Abstract
In the title compound, C20H15ClN2OS, the bond lengths and angles in the thiourea group are typical of thiourea derivatives. The C—N bond lengths in the center of the molecule are shorter than the normal C—N single bond due to the resonance effects in this part of the molecule. The conformation of the title molecule with respect to the thiocarbonyl and carbonyl groups is twisted, as reflected by the C—N—C—O and C—N—C—N torsion angles of −4.4 (6) and −53.3 (5)°, respectively. Pairs of the molecules are linked into centrosymmetric dimers, stacked along the c axis via intermolecular N—H⋯S interactions. There are also weak intermolecular C—H⋯O and C—H⋯S contacts in the structure.
Related literature
For synthesis, see: Özer et al. (2009 ▶); Mansuroğlu et al. (2008 ▶); Uğur et al. (2006 ▶); Arslan et al. (2003c
▶). For general background, see: Koch (2001 ▶); Huebhr et al. (1953 ▶); Madan et al. (1991 ▶); Schroeder (1955 ▶). For related structures, see: Khawar Rauf et al. (2006 ▶, 2009 ▶); Arslan et al. (2003a
▶,b
▶); Yamin & Yusof (2003 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C20H15ClN2OS
M r = 366.85
Triclinic,
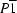
a = 8.196 (5) Å
b = 10.357 (6) Å
c = 11.699 (6) Å
α = 72.565 (10)°
β = 70.495 (10)°
γ = 71.303 (10)°
V = 865.8 (9) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.35 mm−1
T = 120 (2) K
0.49 × 0.32 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2002 ▶) T min = 0.847, T max = 0.966
5401 measured reflections
3490 independent reflections
2290 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.080
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.061
wR(F 2) = 0.146
S = 1.06
3490 reflections
230 parameters
1 restraint
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2002 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2002 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809001639/bq2121sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809001639/bq2121Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯S1i | 0.90 (2) | 2.48 (3) | 3.351 (4) | 162 (2) |
| C13—H13A⋯O1ii | 0.95 | 2.59 | 3.434 (5) | 148 |
| C18—H18A⋯S1iii | 0.95 | 2.87 | 3.609 (5) | 136 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Mersin University Research Fund (Project Nos. BAP-ECZ-F-TBB-(HA) 2004–3 and BAPFEF-KB-(NK) 2006–3). This study is part of the PhD thesis of Gün Binzet.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Thioureas and their metal complexes are an important class of compounds with a wide range of biological applications such as antitubercular, antithroid, anthelmintic, antibacterial, insecticidal and rodenticidal properties (Schroeder, 1955; Huebhr et al., 1953; Madan et al., 1991). Another area of the application of thiourea derivatives is analytical chemistry where some of these compounds have been used in the liquid-liquid extraction and separation of some transition metal ions (Koch, 2001).
Recently, a number of works on the structural and spectral properties of the thiourea derivatives and their metal complexes have appeared in the literature (Özer et al., 2009; Mansuroğlu et al., 2008; Uğur et al., 2006; Arslan et al., 2003c). We report here the crystal structure of one of them. The synthesis involves the reaction of a 3-chlorobenzoyl chloride with potassium thiocyanate in dry acetone followed by condensation of the 3-chlorobenzoyl isothiocyanate with the diphenylamine.
The molecular structure of the title compound, (I), is depicted in Fig. 1. The bond lengths and angles in the thiourea moiety are typical for thiourea derivatives; the C1-S1 (1.659 (3) Å) and C14-O1 (1.216 (4) Å) bonds both show typical double-bond character (Arslan et al., 2003a, 2003b; Khawar Rauf et al. 2009, 2006; Yamin & Yusof, 2003). The C-N bond lengths C14-N1 (1.388 (4) Å), C1-N1 (1.380 (4) Å) and C1-N2 (1.336 (4) Å) are shorter than the normal C-N single-bond length of about 1.48 Å. The shortening of these C-N bonds reveals the effects of resonance in this part of the molecule (Arslan et al., 2003a, 2003b; Khawar Rauf et al., 2009, 2006; Yamin & Yusof, 2003). The conformation of the title molecule with respect to the thiocarbonyl and carbonyl moieties is twisted, as reflected by the C1-N1-C14-O1 and C14-N1-C1-N2 torsion angles of -4.4 (6) o and -53.3 (5) o, respectively.
