Abstract
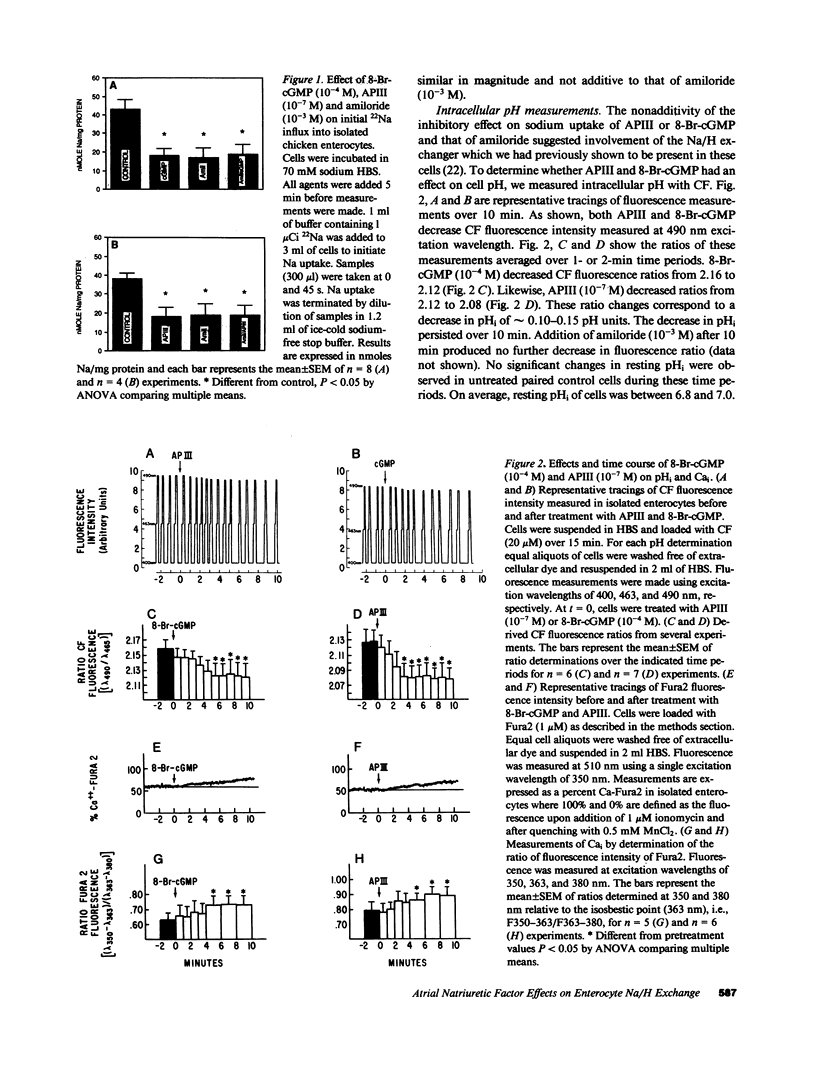
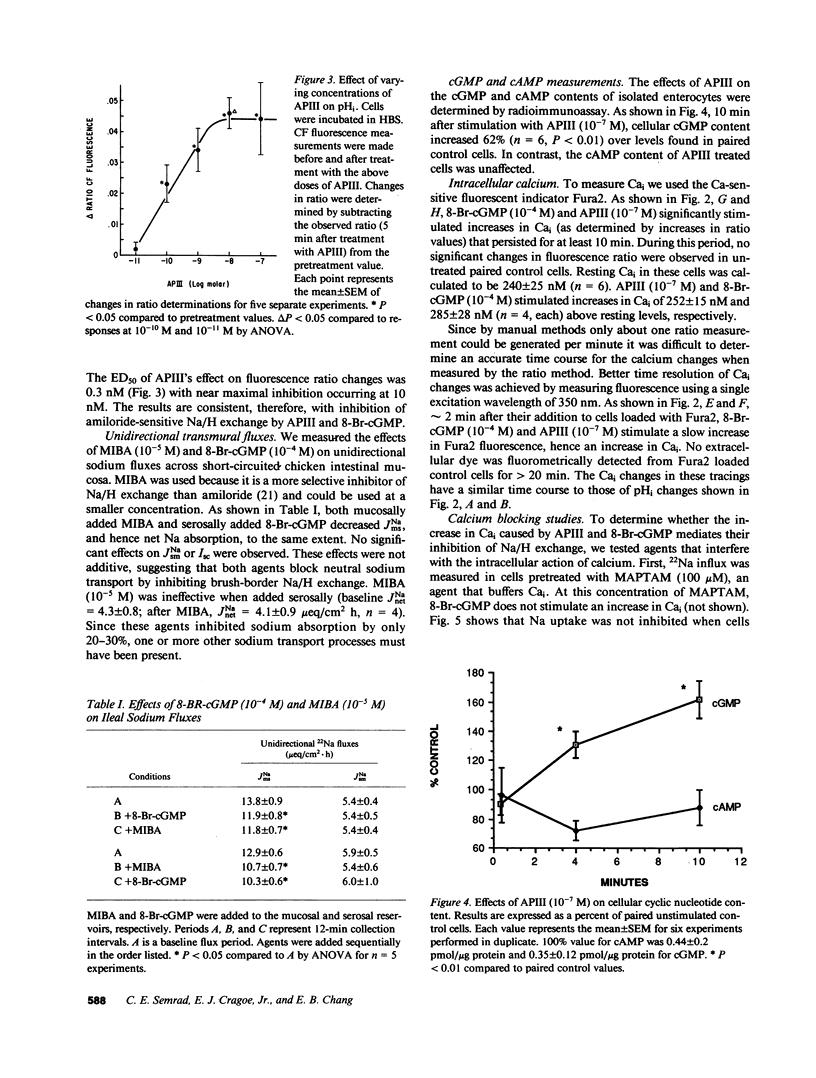
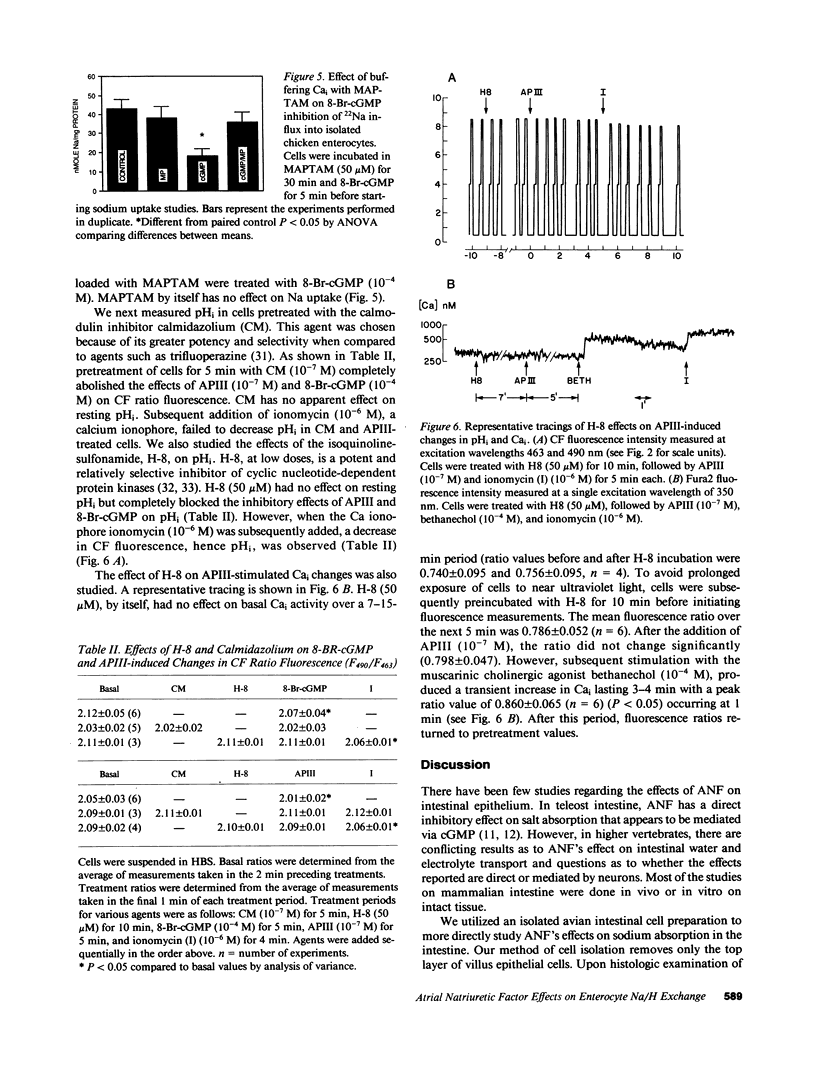
Effects of 8-bromo-cGMP (8-Br-cGMP) and synthetic rat atriopeptin III (APIII) on sodium absorption by isolated chicken villus enterocytes and intact chicken ileal mucosa were determined. In isolated cells, both agents significantly decreased initial rates of influx of 22Na and caused a persistent decrease in intracellular pH (pHi); effects that are not additive to those caused by amiloride (10(-3) M). The ED50 for APIII was 0.3 nM. In intact mucosa, both 8-Br-cGMP (10(-4) M) and 5-(N-methyl-N-isobutyl)amiloride (MIBA) (10(-5) M) reduced JNams and JNa.net, their effects were not additive. APIII (10(-7) M) significantly increased cellular cGMP but not cAMP. Both 8-Br-cGMP (10(-4) M) and APIII (10(-7) M) stimulated a persistent increase in cytosolic calcium (Cai), which could be prevented by pretreating the cells with the cytosolic calcium buffering agent MAPTAM or with H-8, an inhibitor of cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases. Furthermore, pretreatment of cells with H-8 or the calmodulin inhibitor, calmidazolium (CM), prevented the effects of 8-Br-cGMP and APIII on pHi. However, the pHi response to subsequent addition of the calcium-ionophore ionomycin was blocked only by CM and not by H-8. These data suggest that APIII and 8-Br-cGMP inhibit amiloride-sensitive Na/H exchange by increasing Cai, an event requiring activation of cGMP-dependent protein kinase.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bianchi C., Gutkowska J., Thibault G., Garcia R., Genest J., Cantin M. Radioautographic localization of 125I-atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) in rat tissues. Histochemistry. 1985;82(5):441–452. doi: 10.1007/BF02450479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi C., Thibault G., De Léan A., Genest J., Cantin M. Atrial natriuretic factor binding sites in the jejunum. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 1):G436–G441. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.2.G436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantiello H. F., Ausiello D. A. Atrial natriuretic factor and cGMP inhibit amiloride-sensitive Na+ transport in the cultured renal epithelial cell line, LLC-PK1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 29;134(2):852–860. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80498-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesa P. G., Rettig W. J., Melamed M. R. Expression of cytokeratins in normal and neoplastic colonic epithelial cells. Implications for cellular differentiation and carcinogenesis. Am J Surg Pathol. 