Abstract
In the title molecule, C23H15BrO, the prop-2-en-1-one unit is planar and it makes dihedral angles of 20.9 (1) and 45.8 (1)°, respectively, with the 4-bromophenyl ring and the anthracene ring system. The interplanar angle between the 4-bromophenyl ring and the anthracene ring system is 35.52 (7)°. In the crystal structure, molecules are linked into dimers by C—H⋯Br hydrogen bonds, and the dimers are linked into a zigzag network parallel to the bc plane by weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and C—H⋯π interactions involving the central benzene ring of the anthracene ring system.
Related literature
For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶). For related structures, see: Ng et al. (2006 ▶); Patil et al. (2006 ▶); Patil, Chantrapromma et al. (2007 ▶); Suwunwong et al. (2009 ▶). For background and applications of chalcones, see: Jung et al. (2008 ▶); Patil, Chantrapromma et al. (2007 ▶); Patil, Dharmaprakash et al. (2007 ▶); Patil & Dharmaprakash (2008 ▶); Prasad et al. (2008 ▶).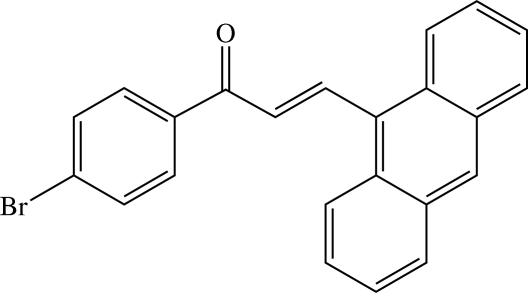
Experimental
Crystal data
C23H15BrO
M r = 387.25
Monoclinic,
a = 5.3792 (1) Å
b = 19.1030 (4) Å
c = 16.3005 (4) Å
β = 95.944 (1)°
V = 1666.02 (6) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 2.47 mm−1
T = 100.0 (1) K
0.57 × 0.27 × 0.15 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.331, T max = 0.714
29994 measured reflections
4866 independent reflections
3803 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.036
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.032
wR(F 2) = 0.076
S = 1.02
4866 reflections
226 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.53 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.54 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: APEX2; data reduction: SAINT (Bruker, 2005 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL and PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809003122/ci2756sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809003122/ci2756Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 is the centroid of the C18–C23 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C8—H8A⋯O1i | 0.93 | 2.42 | 3.308 (2) | 159 |
| C13—H13A⋯O1ii | 0.93 | 2.57 | 3.288 (2) | 135 |
| C21—H21A⋯Br1iii | 0.93 | 2.93 | 3.4722 (19) | 119 |
| C9—H9A⋯Cg1iv | 0.93 | 2.83 | 3.4479 (18) | 125 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 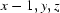 ; (ii)
; (ii) 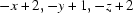 ; (iii)
; (iii) 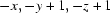 ; (iv)
; (iv) 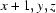 .
.
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the Center of Excellence for Innovation in Chemistry (PERCH-CIC), Commision on Higher Education, Ministry of Education, Thailand, is gratefully acknowledged. The authors also thank the Thailand Research Fund (TRF) and the Prince of Songkla University for financial support, and the Universiti Sains Malaysia for the Research University Golden Goose grant No. 1001/PFIZIK/811012.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Chalcones are compounds which have a wide range of applications covering from non-linear optical (Patil & Dharmaprakash, 2008) and electro-active fluorescent materials (Jung et al., 2008) to materials with various biological activities (Prasad et al., 2008). Our previous work (Patil Dharmaprakash et al., 2007) has reported that 1-(4-bromophenyl)-3-(2,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-propenone shows efficient second-order nonlinear optical properties. The various interesting properties of chalcone derivatives lead us to synthesize the title chalcone derivative in order to study its photoluminescence and antimicrobial activities.
