Abstract
In the title compound, C21H25Cl2NO, the dihedral angle between the two benzene rings is 33.18 (11)°. The five-membered ring adopts an envelope conformation. There is an intramolecular O—H⋯N hydrogen bond. In the crystal, molecules are linked by weak N—H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds, forming a helical chain along the c axis.
Related literature
For related literature on aminophenols, see: Cimarelli et al. (2002 ▶); Joshi & Malhotra (2003 ▶); Li et al. (2004 ▶); Puigjaner et al. (1999 ▶); Watts et al. (2005 ▶). For the synthesis, see: Yang et al. (2005 ▶).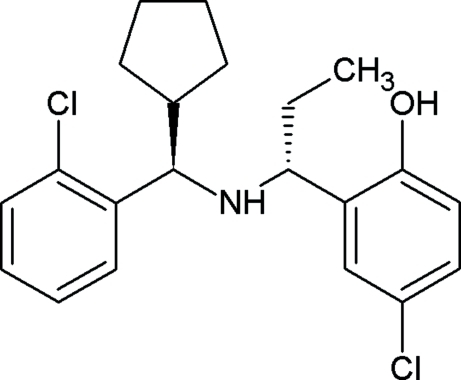
Experimental
Crystal data
C21H25Cl2NO
M r = 378.32
Orthorhombic,

a = 10.9802 (17) Å
b = 11.5607 (18) Å
c = 15.536 (2) Å
V = 1972.1 (5) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.34 mm−1
T = 298 (2) K
0.49 × 0.45 × 0.38 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.852, T max = 0.882
10332 measured reflections
3647 independent reflections
3266 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.025
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.035
wR(F 2) = 0.093
S = 1.03
3647 reflections
231 parameters
1 restraint
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 1556 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: 0.06 (6)
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 1999 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 1999 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808042025/is2364sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808042025/is2364Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯Cl2i | 0.848 (19) | 2.913 (13) | 3.7023 (18) | 156 (2) |
| O1—H1A⋯N1 | 0.82 | 1.93 | 2.642 (2) | 144 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (grant No. G0231) and the Foundation of the Education Ministry of China for Returned Students (grant No. G0220) for financial support. The X-ray data were collected at Shandong Normal University, China.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The synthesis of enantiopure aminophenols that have different functionalities is an important subject of research because compounds of this class are widespread in natural products, show pharmacological activity and have recently found application in asymmetric synthesis as chiral bases, auxiliaries and ligands (Cimarelli et al., 2002). Chiral aminophenols which are similar to amino alcohols have attracted wide attention for the reason that they can be used in catalytic asymmetric reactions (Puigjaner et al., 1999; Li et al., 2004; Watts et al., 2005), which is one of the most active areas of research in organic chemistry (Joshi & Malhotra, 2003). The synthesis of new aminoalkylphenols is therefore of interest because of potential as asymmetric catalysts.
As part of our continuing studies of chiral aminophenols, we now report the crystal structure of the title compound, (I), which was intially prepared to test its asymmetric catalytic activity. These compounds were prepared by conventional condensation of (R)-1-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-cyclopentylmethanamine with 1-(5-chloro-2-hydroxyphenyl)ethanone, followed by reduction using sodium borohydride in a tetrahydrofuran-ethanol (1:1 v/v) mixture. An X-ray study of the title compound, (I), was carried out and the results are presented here. The molecular structure of (I) is shown in Fig. 1.
The molecule has two chiral centres (C7/C10), which have configuration R, R, as shown in Fig. 1. In the molecules of (I), the five-membered rings adopts an envelope conformation. The dihedral angle between the benzene rings is 33.18 (11)°. There is an intramolecular O1—H1A···N1 hydrogen bond (Table 1). Phenol atom O1 acts as a hydrogen bond donor to atom N1, with O1···N1 = 2.647 (2) Å, which indicates a comparatively strong intramolecular hydrogen bond (Table 1); this distance is significantly shorter than the sum (3.07 Å) of the van der Waals radii for N and O atoms. The molecules are linked via N1—H1···Cl2 hydrogen bonds. An interesting feature of the structure is that the N1—H1···Cl2 hydrogen-bond gives rise to a spiral chain of molecules along the c direction. There are no π-π stacking interactions are present in the structure of (I).
