Abstract
In the title compound, C19H12Cl2N2O5S3, the benzene rings of the chlorophenylsulfonyl groups form a dihedral angle of 35.85 (8)° and are inclined at angles of 23.51 (6) and 59.22 (6)° with respect to the essentially planar benzisothiazole ring system [maximum deviation = 0.030 (2) Å]. The molecular conformation is stabilized by an intramolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bond. In the crystal packing, molecules are linked into chains parallel to the a axis by intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and π–π stacking interactions, with centroid–centroid distances of 3.592 (5) Å.
Related literature
For the synthesis and biological activity of 1,2-benzisothiazol-3(2H)-ones and 2-amino-1,2-benzisothiazol-3(2H)-one derivatives, see: Clerici et al. (2007 ▶); Siegemund et al. (2002 ▶); Vicini et al. (1997 ▶). For the synthesis of the title compound, see: Vicini et al. (2009 ▶). For the crystal structures of related benzisothiazole compounds, see: Cavalca et al. (1970 ▶); Ranganathan et al. (2002 ▶); Steinfeld & Kersting (2006 ▶); Kim et al. (1996 ▶); Xu et al. (2006 ▶); Sarma & Mugesh (2007 ▶); Kolberg et al. (1999 ▶).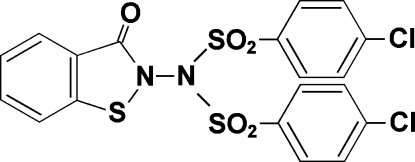
Experimental
Crystal data
C19H12Cl2N2O5S3
M r = 515.39
Triclinic,

a = 9.5358 (12) Å
b = 10.7757 (14) Å
c = 11.0393 (14) Å
α = 102.719 (2)°
β = 94.385 (3)°
γ = 105.598 (2)°
V = 1054.6 (2) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.64 mm−1
T = 295 (2) K
0.22 × 0.14 × 0.12 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART 1000 CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 1997 ▶) T min = 0.872, T max = 0.927
10953 measured reflections
3930 independent reflections
2267 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.037
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.035
wR(F 2) = 0.060
S = 0.94
3930 reflections
280 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 1997 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 1997 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR97 (Altomare et al., 1999 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and SCHAKAL (Keller, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and PARST95 (Nardelli, 1995 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809003195/lh2763sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809003195/lh2763Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C13—H13⋯O1 | 0.93 | 2.42 | 3.275 (4) | 153 |
| C5—H5⋯O2i | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.353 (4) | 140 |
| C6—H6⋯O3ii | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.289 (3) | 133 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the Italian MIUR (Ministero dell’Istruzione, dell’Universitá e della Ricerca) is gratefully acknowledged.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Among 1,2-benzisothiazol-3(2H)-ones, a class of compounds with a wide spectrum of biological activities (Clerici et al., 2007; Siegemund et al., 2002), 2-amino-1,2-benzisothiazol-3(2H)-one derivatives have a rather recent history and 2-amino-1,2-benzisothiazol-3(2H)-one was first synthesized by our group in 1997 (Vicini et al., 1997). Due to their peculiar reactivity, 2-amino-1,2-benzisothiazol-3(2H)-one derivatives have recently emerged as effective antiplatelet, spasmolytic and antimicrobial agents (Clerici et al., 2007; Siegemund et al., 2002). The therapeutic significance of the 2-amino-1,2-benzisothiazol-3(2H)-one ring system with suitably functionalized substituents has encorauged us to develop novel compounds. The title compound was obtained unintentionally as a by-product during the synthesis of 2-(benzenesulfonyl)amino-1,2-benzisothiazol-3(2H)-ones that have been demonstrated to possess anti-HIV-1 activity against wild type virus and against viral strains carrying clinically relevant mutations (Vicini et al., 2008). The unexpected 2-(bisphenylsulfonyl)amino-1,2-benzisothiazol-3(2H)-ones, subjected to biological evaluation as well, resulted fairly active and, interestingly, endowed with lower cytotoxicity with respect to their monophenylsulfonyl substituted counterparts. In view of the structure-activity relationship study of the novel 1,2-benzisothiazol-3(2H)-one benzenesulfonamides aimed at optimizing their antiretroviral potency, the representative title compound was synthesized and its crystal structure is reported here.
