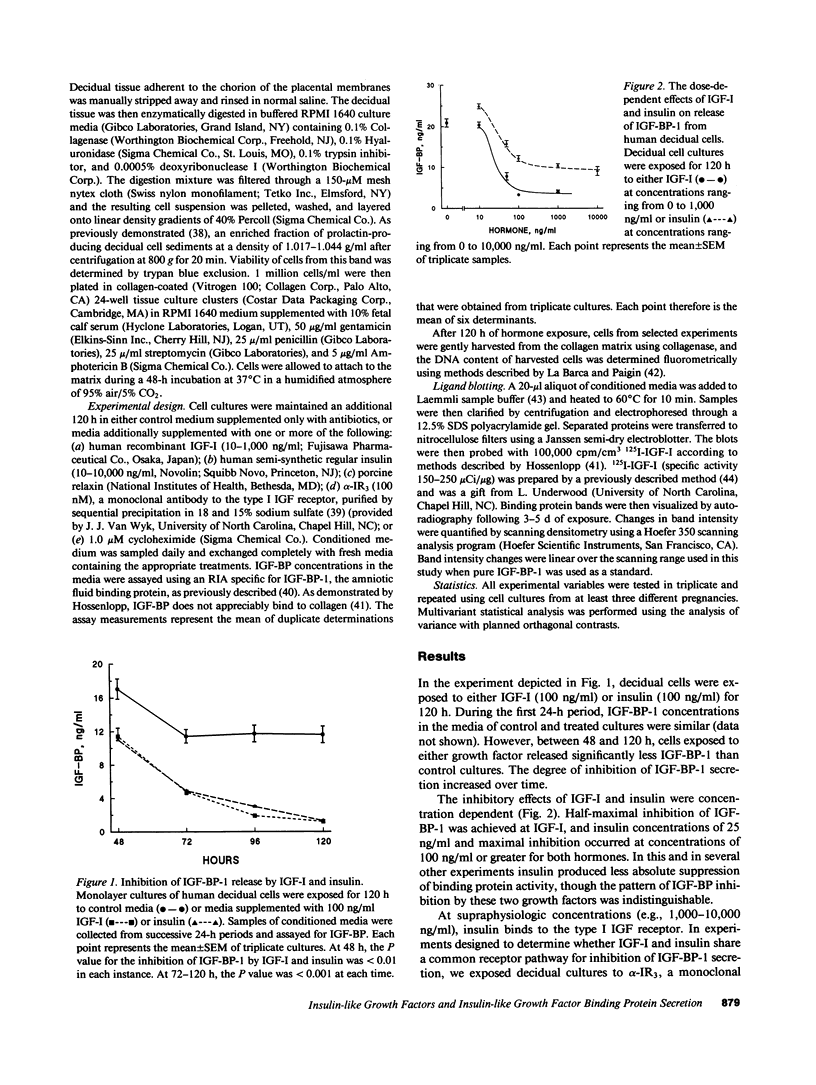
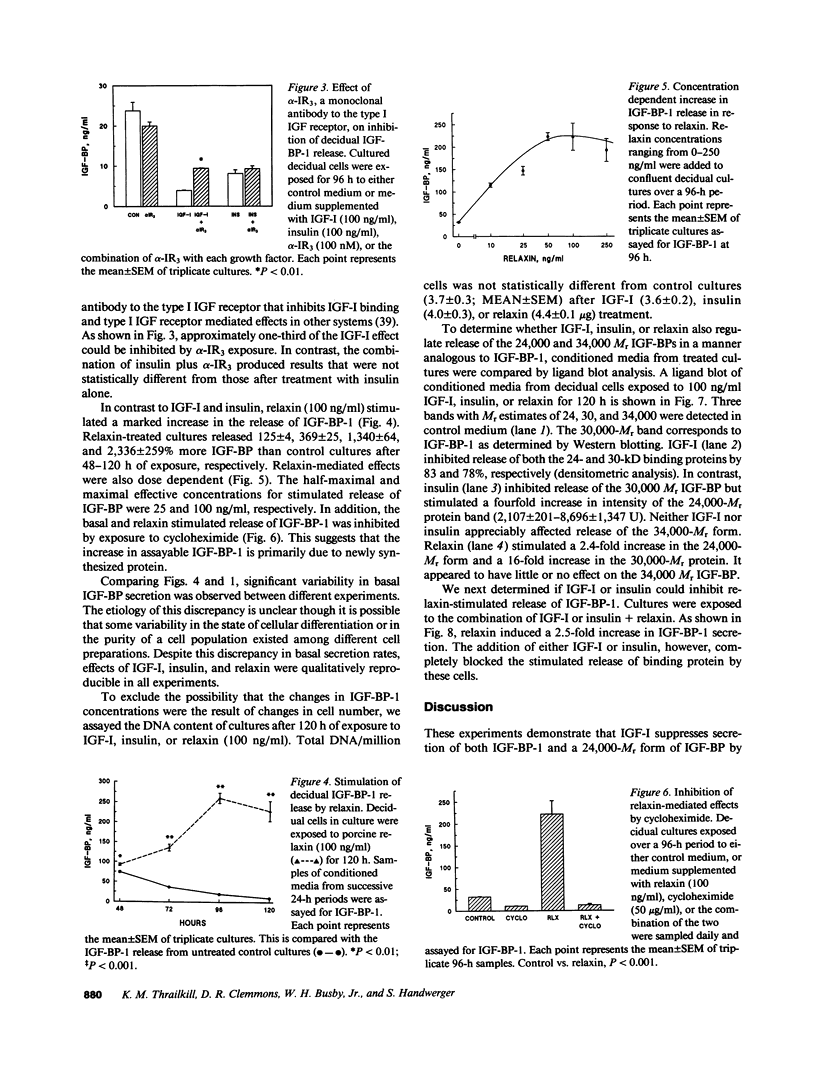
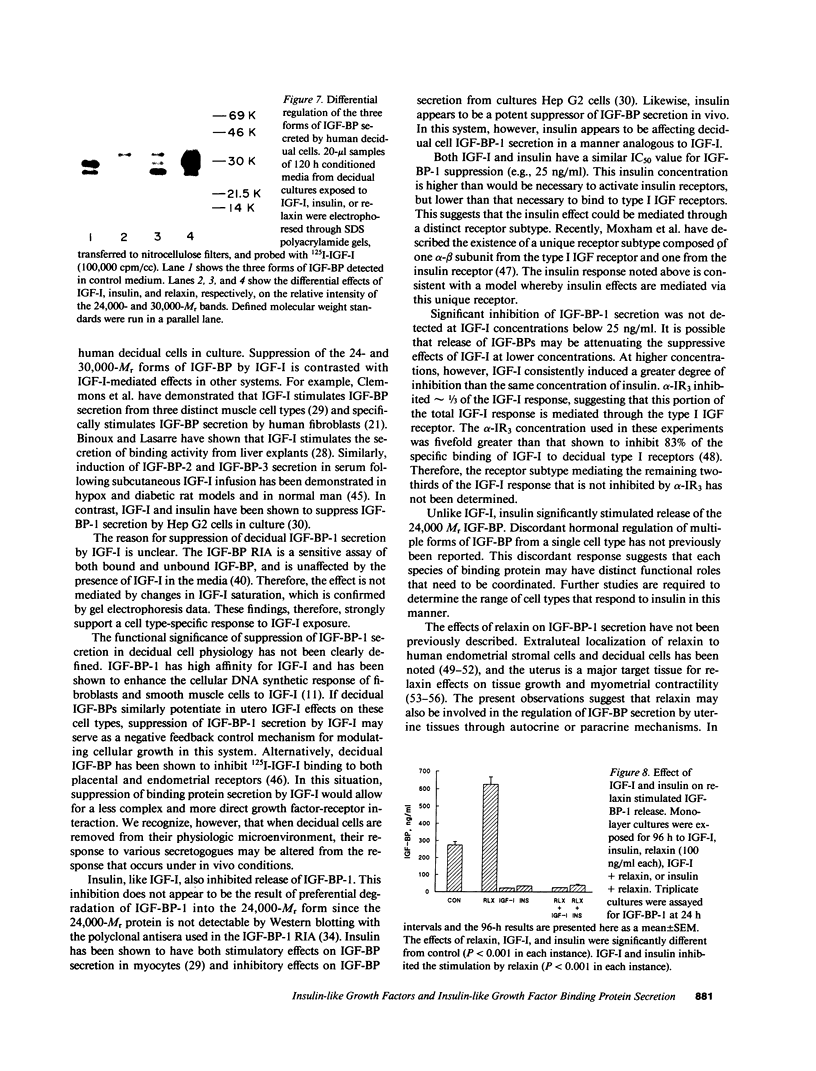
Abstract
Several growth hormone-independent 25-31,000 kD insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGF-BPs) have been identified in plasma, extravascular fluids, and various cell-conditioned media. Cultured human decidual cells release three IGF-BPs with 24,000, 30,000, and 34,000 Mr. Using ligand blot analysis and an RIA for the 30,000-Mr form (IGF-BP-1), we examined the effects of IGF-I (10-1,000 ng/ml), insulin (10-10,000 ng/ml), and relaxin (10-250 ng/ml) on decidual cell IGF-BP release after 120 h of hormone exposure. IGF-I inhibited release of both IGF-BP-1 and the 24,000 Mr form. Inhibition of IGF-BP-1 release was noted after 48 h of treatment and was progressive throughout the subsequent 120 h. Insulin stimulated a fourfold increase in release of the 24,000-Mr protein while inhibiting IGF-BP-1 release comparable to IGF-I, alpha-IR3, a monoclonal antibody to the IGF-I receptor, blocked approximately 33% of the IGF-I response but had no effect on insulin-mediated IGF-BP-1 inhibition. Relaxin stimulated a 2.4-fold increase in release of the 24,000-Mr form and a 16-fold increase in the 30,000-Mr protein after 120 h. Stimulation of the 30,000-Mr protein was inhibited by the addition of cycloheximide (50 micrograms/ml). Both IGF-I and insulin also blocked the relaxin-mediated increase in IGF-BP-1. These studies suggest that three structurally related proteins differentially regulate IGF-BP secretion possibly via activation of distinct receptor subtypes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bar R. S., Harrison L. C., Baxter R. C., Boes M., Dake B. L., Booth B., Cox A. Production of IGF-binding proteins by vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 29;148(2):734–739. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90937-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C. Characterization of the acid-labile subunit of the growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Aug;67(2):265–272. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-2-265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L. Binding proteins for the insulin-like growth factors: structure, regulation and function. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1989;1(1):49–68. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(89)90041-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter R. C., Martin J. L., Wood M. H. Two immunoreactive binding proteins for insulin-like growth factors in human amniotic fluid: relationship to fetal maturity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Sep;65(3):423–431. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-3-423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell S. C., Patel S. R., Jackson J. A., Waites G. T. Major secretory protein of human decidualized endometrium in pregnancy is an insulin-like growth factor-binding protein. J Endocrinol. 1988 Aug;118(2):317–328. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1180317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binoux M., Hossenlopp P., Hardouin S., Seurin D., Lassarre C., Gourmelen M. Somatomedin (insulin-like growth factors)-binding proteins. Molecular forms and regulation. Horm Res. 1986;24(2-3):141–151. doi: 10.1159/000180553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer M. T., Stetler G. L., Squires C. H., Thompson R. C., Busby W. H., Clemmons D. R. Cloning, characterization, and expression of a human insulin-like growth factor binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 16;152(3):1289–1297. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80425-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. L., Chiariotti L., Orlowski C. C., Mehlman T., Burgess W. H., Ackerman E. J., Bruni C. B., Rechler M. M. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a cDNA clone encoding a fetal rat binding protein for insulin-like growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5148–5154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant-Greenwood G. D., Rees M. C., Turnbull A. C. Immunohistochemical localization of relaxin, prolactin and prostaglandin synthase in human amnion, chorion and decidua. J Endocrinol. 1987 Sep;114(3):491–496. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1140491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant-Greenwood G. D. Relaxin as a new hormone. Endocr Rev. 1982 Winter;3(1):62–90. doi: 10.1210/edrv-3-1-62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby W. H., Jr, Klapper D. G., Clemmons D. R. Purification of a 31,000-dalton insulin-like growth factor binding protein from human amniotic fluid. Isolation of two forms with different biologic actions. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14203–14210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby W. H., Snyder D. K., Clemmons D. R. Radioimmunoassay of a 26,000-dalton plasma insulin-like growth factor-binding protein: control by nutritional variables. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Dec;67(6):1225–1230. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-6-1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G. A., Huang J. R., Tseng L. The effect of relaxin on cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate concentrations in human endometrial glandular epithelial cells. Biol Reprod. 1988 Oct;39(3):519–525. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod39.3.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Elgin R. G., Han V. K., Casella S. J., D'Ercole A. J., Van Wyk J. J. Cultured fibroblast monolayers secrete a protein that alters the cellular binding of somatomedin-C/insulinlike growth factor I. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1548–1556. doi: 10.1172/JCI112470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Han V. K., Elgin R. G., D'Ercole A. J. Alterations in the synthesis of a fibroblast surface associated 35 K protein modulates the binding of somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor I. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 May;1(5):339–347. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-5-339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmons D. R., Thrailkill K. M., Handwerger S., Busby W. H., Jr Three distinct forms of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins are released by decidual cells in culture. Endocrinology. 1990 Aug;127(2):643–650. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-2-643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conover C. A., Liu F., Powell D., Rosenfeld R. G., Hintz R. L. Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins from cultured human fibroblasts. Characterization and hormonal regulation. J Clin Invest. 1989 Mar;83(3):852–859. doi: 10.1172/JCI113968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronin M. J., Malaska T., Bakhit C. Human relaxin increases cyclic AMP levels in cultured anterior pituitary cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 13;148(3):1246–1251. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80266-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Drop S. L., Kortleve D. J. Somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor I-binding proteins in human amniotic fluid and in fetal and postnatal blood: evidence of immunological homology. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Oct;61(4):612–617. doi: 10.1210/jcem-61-4-612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drop S. L., Kortleve D. J., Guyda H. J. Isolation of a somatomedin-binding protein from preterm amniotic fluid. Development of a radioimmunoassay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Nov;59(5):899–907. doi: 10.1210/jcem-59-5-899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin R. G., Busby W. H., Jr, Clemmons D. R. An insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein enhances the biologic response to IGF-I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3254–3258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlanetto R. W. The somatomedin C binding protein: evidence for a heterologous subunit structure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980 Jul;51(1):12–19. doi: 10.1210/jcem-51-1-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardouin S., Hossenlopp P., Segovia B., Seurin D., Portolan G., Lassarre C., Binoux M. Heterogeneity of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins and relationships between structure and affinity. 1. Circulating forms in man. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 30;170(1-2):121–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13676.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill D. J., Camacho-Hubner C., Rashid P., Strain A. J., Clemmons D. R. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein release by human fetal fibroblasts: dependency on cell density and IGF peptides. J Endocrinol. 1989 Jul;122(1):87–98. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1220087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L., Liu F. Demonstration of specific plasma protein binding sites for somatomedin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1977 Nov;45(5):988–995. doi: 10.1210/jcem-45-5-988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L. Plasma forms of somatomedin and the binding protein phenomenon. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Mar;13(1):31–42. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(84)80007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossenlopp P., Seurin D., Segovia-Quinson B., Hardouin S., Binoux M. Analysis of serum insulin-like growth factor binding proteins using western blotting: use of the method for titration of the binding proteins and competitive binding studies. Anal Biochem. 1986 Apr;154(1):138–143. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu C. J., McCormack S. M., Sanborn B. M. The effect of relaxin on cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate concentrations in rat myometrial cells in culture. Endocrinology. 1985 May;116(5):2029–2035. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-5-2029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koay E. S., Bagnell C. A., Bryant-Greenwood G. D., Lord S. B., Cruz A. C., Larkin L. H. Immunocytochemical localization of relaxin in human decidua and placenta. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 May;60(5):859–863. doi: 10.1210/jcem-60-5-859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koay E. S., Bryant-Greenwood G. D., Yamamoto S. Y., Greenwood F. C. The human fetal membranes: a target tissue for relaxin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Mar;62(3):513–521. doi: 10.1210/jcem-62-3-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koistinen R., Kalkkinen N., Huhtala M. L., Seppälä M., Bohn H., Rutanen E. M. Placental protein 12 is a decidual protein that binds somatomedin and has an identical N-terminal amino acid sequence with somatomedin-binding protein from human amniotic fluid. Endocrinology. 1986 Apr;118(4):1375–1378. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-4-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Su Y. F., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Monoclonal antibodies to receptors for insulin and somatomedin-C. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6561–6566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. L., Hintz R. L., James P. M., Lee P. D., Shively J. E., Powell D. R. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein complementary deoxyribonucleic acid from human HEP G2 hepatoma cells: predicted protein sequence suggests an IGF binding domain different from those of the IGF-I and IGF-II receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 May;2(5):404–411. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-5-404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewitt M. S., Baxter R. C. Regulation of growth hormone-independent insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (BP-28) in cultured human fetal liver explants. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Aug;69(2):246–252. doi: 10.1210/jcem-69-2-246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan A. H. Relaxin--a review. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 1981 Nov;21(4):195–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-828x.1981.tb00130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markoff E., Zeitler P., Peleg S., Handwerger S. Characterization of the synthesis and release of prolactin by an enriched fraction of human decidual cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 May;56(5):962–968. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-5-962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCusker R. H., Clemmons D. R. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein secretion by muscle cells: effect of cellular differentiation and proliferation. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Dec;137(3):505–512. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041370316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. C., Freinkel A. J., Knowles B. B., Aden D. P. Demonstration that a human hepatoma cell line produces a specific insulin-like growth factor carrier protein. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 May;56(5):1003–1008. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-5-1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham C. P., Duronio V., Jacobs S. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor beta-subunit heterogeneity. Evidence for hybrid tetramers composed of insulin-like growth factor I and insulin receptor heterodimers. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13238–13244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Saekow M., Kroc R. L. Potentiation of insulin binding and insulin action by purified porcine relaxin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;380:200–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb18043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi G. T., Herington A. C. The biological and structural characterization of specific serum binding proteins for the insulin-like growth factors. J Endocrinol. 1988 Jul;118(1):7–18. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1180007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekonen F., Suikkari A. M., Mäkinen T., Rutanen E. M. Different insulin-like growth factor binding species in human placenta and decidua. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Dec;67(6):1250–1257. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-6-1250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritvos O., Ranta T., Jalkanen J., Suikkari A. M., Voutilainen R., Bohn H., Rutanen E. M. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein from human decidua inhibits the binding and biological action of IGF-I in cultured choriocarcinoma cells. Endocrinology. 1988 May;122(5):2150–2157. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-5-2150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutanen E. M., Koistinen R., Sjöberg J., Julkunen M., Wahlström T., Bohn H., Seppälä M. Synthesis of placental protein 12 by human endometrium. Endocrinology. 