Abstract
The title compound, C16H11BrClN3, contains pairs of molecules lying about inversion centers linked by amino–pyrimidine N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds. The eight-membered rings thus formed are represented by the R 2 2(8) motif in graph-set notation. The second H atom of the amine group shows a rather weak interaction with two Br atoms, resulting in bifurcated N—H⋯(Br,Br) hydrogen bonds. The dihedral angles between the mean planes of the benzene rings and the mean plane of the heterocyclic ring are 8.98 (15) and 35.58 (10)°. The Br and Cl atoms show substitutional disorder, with site-occupancy factors of 0.599 (2) and 0.401 (2), respectively.
Related literature
For related structures, see: Bukhari et al. (2008 ▶); Fun et al. (2006 ▶); Gallagher et al. (2004 ▶). For pharmacological activities of pyrimidines, see: Gangjee et al. (1999 ▶); Grivsky et al. (1980 ▶); Malik et al. (2006 ▶); Rao et al. (2003 ▶). For graph-set notation, see: Bernstein et al. (1994 ▶).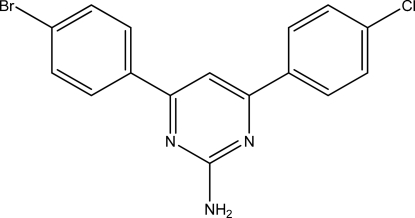
Experimental
Crystal data
C16H11BrClN3
M r = 360.64
Monoclinic,
a = 39.343 (8) Å
b = 3.851 (2) Å
c = 22.620 (6) Å
β = 123.81 (2)°
V = 2847.6 (18) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 3.07 mm−1
T = 173 (2) K
0.20 × 0.03 × 0.02 mm
Data collection
Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SORTAV; Blessing, 1997 ▶) T min = 0.579, T max = 0.941
8088 measured reflections
2589 independent reflections
1944 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.048
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.039
wR(F 2) = 0.094
S = 1.05
2589 reflections
203 parameters
4 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.58 e Å−3
Data collection: COLLECT (Hooft, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: DENZO (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); data reduction: SCALEPACK (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809002748/fj2180sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809002748/fj2180Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N3—H3A⋯Br1i | 0.92 (4) | 2.97 (4) | 3.803 (4) | 153 (3) |
| N3—H3A⋯Br1ii | 0.92 (4) | 3.11 (4) | 3.540 (4) | 111 (3) |
| N3—H3B⋯N2iii | 0.80 (4) | 2.28 (5) | 3.073 (5) | 174 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii) 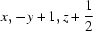 ; (iii)
; (iii) 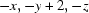 .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Pyrimidines are a class of biologically active compounds having utility in the pharmaceutical and the agrochemical industries. Compounds with the ring system show pharmacological activity such as antitumor (Gangjee et al., 1999; Grivsky et al., 1980), antiviral (Rao et al., 2003), anti-HIV (Malik et al., 2006), etc. In continuation of our research work (Bukhari et al., 2008), we have prepared several pyrimidines. In this article, we report the crystal structure of the title compound, (I).
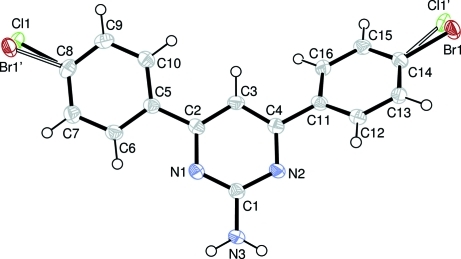
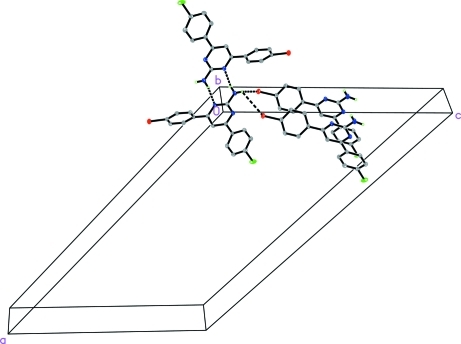
The structure of (I), (Fig. 1), contains dimeric pairs of molecules lying about inversion centers resulting from N3—H3B···N2iii hydrogen bonds (N3···N2 = 3.071 (5) Å; Table 1 and Fig. 2). The 8-membered rings thus formed represent R22(8) motif in the graph set notation (Bernstein et al., 1994). The second H-atom of the amine, N3A, shows rather week interactions with two Br atoms representing bifurcated hydrogen bonds (H3A···Br1 2.97 (4) and 3.11 (4) Å). The mean-planes of the two phenyl rings, C5—C10 and C11—C16, are oriented with respect to the mean-plane of the heterocyclic ring at 8.98 (15) and 35.58 (10)°, respectively. The molecular dimensions in (I) agree with the corresponding molecular dimensions reported for 4,6-(diphenyl)pyrimidin-2-amine (Gallagher et al., 2004; Fun et al., 2006). The structure is devoid of any C—H···π(arene) contacts observed in the structures reported above.
