Abstract
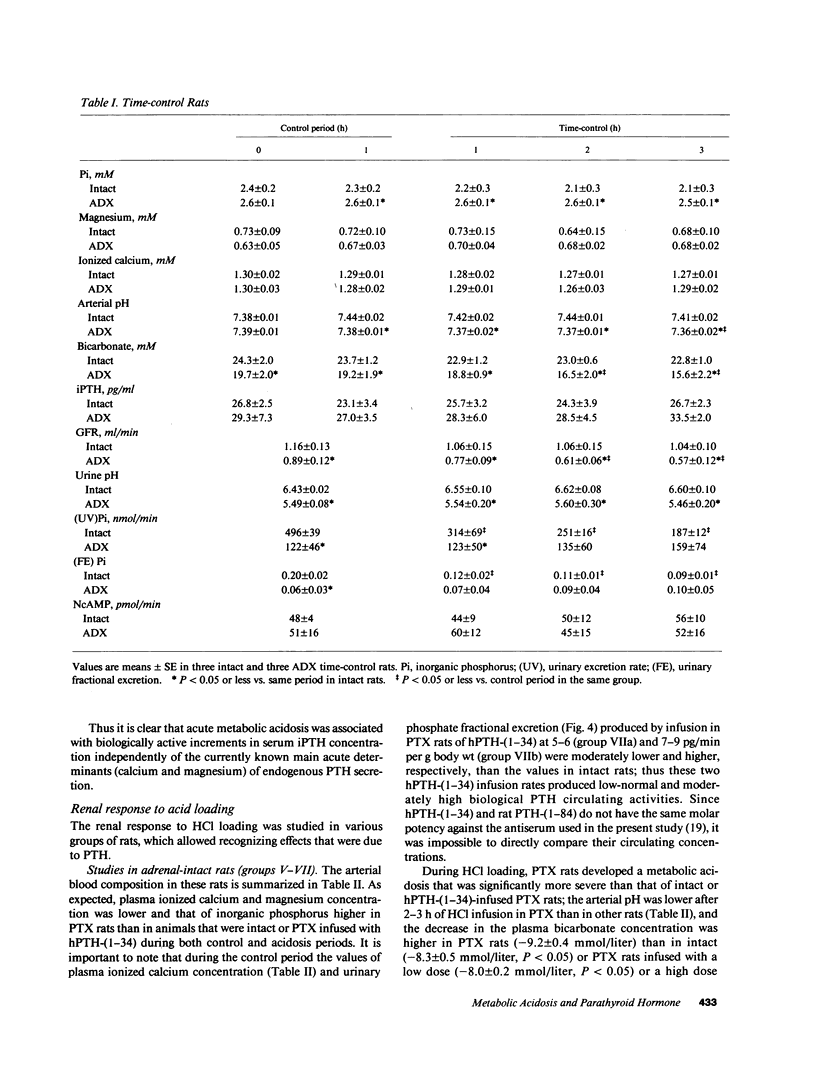
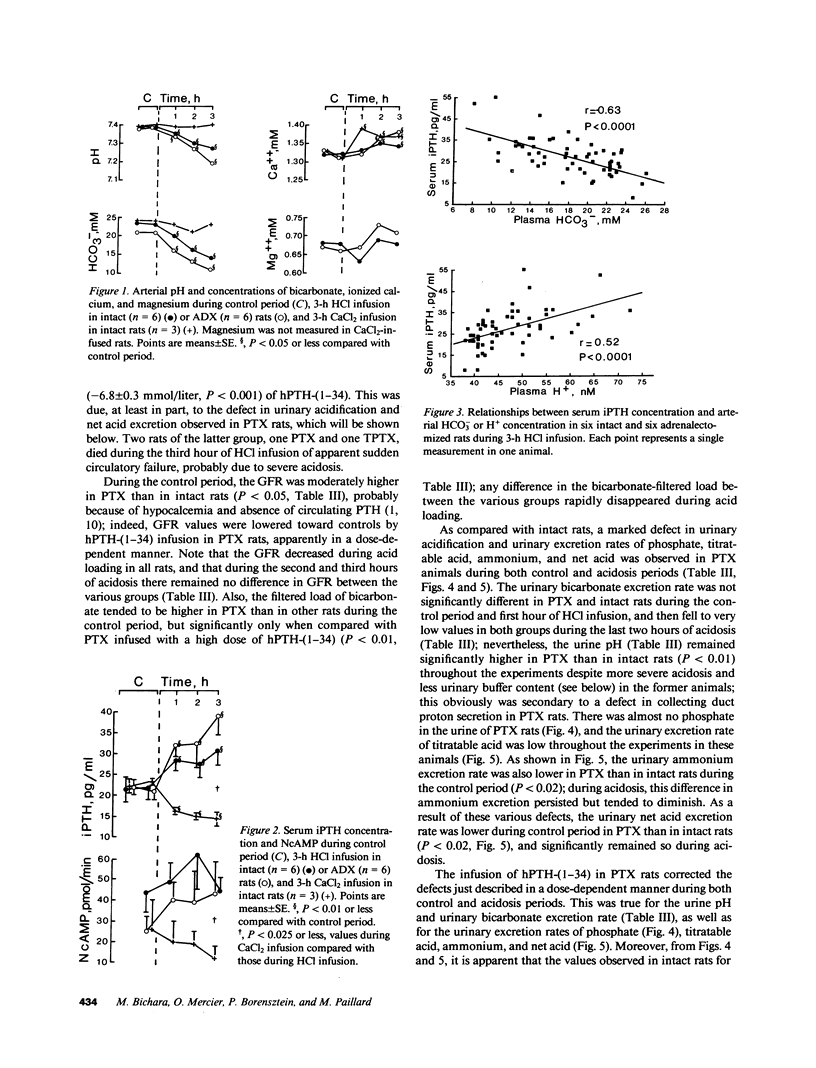
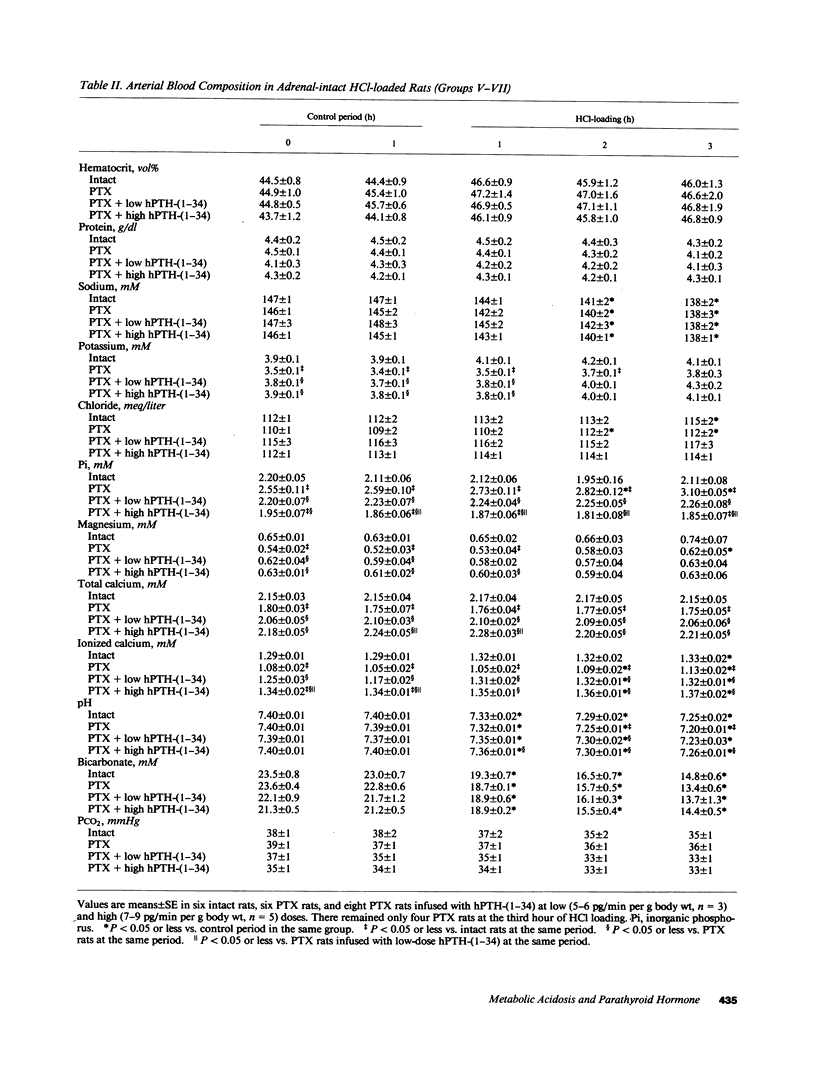
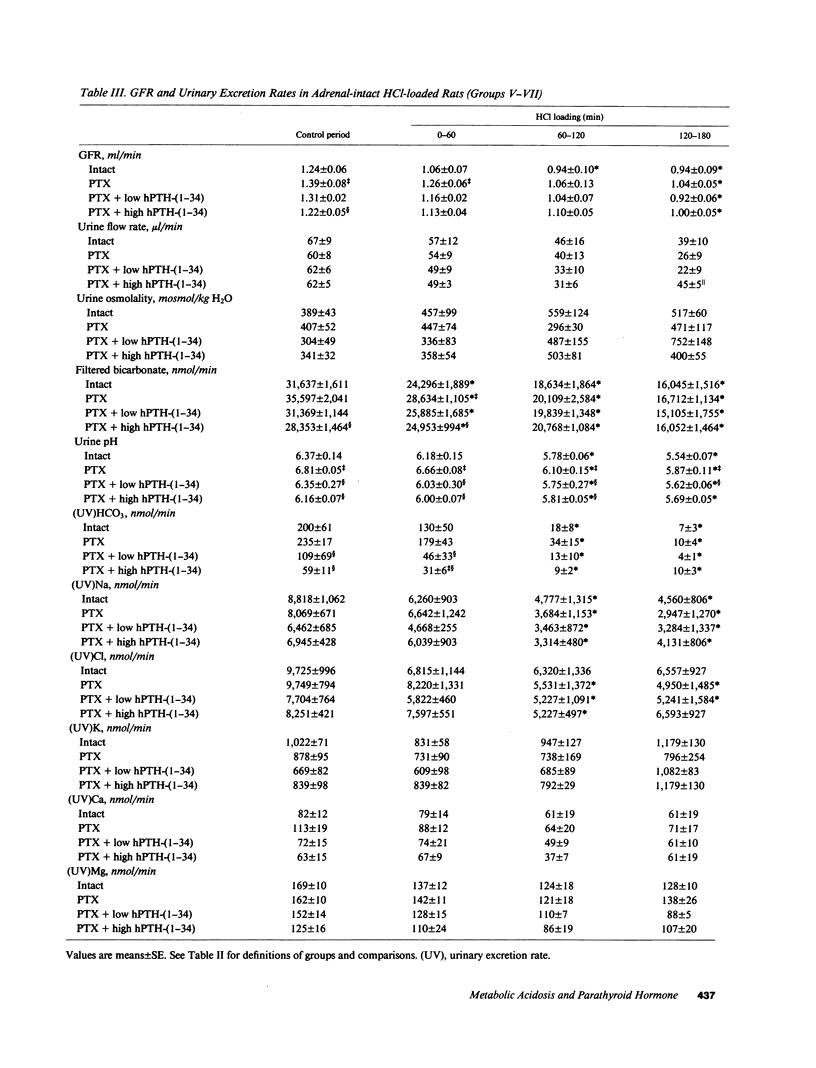
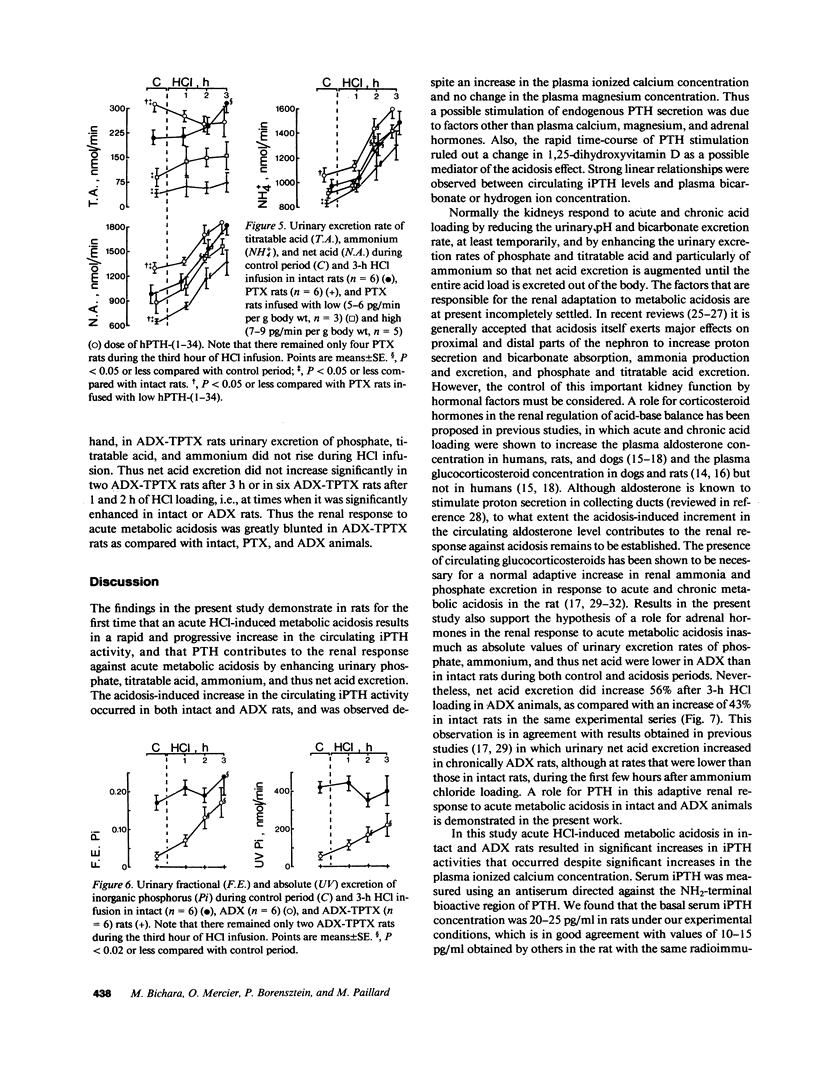
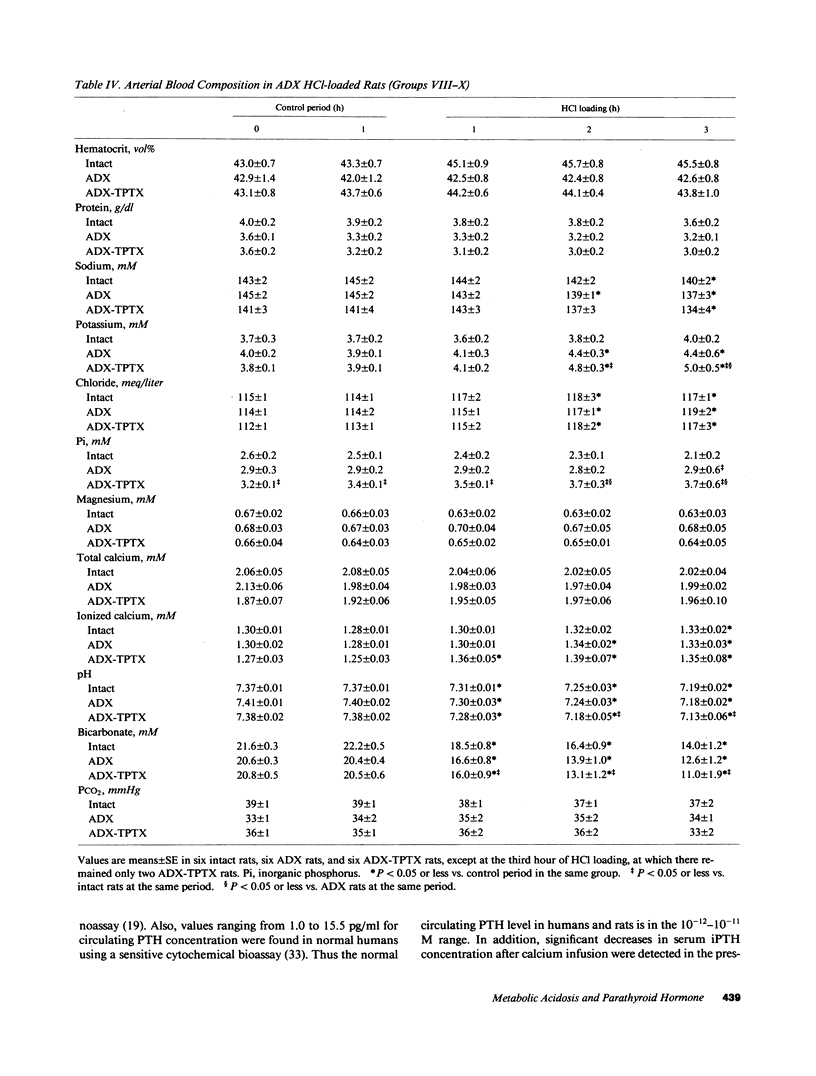
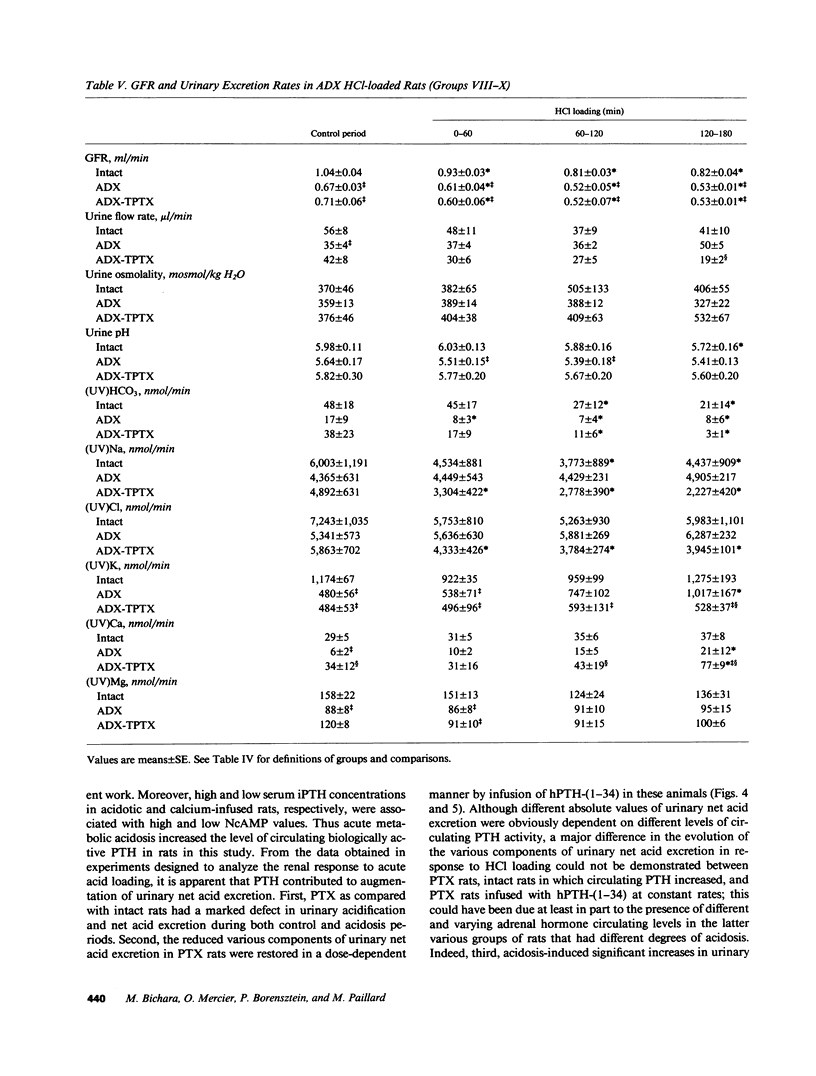
Acute PTH administration enhances final urine acidification in the rat. HCl was infused during 3 h in rats to determine the parathyroid and renal responses to acute metabolic acidosis. Serum immunoreactive PTH (iPTH) concentration significantly increased and nephrogenous adenosine 3H,5H-cyclic monophosphate tended to increase during HCl loading in intact and adrenalectomized (ADX) rats despite significant increments in plasma ionized calcium. Strong linear relationships existed between serum iPTH concentration and arterial bicarbonate or proton concentration (P less than 0.0001). Serum iPth concentration and NcAMP remained stable in intact time-control rats and decreased in CaCl2-infused, nonacidotic animals. Urinary acidification was markedly reduced in parathyroidectomized (PTX) as compared with intact rats during both basal and acidosis states; human PTH-(1-34) infusion in PTX rats restored in a dose-dependent manner the ability of the kidney to acidify the urine and excrete net acid. Acidosis-induced increase in urinary net acid excretion was observed in intact, PTX, and ADX, but not in ADX-thyroparathyroidectomized rats. We conclude that (a) acute metabolic acidosis enhances circulating PTH activity, and (b) PTH markedly contributes to the renal response against acute metabolic acidosis by enhancing urinary acidification.