Abstract
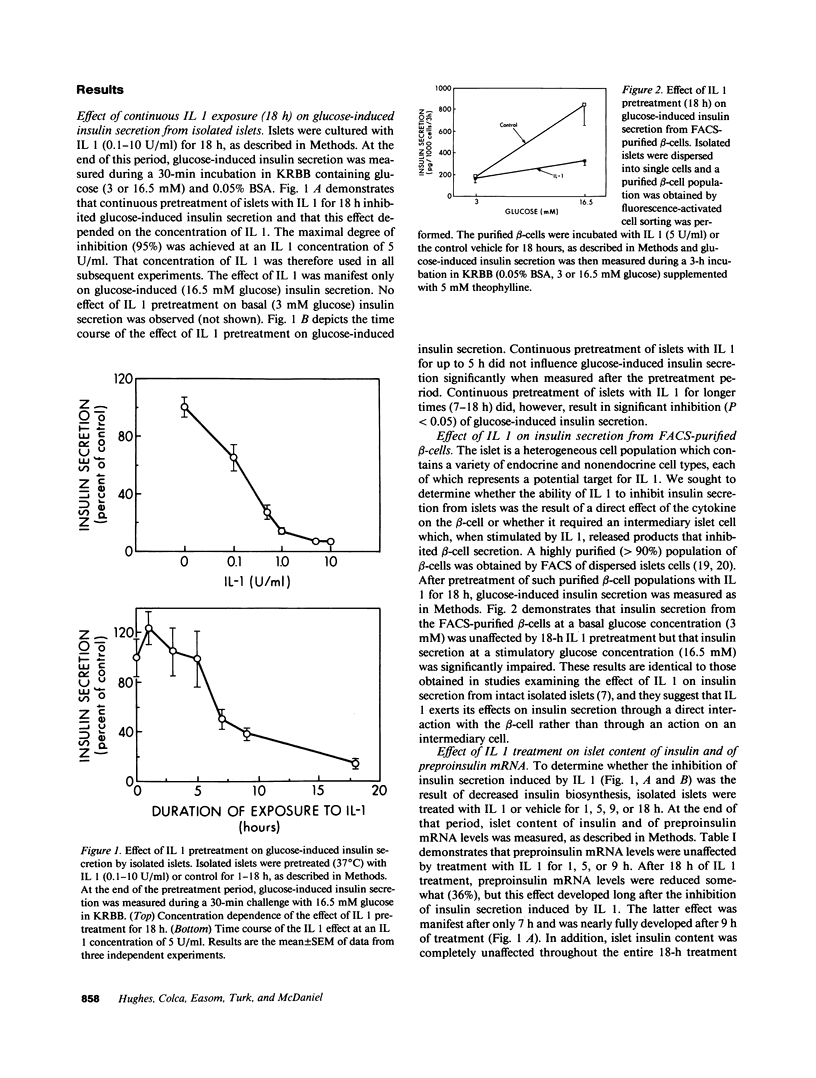
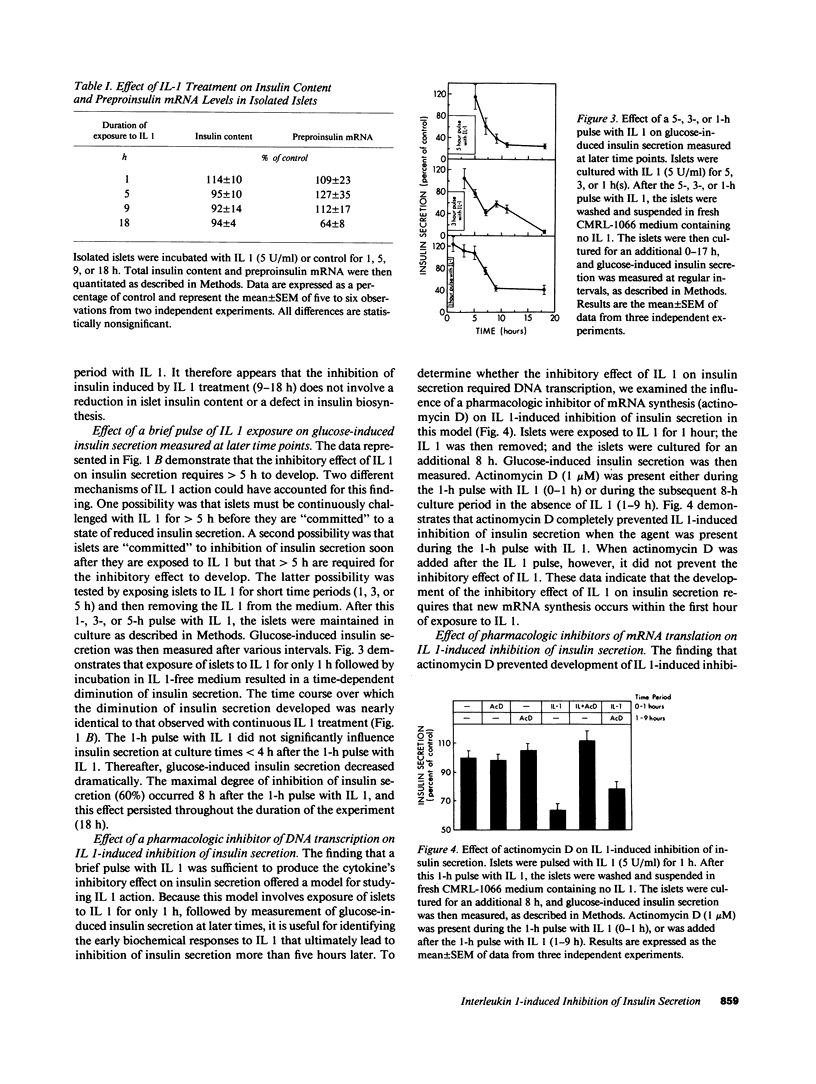
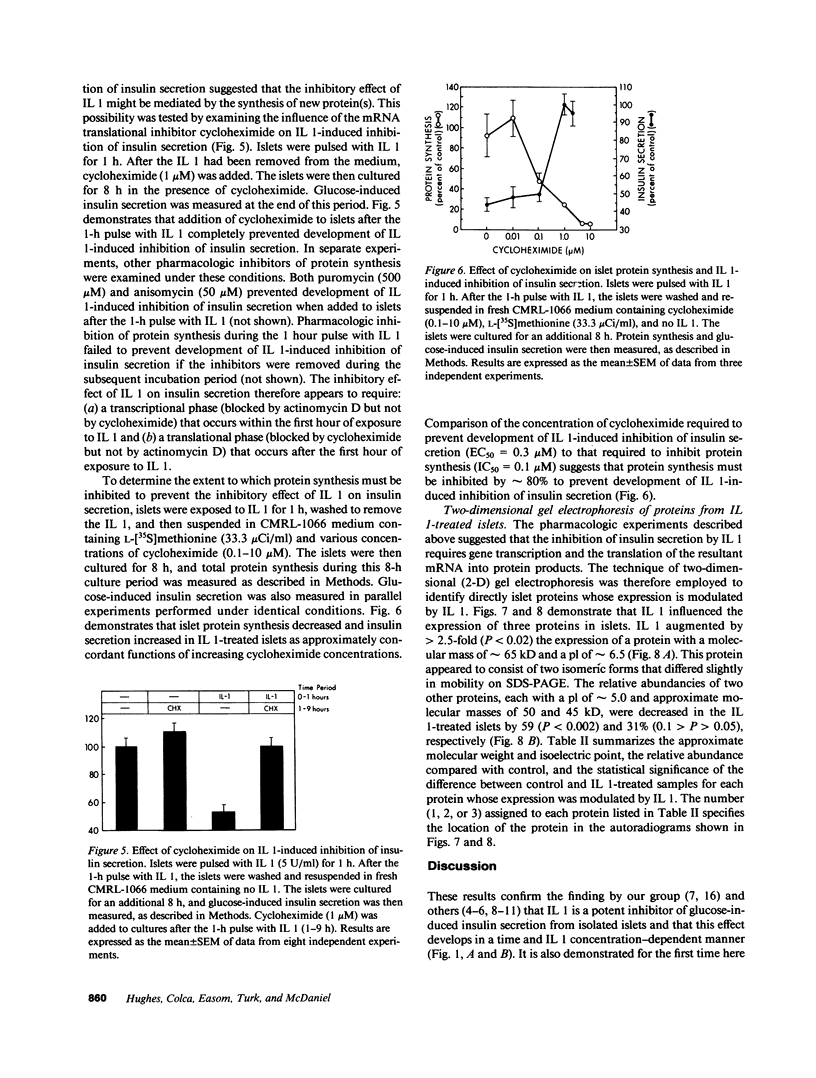
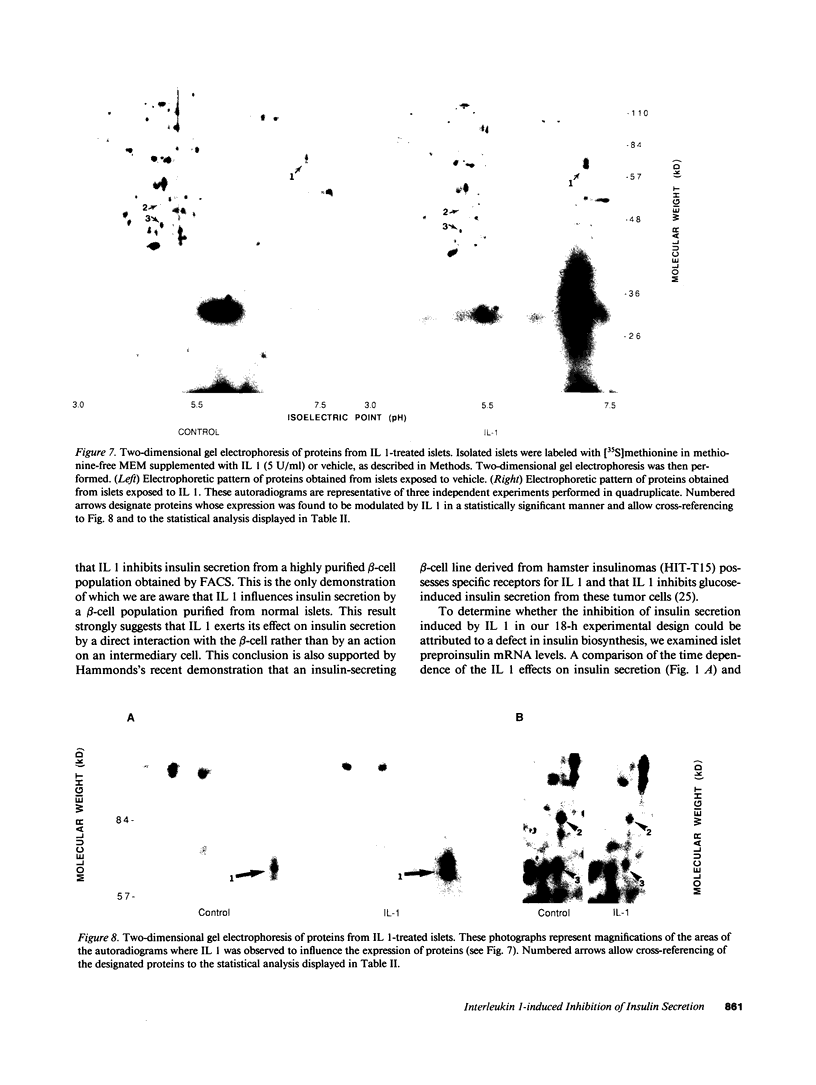
Recombinant human IL 1 beta inhibits glucose-induced insulin secretion from isolated pancreatic islets and from purified beta-cells obtained by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) of dispersed islet cells. Brief (1 h) exposure of isolated islets to IL 1 produces sustained inhibition of insulin secretion for at least 17 h after the IL 1 has been removed from the culture medium. An inhibitory effect of IL 1 on insulin secretion is not observed when islets are coincubated with an inhibitor of DNA transcription (actinomycin D). This finding indicates that the inhibitory effect of IL 1 on insulin secretion requires transcription of one or more genes during the first hour of exposure of islets to IL 1. The inhibitory effect of IL 1 on insulin secretion also requires mRNA translation, because three structurally distinct inhibitors of protein synthesis (cycloheximide, anisomycin, and puromycin) prevent IL 1-induced inhibition of insulin secretion when added to islets after the 1-h exposure to IL 1. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of islet proteins metabolically labeled with [35S]methionine demonstrates that IL 1 augments the expression of a 65-kD (pl approximately 6.5) protein by greater than 2.5-fold. These findings indicate that biochemical events occurring within 1 h of exposure of islets to IL 1 lead to an inhibition of insulin secretion that persists for at least 17 h after the removal of IL 1. One of the early biochemical effects of IL 1 on islets is gene transcription (0-1 h), which is followed by mRNA translation (after 1 h). Our results suggest that the inhibitory effect of IL 1 on insulin secretion is mediated by protein(s) whose synthesis is induced by IL 1.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson N. L., Anderson N. G. Analytical techniques for cell fractions. XXII. Two-dimensional analysis of serum and tissue proteins: multiple gradient-slab gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):341–354. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90230-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comens P. G., Wolf B. A., Unanue E. R., Lacy P. E., McDaniel M. L. Interleukin 1 is potent modulator of insulin secretion from isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Diabetes. 