The molecular structure of the title compound is shown in Fig. 1. The bond lengths and angles are unexceptional. The S1—N1 and S1—C7 bond distances within the benzoisothiazole ring system are 1.7347 (19) and 1.744 (2) Å respectively, in good agreement with those reported is related compounds (Cavalca et al., 1970; Ranganathan et al., 2002; Steinfeld & Kersting, 2006; Kim et al., 1996; Xu et al., 2006; Sarma & Mugesh, 2007). The N1—N2 bond distance (1.381 (2) Å) is not significantly different from the corresponding distance in 4,5-dimethyl-2-(3-nitrobenzenesulfonylamino)isothiazol-3(2H)-one 1,1-dioxide (1.387 (4) Å; Kolberg et al., 1999). The C8–C13 and C14–C19 benzene rings form a dihedral angle of 35.85 (8)° and are tilted by 23.51 (6) and 59.22 (6)° with respect to the essentially planar benzoisothiazole rings system (maximum deviation 0.030 (2) Å for atom N1). The molecular structure is stabilized by an intramolecular C—H···O hydrogen bond (Table 1). In the crystal packing (Fig. 2), molecules are linked into chains running parallel to the a axis by intermolecular C—H···O hydrogen interactions (Table 1) and π-π stacking interactions occurring between the benzene rings of centrosymmetrically related benzisothiazole rings, with a centroid-to-centroid separation of 3.592 (5) Å, a perpendicular interplanar distance of 3.514 (5) Å and a centroid-centroid offset of 0.746 (4) Å (symmetry code linking the adjacent rings: 1 - x, -y, 1 - z).
Experimental
The title compound was synthesized by reaction of 2-amino-1,2-benzisothiazol-3(2H)-one (10 mmol) with 4-chlorobenzenesulfonyl chloride (11 mmol) in pyridine (8 ml) for 2 h at 273K, resulting in a mixture of 4-chloro-N-(3-oxo-1,2-benzisothiazol-2(3H)-yl)benzenesulfonamide and 4-chloro-N-[(4-chlorophenyl)sulfonyl]-N-(3-oxo-1,2-benzisothiazol-2(3H)-yl)benzenesulfonamide (% yield ratio 33/66). Indeed, once the monophenylsulfonyl product is formed, a subsequent sulfonylation yielding the bisphenylsulfonyl derivative readily occurs, by the action of the electrophilic benzenesulfonyl chloride. The two products were simply separated because of the acidic character of the former. The crude product was poured into water (30 ml) and treated with a 10% aqueous sodium carbonate under stirring for 1 h, affording the title compound as insoluble solid that was collected by filtration. Pale yellow crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained on slow evaporation of an ethanol solution at room temperature.
Refinement
All H atoms were placed at calculated positions and refined in the riding model approximation, with C—H = 0.93 Å, and with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Crystal packing of the title compound viewed approximately along the a axis. Red and green dashed lines indicate C–H···O hydrogen bonds and π-π stacking interactions, respectively.
