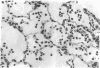
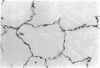
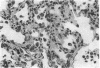
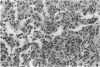
Abstract
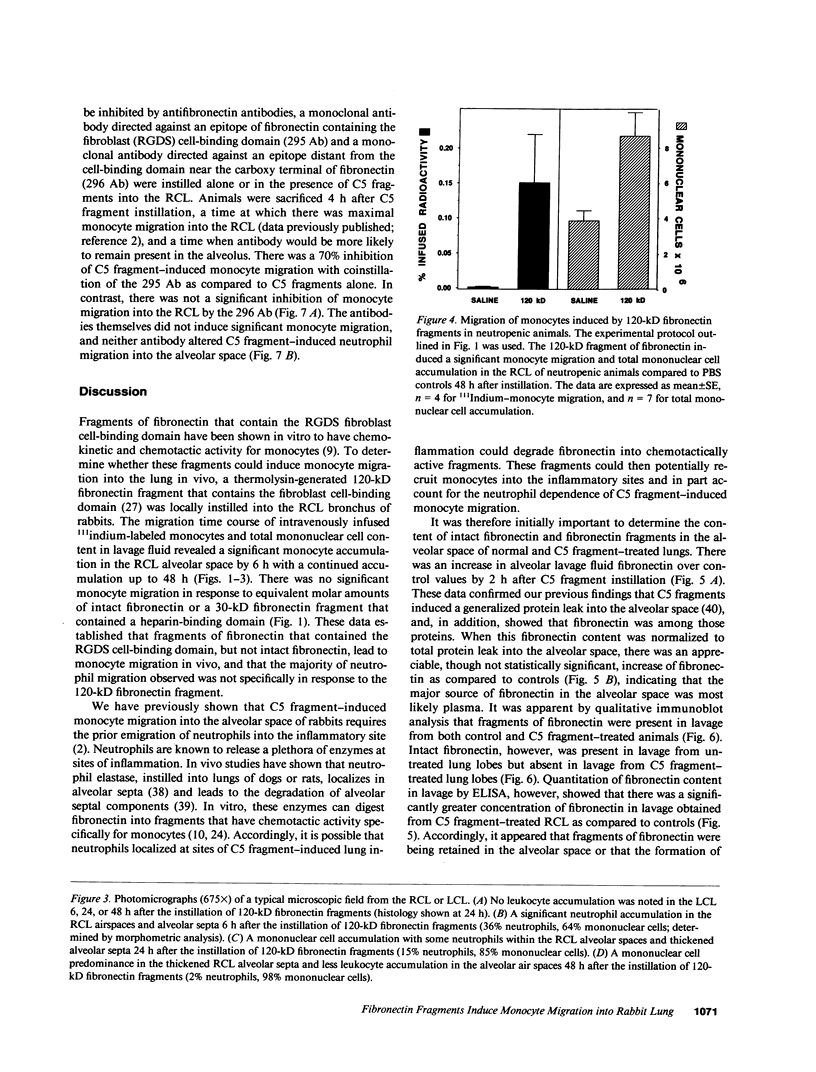
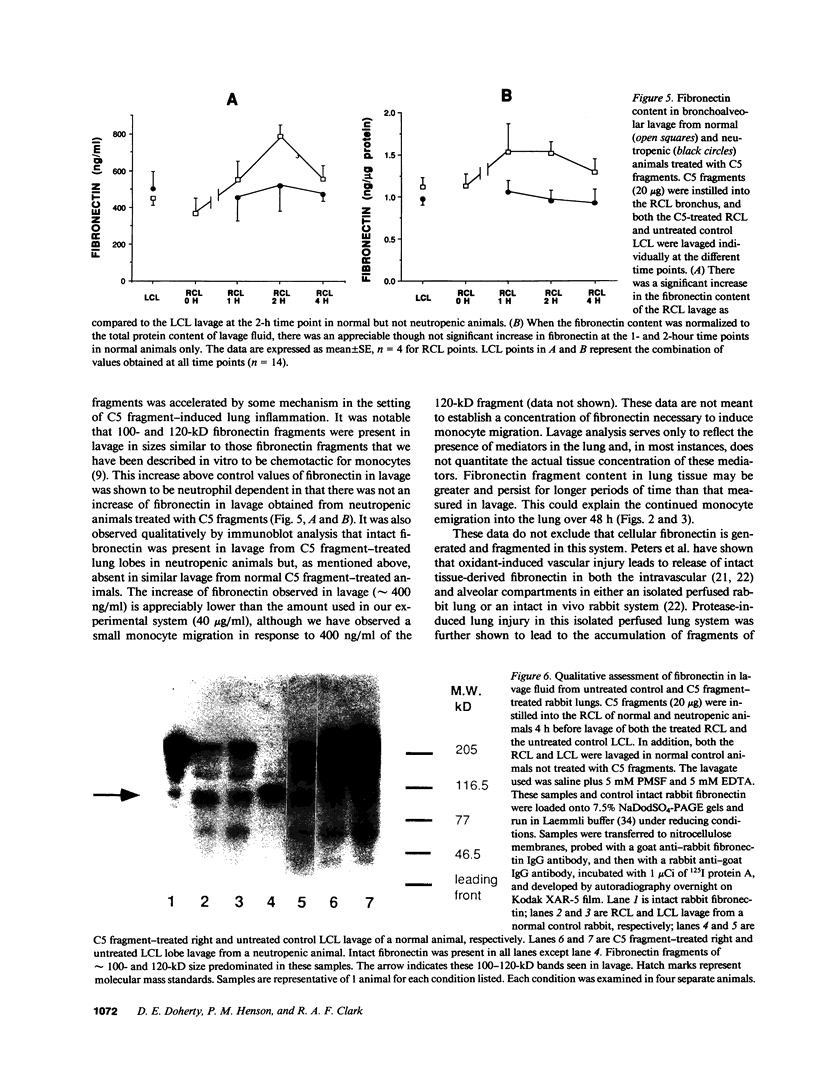
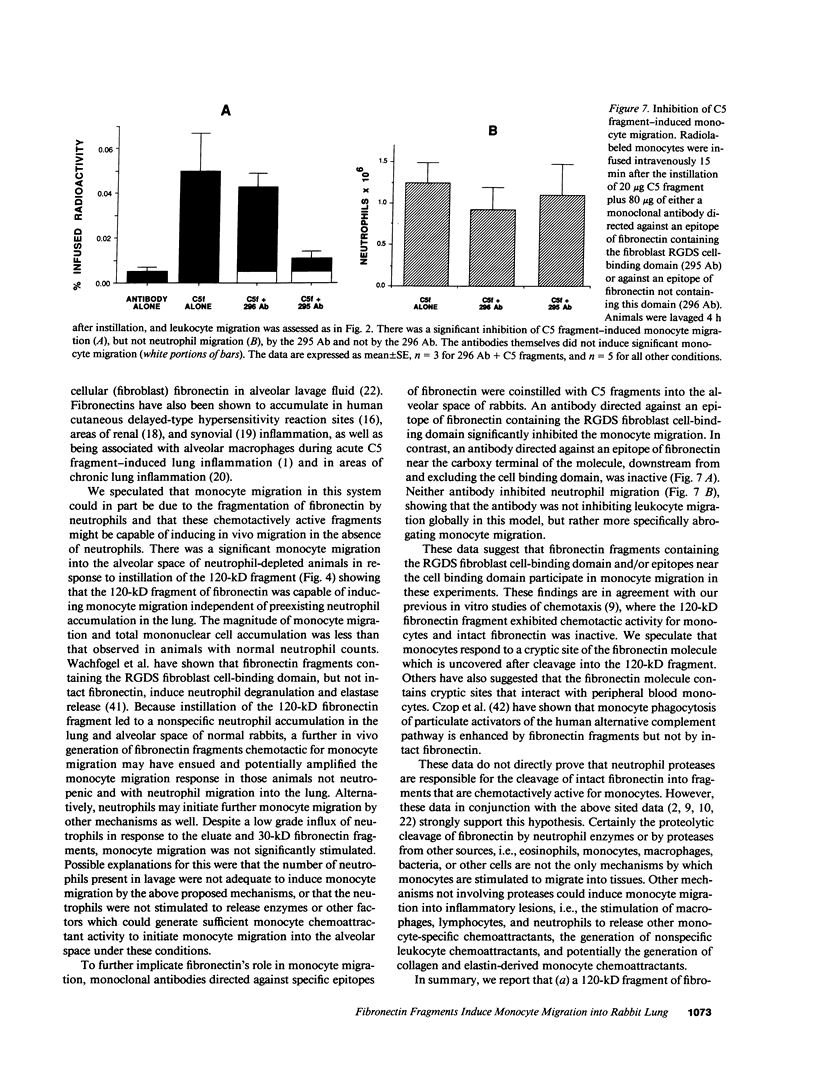
Many inflammatory processes are characterized by an early phase of neutrophil migration and a later phase of monocyte migration into the inflammatory site. Mechanisms that govern the transition between phases are the subject of these investigations. Acute lung inflammation induced by C5 fragments in the rabbit leads to an initial neutrophil influx and plasma leakage into the alveolar space, followed by monocyte influx that we have previously shown to be dependent on prior emigration of neutrophils. Neutrophil enzymes are known to cleave intact fibronectin into fragments that are monocyte chemotaxins in vitro. Accordingly, generation of appropriate fibronectin fragments in situ by proteolytic enzymes from infiltrating neutrophils might represent a potential mechanism for attraction of monocytes into the lung. The studies reported herein demonstrate that a 120-kD fragment of fibronectin containing the RGDS fibroblast cell-binding domain induced monocyte migration into the rabbit lung in vivo. Intact fibronectin was inactive. A significant proportion of the monocyte migration was neutrophil independent. Intact fibronectin was present in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from C5 fragment-treated animals rendered neutropenic, but absent in lavage from normal C5 fragment-treated animals. Fibronectin fragments were present in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from both C5 fragment-treated and control rabbits. In addition, the amount of fibronectin was significantly increased in lavage of C5 fragment-treated normal but not neutropenic animals. Monoclonal antibodies directed against an epitope of fibronectin containing the RGDS cell-binding domain significantly inhibited the C5 fragment-induced monocyte migration, but not neutrophil migration. These studies suggest that chemotactic