Abstract
The title compound, {(C6H16NO)[Cu2(CH3COO)5]·CH2Cl2}n, consists of acetate-bridged Cu2(CH3COO)4 units that are connected via another acetate anion at each terminus to form infinite anionic [{Cu2(CH3COO)4}(CH3COO)]n chains along [100]. The connecting acetate is hydrogen bonded to the diethyl(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonium cation, and the dichloromethane solvent molecule fills the remaining voids in the structure. The O—Cu—Cu angles along the polymeric chain are nearly linear [175.49 (5)°], but individual O—Cu—Cu—O units along the chain are bent and rotated against each other at the bridging acetate ion. Translation of each Cu2(CH3COO)4 unit along the chain, represented by the least-squares plane of the two copper ions along with four of the acetate O atoms, rotated these units by 35.16 (3)°.
Related literature
Shahid, Mazhar, Helliwell et al. (2008 ▶) describe the study of dinuclear Cu complexes; Van Niekerk & Schoening (1953 ▶) provide X-ray evidence for Cu—Cu bonds in cupric acetate; Brown & Chidambaram (1973 ▶) report the redetermination of the structure of cupric acetate by neutron-diffraction; Shahid, Mazhar, Malik et al. (2008 ▶); Hamid et al. (2007 ▶) and Zhang et al. (2004 ▶) describe geometric parameters of organo–copper complexes. 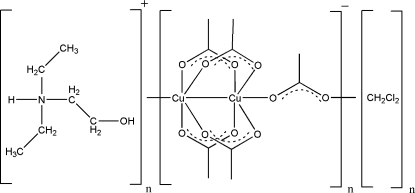
Experimental
Crystal data
(C6H16NO)[Cu2(C2H3O2)5]·CH2Cl2
M r = 625.42
Orthorhombic,
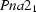
a = 17.6366 (11) Å
b = 12.1078 (8) Å
c = 11.9148 (7) Å
V = 2544.3 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 1.94 mm−1
T = 100 (2) K
0.40 × 0.40 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2001 ▶) T min = 0.657, T max = 0.830
21202 measured reflections
5939 independent reflections
5693 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.029
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.034
wR(F 2) = 0.080
S = 1.08
5939 reflections
306 parameters
1 restraint
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.75 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.40 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 2726 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: 0.017 (11)
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2001 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT-Plus (Bruker, 2003 ▶); data reduction: SAINT-Plus; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808044048/zl2161sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808044048/zl2161Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O10i | 0.93 | 1.97 | 2.832 (4) | 153 |
| N1—H1⋯O9i | 0.93 | 2.45 | 3.056 (3) | 123 |
| O11—H11⋯O9i | 0.84 | 2.04 | 2.840 (3) | 159 |
Symmetry code: (i) 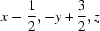 .
.
Acknowledgments
MS is grateful to the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan and the Pakistan Science Foundation for financial support via their PhD program.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
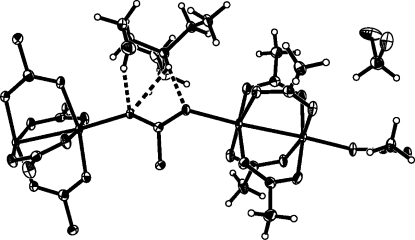
The background of this study has been set out in our previous work on the structural chemistry of metal-organic compounds (Shahid, Mazhar, Helliwell et al., 2008). Herein, as a continuation of these studies, the structure of the title compound is described which consists of acetate bridged Cu2(CH3COO)4 units that are connected via another acetate anion at each terminus to form infinite anionic [{Cu2(CH3COO)4}(CH3COO)]n chains along the [100] direction of the crystal. Crystallographically speaking the chain is generated from a glide related copies of the monomer. The connecting acetate is hydrogen bonded to the (diethylammonium)ethanol cation (Fig. 2). The dichloromethane solvate molecule occupies voids in the structure. The O—Cu—Cu angles along the polymeric chain are nearly linear (175.49 (5)°), but individual O—Cu—Cu—O units along the chain are rotated relative to each other. Representing the orientation of Cu2(CH3COO)4 unit by the least squares plane Cu1 Cu2 O1 O2 O5 O6, translation along the chain rotates the orientation by 35.16 (3)°.
