Abstract
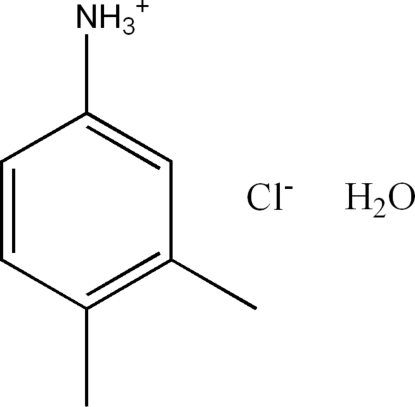
The crystal structure of the title compound, C8H12N+·Cl−·H2O, consists of hydrophobic layers of dimethylanilinium cations parallel to the bc plane alternated by hydrophilic layers of chloride anions and water molecules. The layers are linked by N—H⋯O and N—H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds involving the ammonium groups of the cations. The cohesion of the ionic structure is further stabilized by O—H⋯Cl hydrogen-bonding interactions.
Related literature
For crystal structures containing the dimethylanilinium cation, see: Bouacida (2008 ▶); Singh et al. (2002 ▶); Singh et al. (1995a
▶,b
▶); Linden et al. (1995 ▶); Fábry et al. (2001 ▶, 2002 ▶). For the crystal structures of related protonated amines, see: Bouacida et al. (2005a
▶,b
▶,c
▶, 2006 ▶, 2007 ▶); Benslimane et al. (2007 ▶); Rademeyer (2004a
▶,b
▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C8H12N+·Cl−·H2O
M r = 175.65
Orthorhombic,

a = 18.230 (18) Å
b = 6.7854 (14) Å
c = 7.916 (2) Å
V = 979.2 (10) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.34 mm−1
T = 295 K
0.1 × 0.04 × 0.02 mm
Data collection
Enraf–Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: none
10115 measured reflections
2181 independent reflections
1403 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.078
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.059
wR(F 2) = 0.109
S = 1.15
2181 reflections
109 parameters
1 restraint
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 976 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: 0.01 (11)
Data collection: COLLECT (Nonius, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: SCALEPACK (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); data reduction: DENZO (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); and SCALEPACK program(s) used to solve structure: SIR2002 (Burla et al., 2003 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and DIAMOND (Brandenburg et al., 2001 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809006072/rz2296sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809006072/rz2296Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1A⋯O1W | 0.89 | 1.87 | 2.754 (5) | 174 |
| N1—H1B⋯Cl1i | 0.89 | 2.30 | 3.177 (4) | 167 |
| N1—H1C⋯Cl1ii | 0.89 | 2.31 | 3.181 (4) | 167 |
| O1W—H1W⋯Cl1 | 0.80 (6) | 2.43 (6) | 3.217 (5) | 174 (7) |
| O1W—H2W⋯Cl1iii | 0.81 (5) | 2.36 (5) | 3.174 (5) | 176 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr Thierry Roisnel, Centre de Diffractométrie X (CDIFX) de Rennes, Université de Rennes 1, France, for the data collection facilities. SB thanks Université A. Mira de Béjaia, Algéria, for financial support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound, was prepared as part of our ongoing studies of hydrogen-bonding interactions in the crystal structure of protonated amines (Bouacida et al., 2005a,b,c; Bouacida et al., 2006; Benslimane et al., 2007; Bouacida et al., 2007). Structures containing the dimethylanilinium cation have been already reported with tin chloride (Bouacida, 2008), sulfate (Singh et al., 2002), nitrate and perchlorate (Singh et al., 1995a,b), chloride (Linden et al., 1995), and dihydrogenphosphate (Fabry et al., 2001; Fábry et al., 2002).
The molecular structure of the title compound is illustrated in Fig. 1. A l l bond distances and angles are within the ranges of accepted values. The amino N atom is protonated as in other aminoacids (Bouacida et al., 2006; Rademeyer 2004a,b). A diagram of the layered crystal packing of title compound is shown in Fig. 2, in which the cations are arranged to form zigzag layers parallel the ab plane, with the chloride ions and water molecules located between these layers. The structure may be also described as formed by hydrophobic layers parallel to the bc plane of dimethylanilinium cations alternated by hydrophilic layers of chloride anions and water molecules. In this structure, three types of classical hydrogen bonds are observed, viz. cation–anion, cation–water and water–anion (Fig. 3, Table 1). All three ammonium H atoms are involved in hydrogen bonds. These interactions link the molecules within the layers and also link the layers together, forming a three-dimensional network and reinforcing the cohesion of the ionic structure.
