Abstract
In the molecule of the title compound, C6H5BrN2O2, the dihedral angle between the nitro group and the aromatic ring is 4.57 (4)°. An intramolecular N—H⋯Br interaction results in the formation of a planar five-membered ring, which is oriented with respect to the aromatic ring at a dihedral angle of 1.64 (6)°. In the crystal structure, intermolecular N—H⋯N and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules.
Related literature
For related structures, see: Arshad et al. (2008 ▶, 2009 ▶); McPhail & Sim (1965 ▶); McWilliam et al. (2001 ▶); Krishna Mohan et al. (2004 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C6H5BrN2O2
M r = 217.03
Orthorhombic,

a = 11.098 (3) Å
b = 16.763 (4) Å
c = 3.9540 (9) Å
V = 735.6 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 5.53 mm−1
T = 296 (2) K
0.26 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.450, T max = 0.578
4932 measured reflections
1542 independent reflections
986 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.058
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.039
wR(F 2) = 0.092
S = 1.00
1542 reflections
100 parameters
1 restraint
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.50 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.62 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 469 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: 0.01 (2)
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809004073/hk2621sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809004073/hk2621Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1A⋯N1i | 0.86 | 2.32 | 3.158 (7) | 167.00 |
| N1—H1B⋯Br1 | 0.86 | 2.68 | 3.095 (5) | 111.00 |
| N1—H1B⋯O2ii | 0.86 | 2.32 | 3.049 (7) | 143.00 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
MNA greatfully acknowledges the Higher Education Commission, Islamabad, Pakistan, for providing him with a Scholarship under the Indigenous PhD Program (PIN 042–120607-PS2–183).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound, (I), has been prepared as an intermediate for the synthesis of sulfonamides (Arshad et al., 2009) and benzothiazines (Arshad et al., 2008).
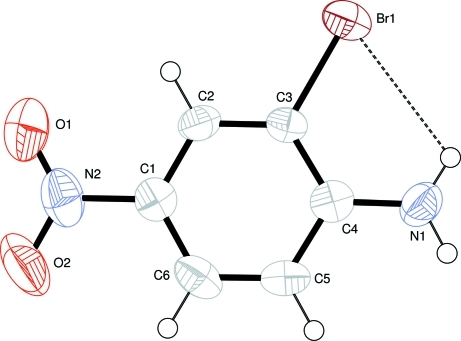
The crystal structures of 2-iodo-4-nitroaniline, (II) (McWilliam et al., 2001) and 2-chloro-4-nitroaniline, (III) (McPhail & Sim, 1965) have been reported. The title compound, (I), (Fig 1) is structural isomer of (III). It is essentially planar. The dihedral angle between the nitro group (O1/O2/N2) and the aromatic ring A (C1-C6) is 4.57 (4)°. The intramolecular N-H···Br interaction (Table 1) results in the formation of a planar five-membered ring (Br1/N1/C3/C4/H1B), which is oriented with respect to ring A at a dihedral angle of 1.64 (6)°. So, they are nearly coplanar.
In the crystal structure, intermolecular N-H···N and N-H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1) link the molecules (Fig. 2), in which they may be effective in the stabilization of the structure.
Experimental
The title compound was synthesized following the method available in literature (Krishna Mohan et al., 2004). 4-Nitro aniline (6 g, 0.0435 mol) and ammonium bromide (4.5 g, 0.0479 mol) were charged to a flask (50 ml) containing acetic acid (30 ml). Hydrogen peroxide (1.629 g, 0.0479 mol, 35%) was added dropwise to the mixture, and stirred at room temperature for 3 h. Then, the obtained precipitate was filtered and washed with water and recrystallized in dichloromethane and methanol.
Refinement
H-atoms were positioned geometrically, with N-H = 0.86 Å (for NH2) and C-H = 0.93 Å for aromatic H, and constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C, N).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title molecule, with the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. Hydrogen bond is shown as dashed line.
Fig. 2.
