Abstract
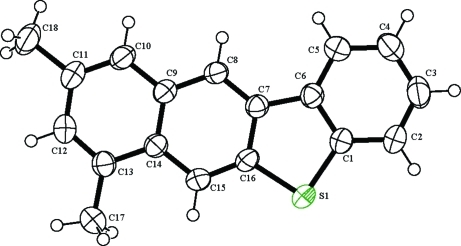
The molecule of the title compound, C18H14S, is approximately planar (r.m.s. deviation = 0.029 Å). The crystal packing is stabilized by weak intermolecular C—H⋯π interactions.
Related literature
For the pharmacological activities of thiophen derivatives, see: Dzhurayev et al. (1992 ▶); El-Maghraby et al. (1984 ▶); Gewald et al. (1996 ▶). For related structures, see: Harrison et al. (2006 ▶); Palani et al. (2006 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶).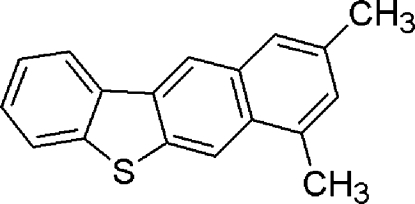
Experimental
Crystal data
C18H14S
M r = 262.35
Monoclinic,
a = 10.0219 (3) Å
b = 5.8692 (5) Å
c = 22.8554 (5) Å
β = 99.787 (1)°
V = 1324.80 (12) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.23 mm−1
T = 295 (2) K
0.26 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.944, T max = 0.961
27929 measured reflections
3030 independent reflections
2574 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.029
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.046
wR(F 2) = 0.137
S = 1.08
3030 reflections
174 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809003456/bt2861sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809003456/bt2861Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 is the centroid of the C7–C9/C14–C16 ring and Cg2 is the centroid of the C1–C6 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C17—H17C⋯Cg1i | 0.96 | 2.68 | 3.486 (2) | 142 |
| C18—H18A⋯Cg2ii | 0.96 | 2.75 | 3.649 (3) | 155 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 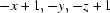 ; (ii)
; (ii) 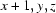 .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Thiophen derivatives possess pharmacological activities such as anti-bacterial, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory (El-Maghraby et al., 1984; Dzhurayev et al., 1992) and anti-toxic properties (Gewald et al., 1996).
The geometric parameters of the title molecule (Fig. 1) agree well with related structures (Harrison et al., 2006; Palani et al., 2006) and literature values (Allen et al., 1987). All non-H atoms lie in a common plane (r.m.s. deviation 0.029Å) .
The crystal packing is stabilized by weak intermolecular C - H···π [C17—H17C···Cg1 (1 - x, -y, 1 - z), H17C···Cg1 = 2.68 Å, C18—H18A··· Cg2 (1 + x, y, z), H18A···Cg1 = 2.75 Å; Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroid of rings defined by atoms C7/C8/C9/C14/C15/C16 and C1—C6, respectively) interactions. No significant intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonds are observed.
Experimental
To a solution of diethyl 2-((2-(bromomethyl)banzo[b]thiophen-3-yl) methylene)malonate (0.35 g, 0.88 mmol) in dry 1,2-DCE (15 ml), ZnBr2 (0.39 g, 1.73 mmol) and m-xylene (0.13 ml, 1.03 mmol), were added. The reaction mixture was then refluxed for 2 h under N2 atmosphere. It was then poured over ice-water (50 ml) containing 2 ml of conc.HCl, extracted with chloroform (3 X 10 ml) and dried (Na2SO4). The removal of solvent followed by flash column chromatographic purification (silica gel, 230–420 mesh, n-hexane/ethyl acetate 99:1) afforded 1,3-dimethylbenzo[2,3-b] dibenzothiophene as a colourless crystal.
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model with C—H = 0.93 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for aromatic H atoms and C—H = 0.96 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I), with atom labels and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms.
