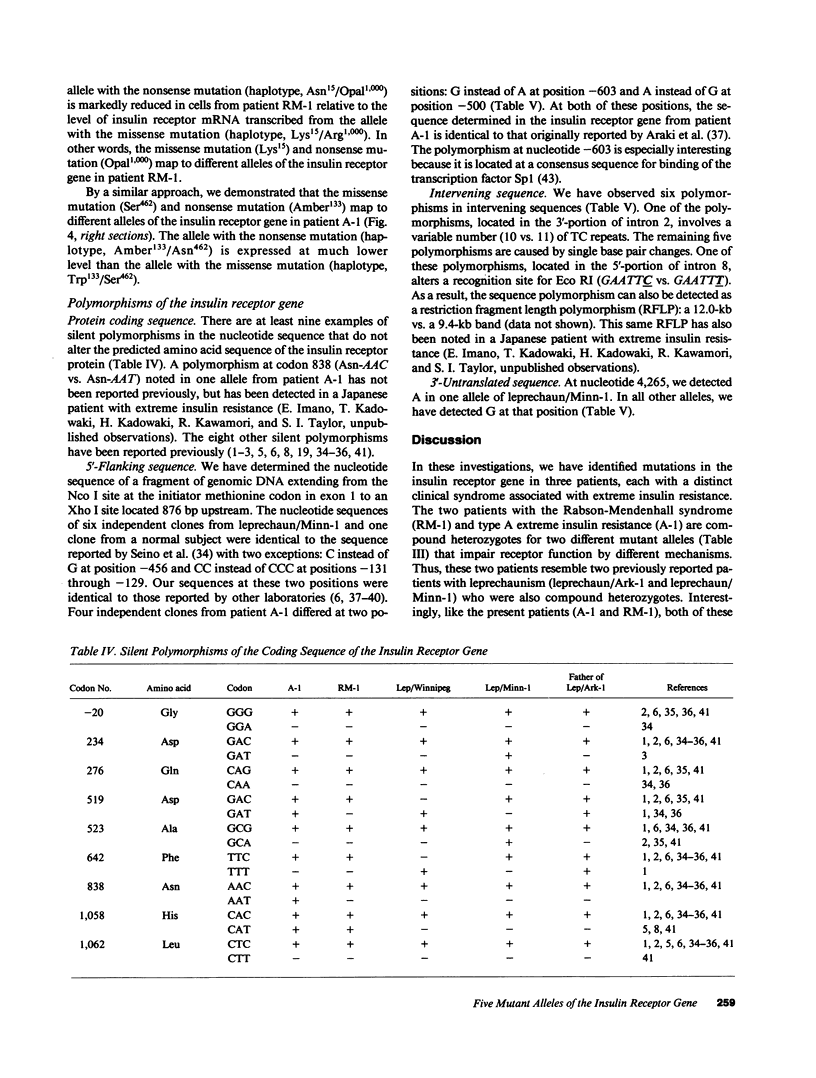
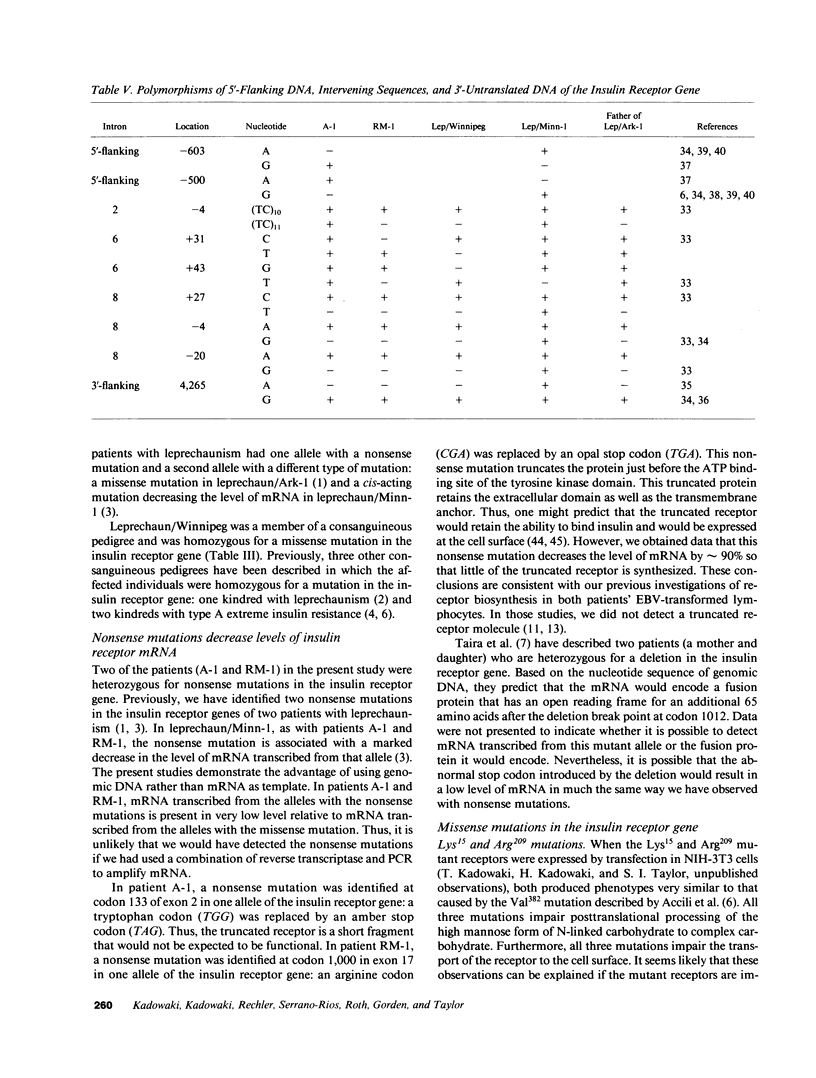
The nucleotide sequence was determined for all 22 exons of the insulin receptor gene from three patients with genetic syndromes associated with extreme insulin resistance. In all three patients, insulin resistance was caused by decreased insulin binding to the cell surface. The patient with leprechaunism (leprechaun/Winnipeg) came from a consanguineous pedigree and was homozygous for a missense mutation substituting arginine for His209 in the alpha-subunit of the insulin receptor. The other two patients were both compound heterozygotes with a nonsense mutation in one allele of the insulin receptor gene, and a missense mutation in the other allele. In the patient with the Rabson-Mendenhall syndrome (patient RM-1), the missense mutation substituted lysine for Asn15 in the alpha-subunit. In the patient with type A extreme insulin resistance (patient A-1), the missense mutation substituted serine for Asn462 in the alpha-subunit. Both nonsense mutations markedly reduced the levels of insulin receptor mRNA transcribed from the alleles with the nonsense mutation as compared to the transcripts from the other allele. The reduction in the level of mRNA would be predicted to greatly reduce the rate at which the truncated receptors would be synthesized. Furthermore, the truncated receptors would be severely impaired in their ability to mediate insulin action.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Accili D., Frapier C., Mosthaf L., McKeon C., Elbein S. C., Permutt M. A., Ramos E., Lander E., Ullrich A., Taylor S. I. A mutation in the insulin receptor gene that impairs transport of the receptor to the plasma membrane and causes insulin-resistant diabetes. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2509–2517. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araki E., Shimada F., Uzawa H., Mori M., Ebina Y. Characterization of the promoter region of the human insulin receptor gene. Evidence for promoter activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16186–16191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atweh G. F., Brickner H. E., Zhu X. X., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Forget B. G. New amber mutation in a beta-thalassemic gene with nonmeasurable levels of mutant messenger RNA in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):557–561. doi: 10.1172/JCI113632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj M., Waterfield M. D., Schlessinger J., Taylor W. R., Blundell T. On the tertiary structure of the extracellular domains of the epidermal growth factor and insulin receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 26;916(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90112-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. The neu oncogene encodes an epidermal growth factor receptor-related protein. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):226–230. doi: 10.1038/319226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cama A., Patterson A. P., Kadowaki T., Kadowaki H., Siegel G., D'Ambrosio D., Lillioja S., Roth J., Taylor S. I. The amino acid sequence of the insulin receptor is normal in an insulin-resistant Pima Indian. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990 Apr;70(4):1155–1161. doi: 10.1210/jcem-70-4-1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Meyts P., Gu J. L., Shymko R. M., Kaplan B. E., Bell G. I., Whittaker J. Identification of a ligand-binding region of the human insulin receptor encoded by the second exon of the gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):409–416. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elders M. J., Schedewie H. K., Olefsky J., Givens B., Char F., Bier D. M., Baldwin D., Fiser R. H., Seyedabadi S., Rubenstein A. Endocrine-metabolic relationships in patients with leprechaunism. J Natl Med Assoc. 1982 Dec;74(12):1195–1210. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fojo S. S., Stalenhoef A. F., Marr K., Gregg R. E., Ross R. S., Brewer H. B., Jr A deletion mutation in the ApoC-II gene (ApoC-II Nijmegen) of a patient with a deficiency of apolipoprotein C-II. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):17913–17916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs R. A., Nguyen P. N., McBride L. J., Koepf S. M., Caskey C. T. Identification of mutations leading to the Lesch-Nyhan syndrome by automated direct DNA sequencing of in vitro amplified cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1919–1923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedo J. A., Moncada V. Y., Taylor S. I. Insulin receptor biosynthesis in cultured lymphocytes from insulin-resistant patients. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2355–2361. doi: 10.1172/JCI112247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Wong M. L., Rutter W. J. Properties of the insulin receptor ectodomain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7516–7520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Bevins C. L., Cama A., Ojamaa K., Marcus-Samuels B., Kadowaki H., Beitz L., McKeon C., Taylor S. I. Two mutant alleles of the insulin receptor gene in a patient with extreme insulin resistance. Science. 1988 May 6;240(4853):787–790. doi: 10.1126/science.2834824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki T., Kadowaki H., Taylor S. I. A nonsense mutation causing decreased levels of insulin receptor mRNA: detection by a simplified technique for direct sequencing of genomic DNA amplified by the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):658–662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Flier J. S., Bar R. S., Archer J. A., Gorden P., Martin M. M., Roth J. The syndromes of insulin resistance and acanthosis nigricans. Insulin-receptor disorders in man. N Engl J Med. 1976 Apr 1;294(14):739–745. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197604012941401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Podskalny J. M. Demonstration of a primary (? genetic) defect in insulin receptors in fibroblasts from a patient with the syndrome of insulin resistance and acanthosis nigricans type A. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Jun;50(6):1139–1141. doi: 10.1210/jcem-50-6-1139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinkhamer M. P., Groen N. A., van der Zon G. C., Lindhout D., Sandkuyl L. A., Krans H. M., Möller W., Maassen J. A. A leucine-to-proline mutation in the insulin receptor in a family with insulin resistance. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2503–2507. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax I., Johnson A., Howk R., Sap J., Bellot F., Winkler M., Ullrich A., Vennstrom B., Schlessinger J., Givol D. Chicken epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor: cDNA cloning, expression in mouse cells, and differential binding of EGF and transforming growth factor alpha. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1970–1978. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh E., Glazer L., Segal D., Schlessinger J., Shilo B. Z. The Drosophila EGF receptor gene homolog: conservation of both hormone binding and kinase domains. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):599–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90208-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamula P. W., Wong K. Y., Maddux B. A., McDonald A. R., Goldfine I. D. Sequence and analysis of promoter region of human insulin-receptor gene. Diabetes. 1988 Sep;37(9):1241–1246. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.9.1241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massague J., Freidenberg G. F., Olefsky J. M., Czech M. P. Parallel decreases in the expression of receptors for insulin and insulin-like growth factor I in a mutant human fibroblast line. Diabetes. 1983 Jun;32(6):541–544. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.6.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon C., Moncada V., Pham T., Salvatore P., Kadowaki T., Accili D., Taylor S. I. Structural and functional analysis of the insulin receptor promoter. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Apr;4(4):647–656. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-4-647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller D. E., Flier J. S. Detection of an alteration in the insulin-receptor gene in a patient with insulin resistance, acanthosis nigricans, and the polycystic ovary syndrome (type A insulin resistance). N Engl J Med. 1988 Dec 8;319(23):1526–1529. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198812083192306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller D. E., Yokota A., Caro J. F., Flier J. S. Tissue-specific expression of two alternatively spliced insulin receptor mRNAs in man. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Aug;3(8):1263–1269. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-8-1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moller D. E., Yokota A., Flier J. S. Normal insulin-receptor cDNA sequence in Pima Indians with NIDDM. Diabetes. 1989 Nov;38(11):1496–1500. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.11.1496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada V. Y., Hedo J. A., Serrano-Rios M., Taylor S. I. Insulin-receptor biosynthesis in cultured lymphocytes from an insulin-resistant patient (Rabson-Mendenhall syndrome). Evidence for defect before insertion of receptor into plasma membrane. Diabetes. 