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arruda J. A., Alla V., Rubinstein H., Cruz-Soto M., Sabatini S., Batlle D. C., Kurtzman N. A. Metabolic and hormonal factors influencing extrarenal buffering of an acute acid load. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1982 Jul;8(1):36–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arruda J. A., Alla V., Rubinstein H., Cruz-Soto M., Sabatini S., Batlle D. C., Kurtzman N. A. Parathyroid hormone and extrarenal acid buffering. Am J Physiol. 1980 Dec;239(6):F533–F538. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.239.6.F533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bank N., Aynediian H. S. A micropuncture study of the effect of parathyroid hormone on renal bicarbonate reabsorption. J Clin Invest. 1976 Aug;58(2):336–344. doi: 10.1172/JCI108477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichara M., Mercier O., Houillier P., Paillard M., Leviel F. Effects of antidiuretic hormone on urinary acidification and on tubular handling of bicarbonate in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1987 Sep;80(3):621–630. doi: 10.1172/JCI113114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichara M., Mercier O., Paillard M., Leviel F. Effects of parathyroid hormone on urinary acidification. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 2):F444–F453. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.3.F444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichara M., Paillard M., Corman B., de Rouffignac C., Leviel F. Volume expansion modulates NaHCO3 and NaCl transport in the proximal tubule and Henle's loop. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jul;247(1 Pt 2):F140–F150. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.1.F140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boross M., Kinsella J., Cheng L., Sacktor B. Glucocorticoids and metabolic acidosis-induced renal transports of inorganic phosphate, calcium, and NH4. Am J Physiol. 1986 May;250(5 Pt 2):F827–F833. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.5.F827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadus A. E., Mahaffey J. E., Bartter F. C., Neer R. M. Nephrogenous cyclic adenosine monophosphate as a parathyroid function test. J Clin Invest. 1977 Oct;60(4):771–783. doi: 10.1172/JCI108831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. M., Pazoles C. J., Creutz C. E., Aurbach G. D., Pollard H. B. Role of anions in parathyroid hormone release from dispersed bovine parathyroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):876–880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushinsky D. A., Favus M. J., Schneider A. B., Sen P. K., Sherwood L. M., Coe F. L. Effects of metabolic acidosis on PTH and 1,25(OH)2D3 response to low calcium diet. Am J Physiol. 1982 Dec;243(6):F570–F575. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.6.F570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers D. J., Dunham J., Zanelli J. M., Parsons J. A., Bitensky L., Chayen J. A sensitive bioassay of parathyroid hormone in plasma. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1978 Oct;9(4):375–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1978.tb02223.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chobanian M. C., Hammerman M. R. Parathyroid hormone stimulates ammoniagenesis in canine renal proximal tubular segments. Am J Physiol. 1988 Nov;255(5 Pt 2):F847–F852. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.5.F847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coe F. L., Firpo J. J., Jr, Hollandsworth D. L., Segil L., Canterbury J. M., Reiss E. Effect of acute and chronic metabolic acidosis on serum immunoreactive parathyroid hormone in man. Kidney Int. 1975 Oct;8(4):263–273. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuBose T. D., Jr, Caflisch C. R. Effect of selective aldosterone deficiency on acidification in nephron segments of the rat inner medulla. J Clin Invest. 1988 Nov;82(5):1624–1632. doi: 10.1172/JCI113774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubrovsky A. H., Nair R. C., Byers M. K., Levine D. Z. Renal net acid excretion in the adrenalectomized rat. Kidney Int. 1981 Apr;19(4):516–528. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraley D. S., Adler S. An extrarenal role for parathyroid hormone in the disposal of acute acid loads in rats and dogs. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):985–997. doi: 10.1172/JCI109399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. W., Burg M. B. Ammonia production by individual segments of the rat nephron. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):602–610. doi: 10.1172/JCI111250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guntupalli J., Eby B., Lau K. Mechanism for the phosphaturia of NH4Cl: dependence on acidemia but not on diet PO4 or PTH. Am J Physiol. 1982 May;242(5):F552–F560. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.5.F552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm L. L., Simon E. E. Roles and mechanisms of urinary buffer excretion. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 2):F595–F605. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.4.F595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann H. O. Metabolic alkalosis in patients with hypercalcemia. Metabolism. 