The atom N2 is sp2-hybridized, because of the sum of the angles around atom N2 is 359.8 (3) °. The phenyl rings are rotated out of the mean plane of the N1-C1-S1-N2 atoms by 80.1 (2) ° (C2-C7 ring) and 69.96 (19) ° (C8-C13 ring). In addition, the dihedral angle between C2-C7 ring and C8-C13 ring is 72.8 (2) °.
As can be seen from the packing diagram (Fig. 2), intermolecular N-H···S hydrogen bond (Table 1) links the molecules into dimers, which are stacked along the c-axis. The other intermolecular contacts, C-H···O and C-H···S, are also listed in Table 1.
Experimental
The title compound was prepared with a procedure similar to that reported in the literature (Arslan et al., 2003a). A solution of 3-chlorobenzoyl chloride (0.01 mol) in acetone (50 cm3) was added dropwise to a suspension of potassium thiocyanate (0.01 mol) in acetone (30 cm3). The reaction mixture was heated under reflux for 30 min, and then cooled to room temperature. A solution of diphenylamine (0.01 mol) in acetone (10 cm3) was added and the resulting mixture was stirred for 2 h. Hydrochloric acid (0.1 N, 300 cm3) was added to the solution, which was then filtered. The solid product was washed with water and purified by recrystalization from an ethanol:dichloromethane mixture (1:2). Anal. Calcd. for C20H15ClN2OS: C, 65.5; H, 4.1; N,7.6. Found: C, 65.4; H, 3.9; N, 7.7%.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I). Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A packing diagram for (I). Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C20H15ClN2OS | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 366.85 | F(000) = 380 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.407 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 8.196 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 710 reflections |
| b = 10.357 (6) Å | θ = 3.0–26.5° |
| c = 11.699 (6) Å | µ = 0.35 mm−1 |
| α = 72.565 (10)° | T = 120 K |
| β = 70.495 (10)° | Prism, colourless |
| γ = 71.303 (10)° | 0.49 × 0.32 × 0.10 mm |
| V = 865.8 (9) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX diffractometer | 3490 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: sealed tube | 2290 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.080 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 26.4°, θmin = 2.1° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2002) | h = −10→10 |
| Tmin = 0.847, Tmax = 0.966 | k = −12→12 |
| 5401 measured reflections | l = −13→14 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.061 | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| wR(F2) = 0.146 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.06 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0629P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3490 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 230 parameters | Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.51239 (14) | −0.17055 (10) | 0.41549 (10) | 0.0406 (3) | |
