Abstract
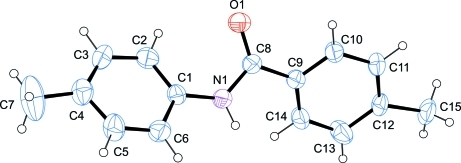
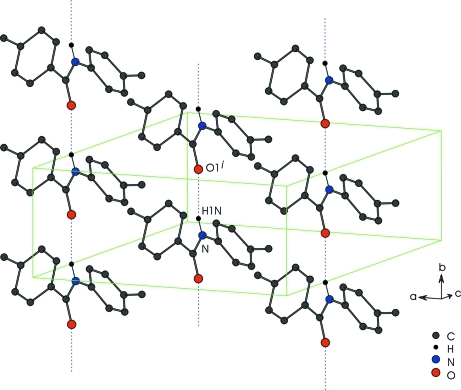
In the title compound, C15H15NO, the amide fragment has an anti conformation. The central amide group is tilted with respect to the benzoyl ring, forming a dihedral angle of 32.3 (5)°. The benzoyl and aniline rings make a dihedral angle of 59.6 (5)°. Molecules are linked into infinite supramolecular chains via N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. The molecule is disordered so that the aromatic rings are disposed across a twofold axis with equal occupancies.
Related literature
For background to our study of the substituent effects on the structures of benzanilides, see: Gowda et al. (2003 ▶). For related structures, see Gowda et al. (2008a ▶,b
▶, 2009 ▶).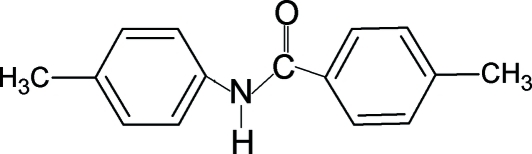
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H15NO
M r = 225.28
Monoclinic,
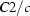
a = 13.3236 (5) Å
b = 5.3591 (2) Å
c = 17.3525 (6) Å
β = 92.248 (3)°
V = 1238.06 (8) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.08 mm−1
T = 295 K
0.26 × 0.25 × 0.07 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur System diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2007 ▶) T min = 0.984, T max = 0.995
8166 measured reflections
1235 independent reflections
775 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.029
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.037
wR(F 2) = 0.103
S = 0.99
1235 reflections
154 parameters
59 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.12 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.12 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis CCD (Oxford Diffraction, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis RED (Oxford Diffraction, 2007 ▶); data reduction: CrysAlis RED; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and DIAMOND (Brandenburg, 2002 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97, PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶) and WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809006497/tk2377sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809006497/tk2377Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1N⋯O1i | 0.883 (15) | 2.416 (19) | 3.202 (3) | 148.3 (6) |
Symmetry code: (i) 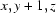 .
.
Acknowledgments
MT and JK thank the Grant Agency of the Slovak Republic (grant No. VEGA 1/0817/08) and the Structural Funds, Interreg IIIA, for financial support in purchasing the diffractometer.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
In the present work, as part of a study of the substituent effects on the structures of benzanilides (Gowda et al., 2003; Gowda et al., 2008a,b), the structure of 4-methyl-N- (4-methylphenyl)benzamide (I) has been determined. The amide adopts an anti-conformation (Fig. 1), similar to that observed in N-(4-methylphenyl)benzamide (N4MPBA) (Gowda et al., 2008a), 4-methyl-N-(phenyl)benzamide (NP4MBA) (Gowda et al., 2009), 2-methyl-N-(4-methylphenyl)benzamide (N4MP2MBA) (Gowda et al., 2008b) and other benzanilides (Gowda et al., 2003). The central amide group is tilted to the benzoyl ring at an angle of 32.3 (5)°, compared to the values of 20.7 (2)°, 33.9 (14)°, 60.0 (1)°, observed for N4MPBA, NP4MBA and N4MP2MBA, respectively. The two aromatic rings form a dihedral angle of 59.6 (5)°, in comparison with the values in the structures cited above of 63.4 (1)°, 61.0 (1)°, and 81.4 (1)°, respectively. The molecules are linked by N—H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1) into supramolecular chains running along the b axis (Fig. 2).
Experimental
Compound (I) was prepared according to the method described by Gowda et al. (2003). Plate-like colourless single crystals were obtained by slow evaporation from an ethanol solution (ca. 30 ml) of (I) (0.5 g) held at room temperature.