1965 Nov;14(11):1137–1152. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(65)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulter H. N., Peterson J. C. Acid-base homeostasis during chronic PTH excess in humans. Kidney Int. 1985 Aug;28(2):187–192. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulter H. N., Sebastian A., Toto R. D., Bonner E. L., Jr, Ilnicki L. P. Renal and systemic acid-base effects of the chronic administration of hypercalcemia-producing agents: calcitriol, PTH, and intravenous calcium. Kidney Int. 1982 Mar;21(3):445–458. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulter H. N., Toto R. D., Ilnicki L. P., Halloran B., Sebastian A. Metabolic alkalosis in models of primary and secondary hyperparathyroid states. Am J Physiol. 1983 Oct;245(4):F450–F461. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.4.F450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B. S., Kraut J. A., Mishler D. R., Crooks P. W. Effect of acute acidemia on phosphate uptake by renal proximal tubular brush-border membranes. Am J Physiol. 1986 Nov;251(5 Pt 2):F889–F896. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.5.F889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Licht J. H., McVicker K. Parathyroid-hormone-induced metabolic alkalosis in dogs. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1982 Aug;8(2):78–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madias N. E., Johns C. A., Homer S. M. Independence of the acute acid-buffering response from endogenous parathyroid hormone. Am J Physiol. 1982 Aug;243(2):F141–F149. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.243.2.F141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercier O., Bichara M., Paillard M., Gardin J. P., Leviel F. Parathyroid hormone contributes to volume expansion-induced inhibition of proximal reabsorption. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jan;248(1 Pt 2):F100–F103. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.1.F100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercier O., Bichara M., Paillard M., Prigent A. Effects of parathyroid hormone and urinary phosphate on collecting duct hydrogen secretion. Am J Physiol. 1986 Nov;251(5 Pt 2):F802–F809. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.5.F802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercier O., Prigent A., Bichara M., Paillard M., Leviel F. Effects of increase in plasma calcium concentration on renal handling of NaCl and NaHCO3. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 2):F441–F450. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.3.F441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitnick P., Greenberg A., Coffman T., Kelepouris E., Wolf C. J., Goldfarb S. Effects of two models of hypercalcemia on renal acid base metabolism. Kidney Int. 1982 Apr;21(4):613–620. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. J. Effect of phorbol myristate acetate on secretion of parathyroid hormone. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jan;254(1 Pt 1):E63–E70. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.1.E63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paillard M., Bichara M. Peptide hormone effects on urinary acidification and acid-base balance: PTH, ADH, and glucagon. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 2):F973–F985. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.6.F973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez G. O., Oster J. R., Katz F. H., Vaamonde C. A. The effect of acute metabolic acidosis on plasma cortisol, renin activity and aldosterone. Horm Res. 1979;11(1):12–21. doi: 10.1159/000179033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez G. O., Oster J. R., Vaamonde C. A., Katz F. H. Effect of NH4Cl on plasma aldosterone, cortisol and renin activity in supine man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Oct;45(4):762–767. doi: 10.1210/jcem-45-4-762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quamme G. A. Effects of metabolic acidosis, alkalosis, and dietary hydrogen ion intake on phosphate transport in the proximal convoluted tubule. Am J Physiol. 1985 Nov;249(5 Pt 2):F769–F779. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.249.5.F769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg J., Pines M., Levy J. J., Nutt R. F., Caulfield M. P., Russell J., Sherwood L. M., Hurwitz S. Renal and adrenal adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate production and corticosteroid secretion in response to synthetic chicken parathyroid hormone-(1-34). Endocrinology. 1989 Aug;125(2):1082–1089. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-2-1082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARTORIUS O. W., CALHOON D., PITTS R. F. Studies on the interrelationships of the adrenal cortex and renal ammonia excretion by the rat. Endocrinology. 1953 Mar;52(3):256–265. doi: 10.1210/endo-52-3-256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schambelan M., Sebastian A., Katuna B. A., Arteaga E. Adrenocortical hormone secretory response to chronic NH4Cl-induced metabolic acidosis. Am J Physiol. 1987 Apr;252(4 Pt 1):E454–E460. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.252.4.E454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannen R. L. Ammonia metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1978 Oct;235(4):F265–F277. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.235.4.F265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toverud S. U., Boass A., Garner S. C., Endres D. B. Circulating parathyroid hormone concentrations in normal and vitamin D-deprived rat pups determined with an N-terminal-specific radioimmunoassay. Bone Miner. 1986 Apr;1(2):145–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber H. P., Gray R. W., Dominguez J. H., Lemann J., Jr The lack of effect of chronic metabolic acidosis on 25-OH-vitamin D metabolism and serum parathyroid hormone in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1976 Nov;43(5):1047–1055. doi: 10.1210/jcem-43-5-1047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welbourne T. C. Acidosis activation of the pituitary-adrenal-renal glutaminase I axis. Endocrinology. 1976 Oct;99(4):1071–1079. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-4-1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox C. S., Cemerikic D. A., Giebisch G. Differential effects of acute mineralo- and glucocorticosteroid administration on renal acid elimination. Kidney Int. 1982 Apr;21(4):546–556. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills M. R. Fundamental physiological role of parathyroid hormone in acid-base homoeostasis. Lancet. 1970 Oct 17;2(7677):802–804. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91463-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