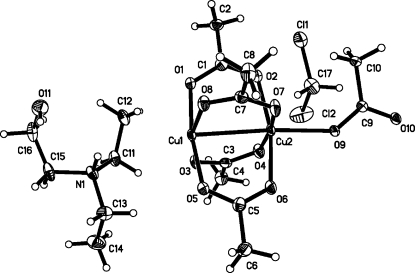
In the title compound (Fig.1), the two metal centers are similar; each has a coordination number of six having a coordination geometry close to octahedral, with a CuO5Cu core similar to that of Cu centers in Cu2(OAc)4(H2O)2. The basal planes of Cu(1) and Cu(2) are each composed of an oxygen from each of the four acetate groups (O(1), O(3), O(5), O(8) and O(2), O(4), O(6), O(7) respectively), which link the two copper atoms in the monomer. Coordination by the fifth acetate's O atoms, O(9) and O(10) (from a symmetry generated copy), form one apical bond for Cu(2) and Cu(1) respectively. The octahedral coordination of the copper atoms is completed by the apical Cu(1)—Cu(2) bond of 2.6259 (4) Å. This is significantly shorter than the 2.64 Å as reported for dinuclear copper (II) acetate monohydrate in 1953 (Van Niekerk & Schoening, 1953), but close to the more accurate value obtained in a redetermination by neutron diffraction analysis (2.6143 (17) Å, Brown & Chidambaram, 1973). The Cu—O bond lengths in the basal planes for both the Cu atoms range from 1.949 (2) to 1.985 (2) Å and the average distance is in good agreement with 1.97 Å, as reported for copper acetate (Van Niekerk & Schoening, 1953). The most striking structural difference between the title compound and the dinuclear units in cupric acetate appears to be the weaker apixal bonds Cu—O which are 2.148 (18) and 2.124 (18) Å for Cu(1) and Cu(2), respectively in the title compound and 2.20 Å in the cupric acetate. The distortion is further evident from the slight deviation of trans angles in the basal plane and axial angle from ideal value of 180°. This is in good agreement with the literature (Shahid, Mazhar, Malik et al., 2008); Hamid et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2004). In the structure, the (diethylamonium)ethanol cations are linked through hydrogen bonds [O(11)—H(11)···O(9)], [N(1)—H(1)···O(9)] and [N(1)—H(1)···O(10)] to the connecting acetate group occupying cis positions at the main polymeric chain (Table 1, Fig. 3).
Experimental
N,N-Diethylaminoethanol (deaeH) (0.27 g, 2.34 mmol) and acetic acid (0.14 g, 2.34 mmol) were added to a stirred suspension of Cu(CH3COO)2.H2O (0.85 g, 4.67 mmol) in 25 ml dichloromethane. After two hours stirring, the mixture was vacuum evaporated to dryness and the solid was redissolved in minimum amount of dichloromethane to give blue block-shaped crystals at room temperature after two weeks.
Refinement
The non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically. H atoms were included in calculated positions with C—H lengths of 0.95(CH), 0.99(CH2) & 0.98(CH3)Å; Uiso(H) values were fixed at 1.2Ueq(C) except for CH3 where it was 1.5Ueq(C). For N—H and O—H the lengths and Uiso were 0.98Å and 1.2Ueq(N) and 0.84Å and 1.5Ueq(O) respectively.
Figures
Fig. 1.
View of the title compound (50% probability displacement ellipsoids)
Fig. 2.
Fragment of the chain showing the H-bonding interactions.
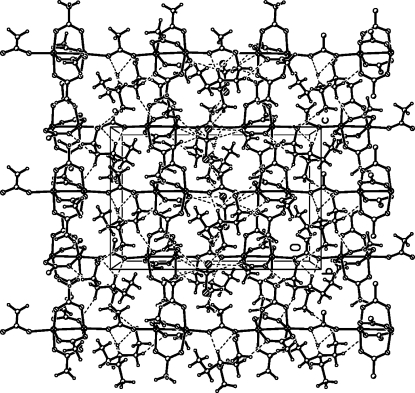
Fig. 3.
View down the b axis showing the infinite chains.