Experimental
The title compound was synthesized by the procedure reported earlier (Bukhari et al., 2008). Crystals of (I) suitable for crystallographic analysis were grown by slow evaporation at 313 K from a solutuion of CHCl3 (Yield 58%; m.p. 512–514 K).
Refinement
The Br and Cl atoms showed substitutional disorder with site occupancy factors refined for Br1 and Cl1 to 0.559 (2) and Br1' and Cl1' to 0.401 (2) values. C—Cl and C—Br distances were constrained using DFIX command in SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008). Though all the H atoms could be distinguished in the difference Fourier map the H-atoms bonded to C-atoms were included at geometrically idealized positions and refined in riding-model approximation with the following constraints: C—H distances were set to 0.95 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). H-atoms bonded to N3 were taken from the difference map and were allowed to refine with Uiso = 1.2 times Ueq of the parent atom. The final difference map was free of any chemically significant features.
Figures
Fig. 1.
ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997) drawing of (I) with displacement ellipsoids plotted at 50% probability level. Hollow bonds represent smaller fractions of the disordered Br and Cl atoms (Br1 and Cl1, respectively).
Fig. 2.
Unit cell packing of (I) showing hydrogen bonds with dashed lines; H-atoms not involved in H-bonds have been omitted.
Crystal data
| C16H11BrClN3 | F(000) = 1440 |
| Mr = 360.64 | Dx = 1.682 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -C 2yc | Cell parameters from 8088 reflections |
| a = 39.343 (8) Å | θ = 3.1–25.3° |
| b = 3.851 (2) Å | µ = 3.07 mm−1 |
| c = 22.620 (6) Å | T = 173 K |
| β = 123.81 (2)° | Needle, colorless |
| V = 2847.6 (18) Å3 | 0.20 × 0.03 × 0.02 mm |
| Z = 8 |
Data collection
| Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer | 2589 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1944 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.048 |
| ω and φ scans | θmax = 25.3°, θmin = 3.1° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SORTAV; Blessing, 1997) | h = −46→45 |
| Tmin = 0.579, Tmax = 0.941 | k = −4→4 |
| 8088 measured reflections | l = −26→26 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.039 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.094 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0319P)2 + 9.7534P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2589 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 203 parameters | Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3 |
| 4 restraints | Δρmin = −0.58 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| Br1 | 0.07275 (3) | 0.3788 (4) | −0.23596 (6) | 0.0284 (2) | 0.599 (2) |
| Cl1 | 0.28850 (8) | 0.8754 (7) | 0.45607 (13) | 0.0257 (5) | 0.599 (2) |
| Br1' | 0.28731 (6) | 0.8681 (5) | 0.47100 (9) | 0.0284 (2) | 0.401 (2) |
| Cl1' | 0.08059 (14) | 0.3789 (17) | −0.2222 (2) | 0.0257 (5) | 0.401 (2) |
| N1 | 0.09743 (9) | 0.9631 (7) | 0.16544 (15) | 0.0239 (6) | |
| N2 | 0.05683 (9) | 0.8645 (8) | 0.03909 (15) | 0.0231 (6) | |
| N3 | 0.02841 (10) | 1.0562 (9) | 0.09907 (18) | 0.0302 (8) | |
| H3A | 0.0318 (12) | 1.151 (11) | 0.139 (2) | 0.036* | |
| H3B | 0.0070 (14) | 1.073 (11) | 0.061 (2) | 0.036* | |
