Abstract
In the molecule of the title compound, C13H10INO4S·H2O, the coordination around the S atom is distorted tetrahedral. The aromatic rings are oriented at a dihedral angle of 74.18 (17)°. Intramolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds result in the formation of non-planar five- and six-membered rings, which adopt envelope and twist conformations, respectively. In the crystal structure, intermolecular N—H⋯O, O—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules. π–π Contacts between the phenyl rings [centroid–centroid distance = 3.726 (3) Å] may further stabilize the structure. There is also a C—H⋯π interaction.
Related literature
For general background, see: Medina et al. (1999 ▶). For related structures, see: Arshad et al. (2008a
▶,b
▶); Nan & Xing (2006 ▶); Deng & Mani (2006 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C13H10INO4S·H2O
M r = 421.20
Monoclinic,

a = 13.8049 (9) Å
b = 8.2756 (5) Å
c = 14.7928 (10) Å
β = 117.472 (3)°
V = 1499.42 (17) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 2.30 mm−1
T = 296 (2) K
0.28 × 0.10 × 0.07 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.754, T max = 0.849
9099 measured reflections
3687 independent reflections
2022 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.041
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.046
wR(F 2) = 0.112
S = 1.01
3687 reflections
193 parameters
1 restraint
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.55 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.54 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808043754/hk2605sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808043754/hk2605Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O4i | 0.86 | 2.03 | 2.860 (6) | 161.00 |
| O3—H3O⋯O5ii | 0.91 (7) | 1.73 (7) | 2.616 (6) | 165 (7) |
| O5—H5A⋯O2iii | 0.81 | 2.20 | 2.924 (6) | 149.00 |
| O5—H5B⋯O1 | 0.88 | 1.98 | 2.791 (6) | 152.00 |
| C6—H6⋯O1 | 0.93 | 2.36 | 2.793 (7) | 108.00 |
| C11—H11⋯O2iv | 0.93 | 2.52 | 3.437 (6) | 171.00 |
| C12—H12⋯O1 | 0.93 | 2.54 | 3.035 (7) | 114.00 |
| C3—H3⋯Cg2v | 0.93 | 2.90 | 3.818 (7) | 168.00 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v)  . Cg2 is the centroid of the C7–C12 ring.
. Cg2 is the centroid of the C7–C12 ring.
Acknowledgments
MNA greatfully acknowledges the Higher Education Commision, Islamabad, Pakistan, for providing him with a Scholaship under the Indigenous PhD Program (PIN 042–120607-PS2–183).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound belongs to the sulfonamide family of the organic compounds. This class of compounds is used as antibecterial agent. The halogenated sulfonamide is used as an inhibitor for the growth of multidrug resistant MCF-7/ADR cancer cells (Medina et al., 1999). In continuation to our researches with sulfonamides (Arshad et al., 2008a,b), the title compound has been prepared, which will be utilized for the syntheses of biologically active heterocyclic molecules with thiazine moiety, and we report herein its crystal structure.
In the title compound, (I), (Fig 1), 2-iodophenyl and p-aminobenzoic acid moieties are connected through the SO2 group. The structure of (I) differs from 4-(tosylamino)benzoic acid, (II) (Nan & Xing, 2006), mainly due to the attachment of the iodo group at ortho position instead of methyl group at the para-position. The coordination around the S atom is a distorted tetrahedral. Rings A(C1-C6) and B(C7-C12) are oriented at a dihedral angle of 74.18 (17)°. The intramolecular C-H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1) result in the formations of nonplanar five- and six-membered rings: C (S1/O1/C1/C6/H6) and D (S1/O1/N1/C7/C12/H12). Ring C adopts envelope conformation with O1 atom displaced by -0.172 (3) Å from the plane of the other rings atoms, while ring D has twisted conformation.