Refinement
H atoms attached to C atoms were placed in calculated positions and refined in the riding model approximation with C–H distances of 0.93 or 0.96 Å. The position of amide-H was refined; N-H = 0.883 (15) Å. The Uiso(H) values were set at 1.2 Ueq(C-aromatic, N) and 1.5 Ueq(C-methyl). The structure was found to be disordered in space group C2/c. The amide-O and -H atoms lie on a 2-fold axis with the aromatic rings disordered about this axis with equal occupancies. The geometries of the rings were restrained using the SADI and FLAT commands and the anisotropic displacement parameters were restrained with the DELU command in SHELXL-97 (Sheldrick, 2008). The atoms of the aniline moiety exhibit large thermal motion which accounts for the low value of the average ring bond distance of 1.359 (6) Å.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of (I) showing the atom labelling scheme and one orientation of the disordered molecule. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level. H atoms are represented as small spheres of arbitrary radii.
Fig. 2.
Part of the crystal structure of (I) showing supramolecular chains running along the b axis connected by N—H···Oi hydrogen bonds, shown by dashed lines. H atoms not involved in intermolecular bonding have been omitted for reasons of clarity. Symmetry operation (i): x, y +1, z.
Crystal data
| C15H15NO | F(000) = 480 |
| Mr = 225.28 | Dx = 1.209 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -C 2yc | Cell parameters from 2932 reflections |
| a = 13.3236 (5) Å | θ = 3.2–29.2° |
| b = 5.3591 (2) Å | µ = 0.08 mm−1 |
| c = 17.3525 (6) Å | T = 295 K |
| β = 92.248 (3)° | Plate, colorless |
| V = 1238.06 (8) Å3 | 0.26 × 0.25 × 0.07 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur System diffractometer | 1235 independent reflections |
| graphite | 775 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 10.434 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.029 |
| ω scans with κ offsets | θmax = 26.2°, θmin = 3.8° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2007) | h = −16→16 |
| Tmin = 0.984, Tmax = 0.995 | k = −6→6 |
| 8166 measured reflections | l = −21→21 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.037 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.103 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 0.99 | w = [exp(0.90(sinθ/λ)2)]/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.068P)2] where P = 0.33333Fo2 + 0.66667Fc2 |
| 1235 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 154 parameters | Δρmax = 0.12 e Å−3 |
| 59 restraints | Δρmin = −0.12 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| O1 | 0.5 | −0.0539 (2) | 0.25 | 0.0805 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.52889 (16) | 0.1648 (5) | 0.26154 (14) | 0.0581 (6) | 0.5 |
| C9 | 0.6171 (5) | 0.2387 (10) | 0.3106 (4) | 0.0555 (13) | 0.5 |
| C10 | 0.6994 (7) | 0.0833 (15) | 0.3106 (7) | 0.0633 (14) | 0.5 |
| H10 | 0.6972 | −0.0616 | 0.2811 | 0.076* | 0.5 |
| C11 | 0.7862 (10) | 0.142 (3) | 0.3548 (6) | 0.0640 (17) | 0.5 |
| H11 | 0.8413 | 0.0354 | 0.3549 | 0.077* | 0.5 |
| C12 | 0.7905 (9) | 0.361 (3) | 0.3989 (11) | 0.061 (2) | 0.5 |
| C13 | 0.7076 (9) | 0.522 (3) | 0.3987 (9) | 0.085 (3) | 0.5 |
| H13 | 0.7087 | 0.6686 | 0.4272 | 0.102* | 0.5 |
| C14 | 0.6229 (6) | 0.4507 (13) | 0.3538 (6) | 0.0705 (18) | 0.5 |
| H14 | 0.5671 | 0.555 | 0.3533 | 0.085* | 0.5 |
| C15 | 0.8883 (6) | 0.3929 (11) | 0.4511 (4) | 0.0850 (19) | 0.5 |