Crystal data
| (C6H16NO)[Cu2(C2H3O2)5]·CH2Cl2 | Dx = 1.633 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 625.42 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Orthorhombic, Pna21 | Cell parameters from 7814 reflections |
| a = 17.6366 (11) Å | θ = 2.4–28.1° |
| b = 12.1078 (8) Å | µ = 1.94 mm−1 |
| c = 11.9148 (7) Å | T = 100 K |
| V = 2544.3 (3) Å3 | Plate, turquoise |
| Z = 4 | 0.40 × 0.40 × 0.10 mm |
| F(000) = 1288 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 5939 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 5693 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.029 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 28.3°, θmin = 2.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2001) | h = −22→22 |
| Tmin = 0.657, Tmax = 0.830 | k = −16→15 |
| 21202 measured reflections | l = −15→15 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.034 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.080 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0393P)2 + 1.2652P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.08 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.013 |
| 5939 reflections | Δρmax = 0.75 e Å−3 |
| 306 parameters | Δρmin = −0.40 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 2726 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: 0.017 (11) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O10 | 1.03029 (10) | 0.66475 (16) | 0.5408 (2) | 0.0152 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.75148 (17) | 0.9544 (3) | 0.6165 (2) | 0.0176 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.77083 (18) | 1.0672 (3) | 0.6609 (3) | 0.0206 (6) | |
| H2A | 0.7588 | 1.0707 | 0.7411 | 0.031* | |
| H2B | 0.7413 | 1.1230 | 0.6206 | 0.031* | |
| H2C | 0.8250 | 1.0813 | 0.6500 | 0.031* | |
| C3 | 0.73249 (17) | 0.8234 (2) | 0.3482 (2) | 0.0166 (6) | |
| C4 | 0.73934 (19) | 0.8662 (3) | 0.2292 (3) | 0.0222 (7) | |
| H4A | 0.7896 | 0.8478 | 0.1994 | 0.033* | |
| H4B | 0.7327 | 0.9465 | 0.2289 | 0.033* | |
| H4C | 0.7002 | 0.8319 | 0.1823 | 0.033* | |
| C5 | 0.68347 (17) | 0.5689 (3) | 0.4849 (3) | 0.0191 (6) | |
| C6 | 0.66262 (19) | 0.4540 (3) | 0.4463 (3) | 0.0283 (8) | |
| H6A | 0.7085 | 0.4087 | 0.4414 | 0.042* | |
| H6B | 0.6384 | 0.4581 | 0.3724 | 0.042* | |
| H6C | 0.6274 | 0.4208 | 0.5002 | 0.042* | |
| C7 | 0.71363 (17) | 0.6985 (3) | 0.7522 (3) | 0.0173 (6) | |
| C8 | 0.71030 (19) | 0.6623 (3) | 0.8732 (3) | 0.0257 (7) | |
| H8A | 0.6693 | 0.7017 | 0.9116 | 0.039* | |
| H8B | 0.7587 | 0.6791 | 0.9100 | 0.039* | |
| H8C | 0.7008 | 0.5826 | 0.8767 | 0.039* | |
| C9 | 0.96959 (15) | 0.7062 (2) | 0.5798 (2) | 0.0133 (6) | |
| C10 | 0.97463 (17) | 0.7894 (3) | 0.6744 (3) | 0.0189 (6) | |
| H10A | 1.0156 | 0.7682 | 0.7256 | 0.028* | |
| H10B | 0.9265 | 0.7909 | 0.7154 | 0.028* | |
| H10C | 0.9851 | 0.8628 | 0.6433 | 0.028* | |
| C11 | 0.54065 (17) | 0.9990 (3) | 0.2860 (3) | 0.0210 (7) | |
| H11A | 0.5795 | 0.9515 | 0.2504 | 0.025* | |