A partial packing diagram of the title compound. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C6H5BrN2O2 | F(000) = 424 |
| Mr = 217.03 | Dx = 1.960 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pna21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2c -2n | Cell parameters from 1542 reflections |
| a = 11.098 (3) Å | θ = 3.1–28.6° |
| b = 16.763 (4) Å | µ = 5.53 mm−1 |
| c = 3.9540 (9) Å | T = 296 K |
| V = 735.6 (3) Å3 | Needle, yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.26 × 0.12 × 0.10 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 1542 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 986 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.058 |
| Detector resolution: 7.40 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 28.6°, θmin = 3.1° |
| ω scans | h = −13→14 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | k = −22→22 |
| Tmin = 0.450, Tmax = 0.578 | l = −3→5 |
| 4932 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.039 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.092 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0302P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.00 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 1542 reflections | Δρmax = 0.50 e Å−3 |
| 100 parameters | Δρmin = −0.62 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 469 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: 0.01 (2) |
Special details
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | 0.34261 (5) | 0.56438 (3) | 0.7237 (2) | 0.0524 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.4834 (5) | 0.2673 (3) | 0.5214 (15) | 0.088 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.3637 (4) | 0.1882 (2) | 0.763 (3) | 0.101 (2) | |
| N1 | 0.1095 (4) | 0.5118 (3) | 1.0912 (13) | 0.0510 (18) | |
| N2 | 0.3960 (5) | 0.2544 (3) | 0.689 (2) | 0.064 (2) | |
| C1 | 0.3231 (4) | 0.3212 (3) | 0.8007 (18) | 0.043 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.3615 (4) | 0.3974 (3) | 0.730 (3) | 0.0420 (17) | |
| C3 | 0.2913 (5) | 0.4600 (3) | 0.8270 (13) | 0.0347 (19) | |
| C4 | 0.1833 (5) | 0.4491 (3) | 0.9987 (15) | 0.0377 (17) | |
| C5 | 0.1479 (5) | 0.3705 (4) | 1.0711 (16) | 0.048 (2) | |
| C6 | 0.2169 (5) | 0.3076 (3) | 0.9745 (17) | 0.051 (2) | |
| H1A | 0.04332 | 0.50258 | 1.19738 | 0.0611* | |
| H1B | 0.12976 | 0.55993 | 1.04260 | 0.0611* | |
| H2 | 0.43405 | 0.40604 | 0.61823 | 0.0502* | |
| H5 | 0.07627 | 0.36137 | 1.18676 | 0.0576* | |
| H6 | 0.19297 | 0.25579 | 1.02478 | 0.0605* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.0557 (3) | 0.0436 (3) | 0.0578 (4) | −0.0094 (3) | −0.0026 (7) | 0.0100 (5) |
| O1 | 0.075 (4) | 0.077 (4) | 0.112 (5) | 0.028 (3) | 0.016 (4) | −0.009 (3) |
| O2 | 0.110 (4) | 0.037 (2) | 0.157 (6) | 0.010 (2) | 0.000 (5) | −0.006 (5) |
| N1 | 0.035 (2) | 0.056 (3) | 0.062 (4) | 0.001 (2) | 0.003 (2) | −0.008 (2) |
| N2 | 0.063 (3) | 0.051 (3) | 0.078 (5) | 0.017 (3) | −0.018 (5) | −0.007 (5) |
| C1 | 0.041 (3) | 0.046 (3) | 0.041 (7) | 0.001 (2) | −0.010 (3) | 0.000 (3) |
| C2 | 0.034 (3) | 0.049 (3) | 0.043 (3) | −0.001 (2) | 0.005 (5) | 0.009 (6) |
| C3 | 0.034 (3) | 0.037 (3) | 0.033 (4) | −0.007 (2) | −0.007 (2) | 0.002 (2) |
| C4 | 0.038 (3) | 0.049 (3) | 0.026 (3) | −0.002 (3) | −0.012 (3) | 0.000 (3) |
| C5 | 0.043 (3) | 0.053 (4) | 0.047 (4) | −0.015 (3) | 0.002 (3) | 0.006 (3) |
| C6 | 0.056 (4) | 0.037 (3) | 0.059 (5) | −0.008 (3) | −0.018 (4) | 0.005 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Br1—C3 | 1.885 (5) | C1—C2 | 1.375 (7) |
| O1—N2 | 1.195 (9) | C2—C3 | 1.362 (8) |
| O2—N2 | 1.202 (7) | C3—C4 | 1.390 (8) |
| N1—C4 | 1.382 (7) | C4—C5 | 1.404 (8) |
| N2—C1 | 1.450 (8) | C5—C6 | 1.358 (8) |
| N1—H1B | 0.8600 | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| N1—H1A | 0.8600 | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C6 | 1.383 (8) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| Br1···N1 | 3.095 (5) | C5···C1ix | 3.576 (9) |