Crystal data
| C19H12Cl2N2O5S3 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 515.39 | F(000) = 524 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.623 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.5358 (12) Å | Cell parameters from 1477 reflections |
| b = 10.7757 (14) Å | θ = 4.8–47.8° |
| c = 11.0393 (14) Å | µ = 0.64 mm−1 |
| α = 102.719 (2)° | T = 295 K |
| β = 94.385 (3)° | Prism, pale yellow |
| γ = 105.598 (2)° | 0.22 × 0.14 × 0.12 mm |
| V = 1054.6 (2) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART 1000 CCD area-detector diffractometer | 3930 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2267 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.037 |
| ω scans | θmax = 25.5°, θmin = 1.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 1997) | h = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.872, Tmax = 0.927 | k = −13→13 |
| 10953 measured reflections | l = −13→13 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.035 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.060 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 0.94 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0145P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3930 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 280 parameters | Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.30528 (10) | 0.89637 (7) | 0.94340 (8) | 0.0862 (3) | |
| Cl2 | 0.37123 (10) | 0.47508 (9) | 1.37354 (8) | 0.1051 (3) | |
| S1 | 0.13674 (7) | −0.02399 (6) | 0.62308 (7) | 0.0550 (2) | |
| S2 | 0.14511 (8) | 0.31023 (7) | 0.62932 (7) | 0.0539 (2) | |
| S3 | 0.01047 (7) | 0.21135 (7) | 0.84324 (7) | 0.0515 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.43050 (18) | 0.27563 (17) | 0.83915 (17) | 0.0630 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.2660 (2) | 0.28393 (17) | 0.57181 (16) | 0.0677 (5) | |
| O3 | 0.00450 (19) | 0.27802 (16) | 0.55643 (16) | 0.0687 (6) | |
| O4 | −0.07297 (17) | 0.29573 (16) | 0.81554 (16) | 0.0605 (5) | |
| O5 | −0.05678 (18) | 0.07361 (16) | 0.83264 (17) | 0.0639 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.2112 (2) | 0.12783 (18) | 0.73222 (19) | 0.0501 (6) | |
| N2 | 0.1337 (2) | 0.22006 (18) | 0.74166 (18) | 0.0476 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.3647 (3) | 0.1683 (3) | 0.7692 (2) | 0.0478 (7) | |
| C2 | 0.4188 (3) | 0.0593 (2) | 0.7077 (2) | 0.0451 (6) | |
| C3 | 0.5641 (3) | 0.0591 (3) | 0.7197 (2) | 0.0554 (7) | |
| H3 | 0.6367 | 0.1309 | 0.7718 | 0.066* | |
| C4 | 0.5991 (3) | −0.0492 (3) | 0.6532 (3) | 0.0654 (8) | |
| H4 | 0.6964 | −0.0507 | 0.6600 | 0.078* | |
| C5 | 0.4911 (3) | −0.1560 (3) | 0.5762 (3) | 0.0638 (8) | |
| H5 | 0.5174 | −0.2288 | 0.5330 | 0.077* | |
| C6 | 0.3462 (3) | −0.1582 (3) | 0.5614 (2) | 0.0575 (7) | |
| H6 | 0.2744 | −0.2306 | 0.5090 | 0.069* | |
| C7 | 0.3110 (3) | −0.0472 (2) | 0.6283 (2) | 0.0462 (6) | |
| C8 | 0.1916 (3) | 0.4758 (2) | 0.7178 (2) | 0.0477 (7) | |
| C9 | 0.0978 (3) | 0.5504 (3) | 0.7018 (2) | 0.0560 (7) | |
| H9 | 0.0109 | 0.5132 | 0.6456 | 0.067* | |
| C10 | 0.1350 (3) | 0.6819 (3) | 0.7707 (3) | 0.0611 (8) | |
| H10 | 0.0739 | 0.7342 | 0.7603 | 0.073* | |
| C11 | 0.2626 (3) | 0.7341 (2) | 0.8544 (2) | 0.0561 (7) | |
| C12 | 0.3557 (3) | 0.6602 (3) | 0.8706 (3) | 0.0657 (8) | |