| H15A | 0.8777 | 0.5189 | 0.4893 | 0.127* | 0.5 |
| H15B | 0.9428 | 0.4419 | 0.4198 | 0.127* | 0.5 |
| H15C | 0.9044 | 0.2375 | 0.4762 | 0.127* | 0.5 |
| N1 | 0.47296 (14) | 0.3550 (4) | 0.23226 (11) | 0.0625 (6) | 0.5 |
| H1N | 0.5 | 0.495 (4) | 0.25 | 0.075* | |
| C1 | 0.3832 (5) | 0.3400 (10) | 0.1864 (4) | 0.0567 (15) | 0.5 |
| C2 | 0.3155 (8) | 0.1540 (16) | 0.1904 (7) | 0.0730 (18) | 0.5 |
| H2 | 0.3287 | 0.0205 | 0.2235 | 0.088* | 0.5 |
| C3 | 0.2279 (10) | 0.157 (3) | 0.1466 (8) | 0.083 (3) | 0.5 |
| H3 | 0.1838 | 0.0245 | 0.1517 | 0.099* | 0.5 |
| C4 | 0.2007 (11) | 0.343 (3) | 0.0962 (12) | 0.076 (3) | 0.5 |
| C5 | 0.2728 (8) | 0.520 (3) | 0.0939 (8) | 0.081 (2) | 0.5 |
| H5 | 0.2613 | 0.6482 | 0.0586 | 0.097* | 0.5 |
| C6 | 0.3605 (6) | 0.5322 (14) | 0.1370 (6) | 0.0728 (17) | 0.5 |
| H6 | 0.4035 | 0.6677 | 0.1329 | 0.087* | 0.5 |
| C7 | 0.1050 (8) | 0.3838 (19) | 0.0558 (5) | 0.146 (4) | 0.5 |
| H7A | 0.0578 | 0.2603 | 0.0714 | 0.219* | 0.5 |
| H7B | 0.1134 | 0.3716 | 0.0012 | 0.219* | 0.5 |
| H7C | 0.0805 | 0.547 | 0.068 | 0.219* | 0.5 |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0817 (8) | 0.0553 (7) | 0.1022 (9) | 0 | −0.0262 (7) | 0 |
| C8 | 0.0577 (18) | 0.0537 (13) | 0.0624 (16) | −0.0023 (10) | −0.0047 (12) | −0.0014 (11) |
| C9 | 0.0529 (18) | 0.053 (3) | 0.0602 (18) | 0.001 (2) | −0.0042 (13) | −0.004 (2) |
| C10 | 0.052 (2) | 0.063 (4) | 0.074 (2) | 0.004 (2) | −0.0032 (17) | −0.016 (3) |
| C11 | 0.046 (3) | 0.078 (4) | 0.067 (3) | 0.003 (3) | −0.0077 (19) | −0.001 (2) |
| C12 | 0.045 (3) | 0.077 (4) | 0.058 (4) | −0.005 (2) | −0.016 (2) | 0.000 (3) |
| C13 | 0.087 (5) | 0.082 (4) | 0.084 (4) | 0.024 (4) | −0.023 (3) | −0.008 (3) |
| C14 | 0.056 (2) | 0.070 (5) | 0.084 (4) | 0.011 (3) | −0.019 (2) | −0.004 (4) |
| C15 | 0.052 (2) | 0.104 (3) | 0.097 (5) | −0.017 (2) | −0.021 (2) | 0.001 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0602 (15) | 0.0521 (11) | 0.0736 (15) | −0.0012 (9) | −0.0166 (9) | −0.0010 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0564 (17) | 0.057 (4) | 0.056 (2) | 0.004 (3) | −0.0120 (15) | 0.004 (3) |
| C2 | 0.075 (5) | 0.064 (4) | 0.080 (3) | 0.000 (3) | −0.003 (3) | 0.024 (3) |
| C3 | 0.058 (5) | 0.085 (4) | 0.104 (5) | −0.017 (3) | −0.004 (3) | 0.002 (3) |
| C4 | 0.069 (5) | 0.096 (5) | 0.063 (4) | 0.003 (3) | −0.007 (4) | −0.015 (3) |
| C5 | 0.073 (4) | 0.104 (5) | 0.063 (3) | 0.003 (3) | −0.017 (3) | 0.016 (3) |
| C6 | 0.074 (4) | 0.068 (4) | 0.076 (3) | −0.007 (3) | −0.007 (3) | 0.013 (3) |
| C7 | 0.100 (5) | 0.274 (11) | 0.061 (3) | 0.040 (5) | −0.025 (3) | 0.001 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C8 | 1.247 (3) | N1—N1i | 0.929 (3) |
| O1—C8i | 1.247 (3) | N1—C1 | 1.413 (6) |
| C8—C8i | 0.854 (4) | N1—H1N | 0.883 (15) |
| C8—C9 | 1.478 (7) | C1—C2 | 1.348 (5) |
| C9—C14 | 1.362 (6) | C1—C6 | 1.366 (5) |
| C9—C10 | 1.377 (5) | C2—C3 | 1.368 (7) |
| C10—C11 | 1.398 (7) | C2—H2 | 0.93 |
| C10—H10 | 0.93 | C3—C4 | 1.363 (7) |
| C11—C12 | 1.402 (7) | C3—H3 | 0.93 |
| C11—H11 | 0.93 | C4—C5 | 1.352 (7) |
| C12—C13 | 1.400 (6) | C4—C7 | 1.447 (14) |
| C12—C15 | 1.567 (11) | C5—C6 | 1.363 (8) |
| C13—C14 | 1.398 (10) | C5—H5 | 0.93 |
| C13—H13 | 0.93 | C6—H6 | 0.93 |
| C14—H14 | 0.93 | C7—H7A | 0.96 |
| C15—H15A | 0.96 | C7—H7B | 0.96 |
| C15—H15B | 0.96 | C7—H7C | 0.96 |
| C15—H15C | 0.96 | ||
| C8i—C8—C9 | 162.2 (4) | C2—C1—N1 | 124.5 (6) |
| O1—C8—C9 | 125.3 (3) | C6—C1—N1 | 118.2 (6) |
| C14—C9—C10 | 118.4 (6) | C1—C2—C3 | 121.3 (9) |
