Abstract
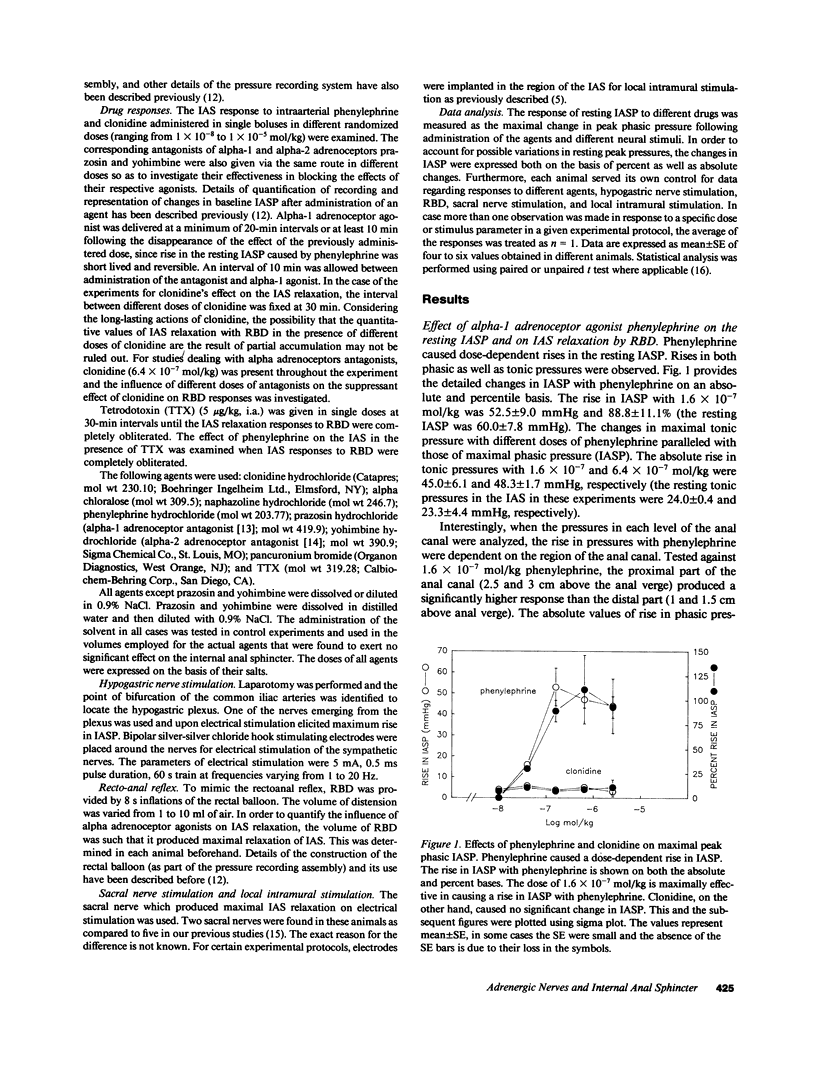
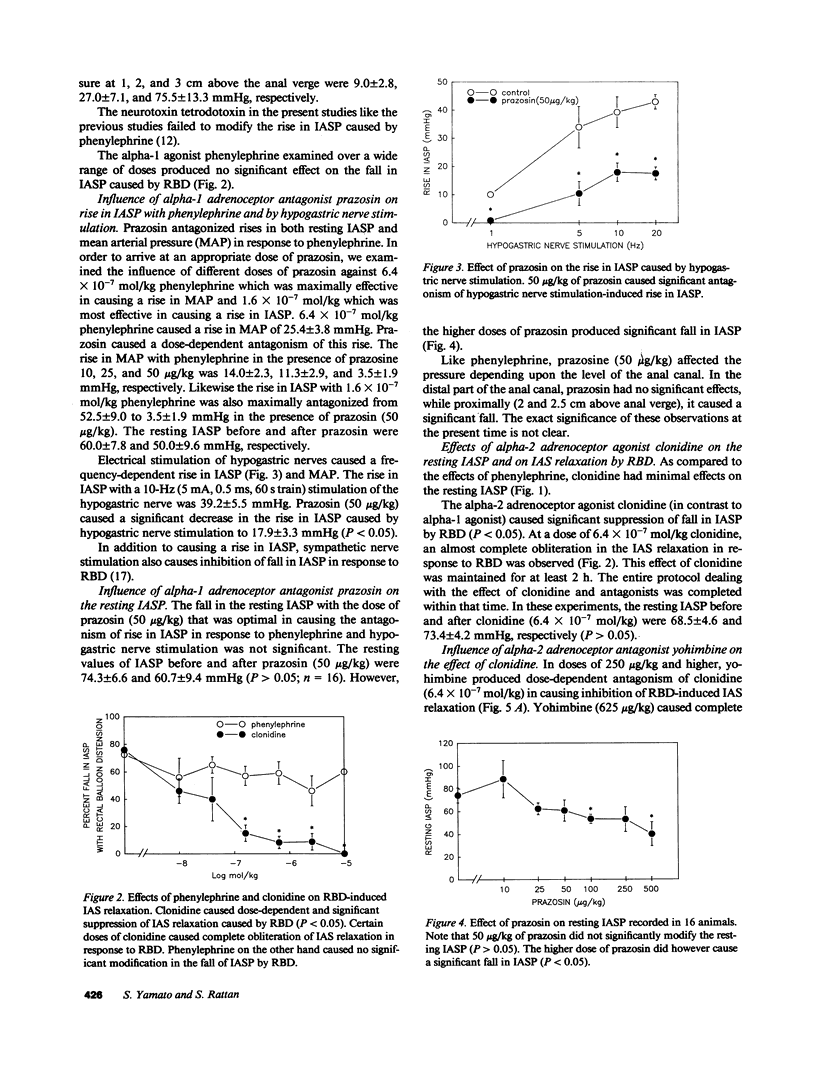
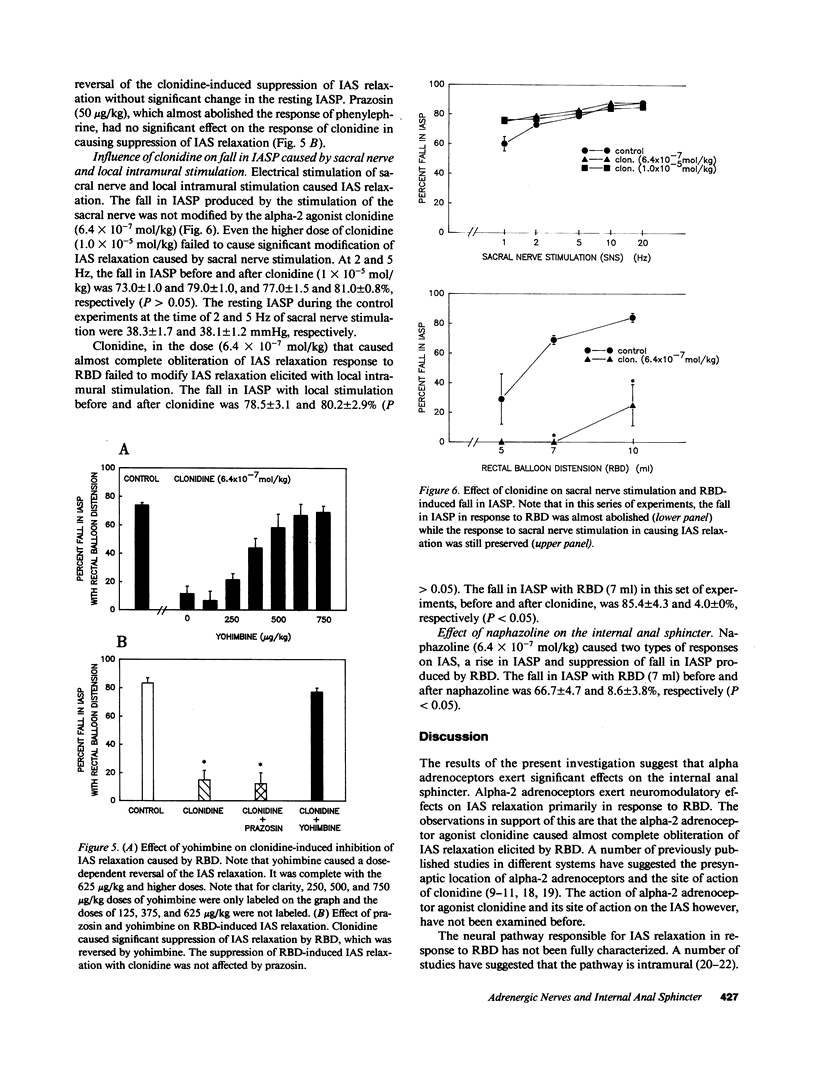
The purpose of the present investigation was to examine the role of alpha adrenoceptors in the internal anal sphincter (IAS). Studies wer performed on alpha-chloralose anesthetized opossums. Resting pressure in the IAS (IASP) was recorded using low compliant continuously perfused catheters. The effects of the alpha-1 adrenoceptor agonist phenylephrine and alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonist clonidine and their corresponding selective antagonists, prazosin and yohimbine, respectively, were examined on the resting IASP, and on rectal balloon distension (RBD)-mediated IAS relaxation. Phenylephrine caused a rise in the IASP that was blocked by prazosin and not by yohimbine. Phenylephrine had no effect on IAS relaxation caused by RBD. Clonidine on the other hand caused significant suppression of IAS relaxation in response to RBD, but caused minimal changes in the resting IASP. The suppression of IAS relaxation by clonidine was selectively antagonized by yohimbine but not by prazosin. From these studies we conclude that alpha-2 adrenoceptors exert important neuromodulatory influences on rectoanal inhibitory reflex, while alpha-1 adrenoceptors may exert modulatory effects on the resting IAS tone.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biancani P., Walsh J., Behar J. Vasoactive intestinal peptide: a neurotransmitter for relaxation of the rabbit internal anal sphincter. Gastroenterology. 1985 Oct;89(4):867–874. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90585-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvier M., Gonella J. Nervous control of the internal anal sphincter of the cat. J Physiol. 1981 Jan;310:457–469. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burleigh D. E., D'Mello A. Neural and pharmacologic factors affecting motility of the internal anal sphincter. Gastroenterology. 1983 Feb;84(2):409–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülbring E., Tomita T. Catecholamine action on smooth muscle. Pharmacol Rev. 1987 Mar;39(1):49–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culver P. J., Rattan S. Genesis of anal canal pressures in the opossum. Am J Physiol. 