fibronectin fragments may in part be responsible for the recruitment of monocytes into areas of acute lung inflammation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brada D., Roth J. "Golden blot"--detection of polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies bound to antigens on nitrocellulose by protein A-gold complexes. Anal Biochem. 1984 Oct;142(1):79–83. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90518-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carsons S., Mosesson M. W., Diamond H. S. Detection and quantitation of fibronectin in synovial fluid from patients with rheumatic disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Oct;24(10):1261–1267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Horsburgh C. R., Hoffman A. A., Dvorak H. F., Mosesson M. W., Colvin R. B. Fibronectin deposition in delayed-type hypersensitivity. Reactions of normals and a patient with afibrinogenemia. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):1011–1016. doi: 10.1172/JCI111468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Wikner N. E., Doherty D. E., Norris D. A. Cryptic chemotactic activity of fibronectin for human monocytes resides in the 120-kDa fibroblastic cell-binding fragment. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):12115–12123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czop J. K., Kadish J. L., Austen K. F. Augmentation of human monocyte opsonin-independent phagocytosis by fragments of human plasma fibronectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3649–3653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danpure H. J., Osman S., Brady F. The labelling of blood cells in plasma with 111In-tropolonate. Br J Radiol. 1982 Mar;55(651):247–249. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-55-651-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai U., Kreutzer D. L., Showell H., Arroyave C. V., Ward P. A. Acute inflammatory pulmonary reactions induced by chemotactic factors. Am J Pathol. 