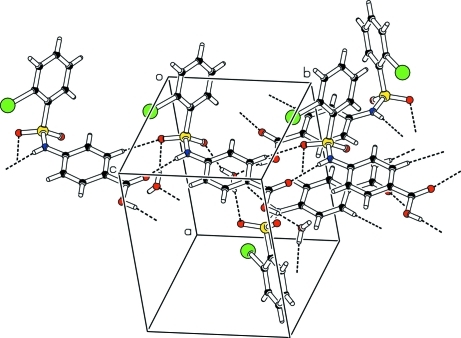
In the crystal structure, intermolecular N-H···O, O-H···O and C-H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1) link the molecules (Fig. 2), in which they may be effective in the stabilization of the structure. The π-π contact between the phenyl rings, Cg1—Cg1i [symmetry code: (i) -x, -y, -z, where Cg1 is centroid of the ring A (C1-C6)] may further stabilize the structure, with centroid-centroid distance of 3.726 (3) Å. There also exists a C–H···π interaction (Table 1).
Experimental
The title compound was synthesized according to a literature method (Deng & Mani, 2006). 4-Aminobenzoic acid (0.23 g, 1.67 mmol) was suspended in distilled water (10 ml) in a round bottom flask. The pH of the solution was adjusted to 8-9 using Na2CO3 (1 M). Then, 2-iodobenzene sulfonyl chloride (0.5 g, 1.66 mmol) was added, and stirred at room temperature. The reaction pH was maintained at 8-9. Completion of reaction was indicated by the dissolvation of the suspended 2-iodobenzene sulfonyl chloride. Then, pH was adjusted to 2-3 using HCl (2 N), the precipitate formed was filtered, washed with distilled water, and then recrystalyzed in methanol.
Refinement
H3O (for OH) atom was located in difference syntheses and refined [O-H = 0.91 (7) Å, Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(O)]. The remaining H atoms were positioned geometrically, with O-H = 0.81 and 0.88 Å (for H2O), N-H = 0.86 Å (for NH) and C-H = 0.93 Å for aromatic H, respectively, and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C,N,O).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title molecule, with the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Fig. 2.
A partial packing diagram of the title compound. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C13H10INO4S·H2O | F(000) = 824 |
| Mr = 421.20 | Dx = 1.866 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 3638 reflections |
| a = 13.8049 (9) Å | θ = 2.8–28.3° |
| b = 8.2756 (5) Å | µ = 2.30 mm−1 |
| c = 14.7928 (10) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 117.472 (3)° | Needle, light brown |
| V = 1499.42 (17) Å3 | 0.28 × 0.10 × 0.07 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3687 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2022 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.041 |
| Detector resolution: 7.40 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 28.3°, θmin = 2.8° |
| ω scans | h = −15→18 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | k = −11→6 |
| Tmin = 0.754, Tmax = 0.849 | l = −19→19 |
| 9099 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.046 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.112 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.01 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0445P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3687 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 193 parameters | Δρmax = 0.55 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Δρmin = −0.54 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| I1 | 0.05915 (3) | −0.04749 (5) | 0.26394 (3) | 0.0542 (2) | |
