Abstract
In the title compound, C9H12NO6P, intramolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds form five- and six-membered rings. In the crystal, inversion dimers lined by pairs of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds occur with ring motifs R 2 2(10). The O atom of the hydroxy group behaves as an accepter and the benzene ring as donor. Adjacent dimers are connected through O—H⋯O links.
Related literature
For related structures, see: Acar et al. (2009 ▶); Tahir et al. (2007 ▶); Chen et al. (2008 ▶); Maliha et al. (2009 ▶). For hydrogen-bond motifs, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C9H12NO6P
M r = 261.17
Monoclinic,
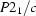
a = 9.8685 (12) Å
b = 7.5081 (11) Å
c = 16.1052 (12) Å
β = 90.341 (1)°
V = 1193.3 (2) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.25 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.26 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm
Data collection
Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer
Absorption correction: ψ scan (MolEN; Fair, 1990 ▶) T min = 0.939, T max = 0.959
2222 measured reflections
2093 independent reflections
1873 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.017
3 standard reflections frequency: 120 min intensity decay: −1.6%
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.057
wR(F 2) = 0.231
S = 1.00
2093 reflections
162 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.70 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.50 e Å−3
Data collection: CAD-4 EXPRESS (Enraf–Nonius, 1992 ▶); cell refinement: CAD-4 EXPRESS; data reduction: MolEN (Fair, 1990 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS86 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809005467/at2724sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809005467/at2724Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1⋯O4i | 0.87 (3) | 1.81 (3) | 2.674 (3) | 171 (4) |
| C6—H6⋯O1 | 0.93 | 2.30 | 2.688 (3) | 104 |
| C6—H6⋯O1ii | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.343 (4) | 140 |
| C7—H7⋯O2 | 0.93 (3) | 2.29 (3) | 2.827 (4) | 116 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 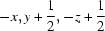 ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
(R)-Dimethyl [(2-chlorophenyl)hydroxymethyl]phosphonate (Tahir et al., 2007) and Dimethyl (1-hydroxy-1,2-diphenylethyl)phosphonate (Acar et al., 2009) have been reported by us. In continuation to the study of phosphonate compounds, we herein report the preparation and crystal structure of the title compound (I), (Fig 1).
Diethyl [hydroxy(2-nitrophenyl)methyl]phosphonate (II) (Chen et al., 2008) have also been published which have similar coordination around the C-atom having α-hydroxy group. But it is observed that the change of diethylphosphonate (II) with dimethylphosphonate (I) results in the S-conformation at the methine. In (I), the P═O is 1.467 (2) Å, whereas P–O and P–C have values of [1.557 (2), 1.563 (2) Å] and 1.829 (2) Å, respectively. The nitro group is oriented at an angle of 27.96 (23)° with the benzene ring A(C1—C6). There exist two intramolecular H-bondings which form five B(O1/C7/C1/C6/H6···O1) and six C(O2/N1/C2/C1/C7/H7···O2) membered rings. The title compound is dimerized (Fig 2) forming ring motifs R22(10) (Bernstein et al., 1995) if only intermolecular H-bonding is concerned. This ten membered ring is splitted into three rings through intramolecular H-bonding resulting in the formation of central four membered ring [O···H···O···H···O]. A similar ring has already been observed in 3-[(methylcarbamoyl)amino]-1H-isoindolium chloride (Maliha et al., 2009). The O-atom of hydroxy group behaves as an accepter and the benzene ring as donar. The adjacent dimers are connected through intermolecular H-bonds of O–H···O type, where the accepter is doubly bonded O the phosphonate group.
Experimental
A solution of O-nitrobenzaldehide (3.01 g, 20 mmole) and dimethylphosphonate (2.20 g, 20 mmole) was prepared in THF (50 ml). To this solution, a powder mixture of an equal amount of KF and commercial Al2O3 (2.5 g + 2.5 g) was added slowly and stirred for 48 h at 273 K. The product was filtered and the filtrate was evaporated at room temperature. The crystalline material obtained after two days was washed with ether and recrystallized in a solution mixture of petroleum ether and THF(1:1), [m.p: 383 K].
Refinement
All H-atoms appeared in Difference Fourier Map. The coordinations of the atom H7 bounded to the atom C7 and the atom H1 of the hydroxyl group were refined isotropically.