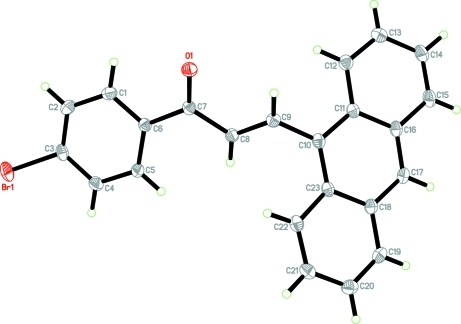
The molecule of the title chalcone derivative (Fig. 1) exists in an E configuration with respect to the C8═C9 double bond [1.333 (2) Å]. The anthracene ring system is planar, with atom C21 deviating a maximum of 0.147 (2) Å. The molecule is twisted as indicated by the interplanar angle between 4-bromophenyl ring and anthracene ring system of 35.52 (7)°, and torsion angles C5–C6–C7–C8 of 22.9 (1)° and C8–C9–C10–C23 of -50.2 (3)°. The pro-2-en-1-one unit (C7-C9/O1) is planar as evidenced by the torsion angle O1–C7–C8–C9 of 0.1 (3)°. The O1/C6-C9 plane makes dihedral angles of 20.9 (1)° and 45.8 (1)°, respectively, with the 4-bromophenyl ring and anthracene ring system. The bond distances show normal values (Allen et al., 1987) and are comparable with those observed in related structures (Ng et al., 2006; Patil et al., 2006; Patil, Chantrapromma et al., 2007; Suwunwong et al., 2009).
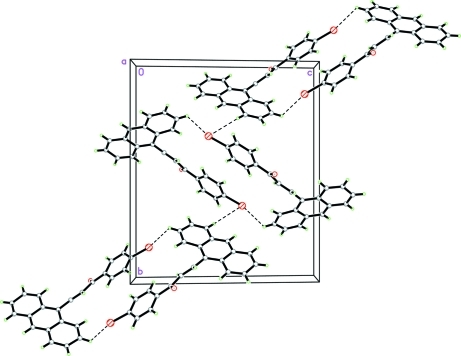
In the crystal packing (Fig. 2), the molecules are linked into dimers by weak C—H···Br interactions (Table 1) and the dimers are further linked into a zigzag network parallel to the bc plane by weak C—H···O and C—H···π interactions (Table 1).
Experimental
The title compound was synthesized by the condensation of anthracene-9-carbaldehyde (0.01 mol) with 4-bromoacetophenone (0.01 mol) in ethanol (40 ml) in the presence of NaOH (10 ml, 10%). After stirring for 2 h, a yellow solid appeared and was then collected by filtration, washed with distilled water, dried and purified by repeated recrystallization from acetone. Yellow plate-shaped single crystals of the title compound suitable for X-ray structure determination were obtained by slow evaporation of an acetone solution at room temperature after several days.
Refinement
All H atoms were placed in calculated positions, with C-H = 0.93 Å, Uiso = 1.2Ueq(C). The highest residual electron density peak is located at 0.76 Å from Br1 and the deepest hole is located at 0.69 Å from Br1.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, showing 60% probability displacement ellipsoids and the atom-numbering scheme.
Fig. 2.
Part of the crystal packing of the title compound, viewed along the a axis, showing hydrogen-bonded (dashed lines) dimers.