1979 Jul;96(1):71–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty D. E., Downey G. P., Worthen G. S., Haslett C., Henson P. M. Monocyte retention and migration in pulmonary inflammation. Requirement for neutrophils. Lab Invest. 1988 Aug;59(2):200–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downey G. P., Gumbay R. S., Doherty D. E., LaBrecque J. F., Henson J. E., Henson P. M., Worthen G. S. Enhancement of pulmonary inflammation by PGE2: evidence for a vasodilator effect. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Feb;64(2):728–741. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.64.2.728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez H. N., Hugli T. E. Partial characterization of human C5a anaphylatoxin. I. Chemical description of the carbohydrate and polypeptide prtions of human C5a. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1688–1694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie M. B., Rifkin D. B. Proteolytically derived fragments of human plasma fibronectin and their localization within the intact molecule. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):3134–3140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell F., Billingham R. E., Burgess L. Distribution of fibronectin during wound healing in vivo. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Mar;76(3):181–189. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12525694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Yamada K. M. Fibronectins: multifunctional modular glycoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):369–377. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Mosher D. F. Synthesis of fibronectin by cultured human endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1978 Jun 1;147(6):1779–1791. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.6.1779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff A., White R., Carp H., Harel S., Dearing R., Lee D. Lung injury induced by leukocytic proteases. Am J Pathol. 1979 Oct;97(1):111–136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen G. L., McCarthy K., Webster R. O., Henson J., Henson P. M. A differential effect of C5a and C5a des Arg in the induction of pulmonary inflammation. Am J Pathol. 