Thermal parameter of these H atoms was taken 1.2 and 1.5 times of the corresponding atoms, respectively.
The H atom (H7) bound to the atom C7 and the H atom (H1) of the hydroxyl group were located in a diffrerence map and their positions refined, with C—H = 0.93 (3) Å and 0.87 (3) Å. The other H atoms were positioned with idealized geometry and refined using a riding model, with C—H distances 0.93–0.96 Å. All H atoms were refined with isotropic displacement parameters (set to 1.2 times of the Ueq of the parent atom). For methyl and hydroxyl group Uiso(H) = 1.5 Ueq.
Figures
Fig. 1.
ORTEP drawing of the title compound, (C9H12NO6P), with the atom numbering scheme. The thermal ellpsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. H-atoms are shown by small circles of arbitrary radii. The broken lines indicate the intermolecular H-bondings.
Fig. 2.
The partial packing figure (PLATON: Spek, 2009) shows the formation of ring motifs through hydrogen bonding.
Crystal data
| C9H12NO6P | F(000) = 544 |
| Mr = 261.17 | Dx = 1.454 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Melting point: 383 K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.8685 (12) Å | Cell parameters from 25 reflections |
| b = 7.5081 (11) Å | θ = 11.7–21.0° |
| c = 16.1052 (12) Å | µ = 0.25 mm−1 |
| β = 90.341 (1)° | T = 296 K |
| V = 1193.3 (2) Å3 | Prismatic, brown |
| Z = 4 | 0.26 × 0.20 × 0.18 mm |
Data collection
| Enraf–Nonius CAD-4 diffractometer | Rint = 0.017 |
| ω/2θ scans | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.5° |
| Absorption correction: ψ scan (MolEN; Fair, 1990) | h = −11→0 |
| Tmin = 0.939, Tmax = 0.959 | k = −8→0 |
| 2222 measured reflections | l = −19→19 |
| 2093 independent reflections | 3 standard reflections every 120 min |
| 1873 reflections with I > 2σ(I) | intensity decay: −1.6% |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.057 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.231 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.199P)2 + 0.3221P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.00 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2093 reflections | Δρmax = 0.70 e Å−3 |
| 162 parameters | Δρmin = −0.50 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints |
Special details
| Experimental. the structure was solved by Patterson method using SHELX86 (Sheldrick, 2008); the whole molecule was recognized |
| Geometry. Bond distances, angles etc. have been calculated using the rounded fractional coordinates. All su's are estimated from the variances of the (full) variance-covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account in the estimation of distances, angles and torsion angles |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| P1 | 0.11199 (7) | 0.14188 (9) | 0.16915 (4) | 0.0429 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.0588 (2) | 0.4641 (3) | 0.12234 (12) | 0.0541 (7) | |
| O2 | 0.4424 (3) | 0.3284 (5) | 0.20368 (16) | 0.0854 (12) | |
| O3 | 0.5644 (3) | 0.1418 (5) | 0.1375 (2) | 0.0989 (14) | |
| O4 | 0.0391 (2) | 0.1450 (3) | 0.24822 (14) | 0.0574 (8) | |
| O5 | 0.0264 (2) | 0.0741 (3) | 0.09399 (13) | 0.0590 (8) | |
| O6 | 0.2419 (2) | 0.0229 (3) | 0.16653 (17) | 0.0679 (9) | |