1986 Jul;35(7):802–807. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.7.802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R., Costigan F. C. The major defect in Ashkenazi Jews with Tay-Sachs disease is an insertion in the gene for the alpha-chain of beta-hexosaminidase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18587–18589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odawara M., Kadowaki T., Yamamoto R., Shibasaki Y., Tobe K., Accili D., Bevins C., Mikami Y., Matsuura N., Akanuma Y. Human diabetes associated with a mutation in the tyrosine kinase domain of the insulin receptor. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):66–68. doi: 10.1126/science.2544998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojamaa K., Hedo J. A., Roberts C. T., Jr, Moncada V. Y., Gorden P., Ullrich A., Taylor S. I. Defects in human insulin receptor gene expression. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Mar;2(3):242–247. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-3-242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podskalny J. M., Kahn C. R. Cell culture studies on patients with extreme insulin resistance. I. Receptor defects on cultured fibroblasts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Feb;54(2):261–268. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-2-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy S. S., Lauris V., Kahn C. R. Insulin receptor function in fibroblasts from patients with leprechaunism. Differential alterations in binding, autophosphorylation, kinase activity, and receptor-mediated internalization. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1359–1365. doi: 10.1172/JCI113739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S., Richardson D. C. Amino acid preferences for specific locations at the ends of alpha helices. Science. 1988 Jun 17;240(4859):1648–1652. doi: 10.1126/science.3381086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. M., Haworth J. C., Degroot G. W., Trevenen C. L., Rechler M. M. A case of leprechaunism with severe hyperinsulinemia. Am J Dis Child. 1980 Feb;134(2):170–175. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1980.02130140044014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling E. E., Rechler M. M., Grunfeld C., Rosenberg A. M. Primary defect of insulin receptors in skin fibroblasts cultured from an infant with leprechaunism and insulin resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5877–5881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seino S., Bell G. I. Alternative splicing of human insulin receptor messenger RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Feb 28;159(1):312–316. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92439-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seino S., Seino M., Bell G. I. Human insulin-receptor gene. Partial sequence and amplification of exons by polymerase chain reaction. Diabetes. 1990 Jan;39(1):123–128. doi: 10.2337/diacare.39.