1986 Dec;251(6 Pt 1):G765–G771. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.6.G765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M. Effects of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists on pre- and postsynaptically located alpha-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976 Apr;36(2):313–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(76)90084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fargeas M. J., Fioramonti J., Bueno L. Central alpha 2-adrenergic control of the pattern of small intestinal motility in rats. Gastroenterology. 1986 Dec;91(6):1470–1475. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90203-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furness J. B., Costa M. The ramifications of adrenergic nerve terminals in the rectum, anal sphincter and anal accessory muscles of the guinea-pig. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1973 May 30;140(1):109–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00520721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. R., Robertson D. Yohimbine: a pharmacological probe for study of the alpha 2-adrenoreceptor. Pharmacol Rev. 1983 Sep;35(3):143–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang Q., Sheldon R. J., Porreca F. Sites of clonidine action to inhibit gut propulsion in mice: demonstration of a central component. Gastroenterology. 1988 Nov;95(5):1265–1271. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90360-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim S. P., Muir T. C. Mechanisms underlying the electrical and mechanical responses of the guinea-pig internal anal sphincter to field stimulation and to drugs. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Oct;86(2):427–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08912.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubowski D. Z., Nicholls R. J., Swash M., Jordan M. J. Neural control of internal anal sphincter function. Br J Surg. 1987 Aug;74(8):668–670. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800740804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlo A., Cohen S. Neuropeptide responses and mechanics of the proximal and distal feline colon in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 1):G787–G793. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1988.255.6.G787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes, inositol phosphates, and sources of cell Ca2+. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Jun;40(2):87–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissan S., Vinograd Y., Hadari A., Merguerian P., Zamir O., Lernau O., Hanani M. Physiological and pharmacological studies of the internal anal sphincter in the rat. J Pediatr Surg. 1984 Feb;19(1):12–14. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3468(84)80006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurko S., Rattan S. Role of neuropeptide Y in opossum internal anal sphincter. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 1):G59–G64. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.258.1.G59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurko S., Rattan S. Role of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in the internal anal sphincter relaxation of the opossum. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1146–1153. doi: 10.1172/JCI113429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rattan S., Shah R. Influence of sacral nerves on the internal anal sphincter of the opossum. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 1):G345–G350. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.253.3.G345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUSTER M. M., HENDRIX T. R., MENDELOFF A. I. The internal anal sphincter response: manometric studies on its normal physiology, neural pathways, and alteration in bowel disorders. J Clin Invest. 1963 Feb;42:196–207. doi: 10.1172/JCI104706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. E., Lefkowitz R. J. Alpha 2 adrenergic receptors are located prejunctionally in the Auerbach's plexus of the guinea pig small intestine: direct demonstration by radioligand binding. Life Sci. 1982 Dec 20;31(25):2899–2905. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90681-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