| N1 | 0.4732 (2) | 0.2487 (4) | 0.14047 (16) | 0.0590 (9) | |
| C1 | 0.2651 (3) | 0.3507 (3) | 0.06417 (15) | 0.0380 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.3983 (3) | 0.2905 (4) | 0.06340 (16) | 0.0449 (8) | |
| C3 | 0.4703 (3) | 0.2673 (5) | −0.0095 (2) | 0.0580 (10) | |
| C4 | 0.4101 (4) | 0.3092 (5) | −0.08461 (19) | 0.0639 (11) | |
| C5 | 0.2801 (3) | 0.3732 (5) | −0.08579 (19) | 0.0590 (11) | |
| C6 | 0.2083 (3) | 0.3926 (4) | −0.01258 (16) | 0.0485 (9) | |
| C7 | 0.1759 (3) | 0.3618 (3) | 0.14019 (16) | 0.0394 (8) | |
| C8 | −0.1193 (4) | 0.0865 (7) | 0.0912 (3) | 0.0860 (16) | |
| C9 | 0.2422 (4) | −0.1632 (5) | 0.1836 (3) | 0.0822 (14) | |
| H1 | 0.031 (4) | 0.514 (5) | 0.168 (2) | 0.0650* | |
| H3 | 0.55850 | 0.22381 | −0.00787 | 0.0697* | |
| H4 | 0.45732 | 0.29422 | −0.13392 | 0.0768* | |
| H5 | 0.23957 | 0.40382 | −0.13609 | 0.0710* | |
| H6 | 0.11979 | 0.43474 | −0.01489 | 0.0582* | |
| H7 | 0.220 (3) | 0.409 (4) | 0.186 (2) | 0.0472* | |
| H8A | −0.15277 | 0.02578 | 0.04276 | 0.1289* | |
| H8B | −0.14567 | 0.20944 | 0.08889 | 0.1289* | |
| H8C | −0.15650 | 0.03237 | 0.14001 | 0.1289* | |
| H9A | 0.33363 | −0.20263 | 0.19280 | 0.1231* | |
| H9B | 0.20387 | −0.22632 | 0.13727 | 0.1231* | |
| H9C | 0.18939 | −0.18618 | 0.23233 | 0.1231* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| P1 | 0.0397 (5) | 0.0498 (6) | 0.0394 (6) | −0.0010 (3) | 0.0118 (3) | 0.0050 (2) |
| O1 | 0.0612 (13) | 0.0632 (12) | 0.0381 (11) | 0.0208 (10) | 0.0100 (9) | −0.0029 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0730 (17) | 0.135 (3) | 0.0482 (14) | 0.0101 (15) | −0.0100 (12) | −0.0049 (14) |
| O3 | 0.0687 (19) | 0.134 (3) | 0.094 (2) | 0.0365 (17) | −0.0079 (17) | 0.0130 (18) |
| O4 | 0.0558 (13) | 0.0733 (14) | 0.0432 (12) | −0.0081 (10) | 0.0176 (10) | 0.0110 (9) |
| O5 | 0.0521 (13) | 0.0700 (14) | 0.0551 (13) | −0.0075 (10) | 0.0116 (9) | −0.0146 (10) |
| O6 | 0.0453 (12) | 0.0551 (13) | 0.1034 (19) | 0.0036 (9) | 0.0211 (11) | 0.0248 (12) |
| N1 | 0.0437 (13) | 0.0792 (18) | 0.0541 (15) | −0.0038 (12) | 0.0011 (11) | 0.0101 (13) |
| C1 | 0.0422 (14) | 0.0397 (13) | 0.0322 (13) | −0.0045 (9) | 0.0082 (10) | 0.0001 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0403 (13) | 0.0502 (14) | 0.0443 (14) | −0.0063 (11) | 0.0059 (10) | 0.0011 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0421 (15) | 0.073 (2) | 0.0590 (17) | −0.0008 (13) | 0.0181 (13) | −0.0008 (14) |
| C4 | 0.0621 (19) | 0.086 (2) | 0.0439 (16) | −0.0039 (17) | 0.0213 (13) | −0.0057 (15) |
| C5 | 0.065 (2) | 0.080 (2) | 0.0322 (14) | −0.0026 (15) | 0.0077 (12) | 0.0027 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0500 (16) | 0.0613 (16) | 0.0341 (14) | 0.0044 (12) | 0.0052 (11) | 0.0036 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0442 (14) | 0.0449 (14) | 0.0291 (13) | 0.0009 (10) | 0.0065 (10) | 0.0001 (9) |
| C8 | 0.056 (2) | 0.114 (3) | 0.088 (3) | −0.004 (2) | −0.0030 (18) | −0.033 (2) |
| C9 | 0.068 (2) | 0.060 (2) | 0.119 (3) | 0.0109 (16) | 0.025 (2) | 0.025 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| P1—O4 | 1.467 (2) | C3—C4 | 1.381 (5) |
| P1—O5 | 1.557 (2) | C4—C5 | 1.370 (5) |
| P1—O6 | 1.563 (2) | C5—C6 | 1.387 (4) |
