Abstract
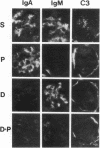
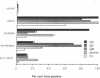
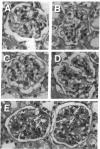
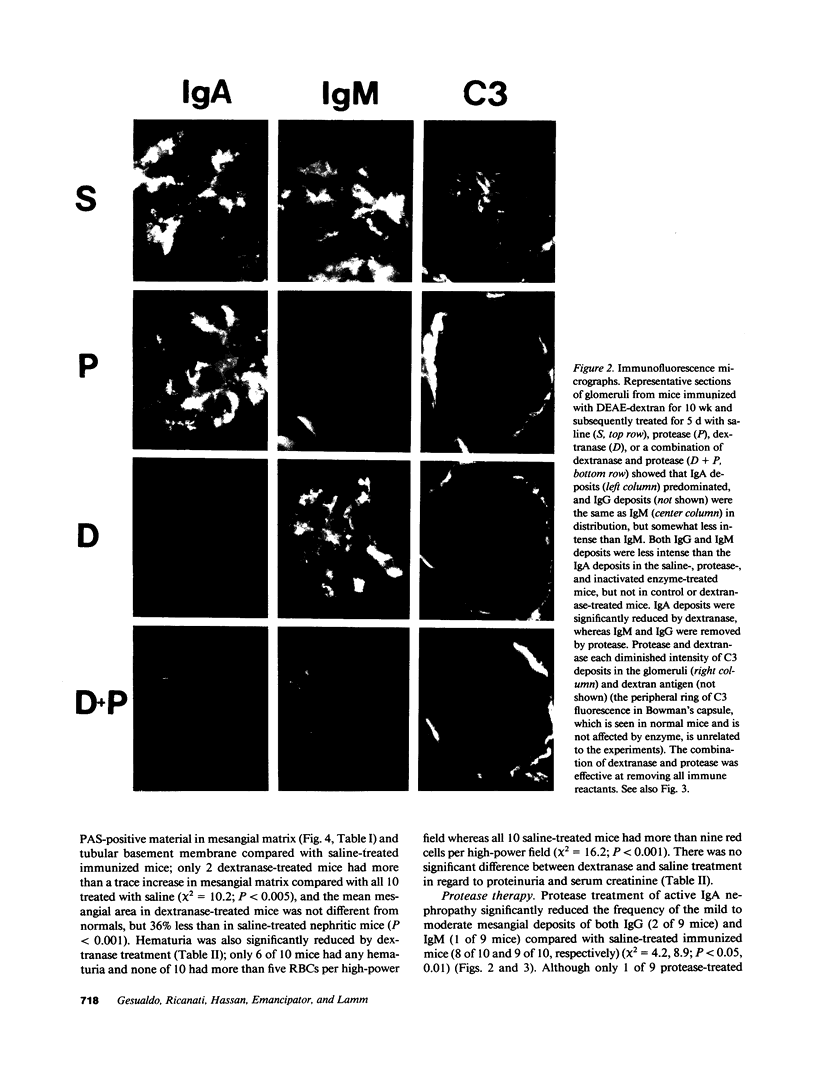
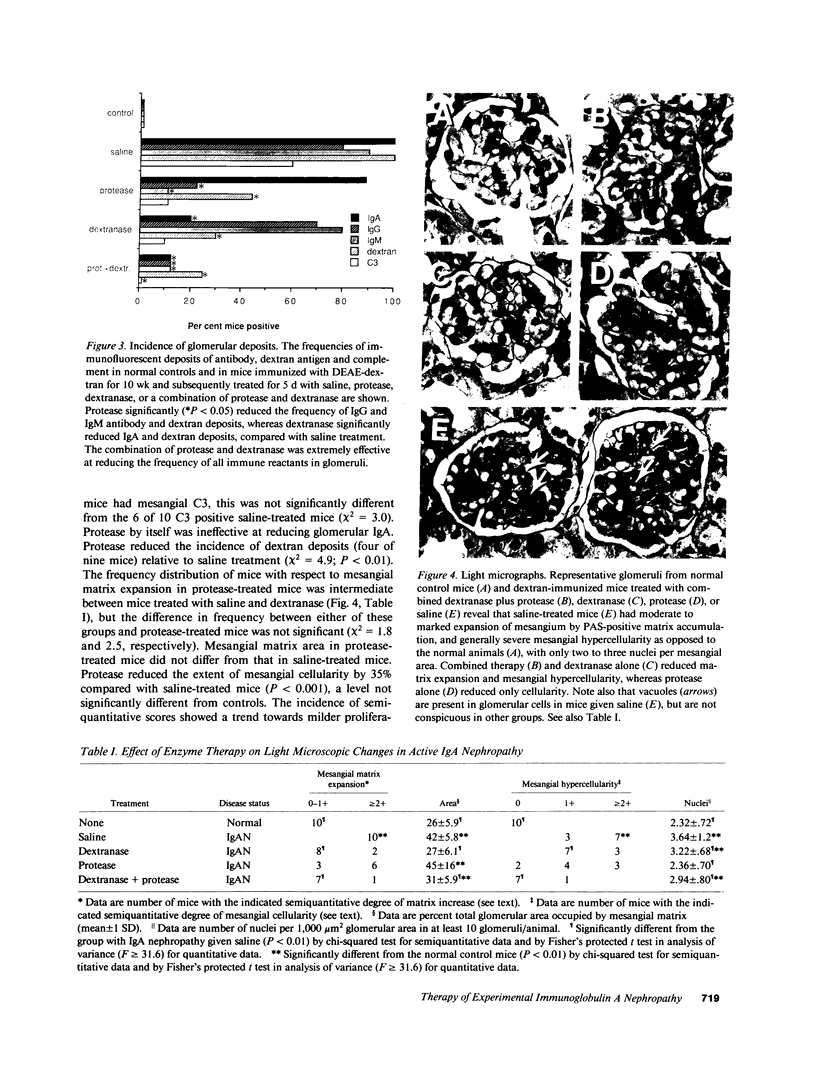
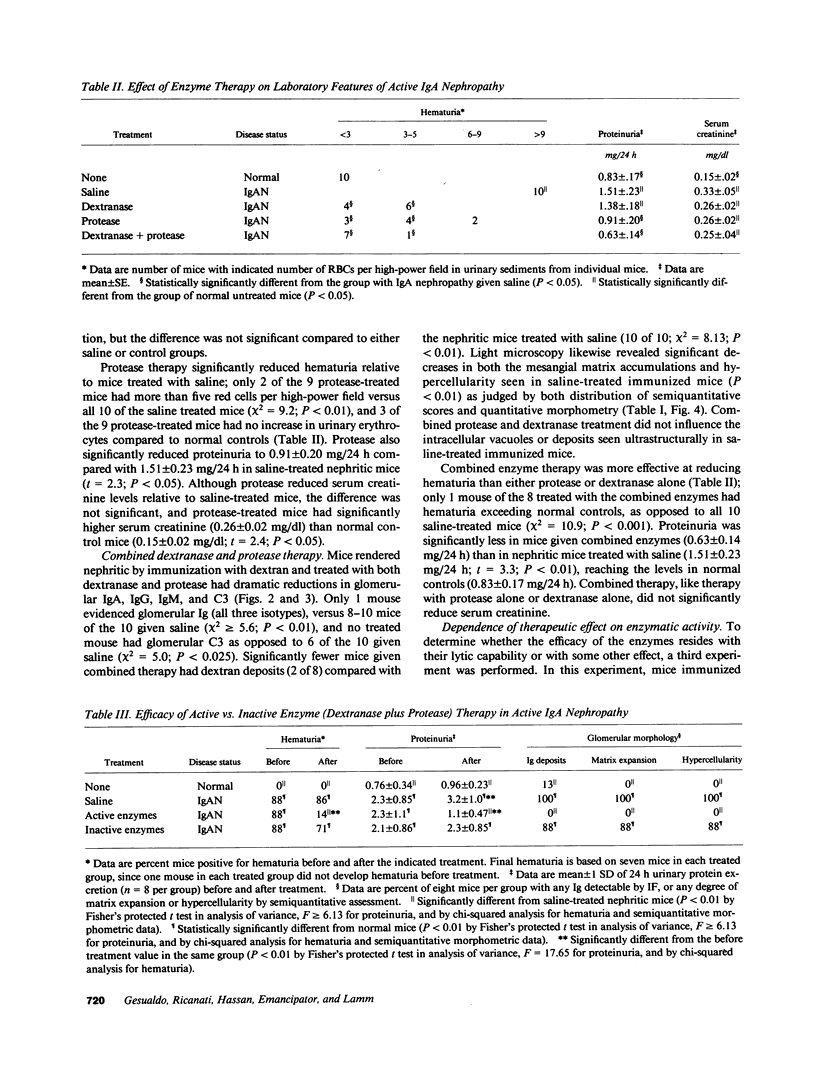
The therapeutic effects of saccharolytic and proteolytic enzymes were investigated in models of IgA nephropathy. Mesangial glomerulonephritis was induced in mice by intravenous injection of preformed soluble immune complexes of dextran sulfate and either IgA (J 558) or IgM (MOPC 104 E) anti-dextran MAb (passive model) or by immunization with DEAE dextran (active model). In the passive model, only 30-40% of dextranase-treated mice given IgA or IgM immune complexes had mesangial Ig or dextran deposits, compared with 100% of saline-treated controls (P less than 0.01). There was no significant difference in mice given only protease. In the active model, dextranase and protease separately each reduced glomerular dextran and C3 deposits, and hematuria (P less than 0.01). Dextranase also reduced the glomerular IgA deposits (20 vs. 100% of saline-treated mice) and the frequency and severity of mesangial matrix expansion (both P less than 0.02), but did not reduce the modest IgG or IgM codeposits. Protease reduced IgG and IgM deposits, proteinuria and mesangial hypercellularity compared with saline (P less than 0.02), but did not diminish IgA, and had no effect on mesangial matrix expansion. The combination of dextranase plus protease attenuated all components of glomerular injury as judged by clinical and pathological parameters, but inactivated dextranase plus inactivated protease had no effect on any parameter. We conclude that enzymatic digestion of antigen and antibody can reduce immune deposits, mesangial