Abstract
The title compound, C9H11BrN2O2, is an important intermediate for the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds such as azoles, 2,5-disubstituted-1,3,4-oxadiazoles and 5-substituted 2-mercapto-1,3,4-oxadiazoles. The bromophenoxy group subtends a dihedral angle of 82.81 (7)° with the plane passing through the propanohydrazide moiety. The crystal structure is stabilized by intermolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds that form columns extending along the b axis.
Related literature
For carboxyhydrazide derivatives with biological activities, see: Belkadi & Othman (2006 ▶); Goswami et al. (1984 ▶); Akhtar et al. (2008 ▶); Akhtar, Hameed et al. (2007 ▶); Ahmad et al. (1996 ▶); Akhtar et al. (2006 ▶); For related structures, see: Akhtar, Khawar Rauf et al. (2007 ▶); Zheng (2008 ▶).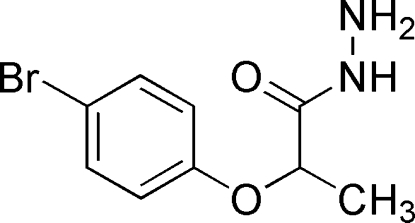
Experimental
Crystal data
C9H11BrN2O2
M r = 259.11
Monoclinic,
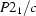
a = 10.2598 (14) Å
b = 4.8009 (7) Å
c = 23.322 (3) Å
β = 112.712 (6)°
V = 1059.7 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 3.86 mm−1
T = 113 (2) K
0.50 × 0.30 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Rigaku/MSC Mercury CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: integration (NUMABS; Higashi, 1999) T min = 0.531, T max = 0.759
8296 measured reflections
2418 independent reflections
2201 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.039
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.048
wR(F 2) = 0.076
S = 1.20
2418 reflections
137 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.59 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.75 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Molecular Structure Corporation & Rigaku, 2001 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: TEXSAN (Molecular Structure Corporation & Rigaku, 2004 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SIR97 (Altomare et al., 1999 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEPII (Johnson, 1976 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and TEXSAN.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809003134/si2151sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809003134/si2151Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O1i | 0.85 (3) | 1.97 (3) | 2.812 (3) | 170 (3) |
| N2—H2A⋯O1ii | 0.83 (3) | 2.33 (3) | 3.127 (3) | 161 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
MKR is grateful to the HEC–Pakistan for financial support for a PhD program under scholarship No. ILC-0363104.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Carboxylic acid hydrazides are important biological agents and intermediates in the synthesis of biologically active heterocycles with two nitrogen atoms at adjacent positions (Belkadi & Othman, 2006). The hydrazides when treated with isocyanates or isothiocyanates afford semicarbazides and thiosemicarbazides, respectively (Goswami et al., 1984). These are important intermediates in the synthesis of azoles under acidic or basic conditions (Akhtar et al., 2007a; Ahmad et al., 1996). In continuation of our previous studies (Akhtar et al., 2006; Akhtar et al., 2007b), the title compound, 2-(4-bromophenoxy)propane hydrazide,was synthesized as an intermediate in the synthesis of certain azole derivatives (Akhtar et al., 2008). The C—N bond length of 1.330 (3)Å is similar to C—N 1.321 (3) Å, indicating the single bond character.The N1—N2 bond length of 1.415 (3) Å in the title compound is longer than the N—N distance [1.366 (3)Å] in the crystal structure of N-propionyl-N'-(3-hydroxy-2-naphthoyl)hydrazide (Zheng, 2008). The Bromo group is coplanar with the phenyl plane C3/C4/C5/C6/C7/C8 with deviation from the plane of 0.030 (4) Å. The molecular packing diagram (Fig. 2) shows the presence of two intermolecular N—H···O hydrogen bonds, (Table 1), one of which is generated via translation along [0 1 0], the other via inversion symmetry.
Experimental
Methyl 2-(4-bromophenoxy)propionate (5.0 g, 0.0193 mol) was dissolved in methanol (20 ml) and hydrazine hydrate (80%, 3.50 mL, 0.0679 mol) added slowly with stirring. The reaction mixture was set to reflux. After completion of the reaction (TLC, 6 hrs), the reaction mixture was concentrated and poured to water. The precipitated solid was filtered and recrystallized from ethanol/ water. The spectroscopic and physical characterization data will be reported separately.
