Abstract
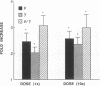
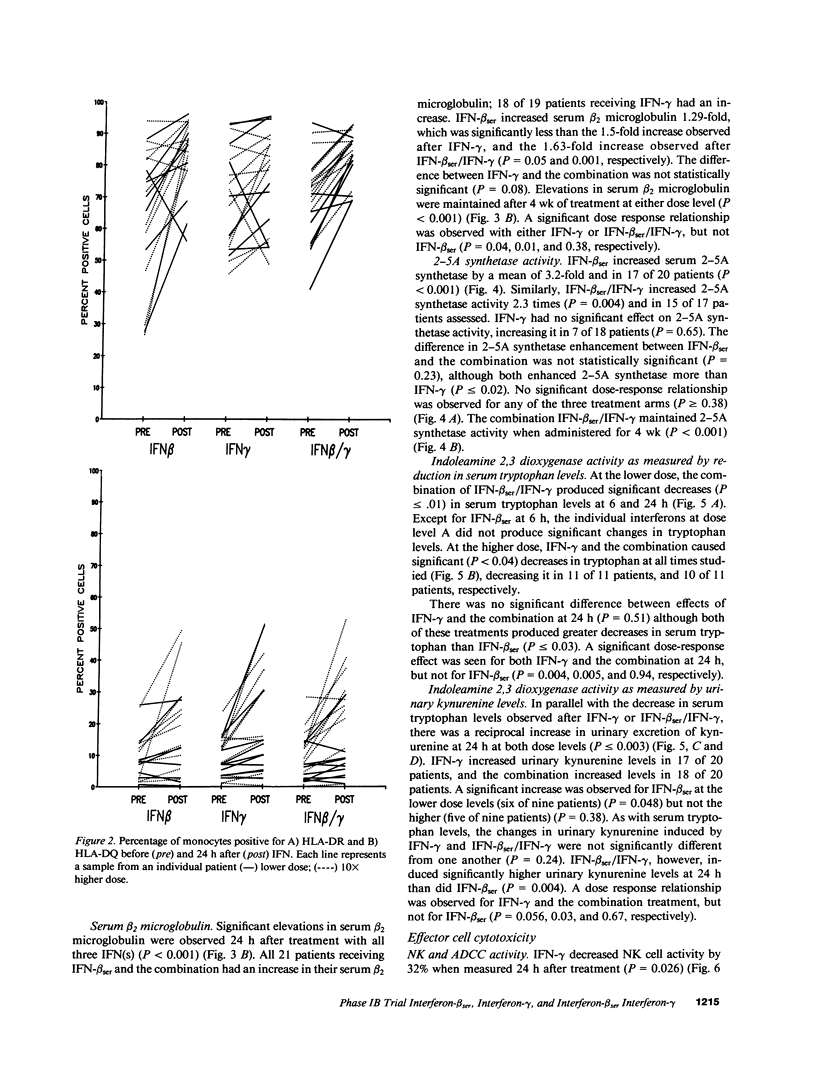
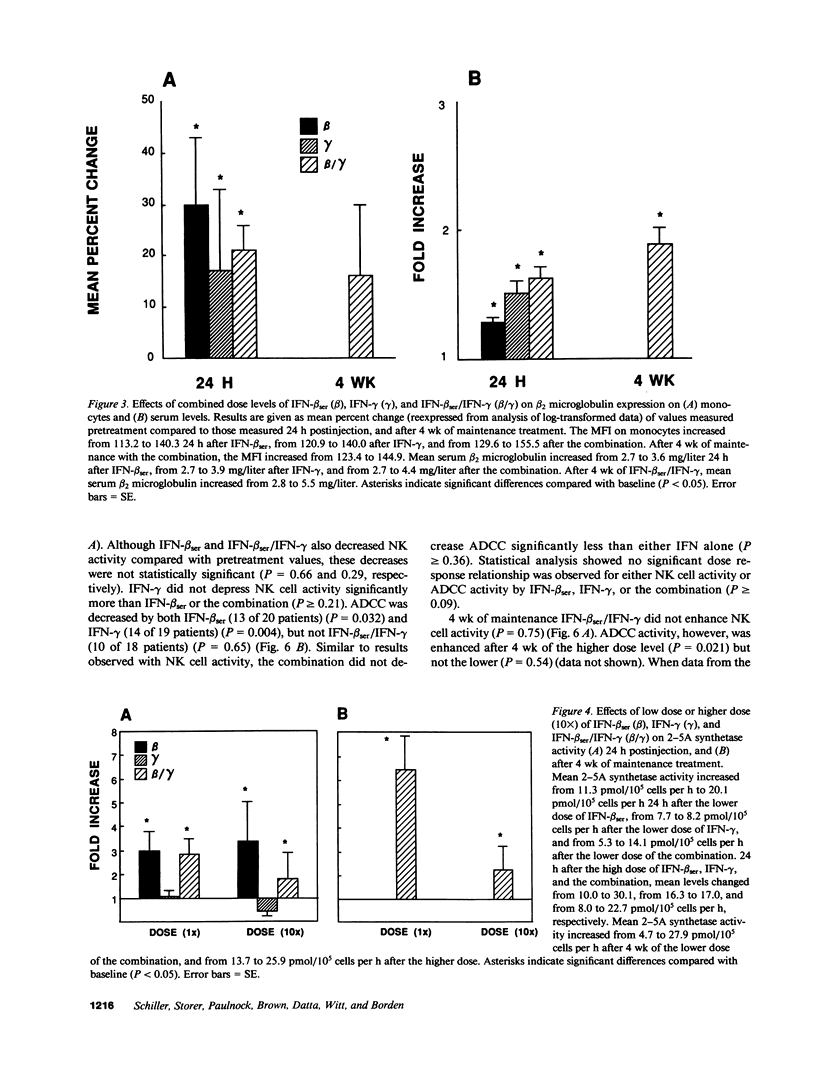
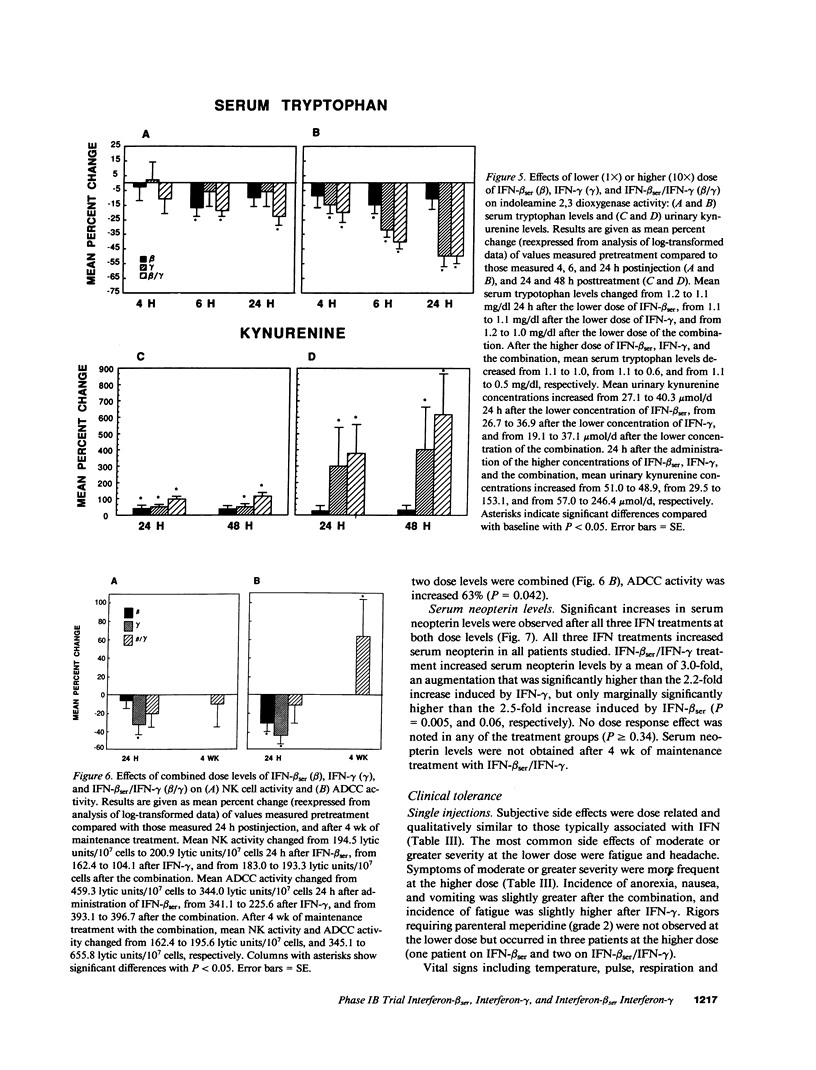
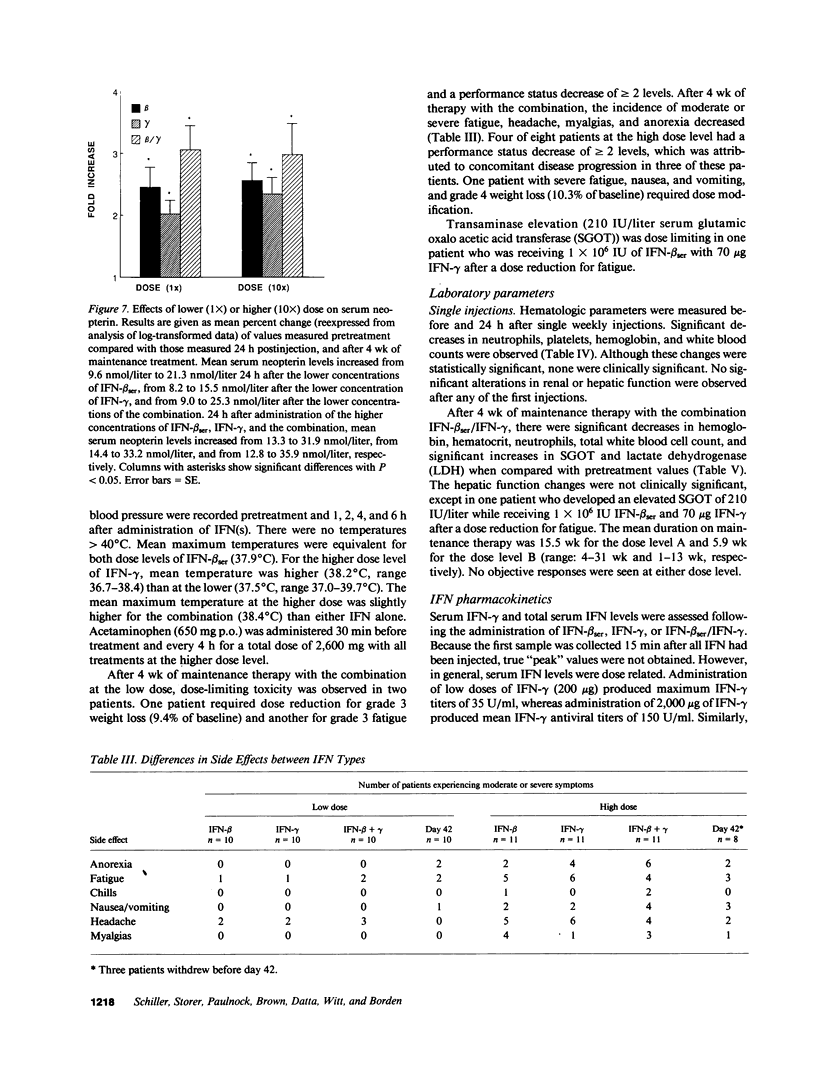
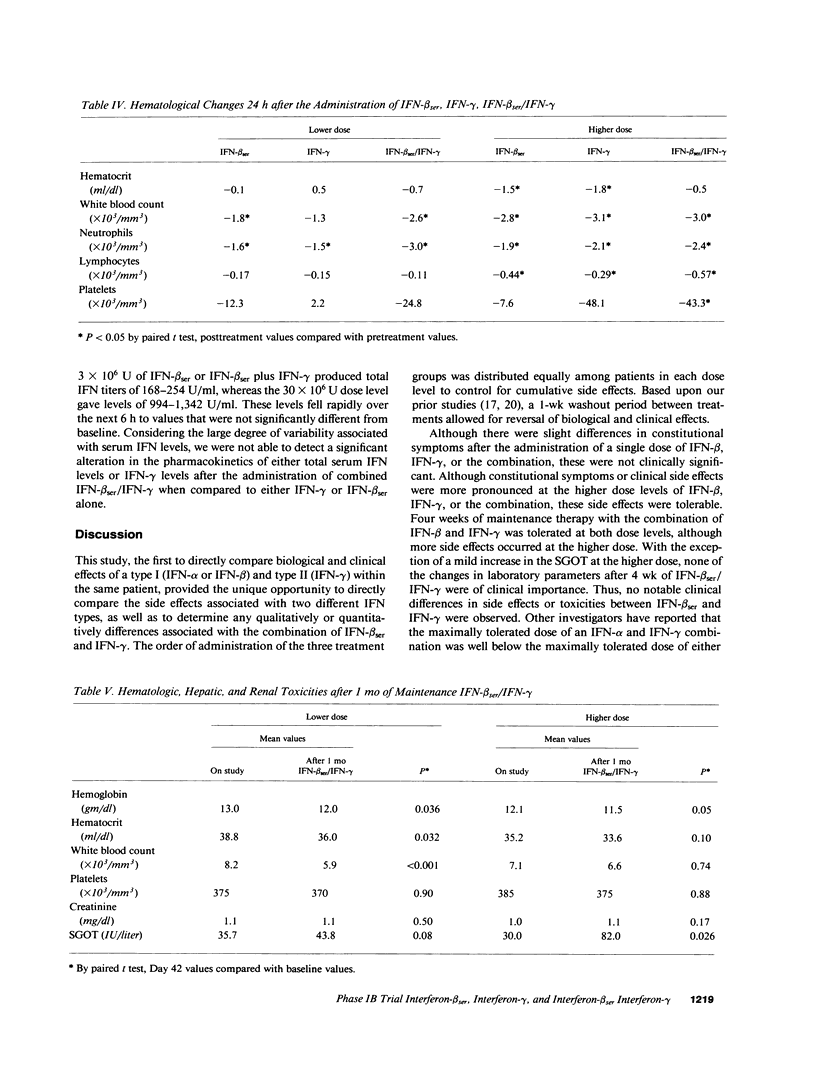
To directly compare clinical side effects and biological response modification, IFN-beta ser, IFN-gamma, or the combination of IFN-beta ser plus IFN-gamma was administered to 21 cancer patients. Each IFN or the combination was given intravenously on days 1, 8, and 15 in varied order. Each IFN and the combination resulted in significant (P less than 0.05) modulation of IFN-induced proteins. IFN-beta ser was more effective than IFN-gamma in enhancing 2-5A synthetase activity (P = 0.001). IFN-gamma was more effective than IFN-beta ser in enhancing serum beta 2 microglobulin expression (P = 0.05) and indoleamine dioxygenase activity, as assessed by decreased serum tryptophan (P = 0.03). The combination enhanced tryptophan catabolism more effectively than IFN-beta ser in a dose-dependent manner (P less than 0.03). IFN-beta ser/IFN-gamma did not potentiate natural killer cells or antibody-dependent cellular toxicity (ADCC). IFN-beta ser/IFN-gamma enhanced monocyte guanylate cyclase activity, as assessed by serum neopterin, more effectively than IFN-gamma alone (P = 0.005). Both IFNs and the combination resulted in increases in HLA class II expression on monocytes. However, no significant difference in the level of induction of HLA DQ and HLA DR expression between IFN-beta ser/IFN-gamma and either IFN-beta ser or IFN-gamma was noted. Although frequency and servity of side effects of IFN-beta ser, IFN-gamma, or the combination were dose related, induction of induced proteins (with exception of influences on tryptophan catabolism) were not a function of dose administered over the 10-fold range. Continued treatment with the combination intravenously three times a week for 4 wk sustained but did not further