Experimental
The title compound were prepared according to the procedure of Yang et al. (2005). (R)-1-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-cyclopentylmethanamine (0.9 mmol) and 1-(5-chloro-2-hydroxyphenyl)propan-1-one (0.9 mmol) were dissolved in methanol (10 ml) and reacted at room temperature for 48 h. After removal of the solvent, NaBH4 (4.5 mmol) was added to the solution in THF/ethanol (1:1 v/v, 20 ml) and stirred at 273 K until the solution became colourless. The solvent was then removed under reduced pressure. Water (10 ml) was added to the residue and 1 N HCl was added dropwise until hydrogen production ceased. The mixture was neutralized with aqueous Na2CO3, then extracted with CHCl3, and the organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure. Further purification was carried out by thin-layer silica-gel chromatography (chloroform) to give a colourless solid (yield 80.5%). Crystals of (I) were grown from a n-hexane solution.
Refinement
The N-bound H atom was located in a Fourier difference map and was refined with a distance restraint of N—H = 0.86 (1) Å, and with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(N). The O-bound and C-bound H atoms were positioned geometrically (O—H = 0.82 Å and C—H = 0.93–0.98 Å) and were treated as riding, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq (C) or 1.5Ueq(O, methyl C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The asymmetric unit of (I), showing the atom-labelling schemes. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level and H atoms are shown as spheres of arbitrary radii.
Fig. 2.
A packing diagram of (I), view down the b axis, showing the formation of helical chains through O1—H1A···N1 and N1—H1···Cl2 hydrogen bonds (dashed lines). H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonds have been omitted.
Crystal data
| C21H25Cl2NO | F(000) = 800 |
| Mr = 378.32 | Dx = 1.274 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 4568 reflections |
| a = 10.9802 (17) Å | θ = 2.2–25.5° |
| b = 11.5607 (18) Å | µ = 0.34 mm−1 |
| c = 15.536 (2) Å | T = 298 K |
| V = 1972.1 (5) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.49 × 0.45 × 0.38 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer | 3647 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3266 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.025 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 25.5°, θmin = 2.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −12→13 |
| Tmin = 0.852, Tmax = 0.882 | k = −13→13 |
| 10332 measured reflections | l = −18→15 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.035 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.093 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0504P)2 + 0.2043P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.03 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 3647 reflections | Δρmax = 0.17 e Å−3 |
| 231 parameters | Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 1556 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: 0.06 (6) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.4025 (2) | 0.9204 (2) | 0.46157 (14) | 0.0567 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.3358 (3) | 0.8241 (2) | 0.43935 (15) | 0.0695 (7) | |