| H11B | 0.5183 | 1.0463 | 0.2268 | 0.025* | |
| C12 | 0.57806 (18) | 1.0711 (3) | 0.3723 (3) | 0.0240 (7) | |
| H12A | 0.5967 | 1.0253 | 0.4342 | 0.036* | |
| H12B | 0.5412 | 1.1246 | 0.4012 | 0.036* | |
| H12C | 0.6206 | 1.1106 | 0.3379 | 0.036* | |
| C13 | 0.4783 (2) | 0.8130 (3) | 0.2850 (3) | 0.0265 (7) | |
| H13A | 0.4413 | 0.7669 | 0.3262 | 0.032* | |
| H13B | 0.5290 | 0.7792 | 0.2947 | 0.032* | |
| C14 | 0.4581 (2) | 0.8124 (4) | 0.1617 (3) | 0.0350 (9) | |
| H14A | 0.4934 | 0.8599 | 0.1205 | 0.052* | |
| H14B | 0.4063 | 0.8399 | 0.1519 | 0.052* | |
| H14C | 0.4615 | 0.7368 | 0.1327 | 0.052* | |
| C15 | 0.40137 (17) | 0.9772 (3) | 0.3296 (3) | 0.0249 (7) | |
| H15A | 0.3913 | 0.9998 | 0.2512 | 0.030* | |
| H15B | 0.3635 | 0.9203 | 0.3499 | 0.030* | |
| C16 | 0.39024 (18) | 1.0753 (3) | 0.4043 (3) | 0.0280 (7) | |
| H16A | 0.4225 | 1.1365 | 0.3771 | 0.034* | |
| H16B | 0.3368 | 1.0996 | 0.3991 | 0.034* | |
| C17 | 0.9547 (2) | 0.9492 (3) | 0.4356 (3) | 0.0292 (8) | |
| H17A | 0.9991 | 0.9018 | 0.4520 | 0.035* | |
| H17B | 0.9086 | 0.9093 | 0.4601 | 0.035* | |
| Cl1 | 0.96272 (5) | 1.07456 (9) | 0.51185 (9) | 0.0367 (2) | |
| Cl2 | 0.94975 (7) | 0.97421 (9) | 0.29049 (9) | 0.0475 (3) | |
| Cu1 | 0.647405 (16) | 0.78765 (2) | 0.55145 (3) | 0.01289 (8) | |
| Cu2 | 0.791704 (16) | 0.73425 (3) | 0.54933 (4) | 0.01346 (8) | |
| N1 | 0.47907 (14) | 0.9266 (2) | 0.3355 (2) | 0.0182 (5) | |
| H1 | 0.4905 | 0.9179 | 0.4112 | 0.022* | |
| O1 | 0.68332 (11) | 0.93608 (17) | 0.59168 (18) | 0.0168 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.80508 (12) | 0.88517 (18) | 0.60953 (19) | 0.0211 (5) | |
| O3 | 0.66724 (12) | 0.82111 (19) | 0.39116 (18) | 0.0184 (4) | |
| O4 | 0.79321 (12) | 0.79520 (19) | 0.39662 (19) | 0.0194 (5) | |
| O5 | 0.62993 (11) | 0.63224 (17) | 0.51139 (19) | 0.0193 (4) | |
| O6 | 0.75254 (11) | 0.59322 (18) | 0.4873 (2) | 0.0202 (5) | |
| O7 | 0.77446 (12) | 0.67809 (19) | 0.70047 (19) | 0.0212 (5) | |
| O8 | 0.65654 (12) | 0.7454 (2) | 0.71140 (18) | 0.0188 (4) | |
| O9 | 0.90593 (10) | 0.67911 (16) | 0.5416 (2) | 0.0172 (4) | |
| O11 | 0.40773 (14) | 1.05419 (19) | 0.5170 (2) | 0.0306 (6) | |
| H11 | 0.3963 | 0.9886 | 0.5327 | 0.046* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O10 | 0.0095 (8) | 0.0212 (9) | 0.0148 (10) | −0.0006 (6) | 0.0011 (8) | −0.0015 (10) |
| C1 | 0.0178 (15) | 0.0243 (16) | 0.0107 (14) | −0.0011 (12) | 0.0035 (11) | 0.0009 (12) |
| C2 | 0.0197 (15) | 0.0206 (16) | 0.0215 (15) | −0.0048 (12) | 0.0025 (13) | −0.0057 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0190 (14) | 0.0160 (14) | 0.0148 (14) | −0.0009 (11) | −0.0020 (12) | −0.0026 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0220 (16) | 0.0293 (17) | 0.0153 (15) | 0.0007 (13) | 0.0025 (12) | 0.0042 (13) |
| C5 | 0.0186 (15) | 0.0205 (15) | 0.0182 (15) | 0.0010 (12) | 0.0025 (12) | 0.0014 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0172 (16) | 0.0200 (16) | 0.048 (2) | −0.0038 (12) | 0.0046 (15) | −0.0101 (15) |
