Abstract
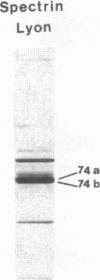
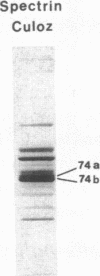
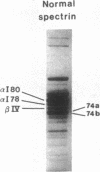
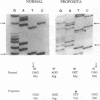
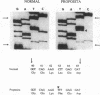
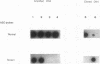
Spectrin alpha I/74 elliptocytosis results from abnormalities involving the "head" region of spectrin dimer. Increased susceptibility to trypsin enhances cleavage of the alpha spectrin chain, yielding an increased amount of the alpha I 74-kD fragment at the expense of the alpha I 80-kD parent fragment. Recently we showed that the mutations causing the Sp alpha I/74 abnormality may lie in the alpha- or the beta-chain, and that spectrin Culoz and spectrin Lyon were two (alpha I/74) alpha-variants, respectively. We now show that the spectrin Culoz alpha I domain undergoes prominent tryptic cleavage after Lys 42, whereas cleavage prevails after Arg 39 in spectrin Lyon. Applying the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique to exon 2 of the spectrin alpha I domain, we have established that the mutation responsible for spectrin Culoz is alpha I 40 Gly----Val; GGT----GTT. Applying the PCR technique to the cDNA derived from reticulocyte mRNA, we have shown that the mutation responsible for spectrin Lyon is alpha I 43 Leu----Phe; CTT----TTT. Studies of normal controls and of family members using dot blot hybridization with allele-specific oligonucleotide probes confirmed these results. Variants such as spectrin Culoz and spectrin Lyon should provide insight into a region that participates in spectrin dimer self-association and whose susceptibility to proteolysis must reflect subtle conformational changes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett V. The membrane skeleton of human erythrocytes and its implications for more complex cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:273–304. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.001421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coetzer T., Lawler J., Prchal J. T., Palek J. Molecular determinants of clinical expression of hereditary elliptocytosis and pyropoikilocytosis. Blood. 1987 Sep;70(3):766–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhermy D., Lecomte M. C., Garbarz M., Feo C., Gautero H., Bournier O., Galand C., Herrera A., Gretillat F., Boivin P. Molecular defect of spectrin in the family of a child with congenital hemolytic poikilocytic anemia. Pediatr Res. 1984 Oct;18(10):1005–1012. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198410000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbarz M., Devaux I., Grandchamp B., Picat C., Dhermy D., Lecomte M. C., Boivin P., Sahr K. E., Forget B. Recherche de l'anomalie génétique dans une forme hémolytique d'elliptocytose héréditaire avec homozygotie pour le variant spectrine alpha I/74. C R Acad Sci III. 1989;308(2):43–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbarz M., Lecomte M. C., Féo C., Devaux I., Picat C., Lefebvre C., Galibert F., Gautero H., Bournier O., Galand C. Hereditary pyropoikilocytosis and elliptocytosis in a white French family with the spectrin alpha I/74 variant related to a CGT to CAT codon change (Arg to His) at position 22 of the spectrin alpha I domain. Blood. 1990 Apr 15;75(8):1691–1698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goblet C., Prost E., Whalen R. G. One-step amplification of transcripts in total RNA using the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):2144–2144. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.2144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman N., Stanislovitis P., Watkins P. C., Klinger K. W., Linnenbach A. J., Forget B. G. Three RFLPs are detected by an alpha spectrin genomic clone. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4696–4696. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh N., Nose K., Okamoto H. Purification and characterization of proinsulin mRNA from rat B-cell tumor. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun;97(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J., Coetzer T. L., Palek J., Jacob H. S., Luban N. Sp alpha I/65: a new variant of the alpha subunit of spectrin in hereditary elliptocytosis. Blood. 1985 Sep;66(3):706–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J., Liu S. C., Palek J., Prchal J. A molecular defect of spectrin in a subset of patients with hereditary elliptocytosis. Alterations in the alpha-subunit domain involved in spectrin self-association. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jun;73(6):1688–1695. doi: 10.1172/JCI111376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J., Liu S. C., Palek J., Prchal J. Molecular defect of spectrin in hereditary pyropoikilocytosis. Alterations in the trypsin-resistant domain involved in spectrin self-association. J Clin Invest. 1982 Nov;70(5):1019–1030. doi: 10.1172/JCI110689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecomte M. C., Dhermy D., Garbarz M., Feo C., Gautero H., Bournier O., Picat C., Chaveroche I., Galand C., Boivin P. Hereditary pyropoikilocytosis and elliptocytosis in a Caucasian family. Transmission of the same molecular defect in spectrin through three generations with different clinical expression. Hum Genet. 1987 Dec;77(4):329–334. doi: 10.1007/BF00291420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecomte M. C., Dhermy D., Gautero H., Bournier O., Galand C., Boivin P. L'elliptocytose héréditaire en Afrique de l'Ouest: fréquence et répartition des variants de la spectrine. C R Acad Sci III. 1988;306(2):43–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
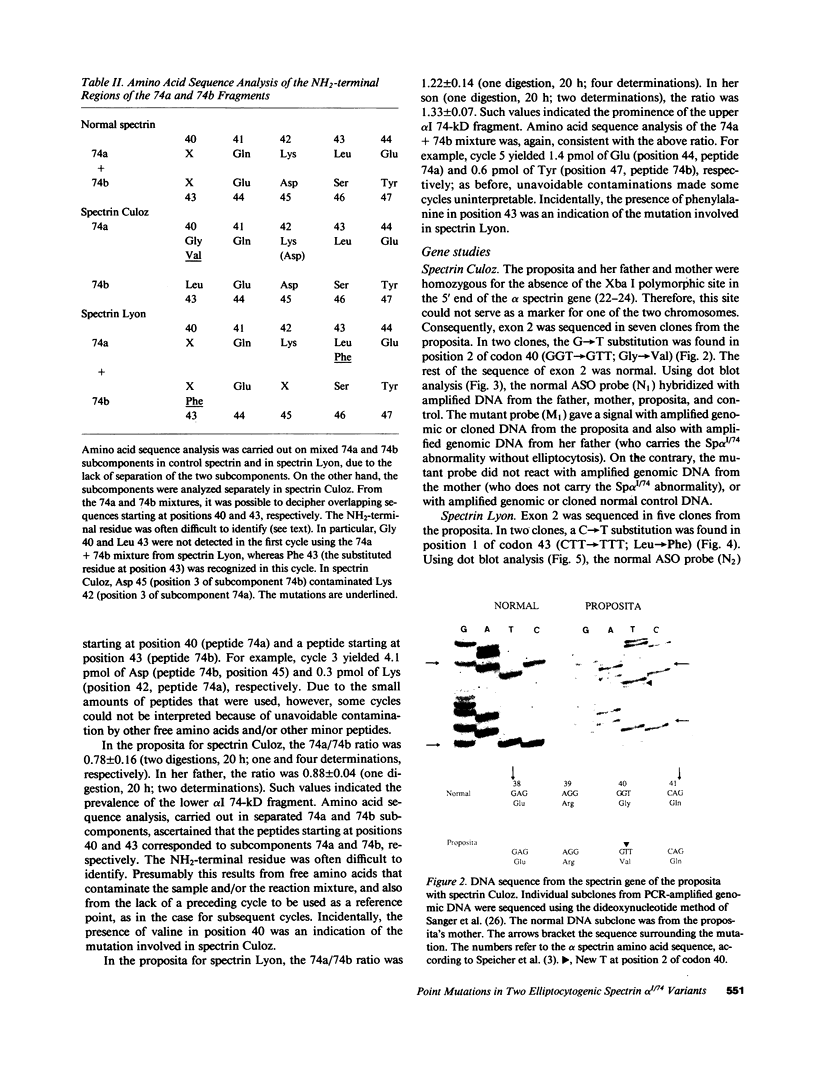
- Lecomte M. C., Dhermy D., Solis C., Ester A., Féo C., Gautero H., Bournier O., Boivin P. A new abnormal variant of spectrin in black patients with hereditary elliptocytosis. Blood. 1985 May;65(5):1208–1217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecomte M. C., Garbarz M., Grandchamp B., Féo C., Gautero H., Devaux I., Bournier O., Galand C., d'Auriol L., Galibert F. Sp alpha I/78: a mutation of the alpha I spectrin domain in a white kindred with HE and HPP phenotypes. Blood. 1989 Aug 15;74(3):1126–1133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linnenbach A. J., Speicher D. W., Marchesi V. T., Forget B. G. Cloning of a portion of the chromosomal gene for human erythrocyte alpha-spectrin by using a synthetic gene fragment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2397–2401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi S. L., Letsinger J. T., Speicher D. W., Marchesi V. T., Agre P., Hyun B., Gulati G. Mutant forms of spectrin alpha-subunits in hereditary elliptocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):191–198. doi: 10.1172/JCI113047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morlé L., Morlé F., Roux A. F., Godet J., Forget B. G., Denoroy L., Garbarz M., Dhermy D., Kastally R., Delaunay J. Spectrin Tunis (Sp alpha I/78), an elliptocytogenic variant, is due to the CGG----TGG codon change (Arg----Trp) at position 35 of the alpha I domain. Blood. 