Crystal data
| C23H15BrO | F(000) = 784 |
| Mr = 387.25 | Dx = 1.544 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 4866 reflections |
| a = 5.3792 (1) Å | θ = 2.1–30.0° |
| b = 19.1030 (4) Å | µ = 2.47 mm−1 |
| c = 16.3005 (4) Å | T = 100 K |
| β = 95.944 (1)° | Plate, yellow |
| V = 1666.02 (6) Å3 | 0.57 × 0.27 × 0.15 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer | 4866 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3803 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.036 |
| Detector resolution: 8.33 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 30.0°, θmin = 2.1° |
| ω scans | h = −7→7 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | k = −26→26 |
| Tmin = 0.331, Tmax = 0.714 | l = −22→22 |
| 29994 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.032 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.076 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0322P)2 + 1.1607P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4866 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 226 parameters | Δρmax = 0.53 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.54 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. The low-temperature data was collected with the Oxford Cyrosystem Cobra low-temperature attachment. |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | 0.32584 (4) | 0.344013 (10) | 0.411244 (11) | 0.02530 (7) | |
| O1 | 0.9073 (2) | 0.51056 (7) | 0.74450 (8) | 0.0213 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.7274 (4) | 0.41439 (9) | 0.62533 (11) | 0.0201 (4) | |
| H1A | 0.8800 | 0.4043 | 0.6552 | 0.024* | |
| C2 | 0.6526 (4) | 0.37631 (10) | 0.55484 (12) | 0.0219 (4) | |
| H2A | 0.7530 | 0.3408 | 0.5374 | 0.026* | |
| C3 | 0.4261 (4) | 0.39203 (9) | 0.51095 (10) | 0.0180 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.2711 (4) | 0.44314 (10) | 0.53719 (11) | 0.0206 (4) | |
| H4A | 0.1176 | 0.4523 | 0.5075 | 0.025* | |
| C5 | 0.3464 (3) | 0.48075 (10) | 0.60836 (10) | 0.0184 (4) | |
| H5A | 0.2419 | 0.5149 | 0.6267 | 0.022* | |
| C6 | 0.5781 (3) | 0.46766 (9) | 0.65244 (10) | 0.0152 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.6813 (3) | 0.51052 (9) | 0.72478 (10) | 0.0159 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.5083 (3) | 0.55087 (9) | 0.77158 (10) | 0.0159 (3) | |
| H8A | 0.3374 | 0.5499 | 0.7555 | 0.019* | |
| C9 | 0.5978 (3) | 0.58858 (9) | 0.83690 (10) | 0.0161 (3) | |
| H9A | 0.7707 | 0.5920 | 0.8471 | 0.019* | |
| C10 | 0.4492 (3) | 0.62533 (9) | 0.89440 (10) | 0.0158 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.5151 (3) | 0.61533 (9) | 0.98020 (10) | 0.0157 (3) | |
| C12 | 0.7151 (4) | 0.57046 (10) | 1.01164 (11) | 0.0195 (4) | |
| H12A | 0.8015 | 0.5452 | 0.9749 | 0.023* | |
| C13 | 0.7822 (4) | 0.56385 (10) | 1.09428 (11) | 0.0219 (4) | |
| H13A | 0.9149 | 0.5349 | 1.1132 | 0.026* | |
| C14 | 0.6506 (4) | 0.60082 (10) | 1.15145 (11) | 0.0220 (4) | |
| H14A | 0.7002 | 0.5970 | 1.2076 | 0.026* | |
| C15 | 0.4527 (4) | 0.64183 (10) | 1.12478 (11) | 0.0224 (4) | |
| H15A | 0.3652 | 0.6648 | 1.1631 | 0.027* | |
| C16 | 0.3767 (3) | 0.65030 (9) | 1.03860 (10) | 0.0169 (3) | |
| C17 | 0.1715 (4) | 0.69108 (9) | 1.01020 (10) | 0.0187 (4) | |
| H17A | 0.0769 | 0.7118 | 1.0482 | 0.022* | |
| C18 | 0.1036 (3) | 0.70178 (9) | 0.92633 (10) | 0.0167 (3) | |
| C19 | −0.1040 (4) | 0.74534 (9) | 0.89840 (11) | 0.0196 (4) | |
| H19A | −0.2054 | 0.7629 | 0.9365 | 0.023* | |
| C20 | −0.1560 (4) | 0.76158 (9) | 0.81740 (11) | 0.0211 (4) | |
| H20A | −0.2925 | 0.7898 | 0.8002 | 0.025* | |
| C21 | −0.0008 (4) | 0.73530 (9) | 0.75909 (11) | 0.0205 (4) | |
