Abstract
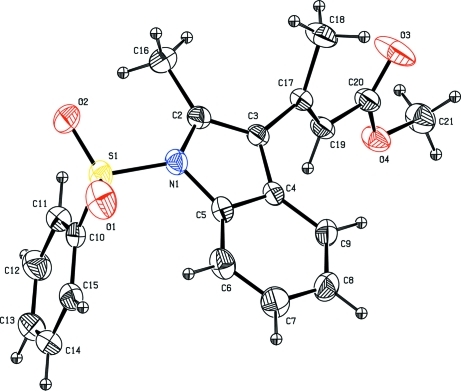
In the title compound, C20H19NO4S, the indole ring system is planar [r.m.s. deviation = 0.023 (2) Å]. The sulfonyl-bound phenyl ring is almost perpendicular to the indole ring system [dihedral angle = 86.75 (7)°]. The ester group is almost planar (r.m.s. deviation = 0.030 Å) and is oriented at an angle of 62.53 (5)° with respect to the indole ring system. Molecules are linked into a two-dimensional network parallel to the ab plane by intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Related literature
For the biological activities of indole and its derivatives, see: Chandrakantha et al. (1992 ▶); Rodriguez et al. (1985 ▶). For related literature For the configuration at the S atom, see: Bassindale (1984 ▶). For the N atom hybridization, see: Beddoes et al. (1986 ▶).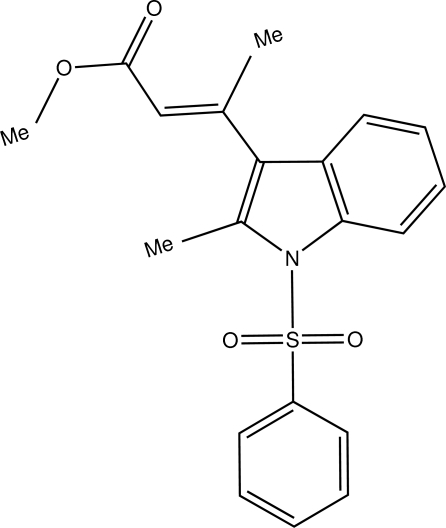
Experimental
Crystal data
C20H19NO4S
M r = 369.42
Monoclinic,
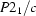
a = 8.9498 (3) Å
b = 8.8427 (2) Å
c = 23.2836 (7) Å
β = 97.085 (1)°
V = 1828.60 (9) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.20 mm−1
T = 293 (2) K
0.25 × 0.20 × 0.16 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2001 ▶) T min = 0.957, T max = 0.968
23203 measured reflections
5673 independent reflections
3833 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.026
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.046
wR(F 2) = 0.137
S = 1.01
5673 reflections
239 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.30 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809002931/ci2752sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809002931/ci2752Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C6—H6⋯O2i | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.391 (2) | 146 |
| C13—H13⋯O3ii | 0.93 | 2.50 | 3.277 (2) | 141 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 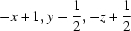 ; (ii)
; (ii) 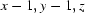 .
.
Acknowledgments
TK thanks Dr Babu Varghese, SAIF, IIT-Madras, Chennai, India, for his help with the data collection.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Indole and its derivatives have long been known for their chemical and biological activities (Chandrakantha et al., 1992). The indole ring system is present in a number of natural products, many of which are found to possess pharmacological properties like anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory and anti-implantation activities (Rodriguez et al., 1985).
Due to Thorpe–Ignold effect (Bassindale, 1984), bond angles around atom S1 show significant deviation from ideal tetrahedral value, with significant deviations in angles O1—S1—O2 [120.37 (9)°] and N1—S1—C10 [104.96 (6)°]. The indole ring system is essentially planar. The sum of the bond angles around atom N1 (355.9°) indicates sp2 hybridization (Beddoes et al., 1986). The sulfonyl bound phenyl ring is oriented almost perpendicular to the indole ring system as can be seen from the dihedral angle of 86.75 (7)°. The ester group attached to the indole ring system adopts an extended conformation which is confirmed by the torsion angles C3—C17—C19—C20 = -177.59 (14)°, C17—C19—C20—O4 = -176.02 (15)° and C19—C20—O4—C21 = -178.62 (15)°.