proliferation, proteinuria, and hematuria in experimental glomerulonephritis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- D'Amico G. The commonest glomerulonephritis in the world: IgA nephropathy. Q J Med. 1987 Sep;64(245):709–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emancipator S. N., Lamm M. E. IgA nephropathy: pathogenesis of the most common form of glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1989 Feb;60(2):168–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haakenstad A. O., Striker G. E., Mannik M. Removal of glomerular immune complex deposits by excess antigen in chronic mouse model of immune complex disease. Lab Invest. 1983 Mar;48(3):323–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura H., Inouye M. In vitro processing of pro-subtilisin produced in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):12959–12963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs K. L., Miller F. Antigen size and charge in immune complex glomerulonephritis. II. Passive induction of immune deposits with dextran-anti-dextran immune complexes. Am J Pathol. 1983 Jun;111(3):298–306. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs K. L., Miller F. Role of antigen size and charge in immune complex glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1982 Aug;47(2):198–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs K., Miller F. Dextran-induced IgA nephropathy. Contrib Nephrol. 1984;40:45–50. doi: 10.1159/000409726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannik M., Striker G. E. Removal of glomerular deposits of immune complexes in mice by administration of excess antigen. Lab Invest. 1980 May;42(5):483–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa M., Emancipator S. N., Lamm M. E. Proteolytic enzyme treatment reduces glomerular immune deposits and proteinuria in passive Heymann nephritis. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):1973–1987. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazawa M., Emancipator S. N., Lamm M. E. Removal of glomerular immune complexes in passive serum sickness nephritis by treatment in vivo with proteolytic enzymes. Lab Invest. 1986 Nov;55(5):551–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi H. The effect of pepsin on autologous immune complex glomerulonephritis. Life Sci. 1983 Aug 15;33(7):671–677. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90256-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira E., Arnon R. Cleavage of one specific disulfide bond in papain. J Biol Chem. 1969 Feb 10;244(3):1026–1032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen C., Menzel J. In-vivo-Abbau von Immunkomplexen in der Niere durch oral applizierte Enzyme. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1987 Aug 7;99(15):525–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura M., Ito A., Ogiso T., Kato K., Asano H. Studies on dextranase. Purification of dextranase from Penicillium funiculosum and its enzymatic properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 6;309(2):357–362. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdes A. J., Senterfit L. B., Pollack A. D., Germuth F. G., Jr The effect of antigen excess on chronic immune complex glomerulonephritis. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1969 Jan;124(1):9–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. Quantitation of acute and chronic serum sickness in the rabbit. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):7s–8s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]