| S1 | 0.25343 (9) | 0.13703 (16) | 0.19929 (10) | 0.0345 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.3085 (3) | 0.2410 (4) | 0.1612 (3) | 0.0454 (14) | |
| O2 | 0.2710 (3) | −0.0328 (4) | 0.2010 (3) | 0.0415 (11) | |
| O3 | 0.4294 (3) | 0.7980 (5) | 0.6032 (3) | 0.0614 (17) | |
| O4 | 0.3555 (4) | 0.9284 (5) | 0.4580 (3) | 0.0710 (17) | |
| O5 | 0.4923 (3) | 0.4220 (5) | 0.1937 (3) | 0.086 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.2852 (3) | 0.1876 (5) | 0.3139 (3) | 0.0377 (16) | |
| C1 | 0.1119 (4) | 0.1750 (5) | 0.1231 (4) | 0.0292 (17) | |
| C2 | 0.0316 (4) | 0.1050 (6) | 0.1405 (4) | 0.0363 (19) | |
| C3 | −0.0775 (4) | 0.1337 (7) | 0.0725 (5) | 0.051 (2) | |
| C4 | −0.1052 (5) | 0.2319 (8) | −0.0099 (5) | 0.056 (2) | |
| C5 | −0.0257 (5) | 0.2994 (7) | −0.0279 (4) | 0.054 (2) | |
| C6 | 0.0834 (4) | 0.2707 (6) | 0.0389 (4) | 0.044 (2) | |
| C7 | 0.3051 (3) | 0.3426 (6) | 0.3580 (4) | 0.0331 (18) | |
| C8 | 0.3537 (4) | 0.3529 (6) | 0.4634 (4) | 0.0392 (19) | |
| C9 | 0.3778 (4) | 0.5001 (6) | 0.5106 (4) | 0.0378 (17) | |
| C10 | 0.3543 (3) | 0.6425 (6) | 0.4554 (4) | 0.0327 (16) | |
| C11 | 0.3061 (4) | 0.6315 (6) | 0.3498 (4) | 0.0391 (19) | |
| C12 | 0.2810 (4) | 0.4842 (6) | 0.3012 (4) | 0.0397 (17) | |
| C13 | 0.3791 (4) | 0.8042 (7) | 0.5038 (5) | 0.0417 (19) | |
| H1 | 0.29097 | 0.10916 | 0.35421 | 0.0453* | |
| H3 | −0.13213 | 0.08538 | 0.08334 | 0.0614* | |
| H3O | 0.440 (5) | 0.896 (8) | 0.634 (5) | 0.0734* | |
| H4 | −0.17827 | 0.25271 | −0.05378 | 0.0676* | |
| H5 | −0.04448 | 0.36446 | −0.08481 | 0.0649* | |
| H6 | 0.13757 | 0.31670 | 0.02652 | 0.0534* | |
| H8 | 0.36997 | 0.25903 | 0.50216 | 0.0469* | |
| H9 | 0.41064 | 0.50465 | 0.58138 | 0.0457* | |
| H11 | 0.29045 | 0.72558 | 0.31126 | 0.0474* | |
| H12 | 0.24791 | 0.47936 | 0.23047 | 0.0474* | |
| H5A | 0.55225 | 0.43714 | 0.24163 | 0.1030* | |
| H5B | 0.44825 | 0.35754 | 0.20513 | 0.1030* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| I1 | 0.0626 (3) | 0.0469 (3) | 0.0680 (3) | 0.0006 (2) | 0.0429 (2) | 0.0116 (2) |
| S1 | 0.0343 (6) | 0.0313 (8) | 0.0384 (9) | −0.0025 (6) | 0.0171 (6) | −0.0039 (6) |
| O1 | 0.049 (2) | 0.043 (2) | 0.056 (3) | −0.0132 (17) | 0.0343 (19) | −0.0061 (19) |
| O2 | 0.0403 (19) | 0.029 (2) | 0.050 (2) | 0.0031 (16) | 0.0165 (17) | −0.0062 (18) |
| O3 | 0.086 (3) | 0.032 (3) | 0.043 (3) | 0.003 (2) | 0.010 (2) | −0.007 (2) |
| O4 | 0.105 (3) | 0.027 (3) | 0.045 (3) | 0.005 (2) | 0.004 (2) | 0.005 (2) |
| O5 | 0.046 (2) | 0.076 (4) | 0.100 (4) | −0.015 (2) | 0.003 (2) | 0.054 (3) |
| N1 | 0.053 (3) | 0.023 (2) | 0.029 (3) | −0.0021 (19) | 0.012 (2) | 0.003 (2) |
| C1 | 0.035 (3) | 0.024 (3) | 0.028 (3) | 0.002 (2) | 0.014 (2) | −0.001 (2) |