| C7 | 0.0172 (15) | 0.0179 (14) | 0.0168 (15) | −0.0019 (11) | 0.0000 (11) | −0.0016 (12) |
| C8 | 0.0232 (16) | 0.0366 (19) | 0.0173 (16) | 0.0060 (14) | 0.0024 (13) | 0.0091 (14) |
| C9 | 0.0139 (13) | 0.0139 (13) | 0.0123 (15) | −0.0011 (10) | −0.0003 (10) | 0.0017 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0144 (14) | 0.0209 (16) | 0.0213 (16) | 0.0000 (11) | −0.0036 (12) | −0.0091 (12) |
| C11 | 0.0150 (15) | 0.0296 (18) | 0.0185 (16) | −0.0010 (12) | 0.0033 (12) | 0.0075 (13) |
| C12 | 0.0144 (15) | 0.0294 (17) | 0.0283 (17) | −0.0048 (13) | −0.0006 (13) | 0.0063 (14) |
| C13 | 0.0315 (19) | 0.0241 (16) | 0.0240 (17) | −0.0013 (14) | −0.0016 (14) | 0.0000 (14) |
| C14 | 0.040 (2) | 0.043 (2) | 0.0215 (17) | −0.0088 (17) | −0.0011 (16) | −0.0045 (16) |
| C15 | 0.0135 (15) | 0.0404 (19) | 0.0208 (16) | −0.0001 (13) | −0.0038 (12) | 0.0141 (14) |
| C16 | 0.0133 (15) | 0.0298 (17) | 0.041 (2) | 0.0028 (13) | 0.0025 (14) | 0.0116 (15) |
| C17 | 0.0277 (18) | 0.036 (2) | 0.0242 (18) | −0.0045 (14) | 0.0010 (15) | 0.0061 (15) |
| Cl1 | 0.0248 (4) | 0.0460 (5) | 0.0393 (5) | 0.0034 (4) | −0.0039 (4) | −0.0083 (4) |
| Cl2 | 0.0826 (8) | 0.0327 (5) | 0.0272 (5) | −0.0082 (5) | 0.0083 (5) | 0.0062 (4) |
| Cu1 | 0.00720 (13) | 0.01831 (15) | 0.01316 (15) | 0.00109 (10) | 0.00003 (17) | −0.00089 (17) |
| Cu2 | 0.00722 (13) | 0.01905 (15) | 0.01411 (15) | 0.00129 (10) | 0.00009 (19) | −0.00129 (18) |
| N1 | 0.0148 (12) | 0.0255 (14) | 0.0142 (12) | −0.0033 (10) | −0.0022 (10) | 0.0056 (11) |
| O1 | 0.0117 (10) | 0.0184 (10) | 0.0205 (10) | 0.0008 (8) | −0.0007 (8) | −0.0027 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0119 (10) | 0.0253 (12) | 0.0260 (12) | 0.0025 (9) | −0.0020 (9) | −0.0077 (10) |
| O3 | 0.0117 (10) | 0.0290 (12) | 0.0145 (10) | 0.0008 (9) | −0.0004 (8) | 0.0014 (9) |
| O4 | 0.0127 (10) | 0.0295 (12) | 0.0161 (11) | 0.0003 (8) | 0.0025 (8) | 0.0018 (9) |
| O5 | 0.0123 (10) | 0.0200 (10) | 0.0255 (11) | −0.0005 (8) | −0.0006 (8) | −0.0045 (8) |
| O6 | 0.0103 (10) | 0.0207 (11) | 0.0295 (13) | −0.0016 (8) | 0.0002 (9) | −0.0022 (9) |
| O7 | 0.0138 (10) | 0.0317 (12) | 0.0183 (11) | 0.0069 (9) | 0.0001 (9) | 0.0054 (9) |
| O8 | 0.0153 (10) | 0.0273 (12) | 0.0137 (10) | 0.0043 (9) | 0.0023 (8) | 0.0023 (9) |
| O9 | 0.0083 (8) | 0.0220 (9) | 0.0213 (11) | 0.0002 (7) | −0.0008 (10) | −0.0075 (10) |
| O11 | 0.0310 (13) | 0.0231 (11) | 0.0378 (15) | −0.0031 (10) | 0.0034 (11) | −0.0001 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O10—C9 | 1.271 (3) | C12—H12A | 0.9800 |
| O10—Cu1i | 2.1482 (18) | C12—H12B | 0.9800 |
| C1—O1 | 1.258 (4) | C12—H12C | 0.9800 |
| C1—O2 | 1.266 (4) | C13—N1 | 1.500 (4) |
| C1—C2 | 1.504 (4) | C13—C14 | 1.512 (5) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9800 | C13—H13A | 0.9900 |
| C2—H2B | 0.9800 | C13—H13B | 0.9900 |
| C2—H2C | 0.9800 | C14—H14A | 0.9800 |
| C3—O3 | 1.260 (4) | C14—H14B | 0.9800 |