Refinement
The H atoms on the N atoms were refined isotropically. Other H atoms were placed in idealized positions and treated as riding atoms with C—H distance in the range 0.95–1.000 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) or 1.5Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) showing the atom labelling and displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
View of the N—H···O hydrogen bonded molecules. The unit cell has been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C9H11BrN2O2 | F(000) = 520 |
| Mr = 259.11 | Dx = 1.624 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.7107 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 2804 reflections |
| a = 10.2598 (14) Å | θ = 3.4–27.5° |
| b = 4.8009 (7) Å | µ = 3.86 mm−1 |
| c = 23.322 (3) Å | T = 113 K |
| β = 112.712 (6)° | Block, colorless |
| V = 1059.7 (3) Å3 | 0.50 × 0.30 × 0.20 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Rigaku/MSC Mercury CCD diffractometer | 2201 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 14.62 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.039 |
| ω scans | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.4° |
| Absorption correction: integration (NUMABS; Higashi, 1999) | h = −13→11 |
| Tmin = 0.531, Tmax = 0.759 | k = −6→4 |
| 8296 measured reflections | l = −26→30 |
| 2418 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.048 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.076 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.20 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0037P)2 + 1.6325P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2418 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 137 parameters | Δρmax = 0.59 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.75 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.4780 (3) | 0.1909 (5) | 0.40801 (12) | 0.0143 (5) | |
| O1 | 0.4868 (2) | −0.0616 (4) | 0.41874 (9) | 0.0203 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.5635 (2) | 0.3771 (4) | 0.44658 (11) | 0.0162 (5) | |
| H1 | 0.551 (3) | 0.551 (6) | 0.4399 (14) | 0.019* | |
| N2 | 0.6750 (3) | 0.3047 (5) | 0.50307 (11) | 0.0200 (5) | |
| H2A | 0.643 (3) | 0.205 (7) | 0.5240 (15) | 0.024* | |
| H2B | 0.740 (3) | 0.209 (6) | 0.4928 (14) | 0.024* | |
| C2 | 0.3698 (3) | 0.3120 (6) | 0.34780 (13) | 0.0188 (6) | |
| H2 | 0.3260 | 0.4839 | 0.3568 | 0.023* | |
| O2 | 0.2635 (2) | 0.1095 (4) | 0.31761 (9) | 0.0199 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.1643 (3) | 0.0534 (5) | 0.34207 (13) | 0.0164 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.0672 (3) | −0.1518 (6) | 0.31070 (12) | 0.0180 (5) | |
| H4 | 0.0761 | −0.2460 | 0.2766 | 0.022* | |
| C5 | −0.0425 (3) | −0.2199 (6) | 0.32900 (13) | 0.0205 (6) | |
| H5 | −0.1092 | −0.3595 | 0.3076 | 0.025* | |
| C6 | −0.0528 (3) | −0.0808 (6) | 0.37882 (14) | 0.0222 (6) | |
| C7 | 0.0439 (3) | 0.1215 (6) | 0.41093 (14) | 0.0218 (6) | |
| H7 | 0.0353 | 0.2140 | 0.4453 | 0.026* | |
| C8 | 0.1534 (3) | 0.1881 (6) | 0.39257 (13) | 0.0190 (6) | |
| H8 | 0.2208 | 0.3256 | 0.4145 | 0.023* | |
| Br1 | −0.20430 (4) | −0.16915 (9) | 0.403569 (18) | 0.04154 (13) | |
| C9 | 0.4395 (4) | 0.3772 (7) | 0.30247 (15) | 0.0332 (8) | |
| H9A | 0.4827 | 0.2076 | 0.2943 | 0.050* | |
| H9B | 0.5125 | 0.5194 | 0.3204 | 0.050* | |
| H9C | 0.3682 | 0.4466 | 0.2634 | 0.050* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0158 (13) | 0.0134 (12) | 0.0163 (13) | −0.0004 (10) | 0.0090 (11) | 0.0010 (10) |
| O1 | 0.0227 (11) | 0.0116 (9) | 0.0254 (11) | −0.0004 (8) | 0.0079 (9) | 0.0015 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0194 (12) | 0.0079 (10) | 0.0167 (12) | 0.0010 (9) | 0.0020 (10) | 0.0014 (9) |
| N2 | 0.0196 (12) | 0.0209 (12) | 0.0168 (12) | 0.0003 (10) | 0.0041 (10) | 0.0026 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0176 (13) | 0.0184 (13) | 0.0176 (14) | −0.0041 (11) | 0.0035 (11) | 0.0023 (11) |
| O2 | 0.0209 (10) | 0.0220 (10) | 0.0152 (10) | −0.0090 (8) | 0.0053 (8) | −0.0031 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0145 (13) | 0.0166 (13) | 0.0146 (13) | 0.0008 (10) | 0.0017 (11) | 0.0041 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0186 (13) | 0.0177 (13) | 0.0140 (13) | 0.0000 (11) | 0.0023 (11) | −0.0006 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0178 (14) | 0.0194 (14) | 0.0194 (15) | −0.0039 (11) | 0.0018 (11) | 0.0008 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0165 (14) | 0.0272 (15) | 0.0218 (15) | 0.0005 (11) | 0.0062 (12) | 0.0047 (12) |
| C7 | 0.0212 (15) | 0.0216 (15) | 0.0200 (15) | 0.0031 (11) | 0.0049 (12) | −0.0021 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0159 (13) | 0.0182 (13) | 0.0176 (14) | −0.0010 (11) | 0.0006 (11) | −0.0019 (11) |