| H12 | 0.4419 | 0.6976 | 0.9275 | 0.079* | |
| C13 | 0.3203 (3) | 0.5293 (3) | 0.8017 (3) | 0.0614 (8) | |
| H13 | 0.3826 | 0.4779 | 0.8117 | 0.074* | |
| C14 | 0.1174 (2) | 0.2839 (2) | 0.9908 (2) | 0.0450 (6) | |
| C15 | 0.1572 (3) | 0.2053 (3) | 1.0622 (3) | 0.0630 (8) | |
| H15 | 0.1308 | 0.1134 | 1.0312 | 0.076* | |
| C16 | 0.2365 (3) | 0.2648 (3) | 1.1799 (3) | 0.0772 (9) | |
| H16 | 0.2630 | 0.2130 | 1.2295 | 0.093* | |
| C17 | 0.2764 (3) | 0.4011 (3) | 1.2242 (3) | 0.0632 (8) | |
| C18 | 0.2397 (3) | 0.4797 (3) | 1.1525 (3) | 0.0593 (8) | |
| H18 | 0.2694 | 0.5718 | 1.1826 | 0.071* | |
| C19 | 0.1583 (3) | 0.4206 (2) | 1.0355 (3) | 0.0531 (7) | |
| H19 | 0.1309 | 0.4726 | 0.9866 | 0.064* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.1137 (7) | 0.0495 (5) | 0.0768 (6) | 0.0059 (4) | 0.0144 (5) | −0.0001 (4) |
| Cl2 | 0.1116 (7) | 0.1090 (7) | 0.0712 (6) | 0.0070 (6) | −0.0208 (5) | 0.0175 (5) |
| S1 | 0.0427 (4) | 0.0480 (4) | 0.0663 (5) | 0.0159 (3) | −0.0044 (4) | −0.0012 (4) |
| S2 | 0.0533 (5) | 0.0505 (5) | 0.0519 (5) | 0.0148 (4) | 0.0004 (4) | 0.0035 (4) |
| S3 | 0.0382 (4) | 0.0465 (4) | 0.0652 (5) | 0.0107 (3) | 0.0072 (4) | 0.0067 (4) |
| O1 | 0.0498 (11) | 0.0554 (12) | 0.0689 (13) | 0.0092 (10) | −0.0101 (10) | −0.0007 (10) |
| O2 | 0.0727 (13) | 0.0704 (13) | 0.0658 (13) | 0.0290 (11) | 0.0304 (11) | 0.0121 (10) |
| O3 | 0.0659 (12) | 0.0604 (12) | 0.0646 (13) | 0.0196 (10) | −0.0240 (10) | −0.0055 (10) |
| O4 | 0.0441 (10) | 0.0671 (12) | 0.0743 (13) | 0.0273 (10) | 0.0043 (9) | 0.0136 (10) |
| O5 | 0.0517 (11) | 0.0423 (11) | 0.0842 (14) | −0.0009 (9) | 0.0102 (10) | 0.0064 (10) |
| N1 | 0.0398 (13) | 0.0440 (13) | 0.0617 (15) | 0.0170 (11) | 0.0009 (11) | −0.0002 (11) |
| N2 | 0.0433 (12) | 0.0427 (13) | 0.0591 (14) | 0.0168 (10) | 0.0119 (11) | 0.0108 (11) |
| C1 | 0.0416 (16) | 0.0511 (18) | 0.0499 (18) | 0.0127 (14) | 0.0007 (14) | 0.0139 (14) |
| C2 | 0.0411 (16) | 0.0508 (17) | 0.0444 (17) | 0.0155 (14) | 0.0053 (13) | 0.0119 (13) |
| C3 | 0.0402 (16) | 0.0617 (19) | 0.068 (2) | 0.0166 (14) | 0.0050 (15) | 0.0228 (16) |
| C4 | 0.0469 (18) | 0.081 (2) | 0.086 (2) | 0.0333 (18) | 0.0151 (17) | 0.0384 (19) |
| C5 | 0.065 (2) | 0.067 (2) | 0.072 (2) | 0.0377 (18) | 0.0179 (18) | 0.0175 (17) |
| C6 | 0.0581 (19) | 0.0574 (19) | 0.0596 (19) | 0.0262 (15) | 0.0077 (15) | 0.0086 (15) |
| C7 | 0.0459 (16) | 0.0517 (17) | 0.0457 (17) | 0.0204 (14) | 0.0083 (14) | 0.0136 (14) |
| C8 | 0.0442 (16) | 0.0445 (16) | 0.0512 (17) | 0.0087 (13) | 0.0069 (14) | 0.0111 (13) |
| C9 | 0.0483 (17) | 0.0503 (18) | 0.065 (2) | 0.0112 (14) | 0.0023 (15) | 0.0121 (15) |
| C10 | 0.0604 (19) | 0.0529 (19) | 0.071 (2) | 0.0164 (16) | 0.0114 (17) | 0.0163 (16) |
| C11 | 0.0647 (19) | 0.0431 (17) | 0.0545 (19) | 0.0032 (15) | 0.0185 (16) | 0.0121 (14) |
| C12 | 0.0598 (19) | 0.056 (2) | 0.064 (2) | 0.0015 (16) | −0.0087 (16) | 0.0054 (16) |
| C13 | 0.0516 (17) | 0.0563 (19) | 0.071 (2) | 0.0160 (15) | −0.0043 (16) | 0.0104 (16) |
| C14 | 0.0384 (15) | 0.0426 (16) | 0.0527 (17) | 0.0126 (13) | 0.0082 (13) | 0.0080 (14) |
| C15 | 0.065 (2) | 0.0434 (17) | 0.081 (2) | 0.0162 (15) | 0.0061 (18) | 0.0180 (17) |
| C16 | 0.079 (2) | 0.069 (2) | 0.086 (3) | 0.0211 (19) | −0.006 (2) | 0.031 (2) |