Crystal data
| C18H14S | F(000) = 552 |
| Mr = 262.35 | Dx = 1.315 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 6370 reflections |
| a = 10.0219 (3) Å | θ = 2.1–27.4° |
| b = 5.8692 (5) Å | µ = 0.23 mm−1 |
| c = 22.8554 (5) Å | T = 295 K |
| β = 99.787 (1)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 1324.80 (12) Å3 | 0.26 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII diffractometer | 3030 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2574 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.029 |
| ω and φ scans | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 1.8° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −13→13 |
| Tmin = 0.944, Tmax = 0.961 | k = −7→7 |
| 27929 measured reflections | l = −29→29 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.046 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.137 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.08 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0636P)2 + 0.5697P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3030 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 174 parameters | Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.07838 (18) | −0.0783 (3) | 0.33166 (8) | 0.0456 (4) | |
| C2 | −0.0587 (2) | −0.0829 (4) | 0.30694 (10) | 0.0567 (5) | |
| H2 | −0.1153 | −0.1953 | 0.3177 | 0.068* | |
| C3 | −0.1081 (2) | 0.0813 (4) | 0.26653 (9) | 0.0603 (6) | |
| H3 | −0.1993 | 0.0801 | 0.2496 | 0.072* | |
| C4 | −0.0245 (2) | 0.2490 (4) | 0.25047 (9) | 0.0579 (5) | |
| H4 | −0.0599 | 0.3589 | 0.2228 | 0.069* | |
| C5 | 0.1110 (2) | 0.2546 (3) | 0.27511 (8) | 0.0494 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.1667 | 0.3678 | 0.2641 | 0.059* | |
| C6 | 0.16390 (17) | 0.0909 (3) | 0.31632 (7) | 0.0403 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.30153 (17) | 0.0662 (3) | 0.34821 (7) | 0.0378 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.41378 (18) | 0.1971 (3) | 0.34603 (7) | 0.0408 (4) | |
| H8 | 0.4071 | 0.3228 | 0.3209 | 0.049* | |
| C9 | 0.53930 (17) | 0.1436 (3) | 0.38139 (7) | 0.0390 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.65545 (19) | 0.2770 (3) | 0.37964 (8) | 0.0472 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.6490 | 0.4027 | 0.3545 | 0.057* | |
| C11 | 0.77693 (19) | 0.2268 (3) | 0.41376 (9) | 0.0480 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.78456 (18) | 0.0376 (3) | 0.45225 (8) | 0.0477 (4) | |
| H12 | 0.8674 | 0.0037 | 0.4757 | 0.057* | |
| C13 | 0.67622 (18) | −0.0979 (3) | 0.45659 (8) | 0.0419 (4) | |
| C14 | 0.54908 (17) | −0.0488 (3) | 0.41992 (7) | 0.0381 (4) | |
| C15 | 0.43329 (18) | −0.1822 (3) | 0.42159 (8) | 0.0437 (4) | |
| H15 | 0.4381 | −0.3086 | 0.4464 | 0.052* | |
| C16 | 0.31376 (18) | −0.1253 (3) | 0.38656 (8) | 0.0418 (4) | |
| C17 | 0.6892 (2) | −0.2914 (4) | 0.49988 (9) | 0.0523 (5) | |
| H17A | 0.7795 | −0.2944 | 0.5222 | 0.078* | |
| H17B | 0.6709 | −0.4324 | 0.4787 | 0.078* | |
| H17C | 0.6256 | −0.2714 | 0.5265 | 0.078* | |
| C18 | 0.9007 (2) | 0.3703 (4) | 0.41279 (11) | 0.0648 (6) | |
| H18A | 0.9598 | 0.2941 | 0.3902 | 0.097* | |
| H18B | 0.9471 | 0.3935 | 0.4527 | 0.097* | |
| H18C | 0.8742 | 0.5149 | 0.3949 | 0.097* | |
| S1 | 0.16072 (5) | −0.26890 (9) | 0.38419 (3) | 0.0592 (2) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0419 (9) | 0.0449 (10) | 0.0474 (9) | −0.0078 (8) | 0.0001 (7) | −0.0003 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0429 (10) | 0.0597 (12) | 0.0632 (12) | −0.0153 (9) | −0.0030 (9) | 0.0030 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0429 (10) | 0.0772 (15) | 0.0557 (11) | −0.0015 (10) | −0.0060 (8) | −0.0008 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0542 (11) | 0.0668 (14) | 0.0491 (11) | 0.0049 (10) | −0.0018 (9) | 0.0105 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0511 (10) | 0.0519 (11) | 0.0442 (9) | −0.0012 (8) | 0.0053 (8) | 0.0069 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0406 (9) | 0.0429 (9) | 0.0367 (8) | −0.0034 (7) | 0.0042 (7) | −0.0033 