| C1 | 0.06220 (11) | 0.9592 (9) | 0.10129 (18) | 0.0239 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.13100 (11) | 0.8621 (9) | 0.16862 (18) | 0.0223 (7) | |
| C3 | 0.12903 (11) | 0.7667 (9) | 0.10744 (18) | 0.0249 (8) | |
| H3 | 0.1529 | 0.6995 | 0.1095 | 0.030* | |
| C4 | 0.09094 (11) | 0.7729 (9) | 0.04318 (18) | 0.0223 (8) | |
| C5 | 0.16972 (10) | 0.8644 (9) | 0.24074 (18) | 0.0233 (7) | |
| C6 | 0.17017 (11) | 1.0069 (9) | 0.29802 (19) | 0.0261 (8) | |
| H6 | 0.1458 | 1.1041 | 0.2901 | 0.031* | |
| C7 | 0.20533 (11) | 1.0093 (10) | 0.3658 (2) | 0.0291 (8) | |
| H7 | 0.2053 | 1.1065 | 0.4044 | 0.035* | |
| C8 | 0.24065 (9) | 0.8673 (10) | 0.37647 (15) | 0.0283 (8) | |
| C9 | 0.24130 (11) | 0.7212 (10) | 0.3213 (2) | 0.0294 (8) | |
| H9 | 0.2658 | 0.6224 | 0.3297 | 0.035* | |
| C10 | 0.20581 (11) | 0.7210 (9) | 0.25364 (19) | 0.0267 (8) | |
| H10 | 0.2060 | 0.6216 | 0.2154 | 0.032* | |
| C11 | 0.08642 (11) | 0.6800 (9) | −0.02477 (18) | 0.0233 (8) | |
| C12 | 0.05169 (11) | 0.5079 (9) | −0.07802 (19) | 0.0244 (8) | |
| H12 | 0.0308 | 0.4484 | −0.0708 | 0.029* | |
| C13 | 0.04712 (11) | 0.4215 (9) | −0.14167 (18) | 0.0245 (8) | |
| H13 | 0.0233 | 0.3047 | −0.1782 | 0.029* | |
| C14 | 0.07789 (11) | 0.5087 (9) | −0.15093 (16) | 0.0239 (8) | |
| C15 | 0.11279 (11) | 0.6792 (9) | −0.09883 (19) | 0.0270 (8) | |
| H15 | 0.1336 | 0.7372 | −0.1062 | 0.032* | |
| C16 | 0.11689 (11) | 0.7644 (9) | −0.03569 (19) | 0.0255 (8) | |
| H16 | 0.1408 | 0.8818 | 0.0006 | 0.031* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.0312 (5) | 0.0367 (4) | 0.0141 (5) | 0.0009 (4) | 0.0106 (4) | −0.0020 (4) |
| Cl1 | 0.0220 (8) | 0.0441 (11) | 0.0050 (9) | 0.0017 (7) | 0.0039 (7) | −0.0014 (7) |
| Br1' | 0.0312 (5) | 0.0367 (4) | 0.0141 (5) | 0.0009 (4) | 0.0106 (4) | −0.0020 (4) |
| Cl1' | 0.0220 (8) | 0.0441 (11) | 0.0050 (9) | 0.0017 (7) | 0.0039 (7) | −0.0014 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0256 (16) | 0.0279 (16) | 0.0216 (14) | 0.0007 (13) | 0.0152 (13) | 0.0007 (12) |
| N2 | 0.0241 (15) | 0.0273 (15) | 0.0228 (14) | 0.0024 (13) | 0.0161 (13) | 0.0015 (13) |
| N3 | 0.0247 (16) | 0.045 (2) | 0.0243 (16) | 0.0089 (16) | 0.0157 (14) | 0.0010 (16) |
| C1 | 0.0259 (18) | 0.0262 (19) | 0.0234 (18) | 0.0024 (15) | 0.0161 (16) | 0.0030 (15) |
| C2 | 0.0280 (19) | 0.0195 (17) | 0.0249 (18) | 0.0003 (15) | 0.0181 (16) | 0.0022 (15) |
| C3 | 0.0226 (18) | 0.0301 (19) | 0.0265 (19) | 0.0036 (15) | 0.0164 (17) | 0.0014 (15) |
| C4 | 0.0260 (19) | 0.0199 (17) | 0.0246 (18) | 0.0010 (14) | 0.0163 (17) | 0.0034 (14) |
| C5 | 0.0240 (18) | 0.0244 (18) | 0.0250 (18) | 0.0002 (16) | 0.0159 (16) | 0.0019 (15) |
| C6 | 0.0246 (19) | 0.0292 (19) | 0.0298 (19) | 0.0010 (15) | 0.0184 (17) | 0.0011 (16) |
| C7 | 0.029 (2) | 0.030 (2) | 0.0274 (19) | −0.0011 (16) | 0.0154 (17) | −0.0020 (16) |
| C8 | 0.0229 (19) | 0.0275 (19) | 0.0270 (19) | −0.0033 (16) | 0.0092 (16) | 0.0027 (16) |
| C9 | 0.0251 (19) | 0.030 (2) | 0.035 (2) | 0.0061 (16) | 0.0181 (18) | 0.0052 (16) |
| C10 | 0.029 (2) | 0.029 (2) | 0.0276 (19) | −0.0001 (16) | 0.0193 (18) | 0.0004 (15) |
| C11 | 0.0275 (19) | 0.0218 (19) | 0.0251 (18) | 0.0054 (15) | 0.0173 (16) | 0.0033 (14) |
| C12 | 0.0262 (19) | 0.0240 (18) | 0.0267 (18) | 0.0029 (15) | 0.0169 (17) | 0.0010 (15) |
| C13 | 0.0237 (18) | 0.0240 (19) | 0.0229 (17) | 0.0021 (15) | 0.0112 (16) | −0.0009 (15) |