Experimental
An aqueous solution of SnCl2.2H2O (1 mmol) and 3,4-dimethylaniline (2 mmol) in hydrochloric acid was slowly evaporated to dryness for two weeks. White single crystals of the title compound were carefully isolated under polarizing microscope for X-ray diffraction analysis
Refinement
The water H atoms were located in a difference Fourier map and refined isotropically, with Uiso(H) =1.25(O). All other H atoms were localized in difference Fourier maps but introduced in calculated positions and treated as riding on their parent atoms, with C—H = 0.93–0.96 Å, N—H = 0.89Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C, N) or 1.5 Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The structure of the title compound with the atomic labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A diagram of the layered crystal packing in the title comound, viewed down the a axis.
Fig. 3.
Crystal packing of the title compound viewed down the b axis. H bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C8H12N+·Cl−·H2O | F(000) = 376 |
| Mr = 175.65 | Dx = 1.191 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pca21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2c -2ac | Cell parameters from 9401 reflections |
| a = 18.230 (18) Å | θ = 3.7–27.5° |
| b = 6.7854 (14) Å | µ = 0.34 mm−1 |
| c = 7.916 (2) Å | T = 295 K |
| V = 979.2 (10) Å3 | Stalk, white |
| Z = 4 | 0.1 × 0.04 × 0.02 mm |
Data collection
| Enraf–Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer | Rint = 0.078 |
| CCD rotation images, thick slices scans | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.7° |
| 10115 measured reflections | h = −23→23 |
| 2181 independent reflections | k = −8→8 |
| 1403 reflections with I > 2σ(I) | l = −10→9 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Least-squares matrix: full | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0307P)2 + 0.3106P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.059 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| wR(F2) = 0.109 | Δρmax = 0.20 e Å−3 |
| S = 1.15 | Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3 |
| 2181 reflections | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 976 Friedel pairs |
| 109 parameters | Flack parameter: 0.01 (11) |
| 1 restraint |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.06494 (14) | 0.5513 (4) | 0.2268 (4) | 0.0433 (10) | |
| C1 | 0.14146 (17) | 0.4809 (5) | 0.2159 (4) | 0.0395 (11) | |
| C2 | 0.1556 (2) | 0.3036 (6) | 0.1426 (5) | 0.0447 (12) | |
| C3 | 0.22856 (19) | 0.2362 (5) | 0.1269 (4) | 0.0430 (13) | |
| C4 | 0.28449 (18) | 0.3555 (5) | 0.1893 (5) | 0.0444 (11) | |
| C5 | 0.2677 (2) | 0.5332 (6) | 0.2641 (5) | 0.0517 (14) | |
| C6 | 0.1959 (2) | 0.5966 (5) | 0.2776 (5) | 0.0467 (12) | |
| C7 | 0.2432 (3) | 0.0413 (6) | 0.0454 (6) | 0.0670 (19) | |
| C8 | 0.3636 (2) | 0.2894 (7) | 0.1744 (7) | 0.0693 (16) | |
| O1W | 0.0447 (3) | 0.8297 (5) | 0.4757 (4) | 0.0818 (13) | |
| Cl1 | 0.04002 (5) | 0.77733 (12) | 0.87943 (11) | 0.0507 (3) | |
| H1A | 0.06154 | 0.64300 | 0.30678 | 0.0650* | |
| H1B | 0.03559 | 0.45076 | 0.25217 | 0.0650* | |
| H1C | 0.05158 | 0.60253 | 0.12795 | 0.0650* | |
| H2 | 0.11712 | 0.22655 | 0.10264 | 0.0534* | |
| H5 | 0.30525 | 0.61175 | 0.30623 | 0.0620* | |
| H6 | 0.18505 | 0.71675 | 0.32834 | 0.0559* | |
| H7A | 0.27619 | 0.05896 | −0.04794 | 0.1007* | |
| H7B | 0.19792 | −0.01381 | 0.00532 | 0.1007* | |
| H7C | 0.26488 | −0.04643 | 0.12637 | 0.1007* | |
| H8A | 0.39537 | 0.39319 | 0.21227 | 0.1038* | |
| H8B | 0.37436 | 0.25867 | 0.05870 | 0.1038* | |
| H8C | 0.37112 | 0.17444 | 0.24296 | 0.1038* | |
| H1W | 0.046 (3) | 0.824 (9) | 0.576 (7) | 0.1038* | |
| H2W | 0.022 (3) | 0.927 (8) | 0.447 (7) | 0.1038* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0455 (16) | 0.0461 (17) | 0.0383 (18) | 0.0025 (13) | −0.0007 (14) | 0.0048 (14) |