1980 Jul;100(1):179–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. A., Kelley D. G. Degradation of fibronectin by human leukocyte elastase. Release of biologically active fragments. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8848–8858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald J. A., Quade B. J., Broekelmann T. J., LaChance R., Forsman K., Hasegawa E., Akiyama S. Fibronectin's cell-adhesive domain and an amino-terminal matrix assembly domain participate in its assembly into fibroblast pericellular matrix. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):2957–2967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norris D. A., Clark R. A., Swigart L. M., Huff J. C., Weston W. L., Howell S. E. Fibronectin fragment(s) are chemotactic for human peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1612–1618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. H., Ginsberg M. H., Bohl B. P., Sklar L. A., Cochrane C. G. Intravascular release of intact cellular fibronectin during oxidant-induced injury of the in vitro perfused rabbit lung. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1596–1603. doi: 10.1172/JCI112752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. H., Ginsberg M. H., Case C. M., Cochrane C. G. Release of soluble fibronectin containing an extra type III domain (ED1) during acute pulmonary injury mediated by oxidants or leukocytes in vivo. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Jul;138(1):167–174. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/138.1.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson E. E., Colvin R. B. Cold-insoluble globulin (fibronectin, LETS protein) in normal and diseased human glomeruli: papain-sensitive attachment to normal glomeruli and deposition in crescents. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Dec;11(4):425–436. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwaite A. E., Kang A. H. Collagen-and collagen peptide-induced chemotaxis of human blood monocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1299–1307. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennard S. I., Berg R., Martin G. R., Foidart J. M., Robey P. G. Enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) for connective tissue components. Anal Biochem. 1980 May 1;104(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90300-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revak S. D., Rice C. L., Schraufstätter I. U., Halsey W. A., Jr, Bohl B. P., Clancy R. M., Cochrane C. G. Experimental pulmonary inflammatory injury in the monkey. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):1182–1192. doi: 10.1172/JCI112074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. Fibronectin and its receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:375–413. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhaus R. A., Janoff A. Elastase-induced emphysema: retention of instilled proteinase in the rat. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Nov;126(5):914–920. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.126.5.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saverymuttu S. H., Peters A. M., Danpure H. J., Reavy H. J., Osman S., Lavender J. P. Lung transit of 111Indium-labelled granulocytes. Relationship to labelling techniques. Scand J Haematol. 1983 Feb;30(2):151–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1983.tb01463.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior R. M., Griffin G. L., Mecham R. P. Chemotactic activity of elastin-derived peptides. J Clin Invest. 1980 Oct;66(4):859–862. doi: 10.1172/JCI109926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. O., Henson P. M., Henson J., Webster R. O. Lung inflammation induced by complement-derived chemotactic fragments in the alveolus. Lab Invest. 1980 May;42(5):547–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. O. Leukocytes in chemotactic-fragment-induced lung inflammation. Vascular emigration and alveolar surface migration. Am J Pathol. 1980 Nov;101(2):283–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun J. W., Hynes R. O. Plasma fibronectin is synthesized and secreted by hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4641–4647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torikata C., Villiger B., Kuhn C., 3rd, McDonald J. A. Ultrastructural distribution of fibronectin in normal and fibrotic human lung. Lab Invest. 