1986 Dec;10(12):829–835. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198612000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cragoe E. J., Jr, Woltersdorf O. W., Jr, Bicking J. B., Kwong S. F., Jones J. H. Pyrazine diuretics. II. N-amidino-3-amino-5-substituted 6-halopyrazinecarboxamides. J Med Chem. 1967 Jan;10(1):66–75. doi: 10.1021/jm00313a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Fromm D., McColl I. Ion transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. I. Na and Cl fluxes and short-circuit current. Am J Physiol. 1971 May;220(5):1388–1396. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.5.1388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Cohen S. Cytoplasmic [Ca2+] and intracellular pH in lymphocytes. Role of membrane potential and volume-activated Na+/H+ exchange. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Feb;89(2):185–213. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.2.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Deth R. C. Influence of atrial natriuretic factor on 5-(N-ethyl-N-isopropyl)amiloride-sensitive 22Na+ uptake in rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Mar;248(3):991–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F., Brooker G. Femtomole sensitive radioimmunoassay for cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP after 2'0 acetylation by acetic anhydride in aqueous solution. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;1(4):207–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Moore J. P., Taylor M. V., Metcalfe J. C. Free cytoplasmic calcium concentration and the mitogenic stimulation of lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4876–4882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyun C. S., Kimmich G. A. Effect of cholera toxin on cAMP levels and Na+ influx in isolated intestinal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1982 Sep;243(3):C107–C115. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.243.3.C107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai Y., Ohnuma N., Matsuo H. Rat atrial natriuretic polypeptide increases net water, sodium and chloride absorption across rat small intestine in vivo. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep;45(1):7–13. doi: 10.1254/jjp.45.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman S., Monckton E. Influence of right atrial stretch and atrial natriuretic factor on rat intestinal fluid content. J Physiol. 