| C14 | 0.032 (2) | 0.0217 (17) | 0.0219 (17) | 0.0064 (15) | 0.0171 (17) | 0.0043 (14) |
| C15 | 0.0261 (19) | 0.033 (2) | 0.0278 (19) | 0.0024 (16) | 0.0190 (17) | 0.0043 (16) |
| C16 | 0.0233 (18) | 0.030 (2) | 0.0228 (18) | 0.0000 (16) | 0.0126 (16) | −0.0004 (15) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Br1—C14 | 1.886 (3) | C6—C7 | 1.380 (5) |
| Cl1—C8 | 1.736 (3) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| Br1'—C8 | 1.891 (3) | C7—C8 | 1.384 (5) |
| Cl1'—C14 | 1.746 (4) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C1 | 1.337 (5) | C8—C9 | 1.382 (5) |
| N1—C2 | 1.340 (4) | C9—C10 | 1.384 (5) |
| N2—C4 | 1.340 (4) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C1 | 1.352 (4) | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| N3—C1 | 1.354 (4) | C11—C12 | 1.388 (5) |
| N3—H3A | 0.92 (4) | C11—C16 | 1.391 (5) |
| N3—H3B | 0.80 (4) | C12—C13 | 1.388 (5) |
| C2—C3 | 1.392 (5) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C5 | 1.489 (5) | C13—C14 | 1.380 (5) |
| C3—C4 | 1.391 (5) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C14—C15 | 1.380 (5) |
| C4—C11 | 1.489 (5) | C15—C16 | 1.385 (5) |
| C5—C10 | 1.395 (5) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C5—C6 | 1.398 (5) | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| C1—N1—C2 | 116.8 (3) | C9—C8—Br1' | 121.8 (3) |
| C4—N2—C1 | 115.4 (3) | C7—C8—Br1' | 116.4 (3) |
| C1—N3—H3A | 118 (3) | C10—C9—C8 | 119.0 (3) |
| C1—N3—H3B | 119 (3) | C10—C9—H9 | 120.5 |
| H3A—N3—H3B | 121 (4) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.5 |
| N1—C1—N2 | 126.8 (3) | C9—C10—C5 | 121.0 (3) |
| N1—C1—N3 | 116.1 (3) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.5 |
| N2—C1—N3 | 117.0 (3) | C5—C10—H10 | 119.5 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 121.0 (3) | C12—C11—C16 | 119.2 (3) |
| N1—C2—C5 | 115.7 (3) | C12—C11—C4 | 120.3 (3) |
| C3—C2—C5 | 123.2 (3) | C16—C11—C4 | 120.5 (3) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 117.8 (3) | C11—C12—C13 | 120.8 (3) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 121.1 | C11—C12—H12 | 119.6 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 121.1 | C13—C12—H12 | 119.6 |
| N2—C4—C3 | 122.1 (3) | C14—C13—C12 | 118.7 (3) |
| N2—C4—C11 | 116.9 (3) | C14—C13—H13 | 120.6 |
| C3—C4—C11 | 121.0 (3) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.6 |
| C10—C5—C6 | 118.4 (3) | C13—C14—C15 | 121.8 (3) |
| C10—C5—C2 | 121.9 (3) | C13—C14—Cl1' | 125.4 (3) |
| C6—C5—C2 | 119.7 (3) | C15—C14—Cl1' | 112.4 (3) |
| C7—C6—C5 | 121.4 (3) | C13—C14—Br1 | 119.0 (3) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 119.3 | C15—C14—Br1 | 119.2 (3) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.3 | C14—C15—C16 | 118.9 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 118.6 (3) | C14—C15—H15 | 120.6 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 120.7 | C16—C15—H15 | 120.6 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 120.7 | C15—C16—C11 | 120.7 (3) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 121.7 (3) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.6 |
| C9—C8—Cl1 | 112.9 (3) | C11—C16—H16 | 119.6 |
| C7—C8—Cl1 | 125.3 (3) | ||
| C2—N1—C1—N2 | −0.1 (5) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.8 (6) |
| C2—N1—C1—N3 | 178.9 (3) | Cl1—C8—C9—C10 | −175.4 (3) |