| C14—C9—C8 | 124.6 (6) | C1—C2—H2 | 119.3 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 117.0 (6) | C3—C2—H2 | 119.3 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 120.4 (9) | C4—C3—C2 | 124.5 (12) |
| C9—C10—H10 | 119.8 | C4—C3—H3 | 117.8 |
| C11—C10—H10 | 119.8 | C2—C3—H3 | 117.8 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 120.2 (11) | C5—C4—C3 | 111.0 (12) |
| C10—C11—H11 | 119.9 | C5—C4—C7 | 119.5 (11) |
| C12—C11—H11 | 119.9 | C3—C4—C7 | 129.0 (10) |
| C13—C12—C11 | 119.9 (10) | C4—C5—C6 | 127.8 (13) |
| C13—C12—C15 | 124.9 (9) | C4—C5—H5 | 116.1 |
| C11—C12—C15 | 114.9 (8) | C6—C5—H5 | 116.1 |
| C14—C13—C12 | 116.9 (10) | C5—C6—C1 | 118.1 (10) |
| C14—C13—H13 | 121.5 | C5—C6—H6 | 121 |
| C12—C13—H13 | 121.5 | C1—C6—H6 | 121 |
| C9—C14—C13 | 124.1 (8) | C4—C7—H7A | 109.5 |
| C9—C14—H14 | 117.9 | C4—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| C13—C14—H14 | 117.9 | H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| N1i—N1—C1 | 172.2 (4) | C4—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| N1i—N1—H1N | 58.3 (7) | H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C1—N1—H1N | 124.7 (6) | H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 117.2 (6) | ||
| C8i—O1—C8—C9 | 169.7 (6) | C8—C9—C14—C13 | −178.6 (11) |
| C8i—C8—C9—C14 | 1.0 (19) | C12—C13—C14—C9 | 0(2) |
| O1—C8—C9—C14 | −145.7 (6) | C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.1 (17) |
| C8i—C8—C9—C10 | −177.5 (15) | N1—C1—C2—C3 | 176.9 (10) |
| O1—C8—C9—C10 | 35.8 (9) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0(3) |
| C14—C9—C10—C11 | 0.6 (15) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1(3) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 179.2 (9) | C2—C3—C4—C7 | −170.1 (17) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | −1(2) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −3(3) |
| C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0(3) | C7—C4—C5—C6 | 169.1 (16) |
| C10—C11—C12—C15 | 175.0 (12) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | 4(3) |
| C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0(3) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | −1.7 (15) |
| C15—C12—C13—C14 | −174.0 (15) | N1—C1—C6—C5 | −178.8 (10) |
| C10—C9—C14—C13 | −0.2 (16) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y, −z+1/2.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1N···O1ii | 0.88 (2) | 2.42 (2) | 3.202 (3) | 148 (1) |
Symmetry codes: (ii) x, y+1, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: TK2377).
References
- Brandenburg, K. (2002). DIAMOND Crystal Impact, Bonn, Germany.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 837–838.
- Gowda, B. T., Foro, S., Sowmya, B. P. & Fuess, H. (2009). Z. Naturforsch. Teil A In preparation. CCDC deposition No. 691312, CCDC, Cambridge, England.
- Gowda, B. T., Jyothi, K., Paulus, H. & Fuess, H. (2003). Z. Naturforsch. Teil A, 58, 225–230.
- Gowda, B. T., Tokarčík, M., Kožíšek, J. & Sowmya, B. P. (2008a). Acta Cryst. E64, o83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gowda, B. T., Tokarčík, M., Kožíšek, J., Sowmya, B. P. & Fuess, H. (2008b). Acta Cryst. E64, o1494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Oxford Diffraction (2007). CrysAlis CCD and CrysAlis RED Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Abingdon, Oxfordshire, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809006497/tk2377sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809006497/tk2377Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report