1988 Aug;402:1–8. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knickelbein R. G., Aronson P. S., Dobbins J. W. Membrane distribution of sodium-hydrogen and chloride-bicarbonate exchangers in crypt and villus cell membranes from rabbit ileum. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):2158–2163. doi: 10.1172/JCI113838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno T., Andresen J. W., Kamisaki Y., Waldman S. A., Chang L. Y., Saheki S., Leitman D. C., Nakane M., Murad F. Co-purification of an atrial natriuretic factor receptor and particulate guanylate cyclase from rat lung. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5817–5823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz A., Della Bruna R., Pfeilschifter J., Bauer C. Effect of synthetic atrial natriuretic peptide on rat renal juxtaglomerular cells. J Hypertens Suppl. 1986 Jun;4(2):S57–S60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maack T., Marion D. N., Camargo M. J., Kleinert H. D., Laragh J. H., Vaughan E. D., Jr, Atlas S. A. Effects of auriculin (atrial natriuretic factor) on blood pressure, renal function, and the renin-aldosterone system in dogs. Am J Med. 1984 Dec;77(6):1069–1075. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90190-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martïnez Seeber A., Vidal N. A., Carchio S. M., Karara A. L. Inhibition of water-sodium intestinal absorption by an atrial extract. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1986 Mar;64(3):244–247. doi: 10.1139/y86-039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoguchi H., Sands J. M., Knepper M. A. ANF inhibits NaCl and fluid absorption in cortical collecting duct of rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 2):F179–F186. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.1.F179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell M. E., Owen N. E. Atrial natriuretic factor stimulates Na/K/Cl cotransport in vascular smooth muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6132–6136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Grady S. M., Field M., Nash N. T., Rao M. C. Atrial natriuretic factor inhibits Na-K-Cl cotransport in teleost intestine. Am J Physiol. 1985 Nov;249(5 Pt 1):C531–C534. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.5.C531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'grady S. M. Cyclic nucleotide-mediated effects of ANF and VIP on flounder intestinal ion transport. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jan;256(1 Pt 1):C142–C146. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.1.C142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenk D. B., Phelps M. N., Porter J. G., Fuller F., Cordell B., Lewicki J. A. Purification and subunit composition of atrial natriuretic peptide receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1521–1525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner A. L., Parker C. W., Kipnis D. M. Radioimmunoassay for cyclic nucleotides. I. Preparation of antibodies and iodinated cyclic nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1106–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes T. J., Jr, McConkey C. L., Jr, Martin K. J. Atriopeptin III increases cGMP in glomeruli but not in proximal tubules of dog kidney. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jan;250(1 Pt 2):F27–F31. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.250.1.F27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay J., Gerzer R., Vinay P., Pang S. C., Béliveau R., Hamet P. The increase of cGMP by atrial natriuretic factor correlates with the distribution of particulate guanylate cyclase. FEBS Lett. 1985 Feb 11;181(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)81105-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Atrial natriuretic factor selectively activates particulate guanylate cyclase and elevates cyclic GMP in rat tissues. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14332–14334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidmann P., Hasler L., Gnädinger M. P., Lang R. E., Uehlinger D. E., Shaw S., Rascher W., Reubi F. C. Blood levels and renal effects of atrial natriuretic peptide in normal man. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):734–742. doi: 10.1172/JCI112368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winquist R. J., Faison E. P., Waldman S. A., Schwartz K., Murad F., Rapoport R. M. Atrial natriuretic factor elicits an endothelium-independent relaxation and activates particulate guanylate cyclase in vascular smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7661–7664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidel M. L., Seifter J. L., Lear S., Brenner B. M., Silva P. Atrial peptides inhibit oxygen consumption in kidney medullary collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol. 1986 Aug;251(2 Pt 2):F379–F383. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.2.F379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