potentiate, most of the changes in interferon-induced proteins. Thus, IFN-beta ser and IFN-gamma each resulted in effective and essentially equivalent patterns of induction of induced proteins. When combined, however, these IFNs did not result in potentiation of biological response modification in vivo.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend R. A., Leklem J. E., Brown R. R. Direct and steam distillation autoanalyzer methods for assay of diazotizable aromatic amine metabolites of tryptophan in urine and in serum. Biochem Med. 1970 Dec;4(5):457–468. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(70)90075-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basham T. Y., Merigan T. C. Recombinant interferon-gamma increases HLA-DR synthesis and expression. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1492–1494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borden E. C., Hogan T. F., Voelkel J. G. Comparative antiproliferative activity in vitro of natural interferons alpha and beta for diploid and transformed human cells. Cancer Res. 1982 Dec;42(12):4948–4953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne G. I., Lehmann L. K., Kirschbaum J. G., Borden E. C., Lee C. M., Brown R. R. Induction of tryptophan degradation in vitro and in vivo: a gamma-interferon-stimulated activity. J Interferon Res. 1986 Aug;6(4):389–396. doi: 10.1089/jir.1986.6.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlin J. M., Borden E. C., Sondel P. M., Byrne G. I. Biologic-response-modifier-induced indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase activity in human peripheral blood mononuclear cell cultures. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2414–2418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarniecki C. W., Fennie C. W., Powers D. B., Estell D. A. Synergistic antiviral and antiproliferative activities of Escherichia coli-derived human alpha, beta, and gamma interferons. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):490–496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.490-496.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denckla W. D., Dewey H. K. The determination of tryptophan in plasma, liver, and urine. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Jan;69(1):160–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolei A., Capobianchi M. R., Ameglio F. Human interferon-gamma enhances the expression of class I and class II major histocompatibility complex products in neoplastic cells more effectively than interferon-alpha and interferon-beta. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):172–176. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.172-176.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards B. S., Hawkins M. J., Borden E. C. Comparative in vivo and in vitro activation of human natural killer cells by two recombinant alpha-interferons differing in antiviral activity. Cancer Res. 1984 Jul;44(7):3135–3139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonwa T. A., Frost J. P., Karr R. W. All human monocytes have the capability of expressing HLA-DQ and HLA-DP molecules upon stimulation with interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):519–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyre P. M., Morganelli P. M., Miller R. Recombinant immune interferon increases immunoglobulin G Fc receptors on cultured human mononuclear phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):393–397. doi: 10.1172/JCI110980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins M. J., Krown S. E., Borden E. C., Krim M., Real F. X., Edwards B. S., Anderson S. A., Cunningham-Rundles S., Oettgen H. F. American cancer society Phase I trial of naturally produced beta-interferon. Cancer Res. 1984 Dec;44(12 Pt 1):5934–5938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins M., Horning S., Konrad M., Anderson S., Sielaff K., Rosno S., Schiesel J., Davis T., DeMets D., Merigan