| C2 | 0.039 (3) | 0.028 (3) | 0.044 (4) | 0.002 (2) | 0.021 (3) | −0.007 (2) |
| C3 | 0.043 (3) | 0.042 (4) | 0.070 (5) | −0.003 (3) | 0.027 (3) | −0.016 (3) |
| C4 | 0.046 (3) | 0.051 (4) | 0.049 (4) | 0.008 (3) | 0.002 (3) | −0.011 (3) |
| C5 | 0.073 (4) | 0.041 (4) | 0.032 (4) | 0.009 (3) | 0.010 (3) | −0.001 (3) |
| C6 | 0.054 (3) | 0.037 (4) | 0.040 (4) | −0.005 (3) | 0.020 (3) | −0.003 (3) |
| C7 | 0.030 (2) | 0.028 (3) | 0.038 (4) | 0.000 (2) | 0.013 (2) | −0.004 (3) |
| C8 | 0.052 (3) | 0.023 (3) | 0.041 (4) | 0.001 (2) | 0.020 (3) | 0.006 (3) |
| C9 | 0.050 (3) | 0.028 (3) | 0.033 (3) | 0.000 (2) | 0.017 (3) | 0.001 (2) |
| C10 | 0.028 (2) | 0.032 (3) | 0.035 (3) | −0.002 (2) | 0.012 (2) | −0.002 (3) |
| C11 | 0.044 (3) | 0.023 (3) | 0.046 (4) | 0.000 (2) | 0.017 (3) | 0.007 (3) |
| C12 | 0.050 (3) | 0.033 (3) | 0.027 (3) | 0.001 (2) | 0.010 (3) | 0.003 (2) |
| C13 | 0.036 (3) | 0.030 (3) | 0.048 (4) | 0.004 (2) | 0.010 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| I1—C2 | 2.105 (5) | C5—C6 | 1.389 (9) |
| S1—O1 | 1.425 (4) | C7—C8 | 1.387 (7) |
| S1—O2 | 1.425 (4) | C7—C12 | 1.390 (7) |
| S1—N1 | 1.599 (4) | C8—C9 | 1.367 (7) |
| S1—C1 | 1.776 (6) | C9—C10 | 1.384 (7) |
| O3—C13 | 1.306 (8) | C10—C13 | 1.481 (8) |
| O4—C13 | 1.191 (7) | C10—C11 | 1.390 (7) |
| O3—H3O | 0.91 (7) | C11—C12 | 1.376 (7) |
| O5—H5A | 0.8100 | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| O5—H5B | 0.8800 | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C7 | 1.408 (6) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| N1—H1 | 0.8600 | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.376 (8) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C6 | 1.372 (7) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.392 (9) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.365 (9) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.363 (10) | ||
| I1···O2 | 3.456 (5) | C4···O2iv | 3.158 (8) |
| I1···N1 | 3.456 (4) | C4···I1xi | 3.853 (7) |
| I1···C4i | 3.853 (7) | C5···C5xii | 3.416 (8) |
| I1···C2i | 3.671 (5) | C8···O1xiii | 3.353 (7) |
| I1···C3i | 3.509 (6) | C9···C9x | 3.530 (9) |
| I1···H1 | 3.1200 | C12···O1 | 3.035 (7) |
| S1···H12 | 2.8800 | C13···O5v | 3.379 (7) |
| S1···H5Aii | 2.9200 | C9···H3xi | 3.1000 |
| O1···O5 | 2.791 (6) | C10···H3xi | 2.8900 |
| O1···C12 | 3.035 (7) | C11···H3xi | 3.0100 |
| O1···C8iii | 3.353 (7) | H1···I1 | 3.1200 |
| O2···C4iv | 3.158 (8) | H1···H8 | 2.3100 |
| O2···O5ii | 2.924 (6) | H1···O4ix | 2.0300 |
| O2···I1 | 3.456 (5) | H3···C10i | 2.8900 |
| O3···O5v | 2.616 (6) | H3···C9i | 3.1000 |
| O4···N1vi | 2.860 (6) | H3···C11i | 3.0100 |
| O5···O3vii | 2.616 (6) | H3O···O5v | 1.73 (7) |
| O5···C13vii | 3.379 (7) | H3O···H5Av | 2.1400 |
| O5···O2viii | 2.924 (6) | H3O···H5Bv | 2.2700 |
| O5···O1 | 2.791 (6) | H4···O2iv | 2.6700 |
| O1···H12 | 2.5400 | H5A···O2viii | 2.2000 |
| O1···H5B | 1.9800 | H5A···H9x | 2.4700 |