| H21A | −0.0309 | 0.7487 | 0.7041 | 0.025* | |
| C22 | 0.1913 (3) | 0.69077 (9) | 0.78224 (10) | 0.0184 (4) | |
| H22A | 0.2862 | 0.6730 | 0.7424 | 0.022* | |
| C23 | 0.2504 (3) | 0.67066 (9) | 0.86689 (10) | 0.0153 (3) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.03907 (13) | 0.02093 (10) | 0.01575 (9) | −0.00663 (8) | 0.00217 (7) | −0.00386 (7) |
| O1 | 0.0137 (7) | 0.0297 (7) | 0.0203 (6) | 0.0009 (5) | 0.0009 (5) | −0.0031 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0181 (10) | 0.0199 (9) | 0.0219 (9) | 0.0037 (7) | 0.0000 (7) | −0.0002 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0238 (10) | 0.0180 (9) | 0.0239 (9) | 0.0060 (7) | 0.0029 (7) | −0.0027 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0238 (10) | 0.0159 (8) | 0.0146 (8) | −0.0052 (7) | 0.0032 (6) | −0.0018 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0170 (10) | 0.0258 (9) | 0.0182 (8) | −0.0003 (7) | −0.0010 (7) | −0.0016 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0158 (9) | 0.0228 (9) | 0.0168 (8) | 0.0022 (7) | 0.0020 (6) | −0.0031 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0155 (9) | 0.0169 (8) | 0.0134 (7) | −0.0013 (6) | 0.0024 (6) | 0.0007 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0156 (9) | 0.0176 (8) | 0.0148 (7) | −0.0011 (7) | 0.0027 (6) | 0.0005 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0119 (9) | 0.0206 (8) | 0.0155 (7) | −0.0010 (7) | 0.0022 (6) | −0.0008 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0133 (9) | 0.0179 (8) | 0.0175 (8) | −0.0016 (7) | 0.0032 (6) | 0.0007 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0157 (9) | 0.0163 (8) | 0.0155 (8) | −0.0035 (7) | 0.0024 (6) | −0.0019 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0163 (9) | 0.0155 (8) | 0.0154 (8) | −0.0034 (7) | 0.0018 (6) | −0.0006 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0195 (10) | 0.0211 (9) | 0.0184 (8) | −0.0005 (7) | 0.0034 (7) | −0.0008 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0209 (10) | 0.0240 (9) | 0.0202 (8) | −0.0003 (8) | −0.0003 (7) | 0.0026 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0292 (11) | 0.0223 (9) | 0.0140 (8) | −0.0036 (8) | −0.0004 (7) | 0.0005 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0307 (11) | 0.0227 (9) | 0.0141 (8) | −0.0017 (8) | 0.0042 (7) | −0.0017 (7) |
| C16 | 0.0210 (9) | 0.0144 (8) | 0.0156 (8) | −0.0040 (7) | 0.0036 (6) | −0.0015 (6) |
| C17 | 0.0225 (10) | 0.0168 (8) | 0.0175 (8) | −0.0003 (7) | 0.0054 (7) | −0.0032 (6) |
| C18 | 0.0182 (9) | 0.0142 (8) | 0.0178 (8) | −0.0032 (7) | 0.0021 (6) | −0.0015 (6) |
| C19 | 0.0193 (10) | 0.0156 (8) | 0.0244 (9) | −0.0002 (7) | 0.0050 (7) | −0.0024 (7) |
| C20 | 0.0200 (10) | 0.0160 (8) | 0.0266 (9) | −0.0010 (7) | −0.0018 (7) | 0.0006 (7) |
| C21 | 0.0216 (10) | 0.0209 (9) | 0.0182 (8) | −0.0033 (7) | −0.0016 (7) | 0.0014 (7) |
| C22 | 0.0192 (10) | 0.0191 (9) | 0.0168 (8) | −0.0029 (7) | 0.0020 (6) | −0.0020 (7) |
| C23 | 0.0155 (9) | 0.0154 (8) | 0.0150 (7) | −0.0048 (6) | 0.0013 (6) | −0.0018 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Br1—C3 | 1.8954 (17) | C12—C13 | 1.364 (2) |
| O1—C7 | 1.225 (2) | C12—H12A | 0.93 |
| C1—C2 | 1.384 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.416 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.396 (2) | C13—H13A | 0.93 |
| C1—H1A | 0.93 | C14—C15 | 1.356 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.380 (3) | C14—H14A | 0.93 |
| C2—H2A | 0.93 | C15—C16 | 1.431 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.380 (3) | C15—H15A | 0.93 |