T. Phase I evaluation of a synthetic mutant of beta-interferon. Cancer Res. 1985 Nov;45(11 Pt 2):5914–5920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber C., Batchelor J. R., Fuchs D., Hausen A., Lang A., Niederwieser D., Reibnegger G., Swetly P., Troppmair J., Wachter H. Immune response-associated production of neopterin. Release from macrophages primarily under control of interferon-gamma. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):310–316. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzrock R., Quesada J. R., Talpaz M., Hersh E. M., Reuben J. M., Sherwin S. A., Gutterman J. U. Phase I study of multiple dose intramuscularly administered recombinant gamma interferon. J Clin Oncol. 1986 Jul;4(7):1101–1109. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1986.4.7.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzrock R., Rosenblum M. G., Quesada J. R., Sherwin S. A., Itri L. M., Gutterman J. U. Phase I study of a combination of recombinant interferon-alpha and recombinant interferon-gamma in cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 1986 Nov;4(11):1677–1683. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1986.4.11.1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling P. D., Warren M. K., Vogel S. N. Antagonistic effect of interferon-beta on the interferon-gamma-induced expression of Ia antigen in murine macrophages. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1857–1863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. A., Borden E. C., Ball L. A. Measurement of 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase in patients receiving interferon-alpha. J Interferon Res. 1985 Winter;5(1):191–198. doi: 10.1089/jir.1985.5.