| C1 | 0.0384 (18) | 0.044 (2) | 0.0361 (19) | 0.0062 (16) | 0.0041 (17) | 0.0089 (18) |
| C2 | 0.051 (2) | 0.043 (2) | 0.040 (2) | −0.0076 (17) | 0.0008 (19) | 0.0070 (18) |
| C3 | 0.060 (3) | 0.039 (2) | 0.0300 (17) | 0.0022 (17) | 0.004 (2) | 0.0089 (17) |
| C4 | 0.047 (2) | 0.051 (2) | 0.0353 (19) | 0.0013 (17) | 0.0013 (19) | 0.010 (2) |
| C5 | 0.052 (2) | 0.051 (2) | 0.052 (3) | −0.0056 (18) | −0.006 (2) | 0.002 (2) |
| C6 | 0.049 (2) | 0.045 (2) | 0.046 (2) | 0.0024 (18) | −0.0018 (19) | 0.0034 (18) |
| C7 | 0.097 (4) | 0.048 (3) | 0.056 (3) | 0.012 (2) | 0.008 (3) | 0.000 (2) |
| C8 | 0.052 (2) | 0.082 (3) | 0.074 (3) | 0.009 (2) | 0.007 (3) | 0.011 (3) |
| O1W | 0.127 (3) | 0.066 (2) | 0.0523 (18) | 0.037 (2) | −0.004 (2) | −0.0054 (17) |
| Cl1 | 0.0555 (4) | 0.0492 (5) | 0.0475 (4) | 0.0042 (4) | −0.0028 (6) | 0.0044 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1W—H2W | 0.81 (5) | C4—C5 | 1.378 (6) |
| O1W—H1W | 0.80 (6) | C5—C6 | 1.382 (5) |
| N1—C1 | 1.477 (4) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| N1—H1A | 0.8900 | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| N1—H1C | 0.8900 | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| N1—H1B | 0.8900 | C7—H7B | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.360 (5) | C7—H7C | 0.9600 |
| C1—C6 | 1.356 (5) | C7—H7A | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.412 (5) | C8—H8C | 0.9600 |
| C3—C7 | 1.496 (6) | C8—H8A | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.392 (5) | C8—H8B | 0.9600 |
| C4—C8 | 1.515 (5) | ||
| Cl1···O1W | 3.217 (5) | C8···H7A | 2.8400 |
| Cl1···N1i | 3.181 (4) | H1A···H2W | 2.3400 |
| Cl1···N1ii | 3.177 (4) | H1A···O1W | 1.8700 |
| Cl1···O1Wiii | 3.174 (5) | H1A···H6 | 2.3100 |
| Cl1···H1W | 2.43 (6) | H1A···H1W | 2.4800 |
| Cl1···H1Ci | 2.3100 | H1B···Cl1vi | 2.3000 |
| Cl1···H1Bii | 2.3000 | H1B···H2 | 2.4300 |
| Cl1···H5iv | 3.0900 | H1C···Cl1vii | 2.3100 |
| Cl1···H2Wiii | 2.36 (5) | H1W···H1A | 2.4800 |
| O1W···Cl1v | 3.174 (5) | H1W···Cl1 | 2.43 (6) |
| O1W···N1 | 2.754 (5) | H2···H1B | 2.4300 |
| O1W···Cl1 | 3.217 (5) | H2···H7B | 2.3300 |
| O1W···H1A | 1.8700 | H2W···Cl1v | 2.36 (5) |
| O1W···H6 | 2.9100 | H2W···H1A | 2.3400 |
| N1···Cl1vi | 3.177 (4) | H5···H8A | 2.3300 |
| N1···Cl1vii | 3.181 (4) | H5···Cl1viii | 3.0900 |
| N1···O1W | 2.754 (5) | H6···H1A | 2.3100 |
| C3···C5viii | 3.509 (6) | H6···C7xi | 3.0800 |
| C3···C4viii | 3.565 (6) | H6···O1W | 2.9100 |
| C4···C3iv | 3.565 (6) | H7A···H8B | 2.4000 |
| C4···C7iv | 3.570 (7) | H7A···C8 | 2.8400 |
| C5···C3iv | 3.509 (6) | H7A···C3viii | 2.8400 |
| C7···C4viii | 3.570 (7) | H7A···C4viii | 3.1000 |
| C3···H7Aiv | 2.8400 | H7B···H2 | 2.3300 |
| C4···H7Aiv | 3.1000 | H7C···C8 | 2.9300 |
| C5···H7Cix | 3.0500 | H7C···C5xii | 3.0500 |
| C6···H7Cix | 2.9800 | H7C···C6xii | 2.9800 |
| C7···H8B | 2.8100 | H8A···H5 | 2.3300 |
| C7···H8C | 2.9500 | H8B···C7 | 2.8100 |
| C7···H6x | 3.0800 | H8B···H7A | 2.4000 |
| C8···H7C | 2.9300 | H8C···C7 | 2.9500 |
| H1W—O1W—H2W | 110 (6) | C3—C2—H2 | 120.00 |
| H1A—N1—H1B | 109.00 | C1—C2—H2 | 120.00 |
| H1A—N1—H1C | 109.00 | C4—C5—H5 | 120.00 |
| C1—N1—H1B | 109.00 | C6—C5—H5 | 119.00 |
| C1—N1—H1C | 109.00 | C5—C6—H6 | 121.00 |
| H1B—N1—H1C | 109.00 | C1—C6—H6 | 120.00 |
| C1—N1—H1A | 109.00 | C3—C7—H7A | 109.00 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 119.3 (3) | C3—C7—H7B | 109.00 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 121.8 (3) | H7A—C7—H7B | 109.00 |
| N1—C1—C6 | 118.9 (3) | H7A—C7—H7C | 109.00 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 120.2 (3) | C3—C7—H7C | 110.00 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 118.1 (3) | H7B—C7—H7C | 109.00 |
| C2—C3—C7 | 119.5 (4) | C4—C8—H8B | 109.00 |
| C4—C3—C7 | 122.4 (3) | C4—C8—H8C | 109.00 |
| C3—C4—C8 | 119.8 (3) | C4—C8—H8A | 109.00 |