| C3—O4 | 1.263 (4) | C14—H14C | 0.9800 |
| C3—C4 | 1.514 (4) | C15—C16 | 1.496 (5) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9800 | C15—N1 | 1.503 (4) |
| C4—H4B | 0.9800 | C15—H15A | 0.9900 |
| C4—H4C | 0.9800 | C15—H15B | 0.9900 |
| C5—O6 | 1.254 (4) | C16—O11 | 1.400 (4) |
| C5—O5 | 1.257 (4) | C16—H16A | 0.9900 |
| C5—C6 | 1.510 (4) | C16—H16B | 0.9900 |
| C6—H6A | 0.9800 | C17—Cl2 | 1.758 (4) |
| C6—H6B | 0.9800 | C17—Cl1 | 1.775 (4) |
| C6—H6C | 0.9800 | C17—H17A | 0.9900 |
| C7—O8 | 1.254 (4) | C17—H17B | 0.9900 |
| C7—O7 | 1.262 (4) | Cu1—O1 | 1.965 (2) |
| C7—C8 | 1.508 (4) | Cu1—O5 | 1.966 (2) |
| C8—H8A | 0.9800 | Cu1—O8 | 1.980 (2) |
| C8—H8B | 0.9800 | Cu1—O3 | 1.983 (2) |
| C8—H8C | 0.9800 | Cu1—O10ii | 2.1482 (18) |
| C9—O9 | 1.255 (3) | Cu1—Cu2 | 2.6259 (4) |
| C9—C10 | 1.514 (4) | Cu2—O7 | 1.949 (2) |
| C10—H10A | 0.9800 | Cu2—O4 | 1.964 (2) |
| C10—H10B | 0.9800 | Cu2—O2 | 1.977 (2) |
| C10—H10C | 0.9800 | Cu2—O6 | 1.985 (2) |
| C11—C12 | 1.502 (5) | Cu2—O9 | 2.1243 (18) |
| C11—N1 | 1.515 (4) | N1—H1 | 0.9300 |
| C11—H11A | 0.9900 | O11—H11 | 0.8400 |
| C11—H11B | 0.9900 | ||
| C9—O10—Cu1i | 133.03 (19) | C13—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| O1—C1—O2 | 125.5 (3) | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 117.4 (3) | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| O2—C1—C2 | 117.1 (3) | C16—C15—N1 | 114.6 (3) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.5 | C16—C15—H15A | 108.6 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 109.5 | N1—C15—H15A | 108.6 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 109.5 | C16—C15—H15B | 108.6 |
| C1—C2—H2C | 109.5 | N1—C15—H15B | 108.6 |
| H2A—C2—H2C | 109.5 | H15A—C15—H15B | 107.6 |
| H2B—C2—H2C | 109.5 | O11—C16—C15 | 113.4 (3) |
| O3—C3—O4 | 125.6 (3) | O11—C16—H16A | 108.9 |
| O3—C3—C4 | 117.4 (3) | C15—C16—H16A | 108.9 |
| O4—C3—C4 | 116.9 (3) | O11—C16—H16B | 108.9 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 109.5 | C15—C16—H16B | 108.9 |
| C3—C4—H4B | 109.5 | H16A—C16—H16B | 107.7 |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 109.5 | Cl2—C17—Cl1 | 111.1 (2) |
| C3—C4—H4C | 109.5 | Cl2—C17—H17A | 109.4 |
| H4A—C4—H4C | 109.5 | Cl1—C17—H17A | 109.4 |
| H4B—C4—H4C | 109.5 | Cl2—C17—H17B | 109.4 |
| O6—C5—O5 | 125.5 (3) | Cl1—C17—H17B | 109.4 |
| O6—C5—C6 | 117.4 (3) | H17A—C17—H17B | 108.0 |
| O5—C5—C6 | 117.1 (3) | O1—Cu1—O5 | 170.19 (8) |
| C5—C6—H6A | 109.5 | O1—Cu1—O8 | 88.59 (10) |
| C5—C6—H6B | 109.5 | O5—Cu1—O8 | 89.95 (10) |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 109.5 | O1—Cu1—O3 | 89.50 (9) |
| C5—C6—H6C | 109.5 | O5—Cu1—O3 | 89.39 (10) |
| H6A—C6—H6C | 109.5 | O8—Cu1—O3 | 164.87 (9) |
| H6B—C6—H6C | 109.5 | O1—Cu1—O10ii | 94.53 (8) |
| O8—C7—O7 | 125.6 (3) | O5—Cu1—O10ii | 95.26 (8) |
| O8—C7—C8 | 118.1 (3) | O8—Cu1—O10ii | 101.81 (9) |
| O7—C7—C8 | 116.3 (3) | O3—Cu1—O10ii | 93.31 (9) |
| C7—C8—H8A | 109.5 | O1—Cu1—Cu2 | 85.13 (6) |