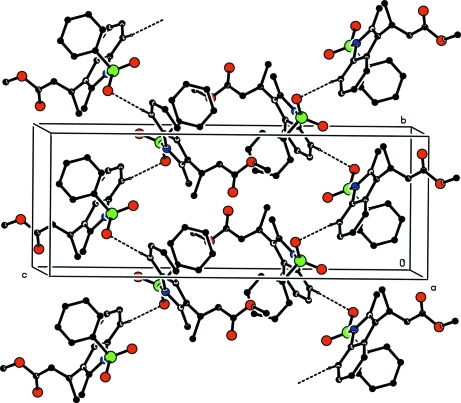
In the crystal structure, intermolecular C—H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1) link the molecules into a two-dimensional network parallel to the ab plane (Fig. 2).
Experimental
To a stirred suspension of NaH (29 mg, 1.20 mmol, hexane washed) in THF (5 ml), a solution of vinyl indole (0.23 g, 1 mmol) in THF (5 ml) was added and stirred for 30 min at room temperature. To the reaction mixture, a solution of PhSO2Cl (0.21 g, 1.20 mmol) was added and stirring was continued for further 6 h. After the indole was consumed (monitored by TLC), the reaction mixture was quenched with cold diluted HCl (25 ml), extracted with ethyl acetate (2 × 10 ml) and dried (Na2SO4). Removal of solvent followed by recrystallization (MeOH) afforded yellow crystals of the title compound.
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically (C—H = 0.93–0.96 Å) and allowed to ride on their parent atoms, with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C) for methyl H and 1.2Ueq(C) for other H atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 20% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Crystal packing of the title compound, viewed down the a axis. H atoms not involved in hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C20H19NO4S | F(000) = 776 |
| Mr = 369.42 | Dx = 1.342 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 5673 reflections |
| a = 8.9498 (3) Å | θ = 2.3–31.0° |
| b = 8.8427 (2) Å | µ = 0.20 mm−1 |
| c = 23.2836 (7) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 97.085 (1)° | Block, yellow |
| V = 1828.60 (9) Å3 | 0.25 × 0.20 × 0.16 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer | 5673 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3833 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.026 |
| ω and φ scans | θmax = 31.0°, θmin = 2.3° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2001) | h = −12→11 |
| Tmin = 0.957, Tmax = 0.968 | k = −7→12 |
| 23203 measured reflections | l = −32→33 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.046 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.137 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0625P)2 + 0.402P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.01 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.016 |
| 5673 reflections | Δρmax = 0.30 e Å−3 |
| 239 parameters | Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0057 (11) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C2 | 0.71830 (17) | 0.73053 (17) | 0.13969 (7) | 0.0461 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.85936 (15) | 0.68775 (16) | 0.13101 (6) | 0.0406 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.89541 (15) | 0.54808 (16) | 0.16149 (6) | 0.0408 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.77241 (15) | 0.50989 (17) | 0.19043 (6) | 0.0430 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.77105 (19) | 0.3804 (2) | 0.22371 (7) | 0.0587 (4) | |
