Abstract
The title compound, C11H9BrClN3O2, is an intermediate in the synthesis of Rynaxypyre, a new insecticidal anthranilic diamide used as a potent and selective ryanodine receptor activator. The dihedral angle between the aromatic ring planes is 78.7 (2)°.
Related literature
For the synthetic procedure, see: Lahm et al. (2007 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C11H9BrClN3O2
M r = 330.57
Orthorhombic,
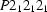
a = 7.404 (2) Å
b = 10.024 (2) Å
c = 17.072 (3) Å
V = 1267.0 (4) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 3.45 mm−1
T = 298 (2) K
0.40 × 0.30 × 0.30 mm
Data collection
Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer
Absorption correction: ψ scan (North et al., 1968 ▶) T min = 0.339, T max = 0.424 (expected range = 0.284–0.355)
2295 measured reflections
1347 independent reflections
959 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.051
3 standard reflections every 200 reflections intensity decay: 1%
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.056
wR(F 2) = 0.129
S = 1.00
1347 reflections
163 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.42 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 15 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: 0.37
Data collection: CAD-4 Software (Enraf–Nonius, 1985 ▶); cell refinement: CAD-4 Software; data reduction: XCAD4 (Harms & Wocadlo, 1995 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808039329/im2086sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808039329/im2086Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Center of Testing and Analysis, Nanjing University, for support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Ethyl 3-bromo-1-(3-chloropyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylate is one of the important intermediates in the synthesis of Rynaxypyre, a new insecticidal anthranilic diamide used as a potent and selective ryanodine receptor activator (Lahm et al., 2007).
The molecular structure of (I) is shown in Fig. 1, a full list of geometric parameters is given in the supplementary material. The bond lengths and angles are within normal ranges (Allen et al., 1987). The dihedral angle of the rings A (C1—C5/N1) and B(C9—C11/N2/N3) is measured to 78.7 (2)°.
No obvious intra- or inter-molecular hydrogen bonds were observed in the crystal structure (Fig. 2).
Experimental
The title compound (I) was synthesized by a method reported in the literature (Lahm et al., 2007). Crystals of the title compound were obtained by dissolving ethyl 3-bromo-1-(3-chloropyridin-2-yl)-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxylate (3.3 g, 10.0 mmol) in acetonitrile (60 ml) and evaporating the solvent slowly at room temperature for about 20 d.
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically, with O—H = 0.82 Å and C—H = 0.93Å for aromatic H, 0.97 Å for CH2 and 0.96 Å for CH3 groups. Hydrogen atoms were constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with Uiso(H) = xUeq(C/O), where x = 1.2 for aromatic H and x = 1.5 for other H.
Figures
Fig. 1.
A drawing of the title molecular structure, with the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A packing diagram for (I).
Crystal data
| C11H9BrClN3O2 | F(000) = 656 |
| Mr = 330.57 | Dx = 1.733 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 25 reflections |
| a = 7.404 (2) Å | θ = 9–13° |
| b = 10.024 (2) Å | µ = 3.45 mm−1 |
| c = 17.072 (3) Å | T = 298 K |
| V = 1267.0 (4) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.40 × 0.30 × 0.30 mm |
Data collection
| Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer | 959 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.051 |
| graphite | θmax = 25.3°, θmin = 2.4° |
| ω/2θ scans | h = 0→8 |
| Absorption correction: ψ scan (North et al., 1968) | k = 0→12 |