| O1···H6 | 2.3600 | H5A···S1viii | 2.9200 |
| O1···H8iii | 2.8500 | H5A···H3Ovii | 2.1400 |
| O2···H4iv | 2.6700 | H5B···O1 | 1.9800 |
| O2···H11ix | 2.5200 | H5B···O3x | 2.8500 |
| O2···H5Aii | 2.2000 | H5B···H3Ovii | 2.2700 |
| O3···H9 | 2.4500 | H6···O1 | 2.3600 |
| O3···H5Bx | 2.8500 | H8···O4ix | 2.8000 |
| O4···H1vi | 2.0300 | H8···H1 | 2.3100 |
| O4···H8vi | 2.8000 | H8···O1xiii | 2.8500 |
| O4···H11 | 2.5600 | H9···O3 | 2.4500 |
| O5···H3Ovii | 1.73 (7) | H9···H5Ax | 2.4700 |
| N1···O4ix | 2.860 (6) | H11···O2vi | 2.5200 |
| N1···I1 | 3.456 (4) | H11···O4 | 2.5600 |
| C2···I1xi | 3.671 (5) | H12···O1 | 2.5400 |
| C3···I1xi | 3.509 (6) | H12···S1 | 2.8800 |
| O1—S1—O2 | 119.0 (3) | C8—C9—C10 | 121.5 (5) |
| O1—S1—N1 | 109.0 (2) | C9—C10—C11 | 117.9 (5) |
| O1—S1—C1 | 105.9 (2) | C11—C10—C13 | 119.1 (5) |
| O2—S1—N1 | 106.2 (2) | C9—C10—C13 | 123.0 (5) |
| O2—S1—C1 | 108.3 (2) | C10—C11—C12 | 121.3 (5) |
| N1—S1—C1 | 108.1 (3) | C7—C12—C11 | 119.9 (5) |
| C13—O3—H3O | 114 (4) | O3—C13—C10 | 113.2 (5) |
| H5A—O5—H5B | 116.00 | O4—C13—C10 | 124.3 (6) |
| S1—N1—C7 | 129.0 (4) | O3—C13—O4 | 122.6 (6) |
| C7—N1—H1 | 116.00 | C2—C3—H3 | 120.00 |
| S1—N1—H1 | 115.00 | C4—C3—H3 | 120.00 |
| S1—C1—C2 | 123.5 (4) | C5—C4—H4 | 120.00 |
| S1—C1—C6 | 116.7 (5) | C3—C4—H4 | 120.00 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.6 (5) | C4—C5—H5 | 120.00 |
| I1—C2—C1 | 125.2 (4) | C6—C5—H5 | 120.00 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.3 (5) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.00 |
| I1—C2—C3 | 115.6 (4) | C1—C6—H6 | 120.00 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.7 (6) | C7—C8—H8 | 120.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.0 (6) | C9—C8—H8 | 120.00 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.9 (5) | C10—C9—H9 | 119.00 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 120.5 (6) | C8—C9—H9 | 119.00 |
| C8—C7—C12 | 119.0 (5) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.00 |
| N1—C7—C8 | 117.8 (4) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.00 |
| N1—C7—C12 | 123.2 (5) | C7—C12—H12 | 120.00 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 120.4 (5) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.00 |
| O1—S1—N1—C7 | 35.5 (5) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.9 (9) |
| O2—S1—N1—C7 | 164.9 (5) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.9 (10) |
| C1—S1—N1—C7 | −79.1 (5) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.3 (9) |
| O1—S1—C1—C2 | −175.7 (4) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.1 (8) |
| O1—S1—C1—C6 | 9.1 (4) | N1—C7—C8—C9 | 178.2 (5) |
| O2—S1—C1—C2 | 55.6 (5) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | −0.2 (9) |
| O2—S1—C1—C6 | −119.7 (4) | N1—C7—C12—C11 | −177.8 (5) |
| N1—S1—C1—C2 | −59.0 (5) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | 0.4 (9) |