| P1—C7 | 1.829 (2) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| O1—C7 | 1.416 (3) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| O2—N1 | 1.221 (4) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| O3—N1 | 1.207 (4) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| O5—C8 | 1.441 (4) | C7—H7 | 0.93 (3) |
| O6—C9 | 1.424 (4) | C8—H8A | 0.9600 |
| O1—H1 | 0.87 (3) | C8—H8B | 0.9600 |
| N1—C2 | 1.475 (4) | C8—H8C | 0.9600 |
| C1—C6 | 1.390 (4) | C9—H9A | 0.9600 |
| C1—C7 | 1.515 (4) | C9—H9B | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.390 (4) | C9—H9C | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.387 (4) | ||
| P1···H1i | 3.14 (3) | N1···O6 | 2.876 (3) |
| O1···O4 | 3.145 (3) | N1···H7 | 2.87 (3) |
| O1···O5 | 2.981 (3) | C2···O6 | 3.035 (4) |
| O1···C8 | 3.372 (5) | C2···C4ix | 3.566 (5) |
| O1···O4ii | 2.674 (3) | C3···C3ix | 3.556 (5) |
| O1···C6iii | 3.343 (4) | C4···C2ix | 3.566 (5) |
| O2···C7 | 2.827 (4) | C6···O1iii | 3.343 (4) |
| O2···O6 | 3.086 (4) | C7···O2 | 2.827 (4) |
| O3···C8iv | 3.240 (5) | C8···O1 | 3.372 (5) |
| O4···O1 | 3.145 (3) | C8···O3x | 3.240 (5) |
| O4···O1i | 2.674 (3) | C8···O5v | 3.350 (5) |
| O4···C9ii | 3.320 (5) | C9···O4i | 3.320 (5) |
| O5···C8v | 3.350 (5) | H1···P1ii | 3.14 (3) |
| O5···O1 | 2.981 (3) | H1···O4ii | 1.81 (3) |
| O6···O2 | 3.086 (4) | H3···O3 | 2.4200 |
| O6···C2 | 3.035 (4) | H4···H9Axi | 2.3800 |
| O6···N1 | 2.876 (3) | H4···O2xii | 2.7800 |
| O1···H6iii | 2.5800 | H5···O4xii | 2.7300 |
| O1···H6 | 2.3000 | H6···O1 | 2.3000 |
| O1···H8B | 2.8300 | H6···O1iii | 2.5800 |
| O1···H9Bvi | 2.7400 | H7···O2 | 2.29 (3) |
| O2···H7 | 2.29 (3) | H7···N1 | 2.87 (3) |
| O2···H9Avii | 2.7700 | H8A···O5v | 2.6500 |
| O2···H4viii | 2.7800 | H8B···O1 | 2.8300 |
| O3···H3 | 2.4200 | H8C···O3x | 2.8700 |
| O3···H8Civ | 2.8700 | H8C···O4 | 2.7300 |
| O4···H5viii | 2.7300 | H9A···O2xiii | 2.7700 |
| O4···H9C | 2.9100 | H9A···H4xi | 2.3800 |
| O4···H9Cii | 2.6100 | H9B···O1xiv | 2.7400 |
| O4···H8C | 2.7300 | H9C···O4 | 2.9100 |
| O4···H1i | 1.81 (3) | H9C···O4i | 2.6100 |
| O5···H8Av | 2.6500 | ||
| O4—P1—O5 | 114.43 (12) | P1—C7—O1 | 105.03 (19) |
| O4—P1—O6 | 116.05 (14) | C2—C3—H3 | 120.00 |
| O4—P1—C7 | 112.25 (13) | C4—C3—H3 | 120.00 |
| O5—P1—O6 | 103.49 (13) | C3—C4—H4 | 120.00 |
| O5—P1—C7 | 106.44 (12) | C5—C4—H4 | 120.00 |
| O6—P1—C7 | 103.00 (13) | C4—C5—H5 | 120.00 |
| P1—O5—C8 | 122.7 (2) | C6—C5—H5 | 120.00 |
| P1—O6—C9 | 123.8 (2) | C1—C6—H6 | 119.00 |
| C7—O1—H1 | 109 (2) | C5—C6—H6 | 119.00 |
| O2—N1—O3 | 123.3 (3) | P1—C7—H7 | 107.7 (19) |
| O3—N1—C2 | 118.6 (3) | O1—C7—H7 | 109.5 (18) |
| O2—N1—C2 | 118.1 (3) | C1—C7—H7 | 113.1 (19) |
| C2—C1—C7 | 125.4 (2) | O5—C8—H8A | 109.00 |
| C6—C1—C7 | 118.2 (3) | O5—C8—H8B | 109.00 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 116.2 (2) | O5—C8—H8C | 109.00 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 115.4 (3) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.00 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 122.5 (3) | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.00 |