| S1 | 0.36004 (12) | 0.69686 (9) | 0.05276 (9) | 0.0269 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.2248 (3) | 0.3782 (2) | 0.3535 (2) | 0.0276 (6) | |
| N1 | 0.2744 (4) | 0.4535 (3) | 0.1434 (3) | 0.0213 (6) | |
| H1 | 0.364 (3) | 0.430 (3) | 0.078 (2) | 0.020 (9)* | |
| N2 | 0.0613 (3) | 0.6406 (3) | 0.2112 (3) | 0.0210 (6) | |
| C1 | 0.2248 (4) | 0.5945 (3) | 0.1413 (3) | 0.0210 (7) | |
| C2 | 0.0059 (4) | 0.7766 (4) | 0.2405 (3) | 0.0226 (7) | |
| C3 | −0.0764 (5) | 0.8908 (4) | 0.1661 (4) | 0.0330 (9) | |
| H3A | −0.0918 | 0.8827 | 0.0917 | 0.040* | |
| C4 | −0.1364 (5) | 1.0175 (4) | 0.2006 (5) | 0.0464 (11) | |
| H4A | −0.1930 | 1.0975 | 0.1494 | 0.056* | |
| C5 | −0.1154 (6) | 1.0291 (5) | 0.3079 (5) | 0.0506 (12) | |
| H5A | −0.1565 | 1.1169 | 0.3309 | 0.061* | |
| C6 | −0.0344 (6) | 0.9132 (5) | 0.3825 (4) | 0.0442 (11) | |
| H6A | −0.0227 | 0.9205 | 0.4582 | 0.053* | |
| C7 | 0.0294 (5) | 0.7869 (4) | 0.3478 (3) | 0.0322 (9) | |
| H7A | 0.0893 | 0.7075 | 0.3977 | 0.039* | |
| C8 | −0.0738 (4) | 0.5643 (3) | 0.2509 (3) | 0.0205 (7) | |
| C9 | −0.1246 (5) | 0.5352 (4) | 0.1618 (3) | 0.0288 (8) | |
| H9A | −0.0697 | 0.5650 | 0.0763 | 0.035* | |
| C10 | −0.2535 (5) | 0.4636 (4) | 0.1963 (4) | 0.0361 (9) | |
| H10A | −0.2869 | 0.4425 | 0.1349 | 0.043* | |
| C11 | −0.3350 (5) | 0.4219 (4) | 0.3204 (4) | 0.0337 (9) | |
| H11A | −0.4245 | 0.3720 | 0.3447 | 0.040* | |
| C12 | −0.2857 (5) | 0.4530 (4) | 0.4097 (3) | 0.0291 (8) | |
| H12A | −0.3416 | 0.4243 | 0.4952 | 0.035* | |
| C13 | −0.1559 (4) | 0.5254 (4) | 0.3744 (3) | 0.0249 (8) | |
| H13A | −0.1235 | 0.5483 | 0.4353 | 0.030* | |
| C14 | 0.2666 (4) | 0.3508 (4) | 0.2519 (3) | 0.0220 (7) | |
| C15 | 0.3130 (4) | 0.2074 (3) | 0.2337 (3) | 0.0213 (7) | |
| C16 | 0.3799 (4) | 0.0992 (3) | 0.3218 (3) | 0.0235 (8) | |
| H16A | 0.3953 | 0.1180 | 0.3917 | 0.028* | |
| C17 | 0.4235 (5) | −0.0348 (4) | 0.3077 (3) | 0.0279 (8) | |
| C18 | 0.3970 (5) | −0.0663 (4) | 0.2097 (3) | 0.0299 (9) | |
| H18A | 0.4264 | −0.1604 | 0.2021 | 0.036* | |
| C19 | 0.3273 (5) | 0.0413 (4) | 0.1234 (3) | 0.0314 (9) | |
| H19A | 0.3074 | 0.0213 | 0.0557 | 0.038* | |
| C20 | 0.2864 (5) | 0.1766 (4) | 0.1339 (3) | 0.0266 (8) | |
| H20A | 0.2397 | 0.2501 | 0.0731 | 0.032* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0544 (6) | 0.0299 (5) | 0.0360 (6) | −0.0082 (5) | −0.0165 (5) | −0.0022 (4) |
| S1 | 0.0276 (5) | 0.0304 (5) | 0.0239 (5) | −0.0124 (4) | 0.0013 (4) | −0.0112 (4) |
| O1 | 0.0352 (14) | 0.0317 (14) | 0.0189 (13) | −0.0047 (11) | −0.0097 (11) | −0.0103 (11) |
| N1 | 0.0228 (15) | 0.0256 (15) | 0.0138 (15) | −0.0063 (12) | 0.0024 (12) | −0.0093 (12) |