| H2 | 0.3513 | 0.7853 | 0.3881 | 0.083* | |
| C3 | 0.2468 (3) | 0.7864 (2) | 0.49342 (16) | 0.0687 (7) | |
| H3 | 0.2013 | 0.7216 | 0.4786 | 0.082* | |
| C4 | 0.2227 (2) | 0.84331 (19) | 0.57058 (15) | 0.0576 (6) | |
| C5 | 0.29329 (17) | 0.93830 (17) | 0.59471 (12) | 0.0442 (5) | |
| C6 | 0.38307 (18) | 0.97536 (19) | 0.53893 (13) | 0.0476 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.4312 | 1.0384 | 0.5539 | 0.057* | |
| C7 | 0.26917 (18) | 1.00349 (17) | 0.67807 (13) | 0.0453 (5) | |
| H7 | 0.3437 | 1.0439 | 0.6955 | 0.054* | |
| C8 | 0.1659 (2) | 1.0917 (2) | 0.66944 (15) | 0.0621 (6) | |
| H8A | 0.0917 | 1.0509 | 0.6542 | 0.075* | |
| H8B | 0.1528 | 1.1279 | 0.7250 | 0.075* | |
| C9 | 0.1884 (3) | 1.1847 (2) | 0.60364 (17) | 0.0757 (7) | |
| H9A | 0.2633 | 1.2238 | 0.6167 | 0.113* | |
| H9B | 0.1225 | 1.2393 | 0.6048 | 0.113* | |
| H9C | 0.1937 | 1.1506 | 0.5475 | 0.113* | |
| C10 | 0.33131 (17) | 0.84631 (17) | 0.77983 (12) | 0.0420 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.3589 | 0.7969 | 0.7324 | 0.050* | |
| C11 | 0.27940 (18) | 0.76780 (18) | 0.84923 (13) | 0.0479 (5) | |
| H11 | 0.2531 | 0.8162 | 0.8976 | 0.057* | |
| C12 | 0.1718 (2) | 0.6922 (2) | 0.82169 (16) | 0.0626 (6) | |
| H12A | 0.0968 | 0.7366 | 0.8208 | 0.075* | |
| H12B | 0.1855 | 0.6594 | 0.7650 | 0.075* | |
| C13 | 0.1665 (3) | 0.5979 (3) | 0.8899 (2) | 0.0886 (9) | |
| H13A | 0.1118 | 0.6201 | 0.9360 | 0.106* | |
| H13B | 0.1376 | 0.5261 | 0.8649 | 0.106* | |
| C14 | 0.2942 (2) | 0.5833 (2) | 0.92374 (19) | 0.0737 (7) | |
| H14A | 0.3261 | 0.5080 | 0.9081 | 0.088* | |
| H14B | 0.2951 | 0.5901 | 0.9860 | 0.088* | |
| C15 | 0.3705 (2) | 0.67875 (19) | 0.88315 (15) | 0.0563 (5) | |
| H15A | 0.4197 | 0.6482 | 0.8365 | 0.068* | |
| H15B | 0.4240 | 0.7135 | 0.9256 | 0.068* | |
| C16 | 0.44189 (17) | 0.91271 (16) | 0.81295 (12) | 0.0405 (4) | |
| C17 | 0.55907 (18) | 0.89656 (17) | 0.78285 (13) | 0.0466 (5) | |
| C18 | 0.6565 (2) | 0.9581 (2) | 0.81494 (16) | 0.0596 (6) | |
| H18 | 0.7342 | 0.9451 | 0.7932 | 0.071* | |
| C19 | 0.6393 (2) | 1.0384 (2) | 0.87866 (16) | 0.0639 (6) | |
| H19 | 0.7048 | 1.0806 | 0.8999 | 0.077* | |
| C20 | 0.5237 (2) | 1.0559 (2) | 0.91091 (15) | 0.0608 (6) | |
| H20 | 0.5112 | 1.1094 | 0.9547 | 0.073* | |
| C21 | 0.4275 (2) | 0.99458 (18) | 0.87846 (14) | 0.0522 (5) | |
| H21 | 0.3501 | 1.0078 | 0.9007 | 0.063* | |
| Cl1 | 0.58898 (6) | 0.79389 (6) | 0.70334 (4) | 0.0724 (2) | |
| Cl2 | 0.51106 (6) | 0.97523 (8) | 0.39044 (4) | 0.0820 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.23430 (14) | 0.92140 (16) | 0.74620 (11) | 0.0469 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.1982 (19) | 0.9534 (18) | 0.7882 (11) | 0.056* | |
| O1 | 0.13051 (17) | 0.80387 (17) | 0.62012 (11) | 0.0773 (5) | |
| H1A | 0.1323 | 0.8364 | 0.6670 | 0.116* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0571 (12) | 0.0642 (14) | 0.0489 (12) | 0.0175 (12) | −0.0106 (10) | 0.0005 (10) |
| C2 | 0.100 (2) | 0.0584 (14) | 0.0502 (13) | 0.0194 (14) | −0.0232 (14) | −0.0075 (11) |
| C3 | 0.102 (2) | 0.0470 (12) | 0.0576 (14) | −0.0064 (13) | −0.0373 (14) | 0.0001 (12) |
