Abstract
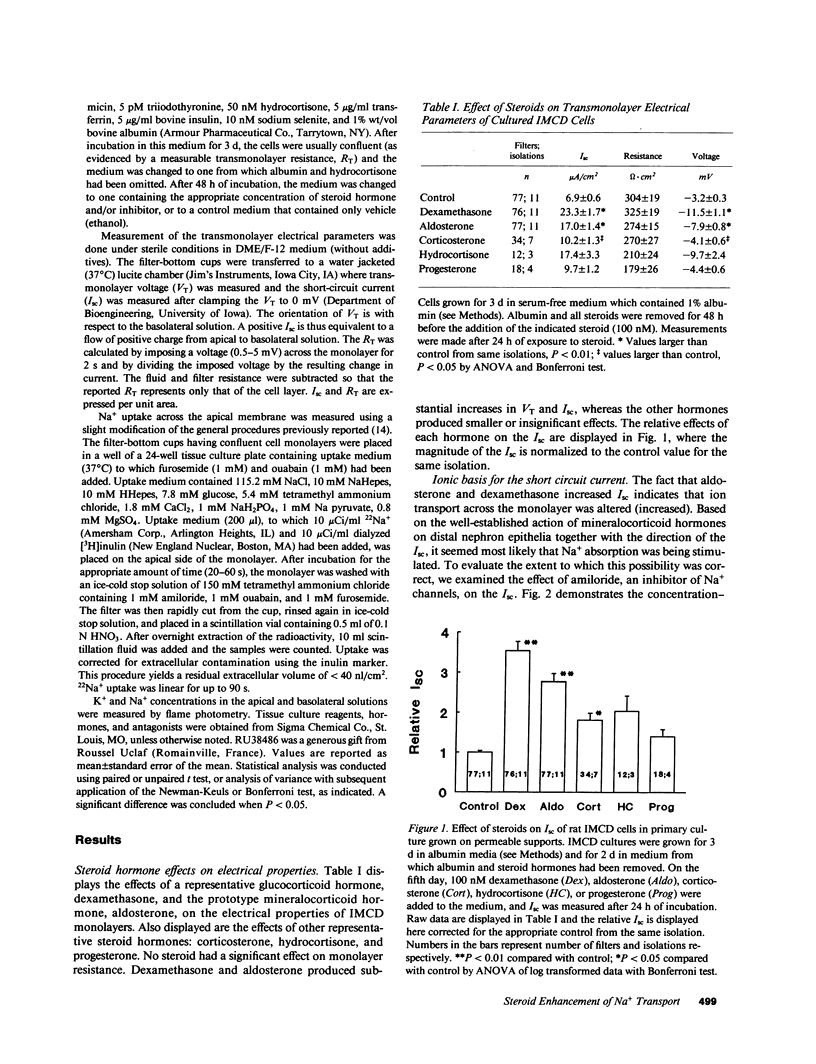
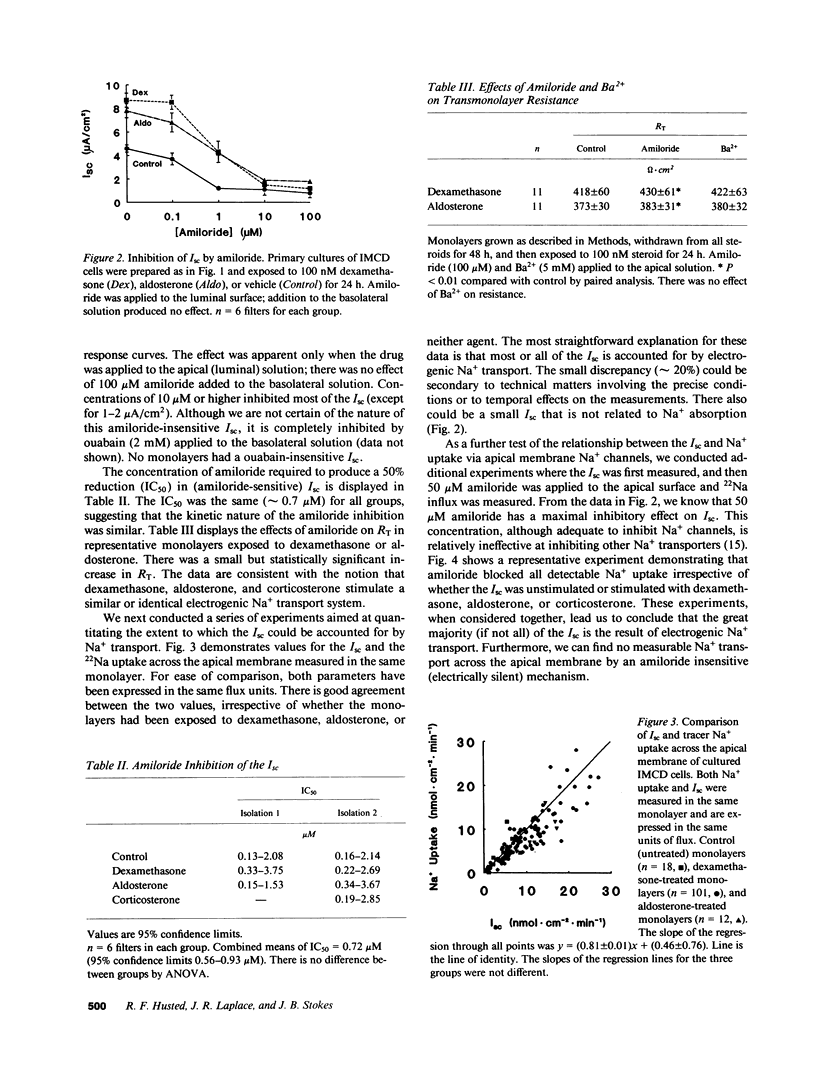
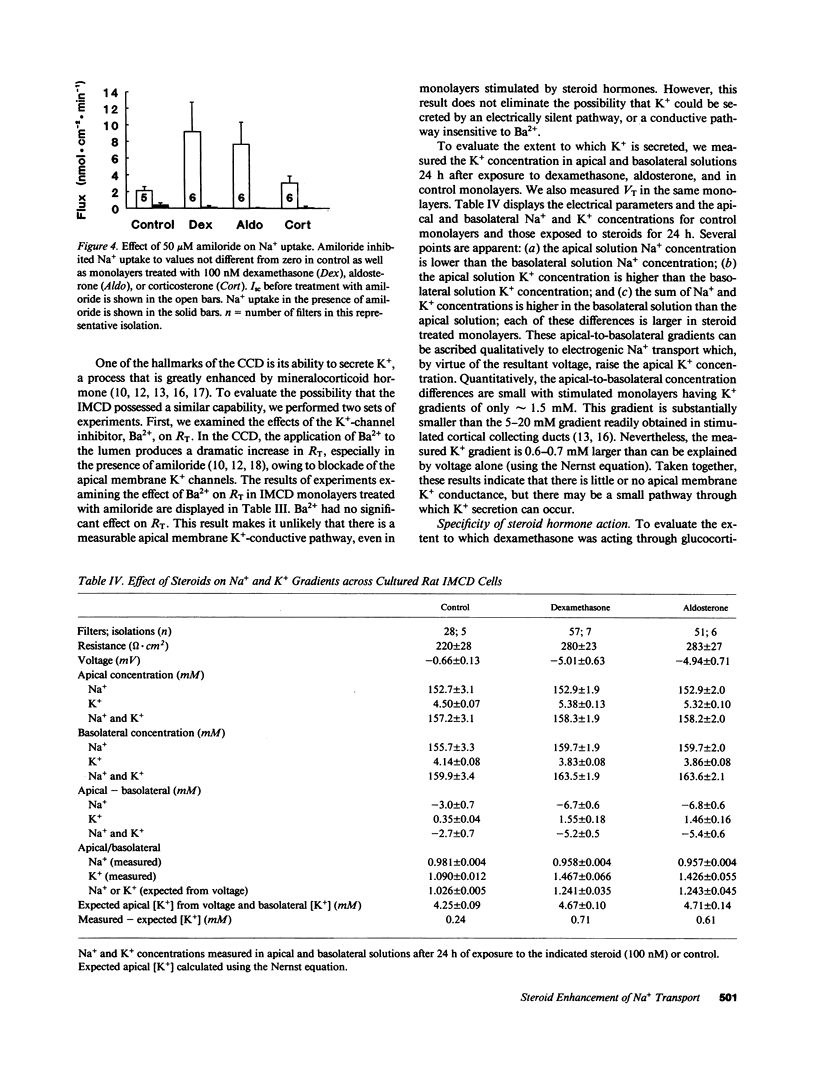
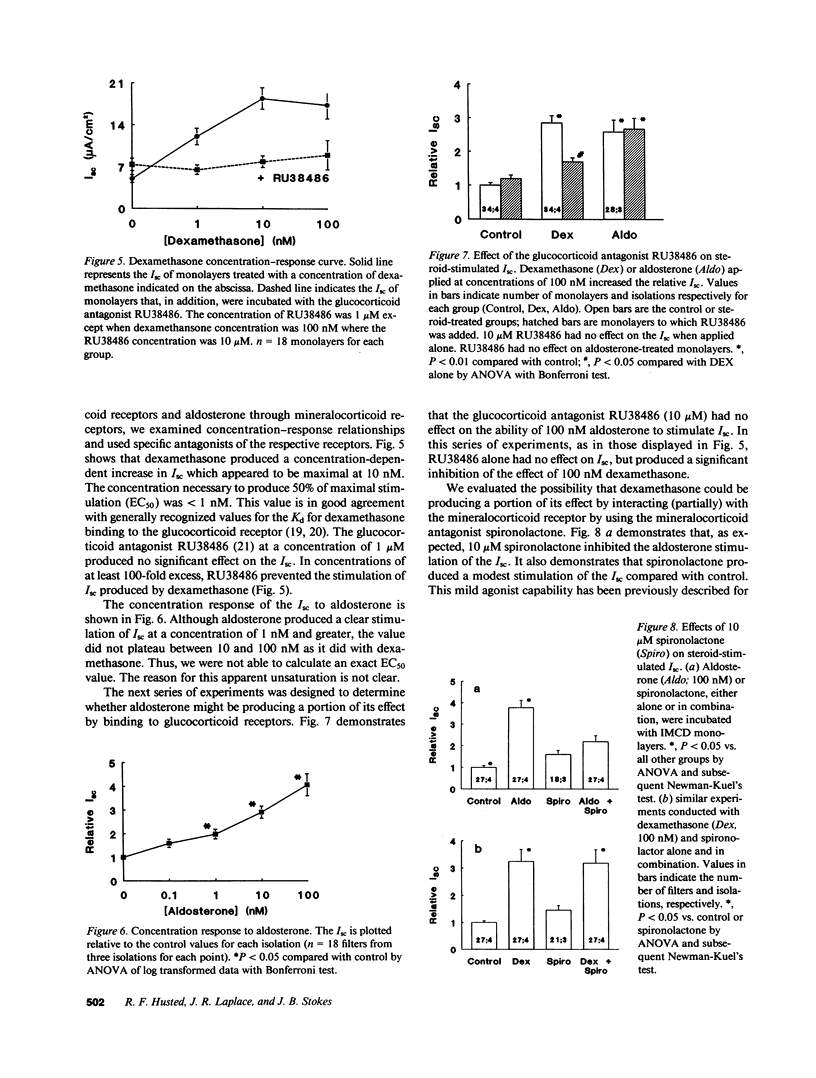
We have investigated the effect of steroid hormones on Na+ transport by rat renal inner medullary collecting duct (IMCD) cells. These cells, grown on permeable supports in primary culture, grow to confluence and develop a transmonolayer voltage oriented such that the apical surface is negative with respect to the basal surface. The results of these experiments demonstrate that this voltage is predominantly (or exclusively) the result of electrogenic Na+ absorption. Na+ transport can be stimulated two- to fourfold by exposure to either dexamethasone or aldosterone (100 nM). Experiments using specific antagonists of the glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors indicate that activation of either receptor stimulates electrogenic Na+ transport; electroneutral Na+ transport is undetectable. Two other features of the IMCD emerge from these studies. (a) These cells appear to have the capacity to metabolize the naturally occurring glucocorticoid hormone corticosterone. (b) The capacity for K+ secretion is minimal and steroid hormones do not induce or stimulate conductive K+ secretion as they do in the cortical collecting duct.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bastl C. P. Effect of spironolactone on glucocorticoid-induced colonic cation transport. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 2):F1235–F1242. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.6.F1235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastl C. P., Schulman G., Cragoe E. J., Jr Low-dose glucocorticoids stimulate electroneutral NaCl absorption in rat colon. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 2):F1027–F1038. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.6.F1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biber T. U., Curran P. F. Direct measurement of uptake of sodium at the outer surface of the frog skin. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jul;56(1):83–99. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brem A. S., Matheson K. L., Conca T., Morris D. J. Effect of carbenoxolone on glucocorticoid metabolism and Na transport in toad bladder. Am J Physiol. 1989 Oct;257(4 Pt 2):F700–F704. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.4.F700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges R. J., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Frizzell R. A., Benos D. J. Inhibition of colonic Na+ transport by amiloride analogues. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 1):C67–C74. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.1.C67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brion L. P., Schwartz J. H., Lachman H. M., Zavilowitz B. J., Schwartz G. J. Development of H+ secretion by cultured renal inner medullary collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 2):F486–F501. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.3.F486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D., Sorscher E. J., Ausiello D. A., Benos D. J. Immunocytochemical localization of Na+ channels in rat kidney medulla. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 2):F366–F369. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.2.F366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrousos G. P., Laue L., Nieman L. K., Kawai S., Udelsman R. U., Brandon D. D., Loriaux D. L. Glucocorticoids and glucocorticoid antagonists: lessons from RU 486. Kidney Int Suppl. 1988 Oct;26:S18–S23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diezi J., Michoud P., Aceves J., Giebisch G. Micropuncture study of electrolyte transport across papillary collecting duct of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1973 Mar;224(3):623–634. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.3.623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funder J. W., Feldman D., Edelman I. S. Glucocorticoid receptors in rat kidney: the binding of tritiated-dexamethasone. Endocrinology. 1973 Apr;92(4):1005–1013. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-4-1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funder J. W., Pearce P. T., Smith R., Smith A. I. Mineralocorticoid action: target tissue specificity is enzyme, not receptor, mediated. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):583–585. doi: 10.1126/science.2845584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaeggeler H. P., Edwards C. R., Rossier B. C. Steroid metabolism determines mineralocorticoid specificity in the toad bladder. Am J Physiol. 1989 Oct;257(4 Pt 2):F690–F695. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.4.F690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garty H. Mechanisms of aldosterone action in tight epithelia. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(3):193–205. doi: 10.1007/BF01870126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geering K., Claire M., Gaeggeler H. P., Rossier B. C. Receptor occupancy vs. induction of Na+-K+-ATPase and Na+ transport by aldosterone. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jan;248(1 Pt 1):C102–C108. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.1.C102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grupp C., Pavenstädt-Grupp I., Grunewald R. W., Bevan C., Stokes J. B., 3rd, Kinne R. K. A Na-K-Cl cotransporter in isolated rat papillary collecting duct cells. Kidney Int. 1989 Aug;36(2):201–209. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halevy J., Boulpaep E. L., Budinger M. E., Binder H. J., Hayslett J. P. Glucocorticoids have a different action than aldosterone on target tissue. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jan;254(1 Pt 2):F153–F158. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.1.F153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOEFOED-JOHNSEN V., USSING H. H. The nature of the frog skin potential. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Jun 2;42(3-4):298–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman J. G., Blumenthal S. S., Wiessner J. H., Reetz K. L., Lewand D. L., Mandel N. S., Mandel G. S., Garancis J. C., Cragoe E. J., Jr Regulation of pH in rat papillary tubule cells in primary culture. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1660–1669. doi: 10.1172/JCI113255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleyman T. R., Cragoe E. J., Jr Amiloride and its analogs as tools in the study of ion transport. J Membr Biol. 1988 Oct;105(1):1–21. doi: 10.1007/BF01871102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppen B. M., Biagi B. A., Giebisch G. H. Intracellular microelectrode characterization of the rabbit cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):F35–F47. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.1.F35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Eaton D. C., Diamond J. M. The mechanism of Na+ transport by rabbit urinary bladder. J Membr Biol. 1976 Aug 27;28(1):41–70. doi: 10.1007/BF01869690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Light D. B., McCann F. V., Keller T. M., Stanton B. A. Amiloride-sensitive cation channel in apical membrane of inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1988 Aug;255(2 Pt 2):F278–F286. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.2.F278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macknight A. D., DiBona D. R., Leaf A. Sodium transport across toad urinary bladder: a model "tight" epithelium. Physiol Rev. 1980 Jul;60(3):615–715. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.3.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marver D., Schwartz M. J. Identification of mineralocorticoid target sites in the isolated rabbit cortical nephron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3672–3676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishina T., Scholer D. W., Edelman I. S. Glucocorticoid receptors in rat kidney cortical tubules enriched in proximal and distal segments. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jan;240(1):F38–F45. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.1.F38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller A., Steinmetz P. R. Spironolactone. An aldosterone agonist in the stimulation of H+ secretion by turtle urinary bladder. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1666–1670. doi: 10.1172/JCI109087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neil R. G., Sansom S. C. Characterization of apical cell membrane Na+ and K+ conductances of cortical collecting duct using microelectrode techniques. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jul;247(1 Pt 2):F14–F24. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.1.F14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty K. J., Kokko J. P., Marver D. Secondary effect of aldosterone on Na-KATPase activity in the rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1514–1521. doi: 10.1172/JCI110405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayson B. M., Lowther S. O. Steroid regulation of Na+-K+-ATPase: differential sensitivities along the nephron. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 2):F656–F662. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.5.F656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reif M. C., Troutman S. L., Schafer J. A. Sodium transport by rat cortical collecting tubule. Effects of vasopressin and desoxycorticosterone. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1291–1298. doi: 10.1172/JCI112433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands J. M., Knepper M. A., Spring K. R. Na-K-Cl cotransport in apical membrane of rabbit renal papillary surface epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 2):F475–F484. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.3.F475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands J. M., Nonoguchi H., Knepper M. A. Hormone effects on NaCl permeability of rat inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 2):F421–F428. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.3.F421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom S. C., O'Neil R. G. Mineralocorticoid regulation of apical cell membrane Na+ and K+ transport of the cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jun;248(6 Pt 2):F858–F868. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.6.F858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer J. A., Troutman S. L. Potassium transport in cortical collecting tubules from mineralocorticoid-treated rat. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 2):F76–F88. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.1.F76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlatter E., Schafer J. A. Electrophysiological studies in principal cells of rat cortical collecting tubules. ADH increases the apical membrane Na+-conductance. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Jun;409(1-2):81–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00584753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz G. J., Burg M. B. Mineralocorticoid effects on cation transport by cortical collecting tubules in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1978 Dec;235(6):F576–F585. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.235.6.F576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaggio A. M., Schwartz J. H., Bengele H. H., Gordon F. D., Alexander E. A. Mechanisms of H+ secretion by inner medullary collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 2):F391–F400. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.254.3.F391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg H. Medullary collecting-duct function in antidiuretic and in salt- or water-diuretic rats. Am J Physiol. 1974 Mar;226(3):501–506. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.3.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton B. A. Characterization of apical and basolateral membrane conductances of rat inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 2):F862–F868. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.5.F862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. H., Osgood R. W., Kunau R. T., Jr Direct measurement of papillary collecting duct sodium transport in the rat. Evidence for heterogeneity of nephron function during Ringer loading. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):767–773. doi: 10.1172/JCI108527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B. Electroneutral NaCl transport in the distal tubule. Kidney Int. 1989 Sep;36(3):427–433. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B. Ion transport by the cortical and outer medullary collecting tubule. Kidney Int. 1982 Nov;22(5):473–484. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. B. Potassium secretion by cortical collecting tubule: relation to sodium absorption, luminal sodium concentration, and transepithelial voltage. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F395–F402. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner L. C., Burg M. B., Orloff J. Ion transport in cortical collecting tubule; effect of amiloride. Am J Physiol. 1974 Aug;227(2):453–459. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.2.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada Y., Knepper M. A. Na+-K+-ATPase activities in renal tubule segments of rat inner medulla. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 2):F218–F223. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.2.F218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. M., Dawson D. C. Sodium uptake across the apical border of the isolated turtle colon: confirmation of the two-barrier model. J Membr Biol. 1978 Sep 25;42(4):357–374. doi: 10.1007/BF01870356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita K., Pisano J. J., Knepper M. A. Control of sodium and potassium transport in the cortical collecting duct of the rat. Effects of bradykinin, vasopressin, and deoxycorticosterone. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):132–136. doi: 10.1172/JCI111935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnamian S. G., Binder H. J. Regulation of active sodium and potassium transport in the distal colon of the rat. Role of the aldosterone and glucocorticoid receptors. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1924–1929. doi: 10.1172/JCI114380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlich E., Baldamus C. A., Ullrich K. J. Einfluss von Aldosteron auf den Natriumtransport in den Sammelrohren der Säugetierniere. Pflugers Arch. 1969;308(2):111–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00587019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich K. J., Papavassiliou F. Sodium reabsorption in the papillary collecting duct of rats. Effect of adrenalectomy, low Na+ diet, acetazolamide, HCO-3-free solutions and of amiloride. Pflugers Arch. 1979 Feb 14;379(1):49–52. doi: 10.1007/BF00622904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade J. B., O'Neil R. G., Pryor J. L., Boulpaep E. L. Modulation of cell membrane area in renal collecting tubules by corticosteroid hormones. J Cell Biol. 1979 May;81(2):439–445. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warden D. H., Hayashi M., Schuster V. L., Stokes J. B. K+ and Rb+ transport by the rabbit CCD: Rb+ reduces K+ conductance and Na+ transport. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jul;257(1 Pt 2):F43–F52. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.257.1.F43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warden D. H., Schuster V. L., Stokes J. B. Characteristics of the paracellular pathway of rabbit cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):F720–F727. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.4.F720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warden D. H., Schuster V. L., Stokes J. B. Characteristics of the paracellular pathway of rabbit cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):F720–F727. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.4.F720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigt M., Dietl P., Silbernagl S., Oberleithner H. Activation of luminal Na+/H+ exchange in distal nephron of frog kidney. An early response to aldosterone. Pflugers Arch. 1987 May;408(6):609–614. doi: 10.1007/BF00581163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. R., Honrath U., Sonnenberg H. Furosemide action on collecting ducts: effect of prostaglandin synthesis inhibition. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jun;244(6):F666–F673. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.6.F666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidel M. L., Kikeri D., Silva P., Burrowes M., Brenner B. M. Atrial natriuretic peptides inhibit conductive sodium uptake by rabbit inner medullary collecting duct cells. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):1067–1074. doi: 10.1172/JCI113663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