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Horowitz C. R., de la Harpe J., Vadhan-Raj S., Sherwin S. A., Oettgen H. F., Krown S. E. Administration of recombinant interferon gamma to cancer patients enhances monocyte secretion of hydrogen peroxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8686–8690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefe J. R., Sullivan J. E., Ayoob M., Phillips E., Smith F. P. Augmented immunity in cancer patients treated with alpha-interferon. Cancer Res. 1985 Feb;45(2):874–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickoloff B. J., Basham T. Y., Merigan T. C., Morhenn V. B. Immunomodulatory and antiproliferative effect of recombinant alpha, beta, and gamma interferons on cultured human malignant squamous cell lines, SCL-1 and SW-1271. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Jun;84(6):487–490. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12273446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki Y., Edelstein M. P., Duch D. S. Induction of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase: a mechanism of the antitumor activity of interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1242–1246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulnock D. M., Havlin K. A., Storer B. M., Spear G. T., Sielaff K. M., Borden E. C. Induced proteins in human peripheral mononuclear cells over a range of clinically tolerable doses of interferon-gamma. J Interferon Res. 1989 Aug;9(4):457–473. doi: 10.1089/jir.1989.9.457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. H., Groveman D. S., Schmid S. M., Willson J. K., Cummings K. B., Borden E. C. Synergistic antiproliferative effects of human recombinant alpha 54- or beta ser-interferon with gamma-interferon on human cell lines of various histogenesis. Cancer Res. 1986 Feb;46(2):483–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. H., Storer B., Willson J. K., Borden E. C. Phase I trial of combinations of recombinant interferons beta(ser) and gamma in patients with advanced malignancy. Cancer Treat Rep. 1987 Oct;71(10):945–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. H., Willson J. K., Bittner G., Wolberg W. H., Hawkins M. J., Borden E. C. Antiproliferative effects of interferons on human melanoma cells in the human tumor colony-forming assay. J Interferon Res. 1986 Dec;6(6):615–625. doi: 10.1089/jir.1986.6.