Abstract
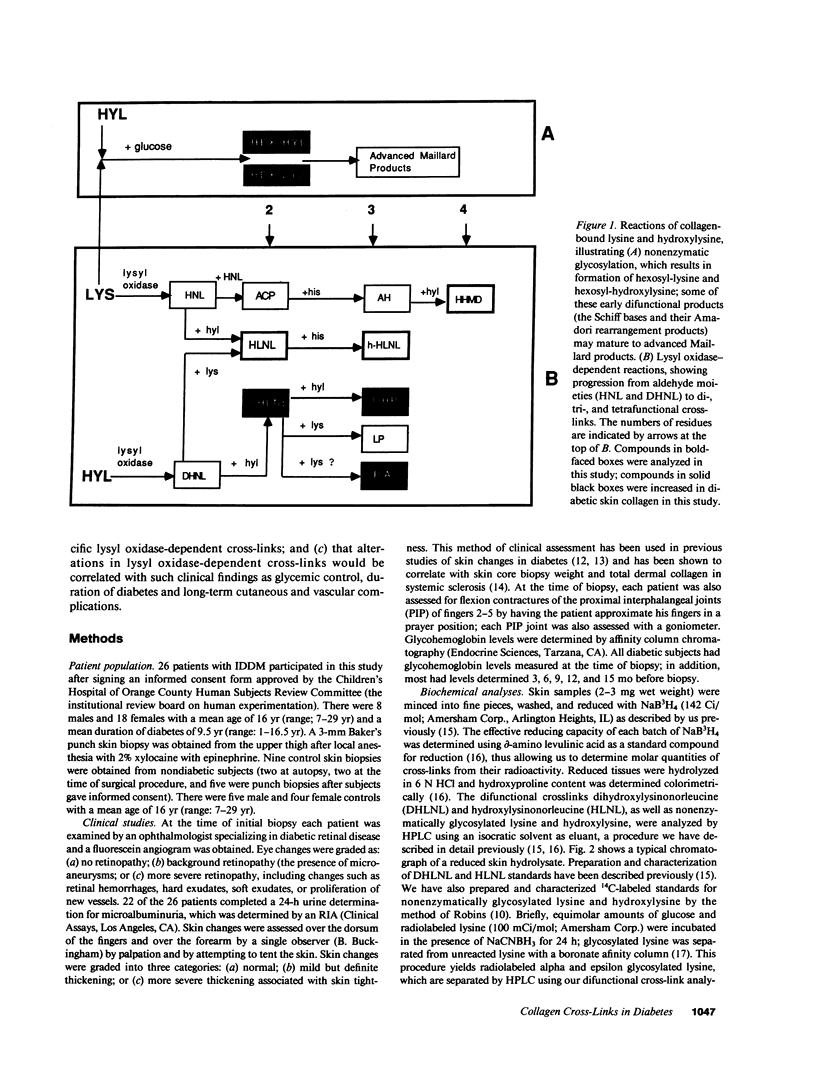
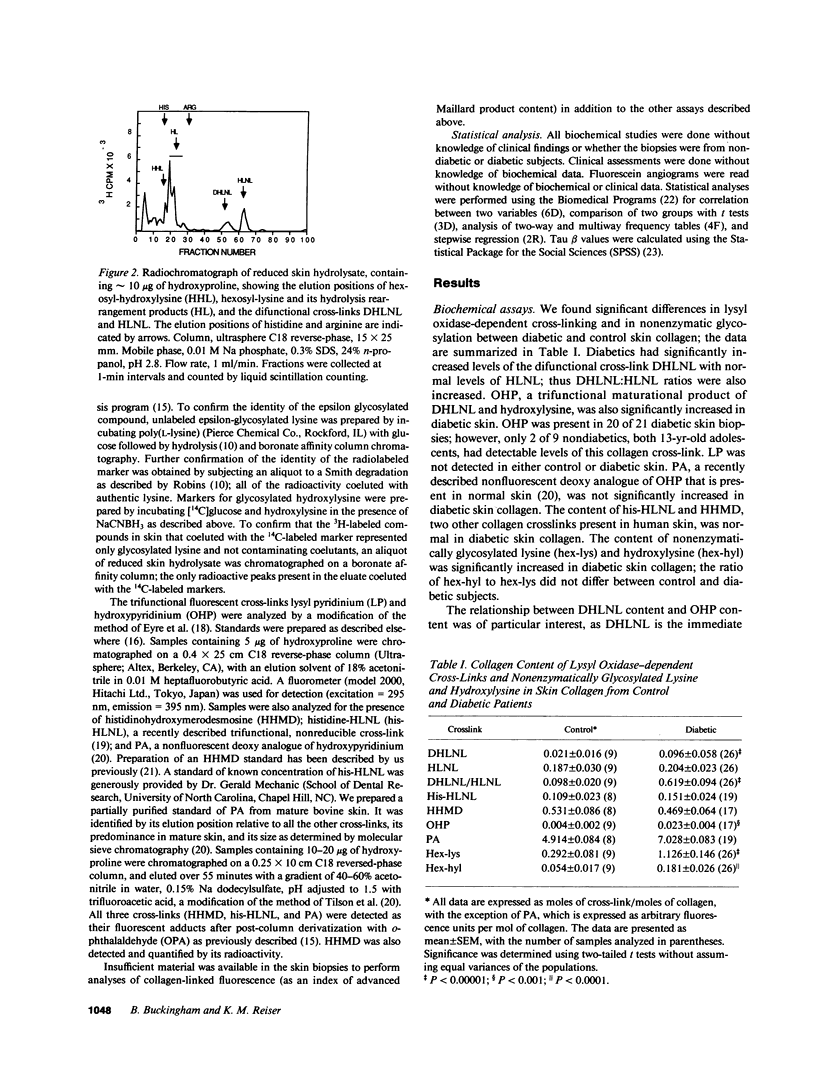
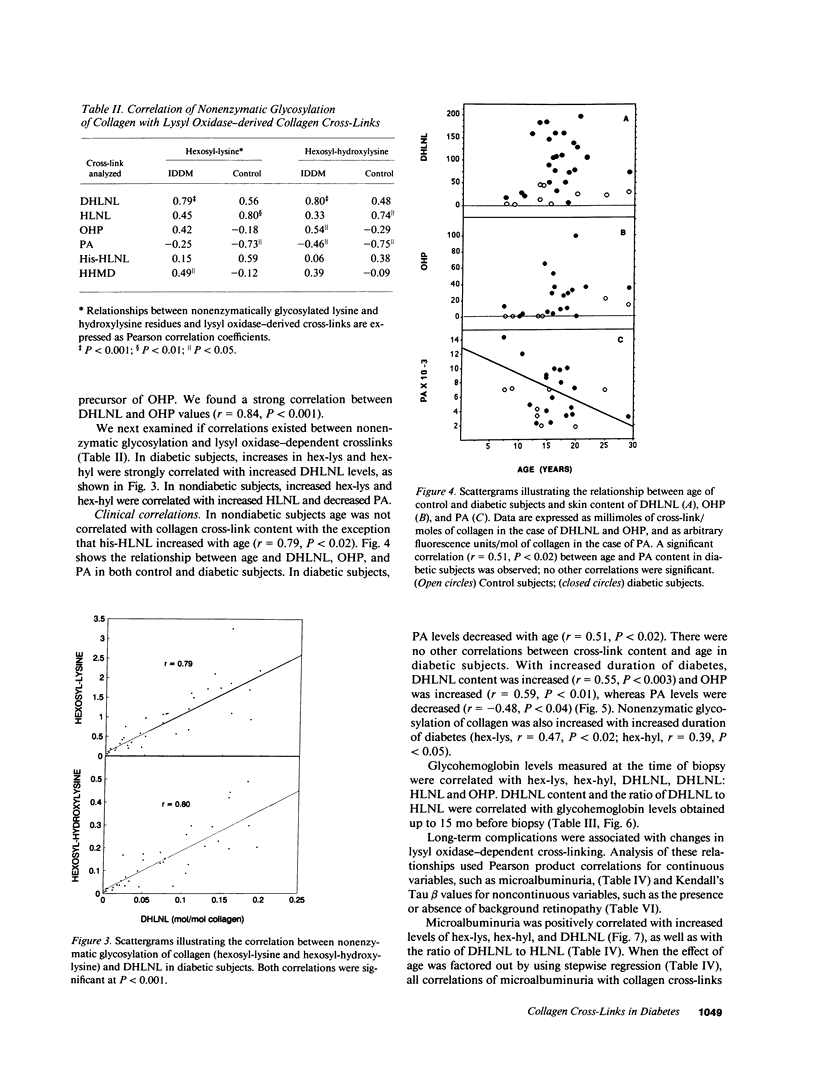
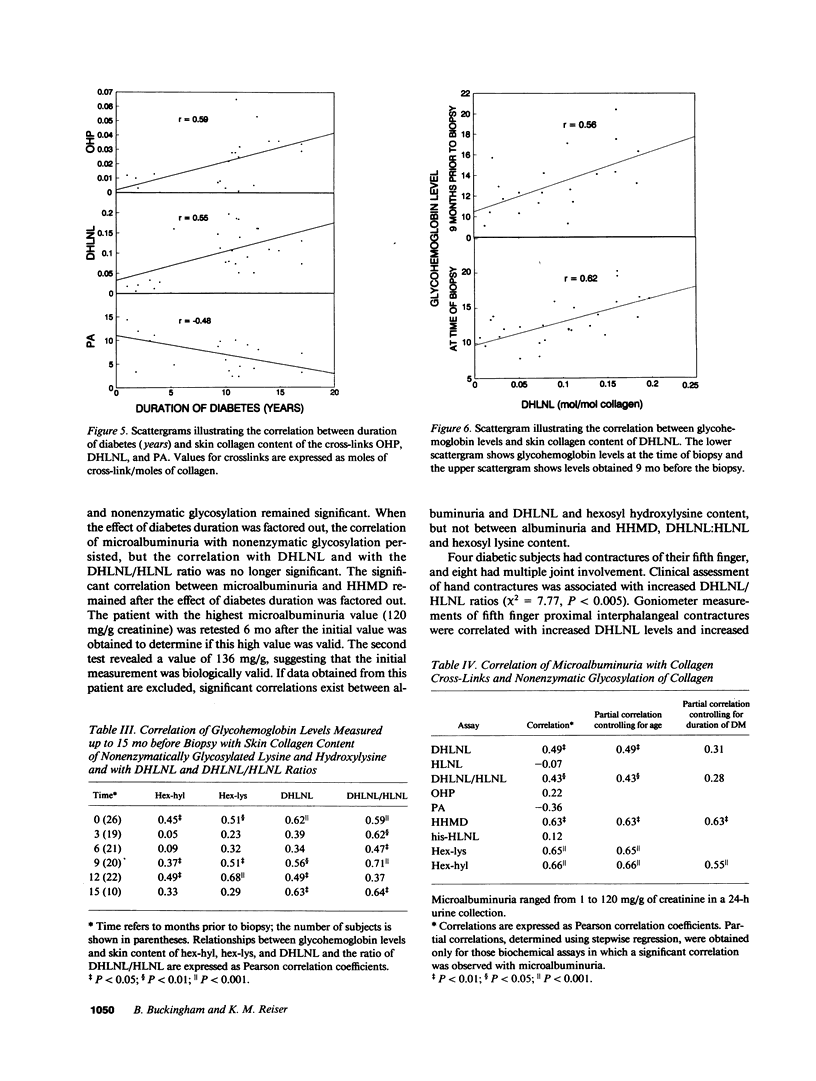
Many abnormalities in collagen have been reported in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, some or all of which have been attributed to increased cross-linking. Although recent work has focused on the role of glucose-derived collagen cross-links in the pathogenesis of diabetic complications, relatively few studies have investigated the role of lysyl oxidase-dependent (LOX) cross-links. In the present study, LOX cross-links and nonenzymatic glycosylation were quantified in skin collagen from diabetic subjects. There was an increase in the difunctional cross-link dihydroxylysinonorleucine (DHLNL) as well as in one of its trifunctional maturation products, hydroxypyridinium. All other LOX crosslinks were normal. Nonenzymatic glycosylation was increased in diabetic skin collagen, and this increase was correlated with increases in DHLNL (P less than 0.001). The biochemical results were examined for correlations with clinical data from the same subjects. Increases in DHLNL content were associated with duration of diabetes (P less than 0.003), glycohemoglobin levels (P less than 0.001), hand contractures (P less than 0.05), skin changes (P less than 0.005), and microalbuminuria (P less than 0.01). In nondiabetic subjects age was not correlated with collagen cross-link content with the exception that his-HLNL increased with age (r = 0.79, P less than 0.02). In diabetic subjects, PA levels decreased with age (r = 0.51, P less than 0.02). With increased duration of diabetes, DHLNL content was increased (r = 0.55, P less than 0.003) and OHP was increased (r = 0.59, P less than 0.01), whereas PA levels were decreased (r = -0.48, P less than 0.04). Nonenzymatic glycosylation of collagen was also increased with increased duration of diabetes (hex-lys, r = 0.47, P less than 0.02; hex-hyl, r = 0.39, P less than 0.05). We conclude that: (a) lysyl oxidase-dependent cross-linking is increased in skin collagen in diabetes and (b) that these changes in skin collagen are correlated with duration of diabetes, glycemic control, and long-term complications.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrass C. K., Peterson C. V., Raugi G. J. Phenotypic expression of collagen types in mesangial matrix of diabetic and nondiabetic rats. Diabetes. 1988 Dec;37(12):1695–1702. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.12.1695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey A. J., Bazin S., Sims T. J., Le Lous M., Nicoletis C., Delaunay A. Characterization of the collagen of human hypertrophic and normal scars. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 20;405(2):412–421. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(75)90106-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisswenger P. J., Spiro R. G. Studies on the human glomerular basement membrane. Composition, nature of the carbohydrate units and chemical changes in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1973 Mar;22(3):180–193. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.3.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brickley-Parsons D., Glimcher M. J., Smith R. J., Albin R., Adams J. P. Biochemical changes in the collagen of the palmar fascia in patients with Dupuytren's disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981 Jun;63(5):787–797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee M., Cerami A., Vlassara H. Advanced glycosylation end products in tissue and the biochemical basis of diabetic complications. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 19;318(20):1315–1321. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805193182007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckingham B. A., Uitto J., Sandborg C., Keens T., Roe T., Costin G., Kaufman F., Bernstein B., Landing B., Castellano A. Scleroderma-like changes in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: clinical and biochemical studies. Diabetes Care. 1984 Mar-Apr;7(2):163–169. doi: 10.2337/diacare.7.2.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckingham B., Perejda A. J., Sandborg C., Kershnar A. K., Uitto J. Skin, joint, and pulmonary changes in type I diabetes mellitus. Am J Dis Child. 1986 May;140(5):420–423. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1986.02140190030018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K., Uitto J., Rowold E. A., Grant G. A., Kilo C., Williamson J. R. Increased collagen cross-linkages in experimental diabetes: reversal by beta-aminopropionitrile and D-penicillamine. Diabetes. 1980 Oct;29(10):778–781. doi: 10.2337/diacare.20.10.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Koob T. J., Van Ness K. P. Quantitation of hydroxypyridinium crosslinks in collagen by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1984 Mar;137(2):380–388. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis M. J., Ellis J. P., Hockaday T. D. Skin collagen in diabetes mellitus in relation to treatment. Proc R Soc Med. 1974 Jan;67(1):35–36. doi: 10.1177/003591577406700121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golub L. M., Greenwald R. A., Zebrowski E. J., Ramamurthy N. S. The effect of experimental diabetes on the molecular characteristics of soluble rat-tail tendon collagen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 24;534(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90477-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlin C. R., Kohn R. R., Luschin J. H. Apparent accelerated aging of human collagen in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1975 Oct;24(10):902–904. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.10.902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A. Biochemical properties of human glomerular basement membrane in normal and diabetic kidneys. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):403–407. doi: 10.1172/JCI107573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy L., Baynes J. W. Non-enzymatic glycosylation and the chronic complications of diabetes: an overview. Diabetologia. 1984 Feb;26(2):93–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00281113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern P., Sebert B., Robert L. Increased type-III/type-I collagen ratios in diabetic human conjunctival biopsies. Clin Physiol Biochem. 1986;4(2):113–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Last J. A., Siefkin A. D., Reiser K. M. Type I collagen content is increased in lungs of patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. Thorax. 1983 May;38(5):364–368. doi: 10.1136/thx.38.5.364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Pape A., Guitton J. D., Gutman N., Legrand Y., Fauvel F., Muh J. P. Nonenzymatic glycosylation of collagen in diabetes: incidence on increased normal platelet aggregation. Haemostasis. 1983;13(1):36–41. doi: 10.1159/000214701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Pape A., Muh J. P., Bailey A. J. Characterization of N-glycosylated type I collagen in streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Biochem J. 1981 Aug 1;197(2):405–412. doi: 10.1042/bj1970405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W. Y., Shen S. Y., Robertson G. A., Khatami M., Rockey J. H. Increased solubility of newly synthesized collagen in retinal capillary pericyte cultures by nonenzymatic glycosylation. Ophthalmic Res. 1984;16(6):315–321. doi: 10.1159/000265336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lien Y. H., Stern R., Fu J. C., Siegel R. C. Inhibition of collagen fibril formation in vitro and subsequent cross-linking by glucose. Science. 