| C7—C8—H8B | 109.5 | O5—Cu1—Cu2 | 85.06 (6) |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 | O8—Cu1—Cu2 | 82.34 (6) |
| C7—C8—H8C | 109.5 | O3—Cu1—Cu2 | 82.54 (6) |
| H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 | O10ii—Cu1—Cu2 | 175.83 (7) |
| H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 | O7—Cu2—O4 | 171.68 (9) |
| O9—C9—O10 | 121.2 (3) | O7—Cu2—O2 | 90.33 (10) |
| O9—C9—C10 | 119.7 (2) | O4—Cu2—O2 | 89.27 (10) |
| O10—C9—C10 | 119.1 (2) | O7—Cu2—O6 | 89.42 (10) |
| C9—C10—H10A | 109.5 | O4—Cu2—O6 | 89.01 (10) |
| C9—C10—H10B | 109.5 | O2—Cu2—O6 | 166.35 (9) |
| H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 | O7—Cu2—O9 | 94.49 (9) |
| C9—C10—H10C | 109.5 | O4—Cu2—O9 | 93.75 (9) |
| H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 | O2—Cu2—O9 | 101.13 (8) |
| H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 | O6—Cu2—O9 | 92.50 (8) |
| C12—C11—N1 | 112.6 (3) | O7—Cu2—Cu1 | 85.74 (6) |
| C12—C11—H11A | 109.1 | O4—Cu2—Cu1 | 85.95 (6) |
| N1—C11—H11A | 109.1 | O2—Cu2—Cu1 | 83.37 (6) |
| C12—C11—H11B | 109.1 | O6—Cu2—Cu1 | 83.00 (6) |
| N1—C11—H11B | 109.1 | O9—Cu2—Cu1 | 175.49 (5) |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 107.8 | C13—N1—C15 | 110.3 (3) |
| C11—C12—H12A | 109.5 | C13—N1—C11 | 112.4 (3) |
| C11—C12—H12B | 109.5 | C15—N1—C11 | 113.5 (3) |
| H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 | C13—N1—H1 | 106.7 |
| C11—C12—H12C | 109.5 | C15—N1—H1 | 106.7 |
| H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 | C11—N1—H1 | 106.7 |
| H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 | C1—O1—Cu1 | 121.79 (19) |
| N1—C13—C14 | 113.4 (3) | C1—O2—Cu2 | 123.1 (2) |
| N1—C13—H13A | 108.9 | C3—O3—Cu1 | 123.84 (19) |
| C14—C13—H13A | 108.9 | C3—O4—Cu2 | 120.88 (19) |
| N1—C13—H13B | 108.9 | C5—O5—Cu1 | 121.84 (19) |
| C14—C13—H13B | 108.9 | C5—O6—Cu2 | 123.3 (2) |
| H13A—C13—H13B | 107.7 | C7—O7—Cu2 | 121.1 (2) |
| C13—C14—H14A | 109.5 | C7—O8—Cu1 | 123.7 (2) |
| C13—C14—H14B | 109.5 | C9—O9—Cu2 | 138.64 (19) |
| H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 | C16—O11—H11 | 109.5 |
| Cu1i—O10—C9—O9 | 163.2 (2) | O8—Cu1—O3—C3 | −7.4 (5) |
| Cu1i—O10—C9—C10 | −17.2 (4) | O10ii—Cu1—O3—C3 | 169.8 (2) |
| N1—C15—C16—O11 | −54.5 (4) | Cu2—Cu1—O3—C3 | −9.9 (2) |
| O1—Cu1—Cu2—O7 | 97.97 (10) | O3—C3—O4—Cu2 | 3.4 (4) |
| O5—Cu1—Cu2—O7 | −81.87 (10) | C4—C3—O4—Cu2 | −178.2 (2) |
| O8—Cu1—Cu2—O7 | 8.74 (10) | O2—Cu2—O4—C3 | −91.6 (2) |
| O3—Cu1—Cu2—O7 | −171.90 (10) | O6—Cu2—O4—C3 | 74.9 (2) |
| O1—Cu1—Cu2—O4 | −82.60 (9) | O9—Cu2—O4—C3 | 167.3 (2) |
| O5—Cu1—Cu2—O4 | 97.56 (10) | Cu1—Cu2—O4—C3 | −8.2 (2) |
| O8—Cu1—Cu2—O4 | −171.83 (10) | O6—C5—O5—Cu1 | 4.7 (4) |
| O3—Cu1—Cu2—O4 | 7.53 (9) | C6—C5—O5—Cu1 | −175.0 (2) |
| O1—Cu1—Cu2—O2 | 7.13 (9) | O8—Cu1—O5—C5 | −91.6 (2) |
| O5—Cu1—Cu2—O2 | −172.71 (10) | O3—Cu1—O5—C5 | 73.3 (2) |
| O8—Cu1—Cu2—O2 | −82.10 (10) | O10ii—Cu1—O5—C5 | 166.5 (2) |
| O3—Cu1—Cu2—O2 | 97.26 (10) | Cu2—Cu1—O5—C5 | −9.3 (2) |