| Tmin = 0.339, Tmax = 0.424 | l = −20→20 |
| 2295 measured reflections | 3 standard reflections every 200 reflections |
| 1347 independent reflections | intensity decay: 1% |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.056 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.129 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.063P)2 + 0.5P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.00 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 1347 reflections | Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3 |
| 163 parameters | Δρmin = −0.42 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 155 Frieldel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: 0.37 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br | 0.03831 (14) | 0.07498 (8) | 0.79256 (5) | 0.0580 (3) | |
| Cl | 0.2975 (3) | 0.5607 (2) | 0.90139 (15) | 0.0661 (6) | |
| O1 | 0.0029 (10) | 0.4767 (5) | 1.0803 (3) | 0.0645 (19) | |
| N1 | −0.2392 (8) | 0.5697 (7) | 0.9219 (4) | 0.0481 (16) | |
| C1 | 0.0862 (11) | 0.6189 (7) | 0.9087 (5) | 0.046 (2) | |
| C2 | 0.0441 (15) | 0.7564 (7) | 0.9030 (4) | 0.056 (2) | |
| H2A | 0.1355 | 0.8190 | 0.8964 | 0.067* | |
| N2 | −0.0180 (10) | 0.3292 (5) | 0.8505 (3) | 0.0457 (17) | |
| O2 | 0.0190 (8) | 0.2604 (4) | 1.1121 (3) | 0.0483 (14) | |
| N3 | −0.0260 (10) | 0.3932 (5) | 0.9196 (3) | 0.0442 (16) | |
| C3 | −0.1273 (14) | 0.7949 (8) | 0.9073 (6) | 0.059 (2) | |
| H3A | −0.1564 | 0.8848 | 0.9027 | 0.071* | |
| C4 | −0.2629 (11) | 0.7014 (8) | 0.9187 (5) | 0.055 (2) | |
| H4A | −0.3801 | 0.7333 | 0.9245 | 0.066* | |
| C5 | −0.0628 (13) | 0.5354 (6) | 0.9191 (4) | 0.045 (2) | |
| C6 | 0.0235 (18) | 0.1666 (8) | 1.2393 (5) | 0.074 (3) | |
| H6A | 0.0324 | 0.1860 | 1.2943 | 0.111* | |
| H6B | 0.1218 | 0.1099 | 1.2241 | 0.111* | |
| H6C | −0.0889 | 0.1224 | 1.2289 | 0.111* | |
| C7 | 0.0317 (13) | 0.2919 (7) | 1.1945 (4) | 0.0476 (19) | |
| H7A | −0.0671 | 0.3499 | 1.2097 | 0.057* | |
| H7B | 0.1444 | 0.3377 | 1.2052 | 0.057* | |
| C8 | 0.0085 (12) | 0.3603 (7) | 1.0617 (4) | 0.046 (2) | |
| C9 | 0.0042 (11) | 0.3108 (6) | 0.9816 (4) | 0.041 (2) | |
| C10 | 0.0303 (12) | 0.1880 (6) | 0.9503 (4) | 0.0413 (17) | |
| H10A | 0.0526 | 0.1092 | 0.9773 | 0.050* | |
| C11 | 0.0173 (11) | 0.2032 (6) | 0.8719 (4) | 0.0383 (18) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br | 0.0822 (6) | 0.0377 (4) | 0.0539 (4) | 0.0033 (5) | 0.0035 (5) | −0.0055 (4) |
| Cl | 0.0537 (13) | 0.0473 (14) | 0.0974 (17) | 0.0016 (12) | 0.0030 (12) | 0.0009 (13) |
| O1 | 0.107 (6) | 0.032 (3) | 0.054 (3) | −0.003 (3) | −0.006 (4) | −0.004 (2) |
| N1 | 0.047 (4) | 0.028 (4) | 0.070 (4) | 0.004 (4) | 0.019 (3) | 0.005 (4) |
| C1 | 0.045 (5) | 0.034 (4) | 0.058 (5) | 0.004 (3) | 0.002 (4) | 0.000 (3) |
| C2 | 0.082 (7) | 0.026 (4) | 0.059 (5) | 0.001 (5) | 0.018 (6) | 0.003 (3) |
| N2 | 0.067 (5) | 0.028 (3) | 0.042 (3) | 0.003 (3) | −0.014 (4) | 0.002 (2) |
| O2 | 0.070 (4) | 0.035 (3) | 0.040 (2) | 0.000 (3) | −0.004 (3) | −0.001 (2) |
| N3 | 0.066 (4) | 0.024 (3) | 0.043 (3) | −0.003 (3) | −0.001 (3) | −0.001 (2) |
| C3 | 0.071 (7) | 0.030 (5) | 0.077 (6) | 0.009 (5) | 0.004 (6) | −0.003 (4) |
| C4 | 0.034 (5) | 0.052 (5) | 0.079 (6) | 0.001 (4) | 0.002 (5) | −0.001 (5) |
| C5 | 0.073 (6) | 0.025 (4) | 0.036 (4) | −0.010 (4) | −0.005 (4) | 0.007 (3) |
| C6 | 0.113 (9) | 0.058 (5) | 0.050 (5) | 0.006 (6) | −0.006 (6) | 0.013 (4) |
| C7 | 0.059 (5) | 0.043 (4) | 0.041 (4) | 0.010 (4) | −0.006 (4) | −0.005 (3) |
| C8 | 0.057 (7) | 0.029 (4) | 0.052 (4) | −0.008 (4) | 0.009 (4) | 0.001 (3) |
| C9 | 0.052 (6) | 0.030 (4) | 0.041 (4) | −0.001 (4) | 0.000 (4) | 0.001 (3) |
| C10 | 0.057 (5) | 0.019 (3) | 0.048 (4) | 0.002 (4) | −0.003 (4) | 0.003 (3) |
| C11 | 0.044 (5) | 0.025 (3) | 0.046 (4) | −0.004 (3) | 0.003 (4) | 0.001 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Br—C11 | 1.874 (6) | N3—C5 | 1.452 (8) |