| C17 | 0.0556 (18) | 0.068 (2) | 0.062 (2) | 0.0124 (16) | 0.0010 (15) | 0.0160 (17) |
| C18 | 0.0550 (18) | 0.0442 (17) | 0.070 (2) | 0.0097 (14) | 0.0032 (16) | 0.0049 (16) |
| C19 | 0.0511 (17) | 0.0461 (18) | 0.0614 (19) | 0.0136 (14) | 0.0074 (15) | 0.0134 (15) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—C11 | 1.729 (3) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| Cl2—C17 | 1.726 (3) | C6—C7 | 1.399 (3) |
| S1—N1 | 1.7347 (19) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| S1—C7 | 1.744 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.379 (3) |
| S2—O2 | 1.4214 (17) | C8—C13 | 1.381 (3) |
| S2—O3 | 1.4239 (16) | C9—C10 | 1.388 (3) |
| S2—N2 | 1.729 (2) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| S2—C8 | 1.754 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.371 (3) |
| S3—O4 | 1.4240 (16) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| S3—O5 | 1.4242 (16) | C11—C12 | 1.368 (3) |
| S3—N2 | 1.684 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.383 (3) |
| S3—C14 | 1.750 (3) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| O1—C1 | 1.213 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| N1—N2 | 1.381 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.379 (3) |
| N1—C1 | 1.409 (3) | C14—C19 | 1.381 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.461 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.376 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.383 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C7 | 1.388 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.377 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.371 (3) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C17—C18 | 1.370 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.380 (3) | C18—C19 | 1.377 (3) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.371 (3) | C19—H19 | 0.9300 |
| N1—S1—C7 | 89.10 (11) | C2—C7—S1 | 113.04 (18) |
| O2—S2—O3 | 120.38 (11) | C6—C7—S1 | 126.2 (2) |
| O2—S2—N2 | 102.15 (10) | C9—C8—C13 | 121.2 (2) |
| O3—S2—N2 | 109.77 (11) | C9—C8—S2 | 118.9 (2) |
| O2—S2—C8 | 110.89 (11) | C13—C8—S2 | 119.9 (2) |
| O3—S2—C8 | 108.61 (12) | C8—C9—C10 | 119.0 (2) |
| N2—S2—C8 | 103.62 (11) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.5 |
| O4—S3—O5 | 121.61 (11) | C10—C9—H9 | 120.5 |
| O4—S3—N2 | 104.10 (10) | C11—C10—C9 | 119.4 (3) |
| O5—S3—N2 | 106.59 (10) | C11—C10—H10 | 120.3 |
| O4—S3—C14 | 109.51 (11) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.3 |
| O5—S3—C14 | 109.23 (12) | C12—C11—C10 | 121.6 (3) |
| N2—S3—C14 | 104.29 (10) | C12—C11—Cl1 | 119.2 (2) |
| N2—N1—C1 | 120.88 (19) | C10—C11—Cl1 | 119.1 (2) |
| N2—N1—S1 | 117.96 (15) | C11—C12—C13 | 119.4 (3) |
| C1—N1—S1 | 116.69 (17) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.3 |
| N1—N2—S3 | 115.94 (15) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.3 |
| N1—N2—S2 | 117.41 (15) | C8—C13—C12 | 119.3 (3) |
| S3—N2—S2 | 125.38 (12) | C8—C13—H13 | 120.4 |
| O1—C1—N1 | 122.8 (2) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.4 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 130.4 (2) | C15—C14—C19 | 120.8 (2) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 106.9 (2) | C15—C14—S3 | 120.4 (2) |