| Br1 | 0.02723 (18) | 0.0649 (3) | 0.0383 (2) | −0.01613 (17) | 0.01901 (15) | −0.01174 (19) |
| C9 | 0.0321 (18) | 0.043 (2) | 0.0216 (16) | −0.0163 (15) | 0.0075 (14) | 0.0044 (14) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—O1 | 1.234 (3) | C4—C5 | 1.389 (4) |
| C1—N1 | 1.330 (3) | C4—H4 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.529 (4) | C5—C6 | 1.379 (4) |
| N1—N2 | 1.415 (3) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| N1—H1 | 0.85 (3) | C6—C7 | 1.384 (4) |
| N2—H2A | 0.83 (3) | C6—Br1 | 1.903 (3) |
| N2—H2B | 0.92 (3) | C7—C8 | 1.385 (4) |
| C2—O2 | 1.427 (3) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C9 | 1.520 (4) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2 | 1.0000 | C9—H9A | 0.9800 |
| O2—C3 | 1.372 (3) | C9—H9B | 0.9800 |
| C3—C8 | 1.385 (4) | C9—H9C | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.392 (4) | ||
| O1—C1—N1 | 123.1 (2) | C5—C4—H4 | 119.8 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 122.0 (2) | C3—C4—H4 | 119.8 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 114.9 (2) | C6—C5—C4 | 118.7 (3) |
| C1—N1—N2 | 123.4 (2) | C6—C5—H5 | 120.7 |
| C1—N1—H1 | 121 (2) | C4—C5—H5 | 120.7 |
| N2—N1—H1 | 115 (2) | C5—C6—C7 | 121.6 (3) |
| N1—N2—H2A | 109 (2) | C5—C6—Br1 | 119.0 (2) |
| N1—N2—H2B | 107 (2) | C7—C6—Br1 | 119.4 (2) |
| H2A—N2—H2B | 111 (3) | C6—C7—C8 | 119.5 (3) |
| O2—C2—C9 | 105.8 (2) | C6—C7—H7 | 120.3 |
| O2—C2—C1 | 109.9 (2) | C8—C7—H7 | 120.3 |
| C9—C2—C1 | 110.3 (2) | C3—C8—C7 | 119.8 (3) |
| O2—C2—H2 | 110.3 | C3—C8—H8 | 120.1 |
| C9—C2—H2 | 110.3 | C7—C8—H8 | 120.1 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 110.3 | C2—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| C3—O2—C2 | 118.5 (2) | C2—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| O2—C3—C8 | 125.4 (2) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| O2—C3—C4 | 114.6 (2) | C2—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C8—C3—C4 | 120.1 (3) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.4 (3) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| O1—C1—N1—N2 | 1.5 (4) | O2—C3—C4—C5 | −177.1 (2) |
| C2—C1—N1—N2 | −176.7 (2) | C8—C3—C4—C5 | 1.1 (4) |
| O1—C1—C2—O2 | 15.9 (4) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.2 (4) |
| N1—C1—C2—O2 | −165.9 (2) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | −0.6 (4) |
| O1—C1—C2—C9 | −100.3 (3) | C4—C5—C6—Br1 | 179.2 (2) |
| N1—C1—C2—C9 | 77.9 (3) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 0.4 (4) |
| C9—C2—O2—C3 | −166.8 (2) | Br1—C6—C7—C8 | −179.3 (2) |
| C1—C2—O2—C3 | 74.1 (3) | O2—C3—C8—C7 | 176.8 (2) |
| C2—O2—C3—C8 | 3.5 (4) | C4—C3—C8—C7 | −1.3 (4) |
| C2—O2—C3—C4 | −178.3 (2) | C6—C7—C8—C3 | 0.5 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O1i | 0.85 (3) | 1.97 (3) | 2.812 (3) | 170 (3) |
| N2—H2A···O1ii | 0.83 (3) | 2.33 (3) | 3.127 (3) | 161 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y+1, z; (ii) −x+1, −y, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SI2151).
References
- Ahmad, R., Zia-ul-Haq, M., Jabeen, R. & Duddeck, H. (1996). Turk. J. Chem.20, 186–193.
- Akhtar, T., Hameed, S., Al-Masoudi, N. A. & Khan, K. M. (2007). Heteroat. Chem.18, 316–322.
- Akhtar, T., Hameed, S., Al-Masoudi, N. A., Loddo, R. & La Colla, P. (2008). Acta Pharm.58, 135–149. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, T., Hameed, S., Lu, X., Yasin, K. A. & Khan, M. H. (2006). Anal. Sci.22, 307–308.
- Akhtar, T., Khawar Rauf, M., Ebihara, M. & Hameed, S. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o2590–o2592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Altomare, A., Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Moliterni, A. G. G., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 115–119.
- Belkadi, M. & Othman, A. A. (2006). ARKIVOC, part xi, pp. 183–195.
- Goswami, B. N., Kataky, J. C. S. & Baruah, J. N. (1984). J. Heterocycl. Chem.21, 1225–1229.
- Higashi, T. (1999). NUMABS Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Johnson, C. K. (1976). ORTEPII Report ORNL-5138. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Tennessee, USA.
- Molecular Structure Corporation & Rigaku (2001). CrystalClear MSC, The Woodlands, Texas, USA, and Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Molecular Structure Corporation & Rigaku (2004). TEXSAN MSC, The Woodlands, Texas, USA, and Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.-Y. (2008). Z. Kristallogr. New Cryst. Struct.223, 295–296.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809003134/si2151sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809003134/si2151Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