| H6 | 0.6889 | 0.3562 | 0.2428 | 0.070* | |
| C7 | 0.8966 (2) | 0.2887 (2) | 0.22744 (8) | 0.0703 (5) | |
| H7 | 0.8983 | 0.2001 | 0.2490 | 0.084* | |
| C8 | 1.0202 (2) | 0.3256 (2) | 0.19985 (9) | 0.0682 (5) | |
| H8 | 1.1036 | 0.2621 | 0.2036 | 0.082* | |
| C9 | 1.02144 (17) | 0.45440 (19) | 0.16699 (7) | 0.0546 (4) | |
| H9 | 1.1050 | 0.4786 | 0.1487 | 0.065* | |
| C10 | 0.42383 (15) | 0.44900 (18) | 0.13523 (7) | 0.0462 (3) | |
| C11 | 0.38591 (18) | 0.4876 (2) | 0.07757 (7) | 0.0550 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.3946 | 0.5871 | 0.0655 | 0.066* | |
| C12 | 0.3352 (2) | 0.3766 (2) | 0.03848 (9) | 0.0702 (5) | |
| H12 | 0.3097 | 0.4009 | −0.0003 | 0.084* | |
| C13 | 0.3223 (2) | 0.2295 (2) | 0.05676 (10) | 0.0739 (6) | |
| H13 | 0.2870 | 0.1553 | 0.0302 | 0.089* | |
| C14 | 0.3607 (2) | 0.1917 (2) | 0.11349 (11) | 0.0720 (5) | |
| H14 | 0.3524 | 0.0919 | 0.1253 | 0.086* | |
| C15 | 0.41202 (19) | 0.3013 (2) | 0.15350 (9) | 0.0598 (4) | |
| H15 | 0.4382 | 0.2760 | 0.1922 | 0.072* | |
| C16 | 0.6333 (2) | 0.8675 (2) | 0.11697 (10) | 0.0724 (5) | |
| H16A | 0.6151 | 0.9315 | 0.1487 | 0.109* | |
| H16B | 0.5389 | 0.8374 | 0.0960 | 0.109* | |
| H16C | 0.6911 | 0.9218 | 0.0916 | 0.109* | |
| C17 | 0.96483 (16) | 0.77322 (16) | 0.09861 (6) | 0.0430 (3) | |
| C18 | 1.0118 (2) | 0.92731 (19) | 0.12070 (8) | 0.0648 (5) | |
| H18A | 1.1128 | 0.9231 | 0.1400 | 0.097* | |
| H18B | 0.9452 | 0.9609 | 0.1474 | 0.097* | |
| H18C | 1.0074 | 0.9967 | 0.0888 | 0.097* | |
| C19 | 1.01726 (16) | 0.70573 (17) | 0.05409 (7) | 0.0466 (3) | |
| H19 | 0.9820 | 0.6090 | 0.0444 | 0.056* | |
| C20 | 1.12631 (18) | 0.77169 (18) | 0.01894 (7) | 0.0497 (4) | |
| C21 | 1.2556 (2) | 0.7283 (2) | −0.06194 (8) | 0.0670 (5) | |
| H21A | 1.2073 | 0.7956 | −0.0909 | 0.101* | |
| H21B | 1.2938 | 0.6419 | −0.0804 | 0.101* | |
| H21C | 1.3373 | 0.7801 | −0.0395 | 0.101* | |
| N1 | 0.66229 (13) | 0.62376 (15) | 0.17753 (5) | 0.0465 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.48023 (16) | 0.53321 (19) | 0.24184 (5) | 0.0801 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.40094 (14) | 0.72716 (15) | 0.16816 (7) | 0.0756 (4) | |
| O3 | 1.1914 (2) | 0.88897 (17) | 0.02638 (7) | 0.0984 (6) | |
| O4 | 1.14823 (13) | 0.67953 (13) | −0.02447 (5) | 0.0583 (3) | |
| S1 | 0.48136 (4) | 0.59233 (5) | 0.185184 (18) | 0.05532 (15) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C2 | 0.0440 (7) | 0.0399 (7) | 0.0552 (8) | −0.0028 (6) | 0.0092 (6) | −0.0070 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0391 (7) | 0.0365 (7) | 0.0464 (7) | −0.0050 (6) | 0.0066 (5) | −0.0042 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0347 (6) | 0.0432 (7) | 0.0444 (7) | −0.0066 (6) | 0.0039 (5) | −0.0023 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0372 (7) | 0.0527 (8) | 0.0390 (7) | −0.0063 (6) | 0.0038 (5) | −0.0022 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0520 (9) | 0.0750 (12) | 0.0489 (8) | −0.0117 (8) | 0.0058 (7) | 0.0168 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0648 (11) | 0.0738 (13) | 0.0695 (11) | −0.0025 (10) | −0.0021 (9) | 0.0318 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0492 (9) | 0.0664 (12) | 0.0872 (13) | 0.0085 (9) | 0.0006 (9) | 0.0222 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0373 (7) | 0.0568 (10) | 0.0698 (10) | 0.0002 (7) | 0.0074 (7) | 0.0080 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0295 (6) | 0.0496 (8) | 0.0607 (9) | 0.0002 (6) | 0.0104 (6) | −0.0014 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0497 (9) | 0.0484 (9) | 0.0661 (10) | −0.0034 (7) | 0.0034 (7) | 0.0018 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0663 (12) | 0.0699 (12) | 0.0706 (12) | −0.0108 (10) | −0.0063 (9) | −0.0070 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0593 (11) | 0.0595 (12) | 0.0994 (15) | −0.0112 (9) | −0.0042 (10) | −0.0160 (11) |
| C14 | 0.0521 (10) | 0.0459 (10) | 0.1173 (17) | −0.0077 (8) | 0.0082 (10) | 0.0056 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0433 (8) | 0.0582 (10) | 0.0782 (11) | −0.0038 (7) | 0.0079 (8) | 0.0114 (9) |
| C16 | 0.0593 (11) | 0.0506 (10) | 0.1084 (16) | 0.0094 (8) | 0.0149 (10) | 0.0063 (10) |
| C17 | 0.0406 (7) | 0.0369 (7) | 0.0511 (8) | −0.0059 (6) | 0.0045 (6) | 0.0012 (6) |
| C18 | 0.0794 (12) | 0.0473 (9) | 0.0714 (11) | −0.0209 (9) | 0.0234 (9) | −0.0137 (8) |
| C19 | 0.0461 (8) | 0.0376 (7) | 0.0576 (8) | −0.0109 (6) | 0.0119 (6) | −0.0019 (6) |
| C20 | 0.0513 (8) | 0.0421 (8) | 0.0574 (9) | −0.0096 (7) | 0.0139 (7) | −0.0024 (7) |
| C21 | 0.0692 (11) | 0.0700 (12) | 0.0673 (11) | −0.0114 (9) | 0.0306 (9) | −0.0010 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0389 (6) | 0.0512 (7) | 0.0510 (7) | −0.0031 (5) | 0.0118 (5) | −0.0068 (5) |
| O1 | 0.0728 (8) | 0.1164 (12) | 0.0584 (7) | −0.0149 (8) | 0.0369 (6) | −0.0148 (7) |
| O2 | 0.0534 (7) | 0.0642 (8) | 0.1135 (11) | 0.0126 (6) | 0.0278 (7) | −0.0269 (8) |
| O3 | 0.1299 (14) | 0.0687 (9) | 0.1106 (12) | −0.0562 (9) | 0.0702 (10) | −0.0333 (8) |
| O4 | 0.0646 (7) | 0.0522 (7) | 0.0626 (7) | −0.0135 (6) | 0.0255 (5) | −0.0074 (5) |
| S1 | 0.0418 (2) | 0.0660 (3) | 0.0624 (3) | −0.00185 (18) | 0.02337 (17) | −0.01782 (19) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C2—C3 | 1.357 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.93 |
| C2—N1 | 1.4241 (19) | C14—C15 | 1.383 (3) |
| C2—C16 | 1.493 (2) | C14—H14 | 0.93 |
| C3—C4 | 1.441 (2) | C15—H15 | 0.93 |
| C3—C17 | 1.4857 (19) | C16—H16A | 0.96 |
| C4—C9 | 1.393 (2) | C16—H16B | 0.96 |
| C4—C5 | 1.4012 (19) | C16—H16C | 0.96 |
| C5—C6 | 1.383 (2) | C17—C19 | 1.331 (2) |
| C5—N1 | 1.415 (2) | C17—C18 | 1.498 (2) |
| C6—C7 | 1.380 (3) | C18—H18A | 0.96 |
| C6—H6 | 0.93 | C18—H18B | 0.96 |
| C7—C8 | 1.385 (3) | C18—H18C | 0.96 |
| C7—H7 | 0.93 | C19—C20 | 1.470 (2) |
| C8—C9 | 1.373 (2) | C19—H19 | 0.93 |
| C8—H8 | 0.93 | C20—O3 | 1.1915 (19) |
| C9—H9 | 0.93 | C20—O4 | 1.3315 (19) |
| C10—C15 | 1.381 (2) | C21—O4 | 1.4415 (19) |
| C10—C11 | 1.386 (2) | C21—H21A | 0.96 |