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seino S., Seino M., Nishi S., Bell G. I. Structure of the human insulin receptor gene and characterization of its promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):114–118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shier P., Watt V. M. Primary structure of a putative receptor for a ligand of the insulin family. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14605–14608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira M., Taira M., Hashimoto N., Shimada F., Suzuki Y., Kanatsuka A., Nakamura F., Ebina Y., Tatibana M., Makino H. Human diabetes associated with a deletion of the tyrosine kinase domain of the insulin receptor. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):63–66. doi: 10.1126/science.2544997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. I., Cama A., Kadowaki H., Kadowaki T., Accili D. Mutations of the human insulin receptor gene. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 1990 JanâFeb;1(3):134–139. doi: 10.1016/1043-2760(90)90024-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
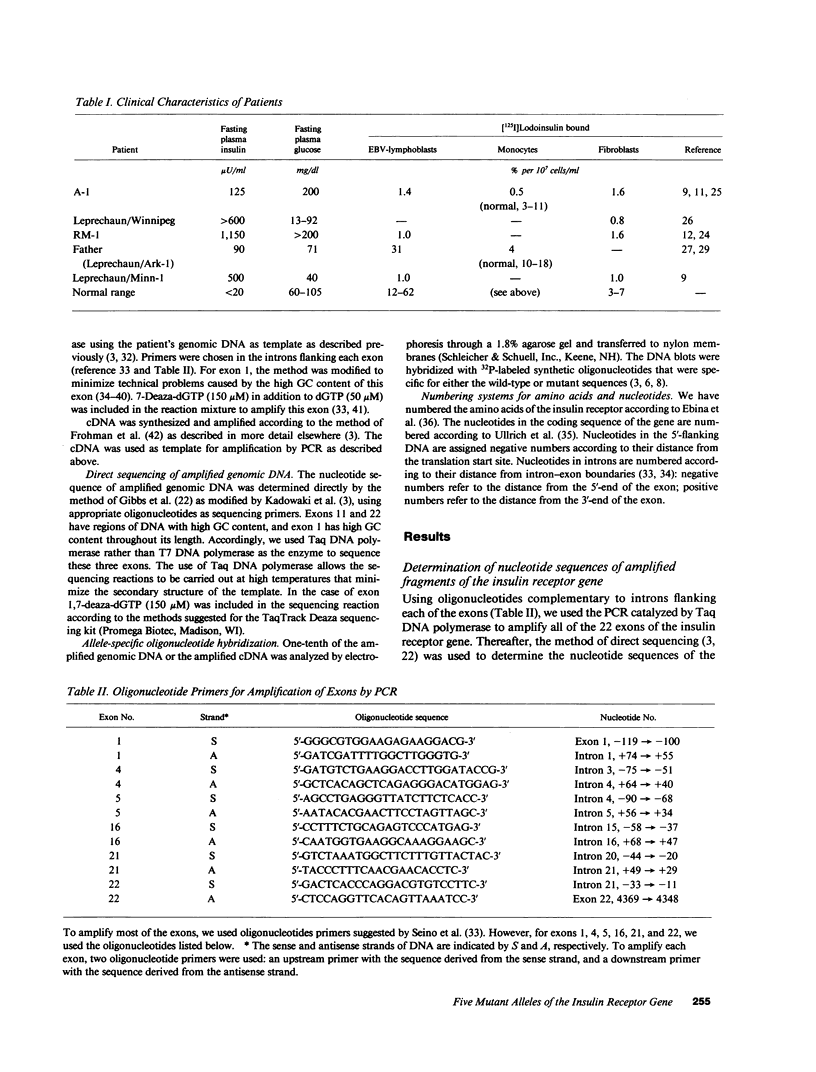
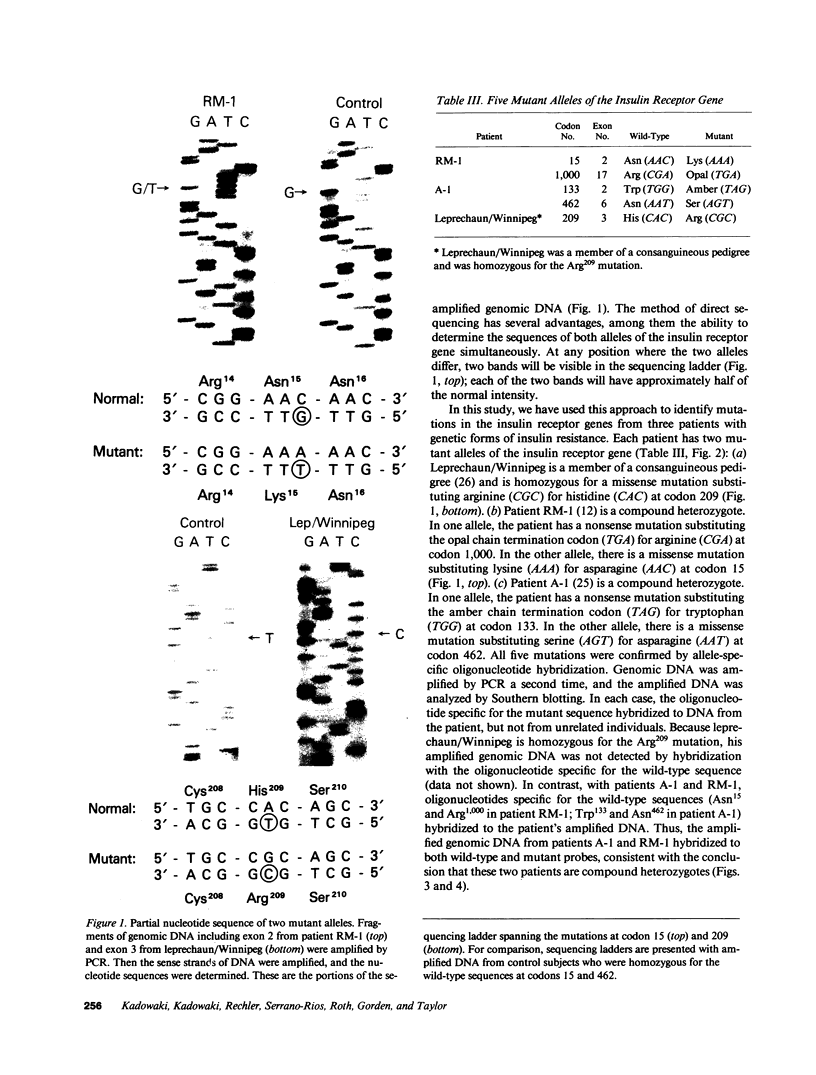
- Taylor S. I., Kadowaki T., Kadowaki H., Accili D., Cama A., McKeon C. Mutations in insulin-receptor gene in insulin-resistant patients. Diabetes Care. 1990 Mar;13(3):257–279. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.3.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. I., Marcus-Samuels B., Ryan-Young J., Leventhal S., Elders M. J. Genetics of the insulin receptor defect in a patient with extreme insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Jun;62(6):1130–1135. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-6-1130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. I., Roth J., Blizzard R. M., Elders M. J. Qualitative abnormalities in insulin binding in a patient with extreme insulin resistance: decreased sensitivity to alterations in temperature and pH. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7157–7161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. I., Samuels B., Roth J., Kasuga M., Hedo J. A., Gorden P., Brasel D. E., Pokora T., Engel R. R. Decreased insulin binding in cultured lymphocytes from two patients with extreme insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 May;54(5):919–930. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-5-919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. I., Underhill L. H., Hedo J. A., Roth J., Rios M. S., Blizzard R. M. Decreased insulin binding to cultured cells from a patient with the Rabson-Mendenhall syndrome: dichotomy between studies with cultured lymphocytes and cultured fibroblasts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Apr;56(4):856–861. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-4-856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari D. S., Cook D. M., Taub R. Characterization of the promoter region and 3' end of the human insulin receptor gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16238–16245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornqvist H. E., Gunsalus J. R., Nemenoff R. A., Frackelton A. R., Pierce M. W., Avruch J. Identification of the insulin receptor tyrosine residues undergoing insulin-stimulated phosphorylation in intact rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):350–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Mitchell P. J., Ciudad C. J., Chasin L. A. Nonsense mutations in the dihydrofolate reductase gene affect RNA processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2868–2880. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen-Schilling E. E., Rechler M. M., Romanus J. A., Knight A. B., Nissley S. P., Humbel R. E. Receptors for insulinlike growth factor I are defective in fibroblasts cultured from a patient with leprechaunism. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1356–1365. doi: 10.1172/JCI110383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh S. M., DiBella E. E., Pilch P. F. Isolation of a proteolytically derived domain of the insulin receptor containing the major site of cross-linking/binding. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3448–3455. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner H., Woloschak M., Adamo M., Shen-Orr Z., Roberts C. T., Jr, LeRoith D. Developmental regulation of the rat insulin-like growth factor I receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7451–7455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Shoelson S. E., Keutmann H., Kahn C. R. A cascade of tyrosine autophosphorylation in the beta-subunit activates the phosphotransferase of the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2969–2980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker J., Okamoto A. Secretion of soluble functional insulin receptors by transfected NIH3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3063–3066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C., Dowling C. E., Saiki R. K., Higuchi R. G., Erlich H. A., Kazazian H. H., Jr Characterization of beta-thalassaemia mutations using direct genomic sequencing of amplified single copy DNA. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):384–386. doi: 10.1038/330384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Ikawa S., Akiyama T., Semba K., Nomura N., Miyajima N., Saito T., Toyoshima K. Similarity of protein encoded by the human c-erb-B-2 gene to epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):230–234. doi: 10.1038/319230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip C. C., Hsu H., Patel R. G., Hawley D. M., Maddux B. A., Goldfine I. D. Localization of the insulin-binding site to the cysteine-rich region of the insulin receptor alpha-subunit. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):321–329. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimasa Y., Seino S., Whittaker J., Kakehi T., Kosaki A., Kuzuya H., Imura H., Bell G. I., Steiner D. F. Insulin-resistant diabetes due to a point mutation that prevents insulin proreceptor processing. Science. 1988 May 6;240(4853):784–787. doi: 10.1126/science.3283938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]