| Br1···H1B | 2.6800 | C5···C2ix | 3.551 (11) |
| Br1···H2i | 2.9700 | C6···C1ix | 3.480 (10) |
| O1···C6ii | 3.391 (8) | C6···O1x | 3.391 (8) |
| O2···N1iii | 3.049 (7) | C4···H1Av | 2.9000 |
| O1···H2 | 2.4200 | H1A···H5 | 2.4000 |
| O1···H5iv | 2.7300 | H1A···N1v | 2.9500 |
| O2···H6 | 2.4400 | H1A···N1vi | 2.3200 |
| O2···H1Biii | 2.3200 | H1A···C4vi | 2.9000 |
| N1···Br1 | 3.095 (5) | H1A···H1Av | 2.2000 |
| N1···N1v | 3.158 (7) | H1A···H1Avi | 2.2000 |
| N1···N1vi | 3.158 (7) | H1A···H1Bvi | 2.5800 |
| N1···O2vii | 3.049 (7) | H1B···Br1 | 2.6800 |
| N1···H1Av | 2.3200 | H1B···H1Av | 2.5800 |
| N1···H1Avi | 2.9500 | H1B···O2vii | 2.3200 |
| C1···C5viii | 3.576 (9) | H2···O1 | 2.4200 |
| C1···C6viii | 3.480 (10) | H2···Br1xi | 2.9700 |
| C2···C5viii | 3.551 (11) | H5···H1A | 2.4000 |
| C3···C4viii | 3.492 (8) | H5···O1xii | 2.7300 |
| C4···C3ix | 3.492 (8) | H6···O2 | 2.4400 |
| O1—N2—O2 | 123.0 (6) | C2—C3—C4 | 122.0 (5) |
| O1—N2—C1 | 118.8 (5) | N1—C4—C5 | 119.6 (5) |
| O2—N2—C1 | 118.2 (6) | N1—C4—C3 | 122.7 (5) |
| H1A—N1—H1B | 120.00 | C3—C4—C5 | 117.7 (5) |
| C4—N1—H1A | 120.00 | C4—C5—C6 | 120.9 (5) |
| C4—N1—H1B | 120.00 | C1—C6—C5 | 119.5 (5) |
| N2—C1—C6 | 120.0 (5) | C1—C2—H2 | 121.00 |
| N2—C1—C2 | 118.8 (5) | C3—C2—H2 | 121.00 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 121.2 (5) | C4—C5—H5 | 120.00 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 118.8 (6) | C6—C5—H5 | 120.00 |
| Br1—C3—C2 | 118.8 (4) | C1—C6—H6 | 120.00 |
| Br1—C3—C4 | 119.2 (4) | C5—C6—H6 | 120.00 |
| O1—N2—C1—C2 | −4.5 (11) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.9 (12) |
| O1—N2—C1—C6 | 175.4 (7) | Br1—C3—C4—N1 | 1.6 (8) |
| O2—N2—C1—C2 | 177.4 (9) | Br1—C3—C4—C5 | 179.9 (4) |
| O2—N2—C1—C6 | −2.8 (11) | C2—C3—C4—N1 | −178.3 (7) |
| N2—C1—C2—C3 | 178.2 (7) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.1 (10) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −1.6 (13) | N1—C4—C5—C6 | 178.1 (6) |
| N2—C1—C6—C5 | −178.5 (6) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.3 (9) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 1.4 (11) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.4 (10) |
| C1—C2—C3—Br1 | −179.0 (6) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, z+1/2; (ii) x+1/2, −y+1/2, z; (iii) −x+1/2, y−1/2, z−1/2; (iv) x+1/2, −y+1/2, z−1; (v) −x, −y+1, z−1/2; (vi) −x, −y+1, z+1/2; (vii) −x+1/2, y+1/2, z+1/2; (viii) x, y, z−1; (ix) x, y, z+1; (x) x−1/2, −y+1/2, z; (xi) −x+1, −y+1, z−1/2; (xii) x−1/2, −y+1/2, z+1.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1A···N1vi | 0.86 | 2.32 | 3.158 (7) | 167.00 |
| N1—H1B···Br1 | 0.86 | 2.68 | 3.095 (5) | 111.00 |
| N1—H1B···O2vii | 0.86 | 2.32 | 3.049 (7) | 143.00 |
Symmetry codes: (vi) −x, −y+1, z+1/2; (vii) −x+1/2, y+1/2, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HK2621).
References
- Arshad, M. N., Tahir, M. N., Khan, I. U., Shafiq, M. & Siddiqui, W. A. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Arshad, M. N., Tahir, M. N., Khan, I. U., Siddiqui, W. A. & Shafiq, M. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2005). SADABS Bruker AXS Inc. Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2007). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc. Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 837–838.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Krishna Mohan, K. V. V., Narender, N., Srinivasu, P., Kulkarni, S. J. & Raghavan, K. V. (2004). Synth. Commun.34, 2143–2152.
- McPhail, A. T. & Sim, G. A. (1965). J. Chem. Soc. pp. 227–236.
- McWilliam, S. A., Skakle, J. M. S., Low, J. N., Wardell, J. L., Garden, S. J., Pinto, A. C., Torres, J. C. & Glidewell, C. (2001). Acta Cryst. C57, 942–945. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809004073/hk2621sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809004073/hk2621Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report