| O1—Cu1—Cu2—O6 | −172.10 (10) | O5—C5—O6—Cu2 | 6.5 (4) |
| O5—Cu1—Cu2—O6 | 8.06 (9) | C6—C5—O6—Cu2 | −173.8 (2) |
| O8—Cu1—Cu2—O6 | 98.67 (10) | O7—Cu2—O6—C5 | 75.7 (2) |
| O3—Cu1—Cu2—O6 | −81.97 (10) | O4—Cu2—O6—C5 | −96.2 (2) |
| C14—C13—N1—C15 | 62.7 (4) | O2—Cu2—O6—C5 | −13.3 (6) |
| C14—C13—N1—C11 | −65.1 (4) | O9—Cu2—O6—C5 | 170.1 (2) |
| C16—C15—N1—C13 | 163.9 (3) | Cu1—Cu2—O6—C5 | −10.1 (2) |
| C16—C15—N1—C11 | −68.9 (3) | O8—C7—O7—Cu2 | 7.2 (4) |
| C12—C11—N1—C13 | −141.1 (3) | C8—C7—O7—Cu2 | −173.0 (2) |
| C12—C11—N1—C15 | 92.8 (3) | O2—Cu2—O7—C7 | 72.4 (2) |
| O2—C1—O1—Cu1 | 6.5 (4) | O6—Cu2—O7—C7 | −94.0 (2) |
| C2—C1—O1—Cu1 | −171.9 (2) | O9—Cu2—O7—C7 | 173.6 (2) |
| O8—Cu1—O1—C1 | 73.2 (2) | Cu1—Cu2—O7—C7 | −11.0 (2) |
| O3—Cu1—O1—C1 | −91.8 (2) | O7—C7—O8—Cu1 | 4.9 (5) |
| O10ii—Cu1—O1—C1 | 174.9 (2) | C8—C7—O8—Cu1 | −174.9 (2) |
| Cu2—Cu1—O1—C1 | −9.2 (2) | O1—Cu1—O8—C7 | −95.1 (3) |
| O1—C1—O2—Cu2 | 3.4 (4) | O5—Cu1—O8—C7 | 75.2 (3) |
| C2—C1—O2—Cu2 | −178.2 (2) | O3—Cu1—O8—C7 | −12.3 (6) |
| O7—Cu2—O2—C1 | −93.5 (2) | O10ii—Cu1—O8—C7 | 170.5 (2) |
| O4—Cu2—O2—C1 | 78.2 (2) | Cu2—Cu1—O8—C7 | −9.9 (2) |
| O6—Cu2—O2—C1 | −4.6 (6) | O10—C9—O9—Cu2 | −166.8 (2) |
| O9—Cu2—O2—C1 | 171.9 (2) | C10—C9—O9—Cu2 | 13.5 (5) |
| Cu1—Cu2—O2—C1 | −7.8 (2) | O7—Cu2—O9—C9 | −75.7 (3) |
| O4—C3—O3—Cu1 | 7.0 (4) | O4—Cu2—O9—C9 | 105.5 (3) |
| C4—C3—O3—Cu1 | −171.4 (2) | O2—Cu2—O9—C9 | 15.5 (3) |
| O1—Cu1—O3—C3 | 75.3 (2) | O6—Cu2—O9—C9 | −165.4 (3) |
| O5—Cu1—O3—C3 | −94.9 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1/2, −y+3/2, z; (ii) x−1/2, −y+3/2, z.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O10ii | 0.93 | 1.97 | 2.832 (4) | 153 |
| N1—H1···O9ii | 0.93 | 2.45 | 3.056 (3) | 123 |
| O11—H11···O9ii | 0.84 | 2.04 | 2.840 (3) | 159 |
Symmetry codes: (ii) x−1/2, −y+3/2, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: ZL2161).
References
- Brown, G. M. & Chidambaram, R. (1973). Acta Cryst. B29, 2393–2403.
- Bruker (2001). SMART and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2003). SAINT-Plus Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Hamid, M., Tahir, A. A., Mazhar, M., Zeller, M. & Hunter, A. D. (2007). Inorg. Chem.46, 4120–4127. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M., Mazhar, M., Helliwell, M., Akhtar, J. & Ahmad, K. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, m1139–m1140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M., Mazhar, M., Malik, M. A., O’Brien, P. & Raftery, J. (2008). Polyhedron, 27, 3337–3342.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Van Niekerk, J. N. & Schoening, F. R. L. (1953). Nature (London), 171, 36–37.
- Zhang, Y.-L., Chen, S.-W., Liu, W.-S. & Wang, D.-Q. (2004). Acta Cryst. E60, m196–m197.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808044048/zl2161sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808044048/zl2161Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report