| C10—S1 | 1.7540 (16) | C21—H21B | 0.96 |
| C11—C12 | 1.377 (3) | C21—H21C | 0.96 |
| C11—H11 | 0.93 | N1—S1 | 1.6740 (12) |
| C12—C13 | 1.378 (3) | O1—S1 | 1.4202 (14) |
| C12—H12 | 0.93 | O2—S1 | 1.4234 (14) |
| C13—C14 | 1.365 (3) | ||
| C3—C2—N1 | 108.20 (13) | C10—C15—H15 | 120.4 |
| C3—C2—C16 | 128.09 (15) | C14—C15—H15 | 120.4 |
| N1—C2—C16 | 123.67 (14) | C2—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 108.77 (12) | C2—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C17 | 126.51 (13) | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C17 | 124.64 (12) | C2—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C9—C4—C5 | 119.20 (14) | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C9—C4—C3 | 133.22 (14) | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 107.57 (13) | C19—C17—C3 | 118.34 (13) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 122.05 (14) | C19—C17—C18 | 124.36 (14) |
| C6—C5—N1 | 130.83 (13) | C3—C17—C18 | 117.20 (13) |
| C4—C5—N1 | 107.12 (13) | C17—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 117.28 (15) | C17—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 121.4 | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 121.4 | C17—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 121.55 (17) | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.2 | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 119.2 | C17—C19—C20 | 125.32 (14) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 121.06 (17) | C17—C19—H19 | 117.3 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.5 | C20—C19—H19 | 117.3 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.5 | O3—C20—O4 | 121.87 (14) |
| C8—C9—C4 | 118.85 (15) | O3—C20—C19 | 127.63 (15) |
| C8—C9—H9 | 120.6 | O4—C20—C19 | 110.48 (13) |
| C4—C9—H9 | 120.6 | O4—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| C15—C10—C11 | 120.80 (16) | O4—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C15—C10—S1 | 120.41 (13) | H21A—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—S1 | 118.76 (12) | O4—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—C10 | 119.07 (17) | H21A—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—H11 | 120.5 | H21B—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C10—C11—H11 | 120.5 | C5—N1—C2 | 108.30 (11) |
| C11—C12—C13 | 120.15 (19) | C5—N1—S1 | 121.12 (10) |
| C11—C12—H12 | 119.9 | C2—N1—S1 | 126.50 (11) |
| C13—C12—H12 | 119.9 | C20—O4—C21 | 116.60 (13) |
| C14—C13—C12 | 120.61 (19) | O1—S1—O2 | 120.37 (9) |
| C14—C13—H13 | 119.7 | O1—S1—N1 | 106.13 (7) |
| C12—C13—H13 | 119.7 | O2—S1—N1 | 107.09 (8) |
| C13—C14—C15 | 120.24 (18) | O1—S1—C10 | 108.35 (9) |
| C13—C14—H14 | 119.9 | O2—S1—C10 | 108.88 (8) |
| C15—C14—H14 | 119.9 | N1—S1—C10 | 104.96 (6) |
| C10—C15—C14 | 119.12 (18) | ||
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | 2.26 (16) | C2—C3—C17—C18 | 60.7 (2) |
| C16—C2—C3—C4 | 179.74 (16) | C4—C3—C17—C18 | −115.44 (17) |
| N1—C2—C3—C17 | −174.38 (13) | C3—C17—C19—C20 | −177.59 (14) |