| C4 | 0.0675 (14) | 0.0481 (11) | 0.0570 (13) | −0.0112 (11) | −0.0277 (11) | 0.0128 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0439 (10) | 0.0445 (11) | 0.0442 (10) | 0.0005 (9) | −0.0147 (8) | 0.0040 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0458 (11) | 0.0477 (11) | 0.0491 (11) | 0.0033 (9) | −0.0125 (9) | −0.0017 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0441 (11) | 0.0458 (11) | 0.0459 (10) | −0.0009 (8) | −0.0084 (8) | 0.0015 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0641 (14) | 0.0609 (13) | 0.0614 (13) | 0.0163 (12) | 0.0008 (11) | 0.0083 (11) |
| C9 | 0.100 (2) | 0.0566 (14) | 0.0705 (15) | 0.0221 (15) | 0.0023 (15) | 0.0104 (12) |
| C10 | 0.0412 (10) | 0.0434 (10) | 0.0414 (10) | 0.0026 (8) | −0.0012 (8) | −0.0017 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0450 (11) | 0.0529 (12) | 0.0457 (11) | 0.0025 (10) | −0.0024 (8) | 0.0038 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0482 (12) | 0.0691 (14) | 0.0706 (15) | −0.0085 (11) | −0.0056 (10) | 0.0153 (13) |
| C13 | 0.0688 (16) | 0.090 (2) | 0.107 (2) | −0.0184 (15) | −0.0105 (16) | 0.0458 (18) |
| C14 | 0.0747 (16) | 0.0628 (14) | 0.0837 (17) | −0.0079 (14) | −0.0110 (13) | 0.0242 (14) |
| C15 | 0.0546 (12) | 0.0533 (12) | 0.0610 (13) | 0.0016 (10) | −0.0084 (10) | 0.0108 (10) |
| C16 | 0.0437 (10) | 0.0379 (9) | 0.0401 (10) | 0.0049 (8) | −0.0029 (8) | 0.0018 (8) |
| C17 | 0.0470 (11) | 0.0439 (10) | 0.0488 (11) | 0.0027 (9) | −0.0002 (9) | 0.0001 (9) |
| C18 | 0.0447 (11) | 0.0578 (13) | 0.0763 (15) | 0.0009 (10) | −0.0047 (11) | 0.0011 (12) |
| C19 | 0.0616 (14) | 0.0532 (13) | 0.0768 (16) | −0.0082 (11) | −0.0235 (12) | −0.0001 (12) |
| C20 | 0.0738 (16) | 0.0472 (12) | 0.0615 (13) | 0.0045 (12) | −0.0138 (12) | −0.0097 (11) |
| C21 | 0.0520 (12) | 0.0485 (12) | 0.0562 (12) | 0.0073 (10) | −0.0037 (10) | −0.0068 (9) |
| Cl1 | 0.0588 (3) | 0.0828 (4) | 0.0757 (4) | 0.0041 (3) | 0.0154 (3) | −0.0274 (3) |
| Cl2 | 0.0672 (4) | 0.1215 (6) | 0.0573 (3) | 0.0189 (4) | 0.0075 (3) | −0.0007 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0392 (9) | 0.0552 (10) | 0.0463 (9) | 0.0065 (8) | −0.0023 (7) | 0.0070 (8) |
| O1 | 0.0815 (12) | 0.0804 (12) | 0.0701 (11) | −0.0394 (10) | −0.0257 (10) | 0.0165 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C6 | 1.376 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.531 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.377 (4) | C11—H11 | 0.9800 |
| C1—Cl2 | 1.745 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.521 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.360 (4) | C12—H12A | 0.9700 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C12—H12B | 0.9700 |
| C3—C4 | 1.393 (4) | C13—C14 | 1.507 (4) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C13—H13A | 0.9700 |
| C4—O1 | 1.351 (3) | C13—H13B | 0.9700 |
| C4—C5 | 1.395 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.522 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.381 (3) | C14—H14A | 0.9700 |
| C5—C7 | 1.522 (3) | C14—H14B | 0.9700 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C15—H15A | 0.9700 |
| C7—N1 | 1.472 (3) | C15—H15B | 0.9700 |
| C7—C8 | 1.531 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.382 (3) |
| C7—H7 | 0.9800 | C16—C21 | 1.399 (3) |
| C8—C9 | 1.504 (3) | C17—C18 | 1.378 (3) |
| C8—H8A | 0.9700 | C17—Cl1 | 1.744 (2) |
| C8—H8B | 0.9700 | C18—C19 | 1.370 (3) |