| C3—C2—C7 | 120.6 (2) | C19—C14—S3 | 118.8 (2) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 125.3 (2) | C16—C15—C14 | 119.1 (3) |
| C7—C2—C1 | 114.1 (2) | C16—C15—H15 | 120.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 118.7 (3) | C14—C15—H15 | 120.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.7 | C15—C16—C17 | 119.9 (3) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.7 | C15—C16—H16 | 120.0 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.6 (2) | C17—C16—H16 | 120.0 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.7 | C18—C17—C16 | 121.2 (3) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.7 | C18—C17—Cl2 | 119.0 (2) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 122.1 (3) | C16—C17—Cl2 | 119.9 (2) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.0 | C17—C18—C19 | 119.2 (3) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.0 | C17—C18—H18 | 120.4 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 117.2 (3) | C19—C18—H18 | 120.4 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 121.4 | C18—C19—C14 | 119.9 (3) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 121.4 | C18—C19—H19 | 120.1 |
| C2—C7—C6 | 120.8 (2) | C14—C19—H19 | 120.1 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C13—H13···O1 | 0.93 | 2.42 | 3.275 (4) | 153 |
| C5—H5···O2i | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.353 (4) | 140 |
| C6—H6···O3ii | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.289 (3) | 133 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (ii) −x, −y, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LH2763).
References
- Altomare, A., Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Moliterni, A. G. G., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 115–119.
- Bruker (1997). SMART, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cavalca, L., Gaetani, A., Mangia, A. & Pelizzi, G. (1970). Gazz. Chim. Ital.100, 629–638.
- Clerici, F., Gelmi, M. L., Pellegrino, S. & Pocar, D. (2007). Top. Heterocycl. Chem.9, 179–264.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Keller, E. (1997). SCHAKAL97 University of Freiburg, Germany.
- Kim, W., Dannaldson, J. & Gates, K. S. (1996). Tetrahedron Lett.37, 5337–5340.
- Kolberg, A., Sieler, J. & Schulze, B. (1999). J. Heterocycl. Chem.36, 1081–1086.
- Nardelli, M. (1995). J. Appl. Cryst.28, 659.
- Ranganathan, S., Muraleedharan, K. M., Bharadwaj, P., Chatterji, D. & Karle, I. (2002). Tetrahedron, 58, 2861–2874.
- Sarma, B. K. & Mugesh, G. (2007). J. Am. Chem. Soc.129, 8872–8881. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Siegemund, A., Taubert, K. & Schulze, B. (2002). Sulfur Rep.23, 279–319.
- Steinfeld, G. & Kersting, B. (2006). Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem.632, 2010–2016.
- Vicini, P., Incerti, M., La Colla, P., Collu, G., Pezzullo, M., Giliberti, G. & Loddo, R. (2009). J. Med. Chem. Submitted.
- Vicini, P., Manotti, C., Caretta, A. & Amoretti, L. (1997). Arzneim. Forsch. Drug Res.47, 1218–1221. [PubMed]
- Xu, F.-L., Lin, Q. & Yin, X.-Q. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o496–o497.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809003195/lh2763sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809003195/lh2763Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