| N1—S1—C1—C6 | 125.7 (4) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.3 (9) |
| S1—N1—C7—C8 | −166.5 (4) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.6 (9) |
| S1—N1—C7—C12 | 11.8 (8) | C8—C9—C10—C13 | 180.0 (6) |
| S1—C1—C2—I1 | 4.0 (6) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.9 (9) |
| S1—C1—C2—C3 | −175.7 (4) | C13—C10—C11—C12 | −179.7 (6) |
| C6—C1—C2—I1 | 179.1 (4) | C9—C10—C13—O3 | 2.8 (8) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.5 (8) | C9—C10—C13—O4 | −176.6 (6) |
| S1—C1—C6—C5 | 176.5 (4) | C11—C10—C13—O3 | −176.6 (5) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 1.0 (8) | C11—C10—C13—O4 | 4.0 (9) |
| I1—C2—C3—C4 | 179.4 (5) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | −0.8 (9) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (iii) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (iv) −x, −y, −z; (v) x, −y+3/2, z+1/2; (vi) x, y+1, z; (vii) x, −y+3/2, z−1/2; (viii) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (ix) x, y−1, z; (x) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (xi) −x, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (xii) −x, −y+1, −z; (xiii) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O4ix | 0.86 | 2.03 | 2.860 (6) | 161.00 |
| O3—H3O···O5v | 0.91 (7) | 1.73 (7) | 2.616 (6) | 165 (7) |
| O5—H5A···O2viii | 0.81 | 2.20 | 2.924 (6) | 149.00 |
| O5—H5B···O1 | 0.88 | 1.98 | 2.791 (6) | 152.00 |
| C6—H6···O1 | 0.93 | 2.36 | 2.793 (7) | 108.00 |
| C11—H11···O2vi | 0.93 | 2.52 | 3.437 (6) | 171.00 |
| C12—H12···O1 | 0.93 | 2.54 | 3.035 (7) | 114.00 |
| C3—H3···Cg2i | 0.93 | 2.90 | 3.818 (7) | 168.00 |
Symmetry codes: (ix) x, y−1, z; (v) x, −y+3/2, z+1/2; (viii) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (vi) x, y+1, z; (i) −x, y−1/2, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HK2605).
References
- Arshad, M. N., Tahir, M. N., Khan, I. U., Ahmad, E. & Shafiq, M. (2008a). Acta Cryst. E64, o2380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Arshad, M. N., Tahir, M. N., Khan, I. U., Shafiq, M. & Siddiqui, W. A. (2008b). Acta Cryst. E64, m1628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2005). SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2007). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc. Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Deng, X. & Mani, N. S. (2006). Green Chem 8, 835–838.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 837–838.
- Medina, J. C., Roche, D., Shan, B., Learned, R. M., Frankmoelle, W. P., Clark, D. L., Rosen, T. & Jaen, J. C. (1999). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.9, 1843–1846. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nan, Z.-H. & Xing, J.-D. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o1978–o1979.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808043754/hk2605sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808043754/hk2605Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report