1984 Sep 28;225(4669):1489–1491. doi: 10.1126/science.6147899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monnier V. M., Vishwanath V., Frank K. E., Elmets C. A., Dauchot P., Kohn R. R. Relation between complications of type I diabetes mellitus and collagen-linked fluorescence. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 13;314(7):403–408. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602133140702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriguchi T., Fujimoto D. Crosslink of collagen in hypertrophic scar. J Invest Dermatol. 1979 Mar;72(3):143–145. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12530609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser K. M., Hennessy S. M., Last J. A. Analysis of age-associated changes in collagen crosslinking in the skin and lung in monkeys and rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Dec 7;926(3):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(87)90220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser K. M., Last J. A. Collagen crosslinking in lungs of rats with experimental silicosis. Coll Relat Res. 1986 Oct;6(4):313–323. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(86)80002-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser K. M., Tryka A. F., Lindenschmidt R. C., Last J. A., Witschi H. R. Changes in collagen cross-linking in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Biochem Toxicol. 1986 Mar;1(1):83–91. doi: 10.1002/jbt.2570010109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins S. P. Analysis of the crosslinking components in collagen and elastin. Methods Biochem Anal. 1982;28:329–379. doi: 10.1002/9780470110485.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodnan G. P., Lipinski E., Luksick J. Skin thickness and collagen content in progressive systemic sclerosis and localized scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Feb;22(2):130–140. doi: 10.1002/art.1780220205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romen W., Lange H. W., Hempel K., Heck T. Studies on collagen metabolism in rats. II. Turnover and amino acid composition of the collagen of glomerular basement membrane in diabetes mellitus. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1981;36(2-3):313–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbloom A. L., Silverstein J. H., Lezotte D. C., Richardson K., McCallum M. Limited joint mobility in childhood diabetes mellitus indicates increased risk for microvascular disease. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jul 23;305(4):191–194. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198107233050403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seibold J. R. Digital sclerosis in children with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1357–1361. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilson M. D., Dreyer R. N., Hudson A., Cotter R. J., Tanzer M. L. Partial characteristics of an analog of pyridinoline isolated from human skin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Feb 15;126(3):1222–1227. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90316-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trüeb B., Flückiger R., Winterhalter K. H. Nonenzymatic glycosylation of basement membrane collagen in diabetes mellitus. Coll Relat Res. 1984 Aug;4(4):239–251. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(84)80032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vishwanath V., Frank K. E., Elmets C. A., Dauchot P. J., Monnier V. M. Glycation of skin collagen in type I diabetes mellitus. Correlation with long-term complications. Diabetes. 1986 Aug;35(8):916–921. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.8.916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi M., London R. E., Guenat C., Hashimoto F., Mechanic G. L. Structure and formation of a stable histidine-based trifunctional cross-link in skin collagen. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11428–11434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi M., Noyes C., Kuboki Y., Mechanic G. L. Collagen structural microheterogeneity and a possible role for glycosylated hydroxylysine in type I collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7684–7688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue D. K., McLennan S., Delbridge L., Handelsman D. J., Reeve T., Turtle J. R. The thermal stability of collagen in diabetic rats: correlation with severity of diabetes and non-enzymatic glycosylation. Diabetologia. 1983 Apr;24(4):282–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00282714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