1986 Mar;118(3):1067–1071. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-3-1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutanen E. M., Koistinen R., Wahlström T., Bohn H., Ranta T., Seppälä M. Synthesis of placental protein 12 by human decidua. Endocrinology. 1985 Apr;116(4):1304–1309. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-4-1304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutanen E. M., Pekonen F., Mäkinen T. Soluble 34K binding protein inhibits the binding of insulin-like growth factor I to its cell receptors in human secretory phase endometrium: evidence for autocrine/paracrine regulation of growth factor action. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Jan;66(1):173–180. doi: 10.1210/jcem-66-1-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakbun V., Koay E. S., Bryant-Greenwood G. D. Immunocytochemical localization of prolactin and relaxin C-peptide in human decidua and placenta. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987 Aug;65(2):339–343. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-2-339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C., Ernst M., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Release of insulin-like growth factor carrier proteins by osteoblasts: stimulation by estradiol and growth hormone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 28;160(2):788–794. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92502-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suikkari A. M., Jalkanen J., Koistinen R., Bützow R., Ritvos O., Ranta T., Seppälä M. Human granulosa cells synthesize low molecular weight insulin-like growth factor-binding protein. Endocrinology. 1989 Feb;124(2):1088–1090. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-2-1088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thrailkill K. M., Golander A., Underwood L. E., Handwerger S. Insulin-like growth factor I stimulates the synthesis and release of prolactin from human decidual cells. Endocrinology. 1988 Dec;123(6):2930–2934. doi: 10.1210/endo-123-6-2930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilenko P., Mead J. P. Growth-promoting effects of relaxin and related compositional changes in the uterus, cervix, and vagina of the rat. Endocrinology. 1987 Apr;120(4):1370–1376. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-4-1370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waites G. T., James R. F., Bell S. C. Immunohistological localization of the human endometrial secretory protein pregnancy-associated endometrial alpha 1-globulin, an insulin-like growth factor-binding protein, during the menstrual cycle. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Nov;67(5):1100–1104. doi: 10.1210/jcem-67-5-1100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Cachianes G., Henzel W. J., Winslow G. A., Spencer S. A., Hellmiss R., Martin J. L., Baxter R. C. Cloning and expression of the growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor-binding protein. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1176–1185. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Waldvogel M., Froesch E. R. Binding of nonsuppressible insulinlike activity to human serum. Evidence for a carrier protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Jun;168(2):638–645. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Koskull H., Ammälä P., Huhtala M. L., Seppälä M. Localization of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein and endometrial beta-lactoglobulin in cultured decidual and chorionic villus cells. Hum Reprod. 1987 Jul;2(5):431–434. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a136563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]