| N2 | 0.0231 (15) | 0.0244 (15) | 0.0165 (15) | −0.0072 (12) | −0.0029 (12) | −0.0068 (12) |
| C1 | 0.0242 (17) | 0.0299 (19) | 0.0124 (17) | −0.0077 (15) | −0.0065 (14) | −0.0065 (14) |
| C2 | 0.0220 (17) | 0.0281 (19) | 0.0188 (18) | −0.0098 (15) | −0.0006 (14) | −0.0079 (15) |
| C3 | 0.033 (2) | 0.034 (2) | 0.028 (2) | −0.0098 (18) | −0.0074 (17) | −0.0003 (17) |
| C4 | 0.031 (2) | 0.029 (2) | 0.064 (3) | −0.0037 (18) | −0.003 (2) | −0.002 (2) |
| C5 | 0.050 (3) | 0.039 (3) | 0.060 (3) | −0.019 (2) | 0.014 (2) | −0.029 (2) |
| C6 | 0.051 (3) | 0.054 (3) | 0.039 (3) | −0.027 (2) | 0.004 (2) | −0.028 (2) |
| C7 | 0.039 (2) | 0.037 (2) | 0.025 (2) | −0.0152 (18) | −0.0062 (17) | −0.0088 (17) |
| C8 | 0.0216 (17) | 0.0235 (17) | 0.0169 (18) | −0.0060 (14) | −0.0047 (14) | −0.0048 (14) |
| C9 | 0.0303 (19) | 0.043 (2) | 0.0161 (18) | −0.0148 (18) | −0.0026 (15) | −0.0084 (16) |
| C10 | 0.042 (2) | 0.045 (2) | 0.031 (2) | −0.0138 (19) | −0.0168 (19) | −0.0099 (19) |
| C11 | 0.028 (2) | 0.040 (2) | 0.038 (2) | −0.0171 (18) | −0.0115 (18) | −0.0034 (18) |
| C12 | 0.0247 (19) | 0.036 (2) | 0.022 (2) | −0.0082 (17) | −0.0016 (16) | −0.0041 (16) |
| C13 | 0.0244 (18) | 0.0297 (19) | 0.0222 (19) | −0.0059 (15) | −0.0062 (15) | −0.0086 (15) |
| C14 | 0.0164 (16) | 0.0313 (19) | 0.0201 (19) | −0.0070 (14) | −0.0038 (14) | −0.0077 (15) |
| C15 | 0.0192 (16) | 0.0293 (19) | 0.0173 (18) | −0.0104 (14) | 0.0000 (14) | −0.0082 (15) |
| C16 | 0.0228 (17) | 0.032 (2) | 0.0175 (18) | −0.0119 (15) | −0.0003 (14) | −0.0081 (15) |
| C17 | 0.0269 (18) | 0.031 (2) | 0.023 (2) | −0.0121 (17) | −0.0033 (15) | −0.0002 (16) |
| C18 | 0.034 (2) | 0.026 (2) | 0.035 (2) | −0.0126 (16) | −0.0063 (17) | −0.0135 (17) |
| C19 | 0.037 (2) | 0.038 (2) | 0.028 (2) | −0.0163 (18) | −0.0071 (18) | −0.0129 (18) |
| C20 | 0.0290 (19) | 0.032 (2) | 0.0213 (19) | −0.0114 (16) | −0.0076 (16) | −0.0045 (16) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—C17 | 1.730 (4) | C8—C9 | 1.382 (4) |
| S1—C1 | 1.659 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.366 (5) |
| O1—C14 | 1.216 (4) | C9—H9A | 0.9500 |
| N1—C1 | 1.380 (4) | C10—C11 | 1.379 (5) |
| N1—C14 | 1.388 (4) | C10—H10A | 0.9500 |
| N1—H1 | 0.894 (10) | C11—C12 | 1.387 (5) |
| N2—C1 | 1.336 (4) | C11—H11A | 0.9500 |
| N2—C8 | 1.437 (4) | C12—C13 | 1.378 (5) |
| N2—C2 | 1.442 (4) | C12—H12A | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.369 (5) | C13—H13A | 0.9500 |
| C2—C7 | 1.372 (5) | C14—C15 | 1.473 (5) |
| C3—C4 | 1.378 (5) | C15—C16 | 1.382 (5) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9500 | C15—C20 | 1.395 (4) |
| C4—C5 | 1.367 (6) | C16—C17 | 1.364 (5) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9500 | C16—H16A | 0.9500 |
| C5—C6 | 1.375 (6) | C17—C18 | 1.380 (5) |
| C5—H5A | 0.9500 | C18—C19 | 1.375 (5) |