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0391 (8) | 0.0378 (8) | 0.0361 (8) | −0.0034 (7) | 0.0054 (6) | −0.0014 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0425 (9) | 0.0404 (9) | 0.0393 (8) | −0.0059 (7) | 0.0068 (7) | 0.0049 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0388 (8) | 0.0408 (9) | 0.0383 (8) | −0.0050 (7) | 0.0089 (6) | −0.0013 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0447 (10) | 0.0488 (10) | 0.0494 (10) | −0.0102 (8) | 0.0120 (8) | 0.0035 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0391 (9) | 0.0550 (11) | 0.0513 (10) | −0.0108 (8) | 0.0116 (8) | −0.0053 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0352 (8) | 0.0562 (11) | 0.0507 (10) | 0.0011 (8) | 0.0042 (7) | −0.0036 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0401 (9) | 0.0432 (9) | 0.0422 (9) | 0.0020 (7) | 0.0066 (7) | −0.0026 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0387 (8) | 0.0371 (9) | 0.0386 (8) | −0.0022 (7) | 0.0068 (6) | −0.0023 (7) |
| C15 | 0.0445 (9) | 0.0353 (9) | 0.0497 (10) | −0.0051 (7) | 0.0036 (7) | 0.0050 (7) |
| C16 | 0.0417 (9) | 0.0364 (9) | 0.0461 (9) | −0.0101 (7) | 0.0036 (7) | 0.0007 (7) |
| C17 | 0.0486 (11) | 0.0520 (11) | 0.0544 (11) | 0.0057 (9) | 0.0033 (8) | 0.0060 (9) |
| C18 | 0.0422 (10) | 0.0745 (15) | 0.0786 (15) | −0.0188 (10) | 0.0127 (10) | −0.0002 (12) |
| S1 | 0.0460 (3) | 0.0503 (3) | 0.0749 (4) | −0.0193 (2) | −0.0080 (2) | 0.0180 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C2 | 1.394 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.362 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.395 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C1—S1 | 1.7425 (19) | C11—C12 | 1.411 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.368 (3) | C11—C18 | 1.502 (3) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C12—C13 | 1.363 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.382 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C13—C14 | 1.430 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.379 (3) | C13—C17 | 1.497 (3) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C14—C15 | 1.406 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.386 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.364 (2) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C7 | 1.454 (2) | C16—S1 | 1.7428 (17) |
| C7—C8 | 1.370 (2) | C17—H17A | 0.9600 |
| C7—C16 | 1.418 (2) | C17—H17B | 0.9600 |
| C8—C9 | 1.410 (2) | C17—H17C | 0.9600 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9300 | C18—H18A | 0.9600 |
| C9—C10 | 1.409 (2) | C18—H18B | 0.9600 |
| C9—C14 | 1.425 (2) | C18—H18C | 0.9600 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 121.14 (18) | C10—C11—C18 | 122.00 (19) |
| C2—C1—S1 | 125.84 (16) | C12—C11—C18 | 119.55 (19) |
| C6—C1—S1 | 113.01 (13) | C13—C12—C11 | 123.04 (17) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 118.62 (19) | C13—C12—H12 | 118.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.7 | C11—C12—H12 | 118.5 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.7 | C12—C13—C14 | 118.76 (16) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.96 (19) | C12—C13—C17 | 120.64 (17) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.5 | C14—C13—C17 | 120.59 (16) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.5 | C15—C14—C9 | 119.19 (16) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.53 (19) | C15—C14—C13 | 121.95 (16) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.7 | C9—C14—C13 | 118.85 (15) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.7 | C16—C15—C14 | 119.62 (16) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.81 (19) | C16—C15—H15 | 120.2 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.1 | C14—C15—H15 | 120.2 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.1 | C15—C16—C7 | 122.13 (16) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 118.93 (16) | C15—C16—S1 | 125.46 (14) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 129.09 (17) | C7—C16—S1 | 112.39 (13) |