| C4—C5 | 1.389 (2) | C16—C17 | 1.391 (3) |
| C4—H4A | 0.93 | C17—C18 | 1.393 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.395 (2) | C17—H17A | 0.93 |
| C5—H5A | 0.93 | C18—C19 | 1.429 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.495 (2) | C18—C23 | 1.440 (2) |
| C7—C8 | 1.480 (2) | C19—C20 | 1.357 (3) |
| C8—C9 | 1.333 (2) | C19—H19A | 0.93 |
| C8—H8A | 0.93 | C20—C21 | 1.420 (3) |
| C9—C10 | 1.472 (2) | C20—H20A | 0.93 |
| C9—H9A | 0.93 | C21—C22 | 1.361 (3) |
| C10—C23 | 1.413 (3) | C21—H21A | 0.93 |
| C10—C11 | 1.420 (2) | C22—C23 | 1.436 (2) |
| C11—C12 | 1.428 (3) | C22—H22A | 0.93 |
| C11—C16 | 1.433 (2) | ||
| C2—C1—C6 | 121.23 (17) | C11—C12—H12A | 119.3 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 119.4 | C12—C13—C14 | 120.32 (18) |
| C6—C1—H1A | 119.4 | C12—C13—H13A | 119.8 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 118.75 (17) | C14—C13—H13A | 119.8 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 120.6 | C15—C14—C13 | 120.41 (17) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 120.6 | C15—C14—H14A | 119.8 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.49 (16) | C13—C14—H14A | 119.8 |
| C4—C3—Br1 | 118.73 (14) | C14—C15—C16 | 121.00 (17) |
| C2—C3—Br1 | 119.78 (14) | C14—C15—H15A | 119.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.44 (17) | C16—C15—H15A | 119.5 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 120.3 | C17—C16—C15 | 121.78 (16) |
| C5—C4—H4A | 120.3 | C17—C16—C11 | 119.28 (16) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.34 (17) | C15—C16—C11 | 118.94 (17) |
| C4—C5—H5A | 119.8 | C16—C17—C18 | 121.81 (16) |
| C6—C5—H5A | 119.8 | C16—C17—H17A | 119.1 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 118.69 (16) | C18—C17—H17A | 119.1 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 123.18 (16) | C17—C18—C19 | 120.98 (16) |
| C1—C6—C7 | 118.04 (16) | C17—C18—C23 | 119.57 (16) |
| O1—C7—C8 | 121.62 (16) | C19—C18—C23 | 119.41 (15) |
| O1—C7—C6 | 119.02 (15) | C20—C19—C18 | 121.24 (17) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 119.35 (15) | C20—C19—H19A | 119.4 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 119.93 (16) | C18—C19—H19A | 119.4 |
| C9—C8—H8A | 120.0 | C19—C20—C21 | 119.62 (18) |
| C7—C8—H8A | 120.0 | C19—C20—H20A | 120.2 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 126.25 (17) | C21—C20—H20A | 120.2 |
| C8—C9—H9A | 116.9 | C22—C21—C20 | 121.16 (16) |
| C10—C9—H9A | 116.9 | C22—C21—H21A | 119.4 |
| C23—C10—C11 | 119.94 (15) | C20—C21—H21A | 119.4 |
| C23—C10—C9 | 122.24 (15) | C21—C22—C23 | 121.31 (17) |
| C11—C10—C9 | 117.80 (16) | C21—C22—H22A | 119.3 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 122.43 (16) | C23—C22—H22A | 119.3 |
| C10—C11—C16 | 119.84 (16) | C10—C23—C22 | 123.65 (16) |
| C12—C11—C16 | 117.72 (15) | C10—C23—C18 | 119.29 (15) |
| C13—C12—C11 | 121.49 (17) | C22—C23—C18 | 116.99 (16) |
| C13—C12—H12A | 119.3 | ||
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.3 (3) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −1.8 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.9 (3) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 178.78 (18) |
| C1—C2—C3—Br1 | 176.90 (14) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | −0.8 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.4 (3) | C10—C11—C16—C17 | 3.0 (3) |