1989 Aug 1;74(2):828–832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris S. A., Ohanian V., Lewis M. L., Chahwala S. B., Rodeck C. H., Mibashan R. S., Gratzer W. B. Prenatal diagnosis of hereditary red cell membrane defect. Br J Haematol. 1986 Apr;62(4):763–772. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1986.tb04100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palek J. Hereditary elliptocytosis, spherocytosis and related disorders: consequences of a deficiency or a mutation of membrane skeletal proteins. Blood Rev. 1987 Sep;1(3):147–168. doi: 10.1016/0268-960x(87)90031-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L. C., Dampier C., Coetzer T., Lawler J., White J., Palek J. Clinical and laboratory study of two Caucasian families with hereditary pyropoikilocytosis and hereditary elliptocytosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987 Jul;88(1):58–65. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/88.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pothier B., Alloisio N., Maréchal J., Morlé L., Ducluzeau M. T., Caldani C., Philippe N., Delaunay J. Assignment of Sp alpha I/74 hereditary elliptocytosis to the alpha- or beta-chain of spectrin through in vitro dimer reconstitution. Blood. 1990 May 15;75(10):2061–2069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pothier B., Morlé L., Alloisio N., Ducluzeau M. T., Caldani C., Féo C., Garbarz M., Chaveroche I., Dhermy D., Lecomte M. C. Spectrin Nice (beta 220/216): a shortened beta-chain variant associated with an increase of the alpha I/74 fragment in a case of elliptocytosis. Blood. 1987 Jun;69(6):1759–1765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux A. F., Morlé F., Guetarni D., Colonna P., Sahr K., Forget B. G., Delaunay J., Godet J. Molecular basis of Sp alpha I/65 hereditary elliptocytosis in North Africa: insertion of a TTG triplet between codons 147 and 149 in the alpha-spectrin gene from five unrelated families. Blood. 1989 Jun;73(8):2196–2201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahr K. E., Tobe T., Scarpa A., Laughinghouse K., Marchesi S. L., Agre P., Linnenbach A. J., Marchesi V. T., Forget B. G. Sequence and exon-intron organization of the DNA encoding the alpha I domain of human spectrin. Application to the study of mutations causing hereditary elliptocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1243–1252. doi: 10.1172/JCI114291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Bugawan T. L., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Analysis of enzymatically amplified beta-globin and HLA-DQ alpha DNA with allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. Nature. 1986 Nov 13;324(6093):163–166. doi: 10.1038/324163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speicher D. W., Davis G., Yurchenco P. D., Marchesi V. T. Structure of human erythrocyte spectrin. I. Isolation of the alpha-I domain and its cyanogen bromide peptides. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14931–14937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speicher D. W., Morrow J. S., Knowles W. J., Marchesi V. T. A structural model of human erythrocyte spectrin. Alignment of chemical and functional domains. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):9093–9101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Renz M. An optimized freeze-squeeze method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):14–19. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90419-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]