| C6—C7 | 1.374 (5) | C18—H18A | 0.9500 |
| C6—H6A | 0.9500 | C19—C20 | 1.367 (5) |
| C7—H7A | 0.9500 | C19—H19A | 0.9500 |
| C8—C13 | 1.370 (5) | C20—H20A | 0.9500 |
| C1—N1—C14 | 123.6 (3) | C9—C10—C11 | 119.9 (3) |
| C1—N1—H1 | 114 (2) | C9—C10—H10A | 120.0 |
| C14—N1—H1 | 115 (2) | C11—C10—H10A | 120.0 |
| C1—N2—C8 | 122.0 (3) | C10—C11—C12 | 119.8 (3) |
| C1—N2—C2 | 121.4 (3) | C10—C11—H11A | 120.1 |
| C8—N2—C2 | 116.3 (3) | C12—C11—H11A | 120.1 |
| N2—C1—N1 | 115.3 (3) | C13—C12—C11 | 120.1 (3) |
| N2—C1—S1 | 123.8 (3) | C13—C12—H12A | 120.0 |
| N1—C1—S1 | 120.9 (3) | C11—C12—H12A | 120.0 |
| C3—C2—C7 | 121.0 (3) | C8—C13—C12 | 119.7 (3) |
| C3—C2—N2 | 120.6 (3) | C8—C13—H13A | 120.2 |
| C7—C2—N2 | 118.3 (3) | C12—C13—H13A | 120.2 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.0 (4) | O1—C14—N1 | 122.1 (3) |
| C2—C3—H3A | 120.5 | O1—C14—C15 | 123.2 (3) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 120.5 | N1—C14—C15 | 114.7 (3) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.6 (4) | C16—C15—C20 | 119.1 (3) |
| C5—C4—H4A | 119.7 | C16—C15—C14 | 118.1 (3) |
| C3—C4—H4A | 119.7 | C20—C15—C14 | 122.7 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.8 (4) | C17—C16—C15 | 119.5 (3) |
| C4—C5—H5A | 120.1 | C17—C16—H16A | 120.3 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 120.1 | C15—C16—H16A | 120.3 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 120.2 (4) | C16—C17—C18 | 121.8 (3) |
| C7—C6—H6A | 119.9 | C16—C17—Cl1 | 119.8 (3) |
| C5—C6—H6A | 119.9 | C18—C17—Cl1 | 118.4 (3) |
| C2—C7—C6 | 119.3 (4) | C19—C18—C17 | 118.6 (3) |
| C2—C7—H7A | 120.3 | C19—C18—H18A | 120.7 |
| C6—C7—H7A | 120.3 | C17—C18—H18A | 120.7 |
| C13—C8—C9 | 120.3 (3) | C20—C19—C18 | 120.7 (3) |
| C13—C8—N2 | 120.9 (3) | C20—C19—H19A | 119.7 |
| C9—C8—N2 | 118.7 (3) | C18—C19—H19A | 119.7 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 120.2 (3) | C19—C20—C15 | 120.3 (3) |
| C10—C9—H9A | 119.9 | C19—C20—H20A | 119.9 |
| C8—C9—H9A | 119.9 | C15—C20—H20A | 119.9 |
| C8—N2—C1—N1 | −20.3 (4) | N2—C8—C9—C10 | −179.6 (3) |
| C2—N2—C1—N1 | 166.0 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.9 (6) |
| C8—N2—C1—S1 | 157.6 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.1 (6) |
| C2—N2—C1—S1 | −16.2 (4) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.0 (6) |
| C14—N1—C1—N2 | −53.3 (4) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | 2.1 (5) |
| C14—N1—C1—S1 | 128.9 (3) | N2—C8—C13—C12 | 179.6 (3) |
| C1—N2—C2—C3 | 91.3 (4) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | −1.1 (5) |
| C8—N2—C2—C3 | −82.8 (4) | C1—N1—C14—O1 | −4.4 (5) |
| C1—N2—C2—C7 | −92.0 (4) | C1—N1—C14—C15 | 175.7 (3) |
| C8—N2—C2—C7 | 93.9 (4) | O1—C14—C15—C16 | −26.1 (5) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | −0.2 (5) | N1—C14—C15—C16 | 153.8 (3) |