| Br1—C3—C4—C5 | −177.43 (14) | C12—C11—C16—C17 | −176.19 (16) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.8 (3) | C10—C11—C16—C15 | −177.41 (16) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −2.4 (3) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | 3.4 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 174.05 (17) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | 177.22 (17) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 1.9 (3) | C11—C16—C17—C18 | −3.2 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | −174.75 (17) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | −178.36 (17) |
| C5—C6—C7—O1 | −158.07 (17) | C16—C17—C18—C23 | −0.7 (3) |
| C1—C6—C7—O1 | 18.4 (2) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | 173.37 (17) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 22.9 (2) | C23—C18—C19—C20 | −4.3 (3) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | −160.59 (16) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | −0.4 (3) |
| O1—C7—C8—C9 | 0.1 (3) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | 3.8 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 179.10 (16) | C20—C21—C22—C23 | −2.3 (3) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −173.26 (16) | C11—C10—C23—C22 | 171.79 (16) |
| C8—C9—C10—C23 | −50.2 (3) | C9—C10—C23—C22 | −6.7 (3) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 131.30 (19) | C11—C10—C23—C18 | −5.1 (3) |
| C23—C10—C11—C12 | −179.68 (17) | C9—C10—C23—C18 | 176.46 (16) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | −1.1 (3) | C21—C22—C23—C10 | −179.25 (18) |
| C23—C10—C11—C16 | 1.1 (3) | C21—C22—C23—C18 | −2.3 (3) |
| C9—C10—C11—C16 | 179.69 (16) | C17—C18—C23—C10 | 4.9 (3) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 177.21 (17) | C19—C18—C23—C10 | −177.42 (16) |
| C16—C11—C12—C13 | −3.6 (3) | C17—C18—C23—C22 | −172.15 (16) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | 1.1 (3) | C19—C18—C23—C22 | 5.5 (2) |
| C12—C13—C14—C15 | 1.6 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C8—H8A···O1i | 0.93 | 2.42 | 3.308 (2) | 159 |
| C13—H13A···O1ii | 0.93 | 2.57 | 3.288 (2) | 135 |
| C21—H21A···Br1iii | 0.93 | 2.93 | 3.4722 (19) | 119 |
| C9—H9A···Cg1iv | 0.93 | 2.83 | 3.4479 (18) | 125 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1, y, z; (ii) −x+2, −y+1, −z+2; (iii) −x, −y+1, −z+1; (iv) x+1, y, z.
Footnotes
This paper is dedicated to the late Her Royal Highness Princess Galyani Vadhana Krom Luang Naradhiwas Rajanagarindra for her patronage of Science in Thailand.
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: CI2756).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Bruker (2005). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Jung, Y. J., Son, K. I., Oh, Y. E. & Noh, D. Y. (2008). Polyhedron, 27, 861–867.
- Ng, S.-L., Shettigar, V., Razak, I. A., Fun, H.-K., Patil, P. S. & Dharmaprakash, S. M. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o1570–o1572.
- Patil, P. S., Chantrapromma, S., Fun, H.-K., Dharmaprakash, S. M. & Babu, H. B. R. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o2612.
- Patil, P. S. & Dharmaprakash, S. M. (2008). Mater. Lett.62, 451–453.
- Patil, P. S., Dharmaprakash, S. M., Ramakrishna, K., Fun, H. K., Sai Santosh Kumar, R. & Narayana Rao, D. (2007). J. Cryst. Growth, 303, 520–524.
- Patil, P. S., Rosli, M. M., Fun, H.-K., Razak, I. A., Puranik, V. G. & Dharmaprakash, S. M. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o4798–o4799.
- Prasad, Y. R., Kumar, P. R., Smile, D. J. & Babu, P. A. (2008). Arkivoc, 11, 266–276.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
- Suwunwong, T., Chantrapromma, S. & Fun, H.-K. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809003122/ci2756sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809003122/ci2756Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report