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C. L., Marshall J. D., Shultz L. D., Gray P. W., Johnson H. M. Gamma-interferon is one of several direct B cell-maturing lymphokines. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):801–804. doi: 10.1038/309801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear G. T., Paulnock D. M., Jordan R. L., Meltzer D. M., Merritt J. A., Borden E. C. Enhancement of monocyte class I and II histocompatibility antigen expression in man by in vivo beta-interferon. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Jul;69(1):107–115. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigent D. A., Langford M. P., Fleischmann W. R., Jr, Stanton G. J. Potentiation of lymphocyte natural killing by mixtures of alpha or beta interferon with recombinant gamma interferon. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):35–38. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.35-38.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasui H., Takai K., Yoshida R., Hayaishi O. Interferon enhances tryptophan metabolism by inducing pulmonary indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase: its possible occurrence in cancer patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6622–6626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Maza L. M., Peterson E. M. Dependence of the in vitro antiproliferative activity of recombinant human gamma-interferon on the concentration of tryptophan in culture media. Cancer Res. 1988 Jan 15;48(2):346–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Burg M., Edelstein M., Gerlis L., Liang C. M., Hirschi M., Dawson A. Recombinant interferon-gamma (immuneron): results of a phase I trial in patients with cancer. J Biol Response Mod. 1985 Jun;4(3):264–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]