1987 Aug;36(8):963–970. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.8.963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayer-Métroz M. D., Wollheim C. B., Seckinger P., Dayer J. M. A natural interleukin 1 (IL-1) inhibitor counteracts the inhibitory effect of IL-1 on insulin production in cultured rat pancreatic islets. J Autoimmun. 1989 Apr;2(2):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(89)90152-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Wolff S. M. Molecular basis of fever in humans. Am J Med. 1982 May;72(5):799–819. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90548-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrels J. I. Quantitative two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:411–423. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00070-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Gershon R. K., Waksman B. H. Potentiation of the T-lymphocyte response to mitogens. I. The responding cell. J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):128–142. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammonds P., Beggs M., Beresford G., Espinal J., Clarke J., Mertz R. J. Insulin-secreting beta-cells possess specific receptors for interleukin-1 beta. FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 12;261(1):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80645-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helqvist S., Sehested Hansen B., Johannesen J., Ullits Andersen H., Hoiriis Nielsen J., Nerup J. Interleukin 1 induces new protein formation in isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1989 Jul;121(1):136–140. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1210136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. H., Easom R. A., Wolf B. A., Turk J., McDaniel M. L. Interleukin 1-induced prostaglandin E2 accumulation by isolated pancreatic islets. Diabetes. 1989 Oct;38(10):1251–1257. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.10.1251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kampschmidt R. F., Upchurch H. F., Eddington C. L., Pulliam L. A. Multiple biological activities of a partially purified leukocytic endogenous mediator. Am J Physiol. 1973 Mar;224(3):530–533. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.3.530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koranyi L., Permutt M. A., Chirgwin J. M., Giddings S. J. Proinsulin I and II gene expression in inbred mouse strains. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1895–1902. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-11-1895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrup-Poulsen T., Bendtzen K., Nerup J., Dinarello C. A., Svenson M., Nielsen J. H. Affinity-purified human interleukin I is cytotoxic to isolated islets of Langerhans. Diabetologia. 1986 Jan;29(1):63–67. doi: 10.1007/BF02427283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrup-Poulsen T., Bendtzen K., Nerup J., Egeberg J., Nielsen J. H. Mechanisms of pancreatic islet cell destruction. Dose-dependent cytotoxic effect of soluble blood mononuclear cell mediators on isolated islets of Langerhans. Allergy. 1986 May;41(4):250–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1986.tb02025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandrup-Poulsen T., Bendtzen K., Nielsen J. H., Bendixen G., Nerup J. Cytokines cause functional and structural damage to isolated islets of Langerhans. Allergy. 1985 Aug;40(6):424–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1985.tb02681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel M. L., Colca J. R., Kotagal N., Lacy P. E. A subcellular fractionation approach for studying insulin release mechanisms and calcium metabolism in islets of Langerhans. Methods Enzymol. 1983;98:182–200. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)98149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel M. L., Hughes J. H., Wolf B. A., Easom R. A., Turk J. W. Descriptive and mechanistic considerations of interleukin 1 and insulin secretion. Diabetes. 1988 Oct;37(10):1311–1315. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.10.1311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerup J., Mandrup-Poulsen T., Mølvig J. The HLA-IDDM association: implications for etiology and pathogenesis of IDDM. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1987 Jul;3(3):779–802. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610030309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orland M. J., Chyn R., Permutt M. A. Modulation of proinsulin messenger RNA after partial pancreatectomy in rats. Relationships to glucose homeostasis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jun;75(6):2047–2055. doi: 10.1172/JCI111924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pukel C., Baquerizo H., Rabinovitch A. Destruction of rat islet cell monolayers by cytokines. Synergistic interactions of interferon-gamma, tumor necrosis factor, lymphotoxin, and interleukin 1. Diabetes. 