| C9—H9A | 0.9600 | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C9—H9B | 0.9600 | C19—C20 | 1.379 (3) |
| C9—H9C | 0.9600 | C19—H19 | 0.9300 |
| C10—N1 | 1.470 (2) | C20—C21 | 1.369 (3) |
| C10—C11 | 1.520 (3) | C20—H20 | 0.9300 |
| C10—C16 | 1.526 (3) | C21—H21 | 0.9300 |
| C10—H10 | 0.9800 | N1—H1 | 0.848 (19) |
| C11—C15 | 1.529 (3) | O1—H1A | 0.8200 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 120.7 (2) | C12—C11—H11 | 108.2 |
| C6—C1—Cl2 | 119.43 (19) | C13—C12—C11 | 104.11 (19) |
| C2—C1—Cl2 | 119.89 (19) | C13—C12—H12A | 110.9 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.1 (2) | C11—C12—H12A | 110.9 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.5 | C13—C12—H12B | 110.9 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.5 | C11—C12—H12B | 110.9 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.1 (2) | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.0 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.4 | C14—C13—C12 | 106.7 (2) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.4 | C14—C13—H13A | 110.4 |
| O1—C4—C3 | 118.2 (2) | C12—C13—H13A | 110.4 |
| O1—C4—C5 | 121.9 (2) | C14—C13—H13B | 110.4 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.8 (2) | C12—C13—H13B | 110.4 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 118.2 (2) | H13A—C13—H13B | 108.6 |
| C6—C5—C7 | 120.31 (17) | C13—C14—C15 | 106.6 (2) |
| C4—C5—C7 | 121.45 (19) | C13—C14—H14A | 110.4 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 121.0 (2) | C15—C14—H14A | 110.4 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.5 | C13—C14—H14B | 110.4 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.5 | C15—C14—H14B | 110.4 |
| N1—C7—C5 | 109.75 (16) | H14A—C14—H14B | 108.6 |
| N1—C7—C8 | 107.43 (17) | C14—C15—C11 | 105.70 (18) |
| C5—C7—C8 | 112.60 (16) | C14—C15—H15A | 110.6 |
| N1—C7—H7 | 109.0 | C11—C15—H15A | 110.6 |
| C5—C7—H7 | 109.0 | C14—C15—H15B | 110.6 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 109.0 | C11—C15—H15B | 110.6 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 114.5 (2) | H15A—C15—H15B | 108.7 |
| C9—C8—H8A | 108.6 | C17—C16—C21 | 116.28 (18) |
| C7—C8—H8A | 108.6 | C17—C16—C10 | 123.98 (17) |
| C9—C8—H8B | 108.6 | C21—C16—C10 | 119.74 (17) |
| C7—C8—H8B | 108.6 | C18—C17—C16 | 122.04 (19) |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 107.6 | C18—C17—Cl1 | 117.49 (16) |
| C8—C9—H9A | 109.5 | C16—C17—Cl1 | 120.46 (15) |
| C8—C9—H9B | 109.5 | C19—C18—C17 | 120.3 (2) |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 | C19—C18—H18 | 119.9 |
| C8—C9—H9C | 109.5 | C17—C18—H18 | 119.9 |
| H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 | C18—C19—C20 | 119.2 (2) |
| H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 | C18—C19—H19 | 120.4 |
| N1—C10—C11 | 109.45 (15) | C20—C19—H19 | 120.4 |
| N1—C10—C16 | 113.53 (16) | C21—C20—C19 | 120.0 (2) |
| C11—C10—C16 | 111.07 (15) | C21—C20—H20 | 120.0 |
| N1—C10—H10 | 107.5 | C19—C20—H20 | 120.0 |
| C11—C10—H10 | 107.5 | C20—C21—C16 | 122.1 (2) |
| C16—C10—H10 | 107.5 | C20—C21—H21 | 119.0 |
| C10—C11—C15 | 113.65 (17) | C16—C21—H21 | 119.0 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 115.59 (17) | C10—N1—C7 | 116.59 (15) |
| C15—C11—C12 | 102.53 (18) | C10—N1—H1 | 108.9 (16) |