| C4—N2—C1—N1 | −1.5 (5) | Br1'—C8—C9—C10 | 178.3 (3) |
| C4—N2—C1—N3 | 179.5 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C5 | −0.2 (6) |
| C1—N1—C2—C3 | 1.5 (5) | C6—C5—C10—C9 | −0.4 (5) |
| C1—N1—C2—C5 | −179.2 (3) | C2—C5—C10—C9 | −179.0 (3) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.3 (5) | N2—C4—C11—C12 | −35.5 (5) |
| C5—C2—C3—C4 | 179.5 (3) | C3—C4—C11—C12 | 145.1 (4) |
| C1—N2—C4—C3 | 1.7 (5) | N2—C4—C11—C16 | 144.5 (3) |
| C1—N2—C4—C11 | −177.7 (3) | C3—C4—C11—C16 | −34.9 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—N2 | −0.4 (5) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | −0.3 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—C11 | 179.0 (3) | C4—C11—C12—C13 | 179.7 (3) |
| N1—C2—C5—C10 | 170.9 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.3 (5) |
| C3—C2—C5—C10 | −9.9 (5) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.2 (5) |
| N1—C2—C5—C6 | −7.7 (5) | C12—C13—C14—Cl1' | 172.1 (4) |
| C3—C2—C5—C6 | 171.5 (3) | C12—C13—C14—Br1 | 177.9 (3) |
| C10—C5—C6—C7 | 0.4 (5) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.0 (5) |
| C2—C5—C6—C7 | 179.1 (3) | Cl1'—C14—C15—C16 | −173.1 (4) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 0.1 (5) | Br1—C14—C15—C16 | −178.1 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −0.7 (6) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | 0.0 (5) |
| C6—C7—C8—Cl1 | 174.9 (3) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | 0.1 (5) |
| C6—C7—C8—Br1' | −178.4 (3) | C4—C11—C16—C15 | −179.9 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N3—H3A···Br1i | 0.92 (4) | 2.97 (4) | 3.803 (4) | 153 (3) |
| N3—H3A···Br1ii | 0.92 (4) | 3.11 (4) | 3.540 (4) | 111 (3) |
| N3—H3B···N2iii | 0.80 (4) | 2.28 (5) | 3.073 (5) | 174 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+2, z+1/2; (ii) x, −y+1, z+1/2; (iii) −x, −y+2, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: FJ2180).
References
- Bernstein, J., Etter, M. C. & Leiserowitz, L. (1994). Structure Correlation, edited by H.-B. Bürgi & J. D. Dunitz, Vol. 2, pp. 431–507. New York: VCH.
- Blessing, R. H. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 421–426.
- Bukhari, M. H., Siddiqui, H. L., Chaudhary, M. A., Hussain, T. & Parvez, M. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Fun, H.-K., Goswami, S., Jana, S. & Chantrapromma, S. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o5332–o5334.
- Gallagher, J. F., Goswami, S., Chatterjee, B., Jana, S. & Dutta, K. (2004). Acta Cryst. C60, o229–o231. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gangjee, A., Aldair, O. & Queener, S. F. (1999). J. Med. Chem.42, 2447–2455. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Grivsky, E. D., Lee, S., Sigel, C. W., Duch, D. S. & Nichol, C. A. (1980). J. Med. Chem.23, 227–229. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Hooft, R. (1998). COLLECT Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Malik, V., Singh, P. & Kumar, S. (2006). Tetrahedron, 62, 5944–5951.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Rao, M. S., Ehso, N., Sergeant, C. & Dembinski, R. (2003). J. Org. Chem.68, 6788–6790. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809002748/fj2180sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809002748/fj2180Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report