1988 Jan;37(1):133–136. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch A., Pukel C., Baquerizo H. Interleukin-1 inhibits glucose-modulated insulin and glucagon secretion in rat islet monolayer cultures. Endocrinology. 1988 Jun;122(6):2393–2398. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-6-2393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler S., Andersson A., Hellerström C. Inhibitory effects of interleukin 1 on insulin secretion, insulin biosynthesis, and oxidative metabolism of isolated rat pancreatic islets. Endocrinology. 1987 Oct;121(4):1424–1431. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-4-1424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinas G. A., Hansen B. S., Linde S., Kastern W., Mølvig J., Mandrup-Poulsen T., Dinarello C. A., Nielsen J. H., Nerup J. Interleukin 1 dose-dependently affects the biosynthesis of (pro)insulin in isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Diabetologia. 1987 Jul;30(7):474–480. doi: 10.1007/BF00279615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. L., McDaniel M. L. Secretagogue-induced oscillations of cytoplasmic Ca2+ in single beta and alpha-cells obtained from pancreatic islets by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jan 30;166(2):813–818. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90882-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf B. A., Hughes J. H., Florholmen J., Turk J., McDaniel M. L. Interleukin-1 inhibits glucose-induced Ca2+ uptake by islets of Langerhans. FEBS Lett. 1989 May 8;248(1-2):35–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80426-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawalich W. S., Diaz V. A. Interleukin 1 inhibits insulin secretion from isolated perifused rat islets. Diabetes. 1986 Oct;35(10):1119–1123. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.10.1119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
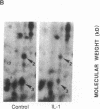
- Zawalich W. S., Dierolf B., Zawalich K. C. Interleukin-1 induces time-dependent potentiation in isolated rat islets: possible involvement of phosphoinositide hydrolysis. Endocrinology. 1989 Feb;124(2):720–726. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-2-720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]