| N2—C2—C3—C4 | 176.4 (3) | O1—C14—C15—C20 | 151.6 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.4 (6) | N1—C14—C15—C20 | −28.4 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.4 (6) | C20—C15—C16—C17 | 2.0 (5) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 1.8 (6) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 179.8 (3) |
| C3—C2—C7—C6 | 1.5 (5) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | −2.3 (5) |
| N2—C2—C7—C6 | −175.1 (3) | C15—C16—C17—Cl1 | 178.4 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—C2 | −2.3 (6) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | 1.1 (5) |
| C1—N2—C8—C13 | 123.8 (4) | Cl1—C17—C18—C19 | −179.7 (3) |
| C2—N2—C8—C13 | −62.2 (4) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | 0.5 (5) |
| C1—N2—C8—C9 | −58.6 (4) | C18—C19—C20—C15 | −0.8 (5) |
| C2—N2—C8—C9 | 115.4 (4) | C16—C15—C20—C19 | −0.5 (5) |
| C13—C8—C9—C10 | −2.0 (5) | C14—C15—C20—C19 | −178.2 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···S1i | 0.90 (2) | 2.48 (3) | 3.351 (4) | 162 (2) |
| C13—H13A···O1ii | 0.95 | 2.59 | 3.434 (5) | 148 |
| C18—H18A···S1iii | 0.95 | 2.87 | 3.609 (5) | 136 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z; (ii) −x, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) x, y−1, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BQ2121).
References
- Arslan, H., Flörke, U. & Külcü, N. (2003a). Acta Cryst. E59, o641–o642.
- Arslan, H., Flörke, U. & Külcü, N. (2003b). J. Chem. Crystallogr.33, 919–924.
- Arslan, H., Külcü, N. & Flörke, U. (2003c). Transition Met. Chem.28, 816–819.
- Bruker (2002). SMART, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Huebhr, O. F., Marsh, J. L., Mizzoni, R. H., Mull, R. P., Schroeder, D. C., Troxell, H. A. & Scholz, C. R. (1953). J. Am. Chem. Soc.75, 2274–2275.
- Khawar Rauf, M., Badshah, A. & Bolte, M. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o4296–o4298.
- Khawar Rauf, M., Bolte, M. & Badshah, A. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Koch, K. R. (2001). Coord. Chem. Rev.216, 473–488.
- Madan, V. K., Taneja, A. D. & Kudesia, V. P. (1991). J. Indian Chem. Soc.68, 471–472.
- Mansuroğlu, D. S., Arslan, H., Flörke, U. & Külcü, N. (2008). J. Coord. Chem.61, 3134–3146.
- Özer, C. K., Arslan, H., VanDerveer, D. & Binzet, G. (2009). J. Coord. Chem.62, 266–276.
- Schroeder, D. C. (1955). Chem. Rev.55, 181–228.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Uğur, D., Arslan, H. & Külcü, N. (2006). Russ. J. Coord. Chem.32, 669–675.
- Yamin, B. M. & Yusof, M. S. M. (2003). Acta Cryst. E59, o151–o152.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809001639/bq2121sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809001639/bq2121Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