1985 Apr;52(4):399–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vartio T., Seppä H., Vaheri A. Susceptibility of soluble and matrix fibronectins to degradation by tissue proteinases, mast cell chymase and cathepsin G. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 10;256(1):471–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
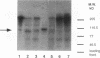
- Wachtfogel Y. T., Abrams W., Kucich U., Weinbaum G., Schapira M., Colman R. W. Fibronectin degradation products containing the cytoadhesive tetrapeptide stimulate human neutrophil degranulation. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1310–1316. doi: 10.1172/JCI113456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
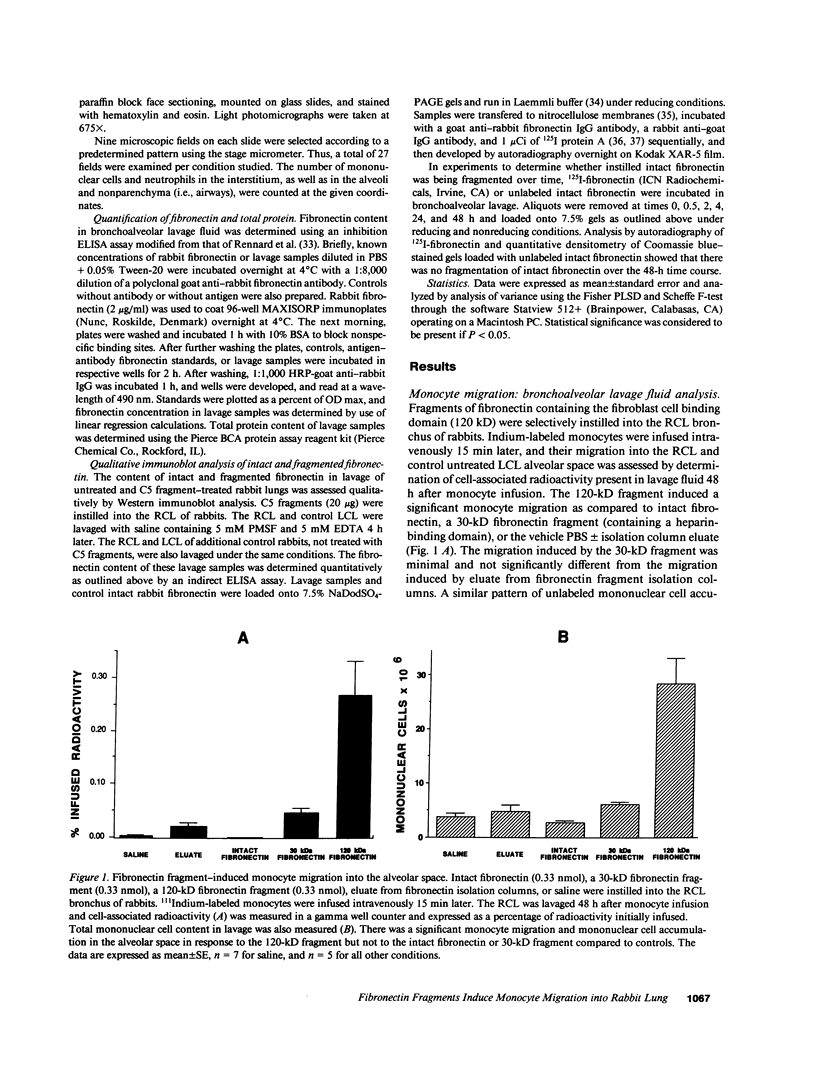
- Webster R. O., Hong S. R., Johnston R. B., Jr, Henson P. M. Biologial effects of the human complement fragments C5a and C5ades Arg on neutrophil function. Immunopharmacology. 1980 Jun;2(3):201–219. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(80)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikner N. E., Clark R. A. Chemotactic fragments of fibronectin. Methods Enzymol. 1988;162:214–222. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)62078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
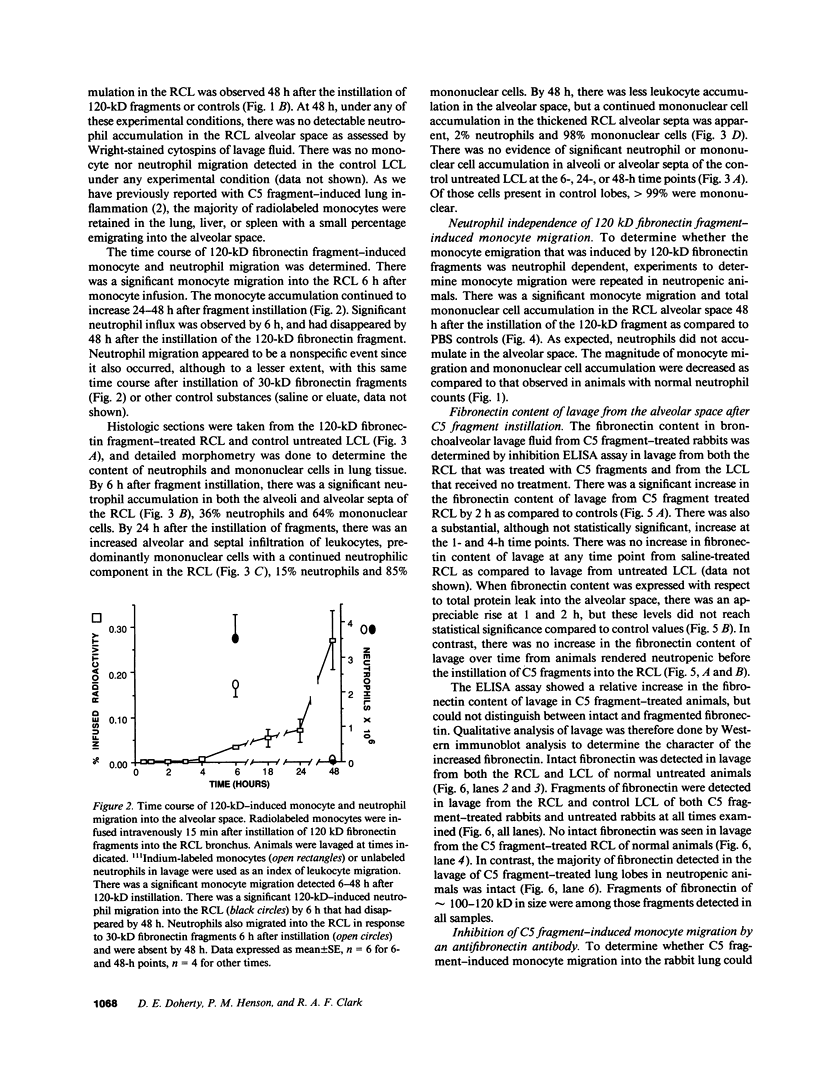
- Yamada K. M., Akiyama S. K., Hasegawa T., Hasegawa E., Humphries M. J., Kennedy D. W., Nagata K., Urushihara H., Olden K., Chen W. T. Recent advances in research on fibronectin and other cell attachment proteins. J Cell Biochem. 1985;28(2):79–97. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240280202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
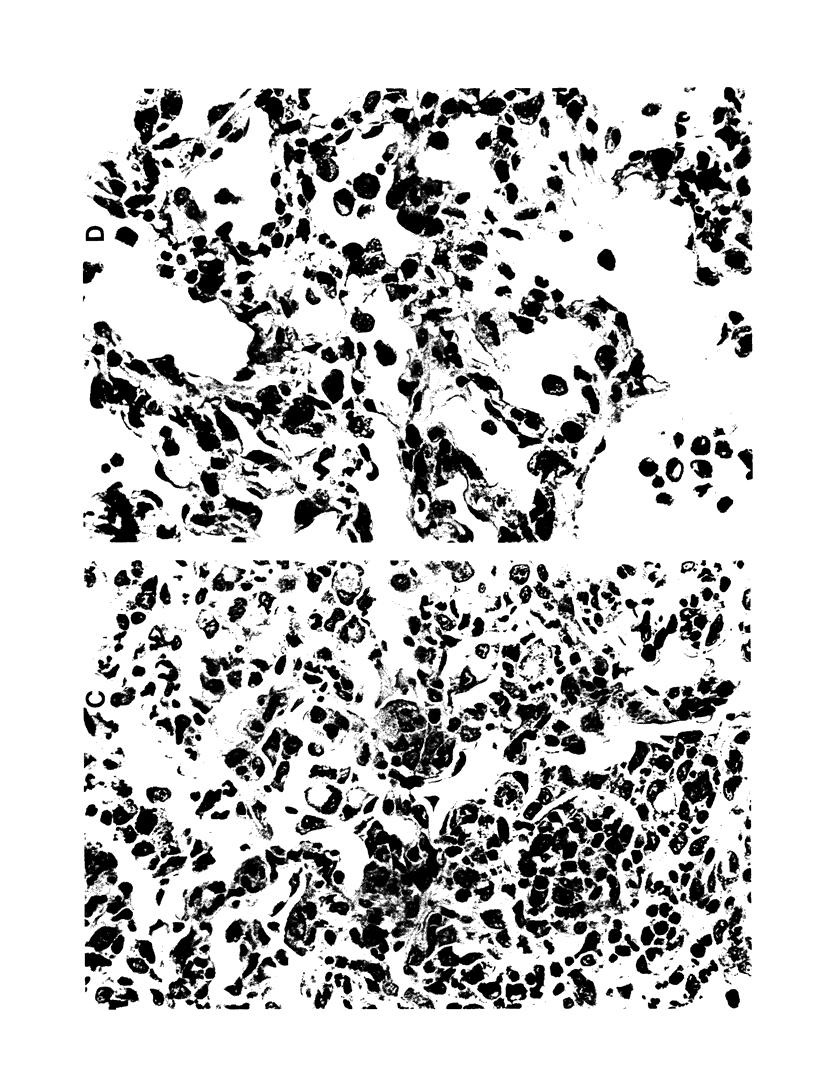
- Yamada K. M., Kennedy D. W. Fibroblast cellular and plasma fibronectins are similar but not identical. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):492–498. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]