| Cl—C1 | 1.675 (8) | C3—C4 | 1.387 (12) |
| O1—C8 | 1.210 (7) | C3—H3A | 0.9300 |
| N1—C4 | 1.334 (9) | C4—H4A | 0.9300 |
| N1—C5 | 1.351 (11) | C6—C7 | 1.472 (9) |
| C1—C5 | 1.396 (11) | C6—H6A | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.416 (10) | C6—H6B | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.328 (12) | C6—H6C | 0.9600 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9300 | C7—H7A | 0.9700 |
| N2—C11 | 1.340 (8) | C7—H7B | 0.9700 |
| N2—N3 | 1.344 (7) | C8—C9 | 1.454 (10) |
| O2—C8 | 1.323 (8) | C9—C10 | 1.356 (9) |
| O2—C7 | 1.445 (7) | C10—C11 | 1.351 (9) |
| N3—C9 | 1.361 (8) | C10—H10A | 0.9300 |
| C4—N1—C5 | 112.2 (6) | H6A—C6—H6B | 109.5 |
| C5—C1—C2 | 114.7 (8) | C7—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| C5—C1—Cl | 122.6 (6) | H6A—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—Cl | 122.6 (7) | H6B—C6—H6C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.3 (9) | O2—C7—C6 | 108.5 (6) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 120.4 | O2—C7—H7A | 110.0 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 120.4 | C6—C7—H7A | 110.0 |
| C11—N2—N3 | 102.7 (5) | O2—C7—H7B | 110.0 |
| C8—O2—C7 | 118.2 (5) | C6—C7—H7B | 110.0 |
| N2—N3—C9 | 112.7 (5) | H7A—C7—H7B | 108.4 |
| N2—N3—C5 | 118.2 (5) | O1—C8—O2 | 124.1 (7) |
| C9—N3—C5 | 129.1 (5) | O1—C8—C9 | 125.1 (7) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.2 (8) | O2—C8—C9 | 110.8 (6) |
| C2—C3—H3A | 119.9 | C10—C9—N3 | 105.5 (6) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 119.9 | C10—C9—C8 | 132.6 (6) |
| N1—C4—C3 | 125.4 (8) | N3—C9—C8 | 121.9 (6) |
| N1—C4—H4A | 117.3 | C11—C10—C9 | 106.1 (6) |
| C3—C4—H4A | 117.3 | C11—C10—H10A | 126.9 |
| N1—C5—C1 | 128.0 (6) | C9—C10—H10A | 126.9 |
| N1—C5—N3 | 115.5 (7) | N2—C11—C10 | 113.0 (6) |
| C1—C5—N3 | 116.2 (8) | N2—C11—Br | 117.8 (5) |
| C7—C6—H6A | 109.5 | C10—C11—Br | 129.2 (5) |
| C7—C6—H6B | 109.5 | ||
| C5—C1—C2—C3 | −0.4 (12) | C8—O2—C7—C6 | 174.4 (8) |
| Cl—C1—C2—C3 | 178.2 (8) | C7—O2—C8—O1 | −2.5 (13) |
| C11—N2—N3—C9 | 0.4 (9) | C7—O2—C8—C9 | 177.6 (7) |
| C11—N2—N3—C5 | 180.0 (7) | N2—N3—C9—C10 | −0.9 (10) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.2 (15) | C5—N3—C9—C10 | 179.6 (8) |
| C5—N1—C4—C3 | 4.9 (12) | N2—N3—C9—C8 | 177.7 (7) |
| C2—C3—C4—N1 | −3.8 (16) | C5—N3—C9—C8 | −1.8 (14) |
| C4—N1—C5—C1 | −4.2 (11) | O1—C8—C9—C10 | 171.0 (10) |
| C4—N1—C5—N3 | −177.9 (6) | O2—C8—C9—C10 | −9.1 (13) |
| C2—C1—C5—N1 | 2.1 (12) | O1—C8—C9—N3 | −7.1 (14) |
| Cl—C1—C5—N1 | −176.5 (6) | O2—C8—C9—N3 | 172.8 (8) |
| C2—C1—C5—N3 | 175.8 (6) | N3—C9—C10—C11 | 0.9 (10) |
| Cl—C1—C5—N3 | −2.8 (10) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −177.4 (9) |
| N2—N3—C5—N1 | 89.5 (9) | N3—N2—C11—C10 | 0.2 (10) |
| C9—N3—C5—N1 | −91.0 (10) | N3—N2—C11—Br | 179.4 (6) |
| N2—N3—C5—C1 | −85.1 (9) | C9—C10—C11—N2 | −0.7 (10) |
| C9—N3—C5—C1 | 94.4 (10) | C9—C10—C11—Br | −179.8 (6) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: IM2086).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Enraf–Nonius (1985). CAD-4 Software Enraf–Nonius, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Harms, K. & Wocadlo, S. (1995). XCAD4 University of Marburg, Germany.
- Lahm, G. P., Stevenson, T. M., Selby, T. P., Freudenberger, J. H., Cordova, D., Flexner, L., Bellin, C. A., Dubas, C. M., Smith, B. K., Hughes, K. A., Hollingshaus, J. G., Clark, C. E. & Benner, E. A. (2007). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.17, 6274–6279. [DOI] [PubMed]
- North, A. C. T., Phillips, D. C. & Mathews, F. S. (1968). Acta Cryst. A24, 351–359.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808039329/im2086sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808039329/im2086Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