| C5—C4—C8 | 120.3 (3) | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.9 (3) | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.00 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.1 (3) | H8A—C8—H8B | 110.00 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 119.0 (3) | ||
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 178.3 (3) | C2—C3—C4—C8 | −179.7 (4) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.9 (6) | C7—C3—C4—C5 | −179.6 (4) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | −178.5 (3) | C7—C3—C4—C8 | 0.5 (6) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.6 (6) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.4 (6) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.4 (5) | C8—C4—C5—C6 | 179.5 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C7 | −179.8 (4) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.0 (6) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.2 (5) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y, z+1; (ii) −x, −y+1, z+1/2; (iii) −x, −y+2, z+1/2; (iv) −x+1/2, y, z+1/2; (v) −x, −y+2, z−1/2; (vi) −x, −y+1, z−1/2; (vii) x, y, z−1; (viii) −x+1/2, y, z−1/2; (ix) x, y+1, z; (x) −x+1/2, y−1, z−1/2; (xi) −x+1/2, y+1, z+1/2; (xii) x, y−1, z.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1A···O1W | 0.8900 | 1.8700 | 2.754 (5) | 174.00 |
| N1—H1B···Cl1vi | 0.8900 | 2.3000 | 3.177 (4) | 167.00 |
| N1—H1C···Cl1vii | 0.8900 | 2.3100 | 3.181 (4) | 167.00 |
| O1W—H1W···Cl1 | 0.80 (6) | 2.43 (6) | 3.217 (5) | 174 (7) |
| O1W—H2W···Cl1v | 0.81 (5) | 2.36 (5) | 3.174 (5) | 176 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (vi) −x, −y+1, z−1/2; (vii) x, y, z−1; (v) −x, −y+2, z−1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: RZ2296).
References
- Benslimane, M., Merazig, H., Bouacida, S., Denbri, S., Beghidja, A. & Ouahab, L. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o3682–o3683.
- Bouacida, S. (2008). PhD thesis, Montouri-Constantine University, Algeria.
- Bouacida, S., Merazig, H., Beghidja, A. & Beghidja, C. (2005a). Acta Cryst. E61, m1153–m1155.
- Bouacida, S., Merazig, H., Beghidja, A. & Beghidja, C. (2005b). Acta Cryst. E61, m2072–m2074.
- Bouacida, S., Merazig, H., Beghidja, A. & Beghidja, C. (2005c). Acta Cryst. E61, m577–m579.
- Bouacida, S., Merazig, H. & Benard-Rocherulle, P. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o838–o840.
- Bouacida, S., Merazig, H., Benard-Rocherulle, P. & Rizzoli, C. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, m379–m381.
- Brandenburg, K. & Berndt, M. (2001). DIAMOND Crystal Impact, Bonn, Germany.
- Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Carrozzini, B., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 1103.
- Fábry, J., Krupková, R. & Studnička, V. (2002). Acta Cryst. E58, o105–o107.
- Fábry, J., Krupková, R. & Vaněk, P. (2001). Acta Cryst. E57, o1058–o1060.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 837–838.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Linden, A., James, B. D. & Liesegang, J. (1995). Acta Cryst. C51, 2317–2320.
- Nonius (1998). COLLECT Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Rademeyer, M. (2004a). Acta Cryst. C60, m55–m56. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rademeyer, M. (2004b). Acta Cryst. E60, m345–m347.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Singh, G., Kapoor, I. P. S. & Mannan, S. M. (1995a). Thermochim. Acta, 262, 117–127.
- Singh, G., Kapoor, I. P. S. & Mannan, S. M. (1995b). J. Energetic Mater.13, 141–156.
- Singh, G., Kapoor, I. P. S., Srivastava, J. & Kaur, J. (2002). J. Therm. Anal. Calorim.69, 681–691.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809006072/rz2296sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809006072/rz2296Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report