| C1—C6—C7 | 111.98 (15) | C13—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C16 | 118.80 (15) | C13—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 129.86 (16) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C16—C7—C6 | 111.34 (15) | C13—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 120.82 (16) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.6 | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.6 | C11—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 121.39 (16) | C11—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C14 | 119.18 (16) | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—C14 | 119.43 (15) | C11—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 121.72 (18) | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—H10 | 119.1 | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—H10 | 119.1 | C1—S1—C16 | 91.28 (9) |
| C10—C11—C12 | 118.42 (17) | ||
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.7 (3) | C18—C11—C12—C13 | 178.60 (19) |
| S1—C1—C2—C3 | 179.28 (17) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.9 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.1 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C17 | −177.74 (17) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.2 (4) | C10—C9—C14—C15 | −179.87 (16) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.0 (3) | C8—C9—C14—C15 | 0.4 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.6 (3) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | 1.3 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −179.00 (19) | C8—C9—C14—C13 | −178.50 (16) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.9 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 179.42 (17) |
| S1—C1—C6—C5 | −179.67 (14) | C17—C13—C14—C15 | −1.9 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 178.73 (18) | C12—C13—C14—C9 | −1.7 (3) |
| S1—C1—C6—C7 | 0.0 (2) | C17—C13—C14—C9 | 176.94 (16) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 0.2 (3) | C9—C14—C15—C16 | −0.2 (3) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | −179.43 (18) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 178.66 (17) |
| C5—C6—C7—C16 | −179.98 (18) | C14—C15—C16—C7 | −0.3 (3) |
| C1—C6—C7—C16 | 0.4 (2) | C14—C15—C16—S1 | −178.84 (14) |
| C16—C7—C8—C9 | −0.3 (3) | C8—C7—C16—C15 | 0.5 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 179.59 (17) | C6—C7—C16—C15 | −179.40 (17) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −179.90 (16) | C8—C7—C16—S1 | 179.24 (13) |
| C7—C8—C9—C14 | −0.1 (3) | C6—C7—C16—S1 | −0.65 (19) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 179.83 (18) | C2—C1—S1—C16 | −179.0 (2) |
| C14—C9—C10—C11 | 0.1 (3) | C6—C1—S1—C16 | −0.29 (15) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.9 (3) | C15—C16—S1—C1 | 179.24 (18) |
| C9—C10—C11—C18 | −179.07 (19) | C7—C16—S1—C1 | 0.54 (14) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.4 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C17—H17C···Cg1i | 0.96 | 2.68 | 3.486 (2) | 142 |
| C18—H18A···Cg2ii | 0.96 | 2.75 | 3.649 (3) | 155 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (ii) x+1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT2861).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Bruker (2004). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Dzhurayev, A. D., Karimkulov, K. M., Makhsumov, A. G. & Amanov, N. (1992). Khim. Farm. Zh.26, 73–75.
- El-Maghraby, A. A., Haroun, B. & &Mohammed, N. A. (1984). Egypt. J. Pharm. Sci.23, 327–336.
- Gewald, K., Schinke, E. & Botcher, H. (1996). Chem. Ber.99, 99–100.
- Harrison, W. T. A., Yathirajan, H. S., Ashalatha, B. V., Vijaya Raj, K. K. & Narayana, B. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o3732–o3734.
- Palani, K., Amaladass, P., Mohanakrishnan, A. K. & Ponnuswamy, M. N. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o49–o51.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809003456/bt2861sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809003456/bt2861Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report