| C10—C11—H11 | 108.2 | C7—N1—H1 | 113.1 (16) |
| C15—C11—H11 | 108.2 | C4—O1—H1A | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 2.6 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −27.7 (3) |
| Cl2—C1—C2—C3 | −176.33 (18) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 6.6 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.2 (3) | C13—C14—C15—C11 | 17.1 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—O1 | 177.9 (2) | C10—C11—C15—C14 | −159.2 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −2.2 (3) | C12—C11—C15—C14 | −33.7 (2) |
| O1—C4—C5—C6 | −177.83 (19) | N1—C10—C16—C17 | −122.7 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 2.2 (3) | C11—C10—C16—C17 | 113.4 (2) |
| O1—C4—C5—C7 | −0.6 (3) | N1—C10—C16—C21 | 58.1 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C7 | 179.43 (19) | C11—C10—C16—C21 | −65.8 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −2.6 (3) | C21—C16—C17—C18 | −0.5 (3) |
| Cl2—C1—C6—C5 | 176.38 (15) | C10—C16—C17—C18 | −179.69 (18) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.1 (3) | C21—C16—C17—Cl1 | 178.20 (14) |
| C7—C5—C6—C1 | −177.13 (18) | C10—C16—C17—Cl1 | −1.0 (3) |
| C6—C5—C7—N1 | −145.10 (17) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | 0.0 (3) |
| C4—C5—C7—N1 | 37.7 (2) | Cl1—C17—C18—C19 | −178.73 (18) |
| C6—C5—C7—C8 | 95.3 (2) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | 0.7 (4) |
| C4—C5—C7—C8 | −81.9 (2) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | −0.9 (4) |
| N1—C7—C8—C9 | 178.4 (2) | C19—C20—C21—C16 | 0.4 (3) |
| C5—C7—C8—C9 | −60.7 (3) | C17—C16—C21—C20 | 0.3 (3) |
| N1—C10—C11—C15 | 175.01 (17) | C10—C16—C21—C20 | 179.5 (2) |
| C16—C10—C11—C15 | −58.8 (2) | C11—C10—N1—C7 | 179.95 (17) |
| N1—C10—C11—C12 | 56.8 (2) | C16—C10—N1—C7 | 55.2 (2) |
| C16—C10—C11—C12 | −177.03 (17) | C5—C7—N1—C10 | 71.5 (2) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 161.7 (2) | C8—C7—N1—C10 | −165.80 (17) |
| C15—C11—C12—C13 | 37.5 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···Cl2i | 0.85 (2) | 2.91 (1) | 3.7023 (18) | 156 (2) |
| O1—H1A···N1 | 0.82 | 1.93 | 2.642 (2) | 144 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1/2, −y+2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: IS2364).
References
- Bruker (1999). SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cimarelli, C., Palmieri, G. & &Volpini, E. (2002). Tetrahedron Asymmetry, 13, 2011–2018.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Joshi, S. N. & Malhotra, S. V. (2003). Tetrahedron Asymmetry, 14, 1763–1766.
- Li, Y., He, B., Qin, B., Feng, X. & Zhang, G. (2004). J. Org. Chem.69, 7910–7913. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Puigjaner, C., Vidal-Ferran, A., Moyano, A., Pericas, M. A., Rieras, M. A. & Riera, A. (1999). J. Org. Chem.64, 7902–7911.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Watts, C. C., Thoniyot, P., Hirayama, L. C., Romano, T. & Singaram, B. (2005). Tetrahedron Asymmetry, 16, 1829–1835.
- Yang, X.-F., Zhang, G.-Y., Zhang, Y., Zhao, J.-Y. & Wang, X.-B. (2005). Acta Cryst. C61, o262–o264. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808042025/is2364sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808042025/is2364Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