| C16—C2—C3—C17 | 3.1 (3) | C18—C17—C19—C20 | −1.3 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C9 | 179.15 (16) | C17—C19—C20—O3 | 5.1 (3) |
| C17—C3—C4—C9 | −4.1 (3) | C17—C19—C20—O4 | −176.02 (15) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.70 (16) | C6—C5—N1—C2 | −178.24 (16) |
| C17—C3—C4—C5 | 175.01 (13) | C4—C5—N1—C2 | 0.92 (15) |
| C9—C4—C5—C6 | −1.0 (2) | C6—C5—N1—S1 | −19.6 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 179.68 (14) | C4—C5—N1—S1 | 159.59 (10) |
| C9—C4—C5—N1 | 179.72 (13) | C3—C2—N1—C5 | −2.00 (16) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | 0.44 (15) | C16—C2—N1—C5 | −179.62 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −0.1 (2) | C3—C2—N1—S1 | −159.21 (11) |
| N1—C5—C6—C7 | 178.98 (16) | C16—C2—N1—S1 | 23.2 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 1.0 (3) | O3—C20—O4—C21 | 0.4 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −0.9 (3) | C19—C20—O4—C21 | −178.62 (15) |
| C7—C8—C9—C4 | −0.3 (3) | C5—N1—S1—O1 | 50.95 (13) |
| C5—C4—C9—C8 | 1.2 (2) | C2—N1—S1—O1 | −154.49 (13) |
| C3—C4—C9—C8 | −179.75 (17) | C5—N1—S1—O2 | −179.29 (11) |
| C15—C10—C11—C12 | 0.4 (2) | C2—N1—S1—O2 | −24.73 (14) |
| S1—C10—C11—C12 | −177.57 (14) | C5—N1—S1—C10 | −63.66 (12) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.2 (3) | C2—N1—S1—C10 | 90.89 (13) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.6 (3) | C15—C10—S1—O1 | −11.22 (15) |
| C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.6 (3) | C11—C10—S1—O1 | 166.71 (12) |
| C11—C10—C15—C14 | −0.4 (2) | C15—C10—S1—O2 | −143.79 (13) |
| S1—C10—C15—C14 | 177.49 (13) | C11—C10—S1—O2 | 34.14 (14) |
| C13—C14—C15—C10 | −0.1 (3) | C15—C10—S1—N1 | 101.83 (13) |
| C2—C3—C17—C19 | −122.74 (17) | C11—C10—S1—N1 | −80.24 (13) |
| C4—C3—C17—C19 | 61.1 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C6—H6···O2i | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.391 (2) | 146 |
| C13—H13···O3ii | 0.93 | 2.50 | 3.277 (2) | 141 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) x−1, y−1, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: CI2752).
References
- Bassindale, A. (1984). The Third Dimension in Organic Chemistry, ch. 1, p. 11. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
- Beddoes, R. L., Dalton, L., Joule, T. A., Mills, O. S., Street, J. D. & Watt, C. I. F. (1986). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. 787–797.
- Bruker (2004). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chandrakantha, T. N., Puttaraja, & Nethaji, M. (1992). Acta Cryst. C48, 60–62.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Rodriguez, J. G., Temprano, F., Esteban-Calderon, C., Martinez-Ripoll, M. & Garcia-Blanco, S. (1985). Tetrahedron, 41, 3813–3823.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2001). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809002931/ci2752sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809002931/ci2752Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report