| N1—C2—C1 | 122.1 (2) | H8B—C8—H8C | 110.00 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.5 (3) | O6—C9—H9A | 109.00 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.3 (3) | O6—C9—H9B | 110.00 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.5 (3) | O6—C9—H9C | 109.00 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 121.8 (3) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.00 |
| P1—C7—C1 | 111.07 (16) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.00 |
| O1—C7—C1 | 110.1 (2) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.00 |
| O4—P1—O5—C8 | 25.6 (3) | C6—C1—C2—N1 | 177.3 (3) |
| O6—P1—O5—C8 | 152.8 (3) | C6—C1—C2—C3 | −2.1 (4) |
| C7—P1—O5—C8 | −99.0 (3) | C7—C1—C2—N1 | −7.1 (4) |
| O4—P1—O6—C9 | 58.0 (3) | C7—C1—C2—C3 | 173.6 (3) |
| O5—P1—O6—C9 | −68.2 (3) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.8 (4) |
| C7—P1—O6—C9 | −179.0 (3) | C7—C1—C6—C5 | −175.2 (3) |
| O4—P1—C7—O1 | −68.02 (19) | C2—C1—C7—P1 | −76.9 (3) |
| O4—P1—C7—C1 | 173.00 (18) | C2—C1—C7—O1 | 167.2 (2) |
| O5—P1—C7—O1 | 57.90 (19) | C6—C1—C7—P1 | 98.6 (2) |
| O5—P1—C7—C1 | −61.1 (2) | C6—C1—C7—O1 | −17.3 (3) |
| O6—P1—C7—O1 | 166.43 (17) | N1—C2—C3—C4 | −177.7 (3) |
| O6—P1—C7—C1 | 47.5 (2) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.7 (5) |
| O2—N1—C2—C1 | −28.4 (4) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.1 (5) |
| O2—N1—C2—C3 | 151.0 (3) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.3 (6) |
| O3—N1—C2—C1 | 153.8 (3) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.9 (5) |
| O3—N1—C2—C3 | −26.8 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) −x, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (iii) −x, −y+1, −z; (iv) x+1, y, z; (v) −x, −y, −z; (vi) x, y+1, z; (vii) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (viii) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (ix) −x+1, −y+1, −z; (x) x−1, y, z; (xi) −x+1, −y, −z; (xii) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (xiii) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (xiv) x, y−1, z.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1···O4ii | 0.87 (3) | 1.81 (3) | 2.674 (3) | 171 (4) |
| C6—H6···O1 | 0.9300 | 2.3000 | 2.688 (3) | 104.00 |
| C6—H6···O1iii | 0.9300 | 2.5800 | 3.343 (4) | 140.00 |
| C7—H7···O2 | 0.93 (3) | 2.29 (3) | 2.827 (4) | 116 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (ii) −x, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (iii) −x, −y+1, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: AT2724).
References
- Acar, N., Tahir, M. N., Yılmaz, H., Chishti, M. S. A. & Malik, M. A. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
- Chen, C., Jin, W. & Li, X. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Enraf–Nonius (1992). CAD-4 EXPRESS Enraf–Nonius, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Fair, C. K. (1990). MolEN Enraf–Nonius, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 837–838.
- Maliha, B., Tariq, M. I., Tahir, M. N., Hussain, I. & Siddiqui, H. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Tahir, M. N., Acar, N., Yilmaz, H., Danish, M. & Ülkü, D. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o3817–o3818.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809005467/at2724sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809005467/at2724Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




