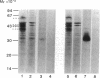
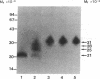
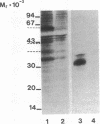
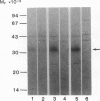
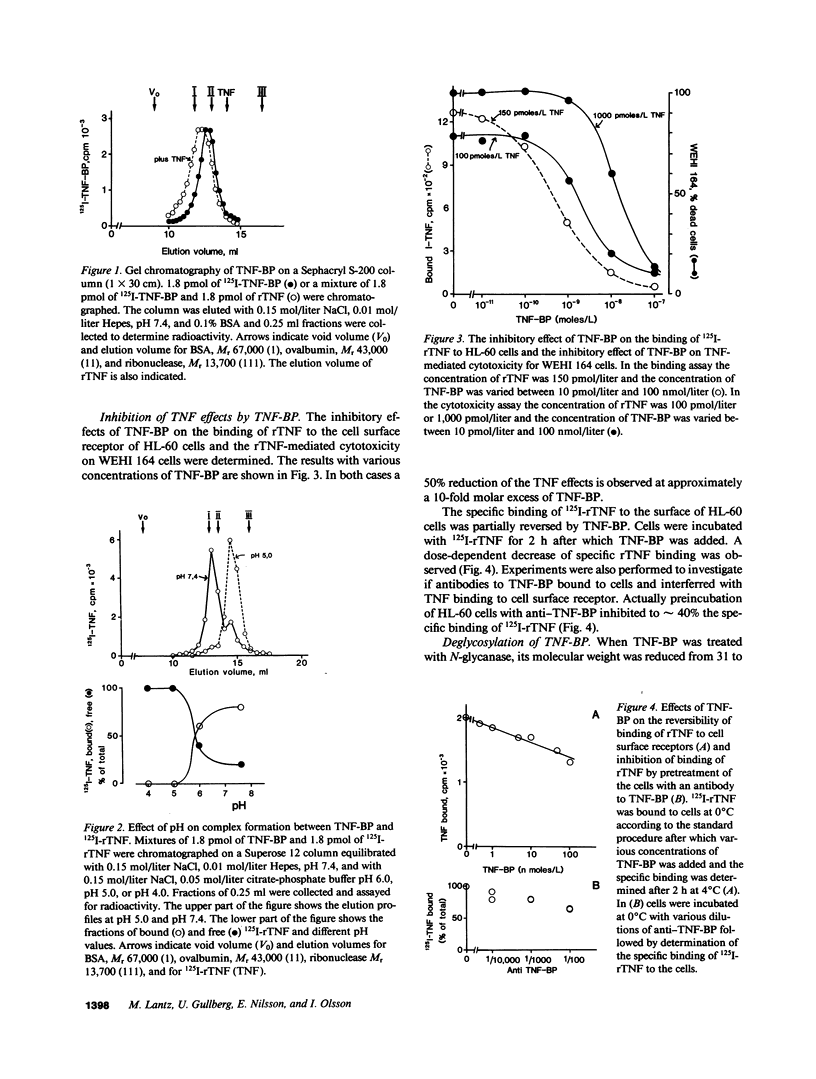
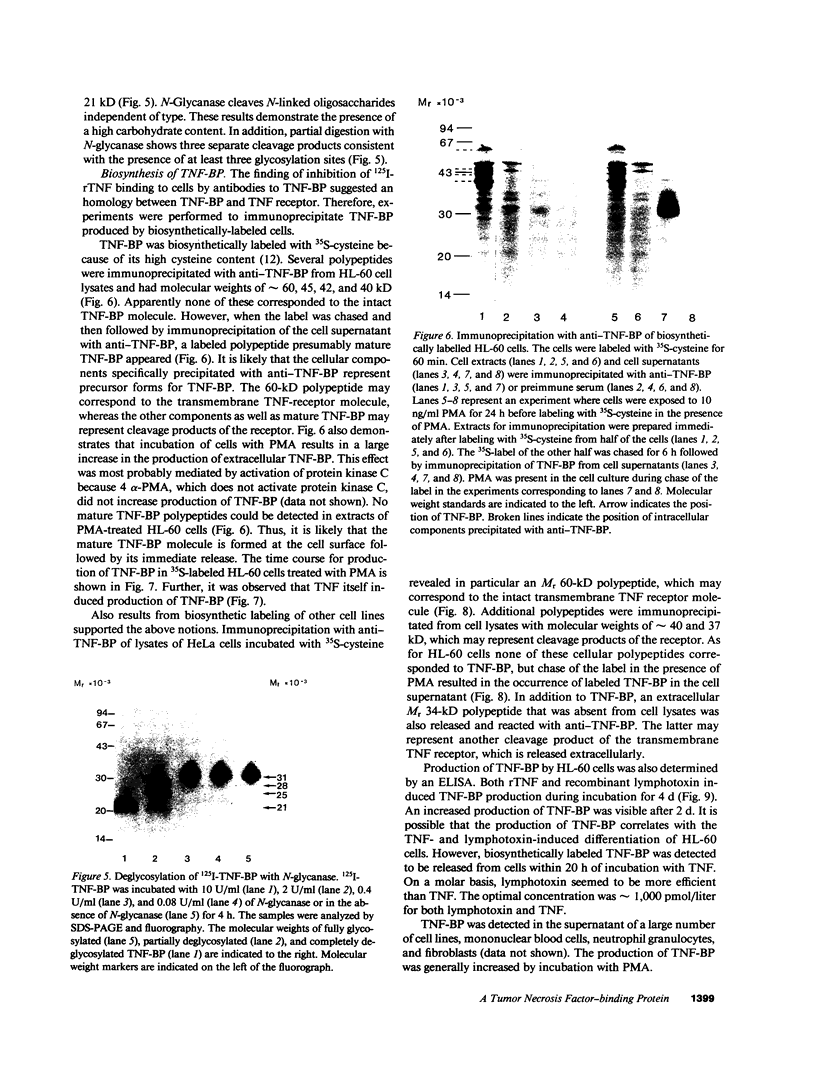
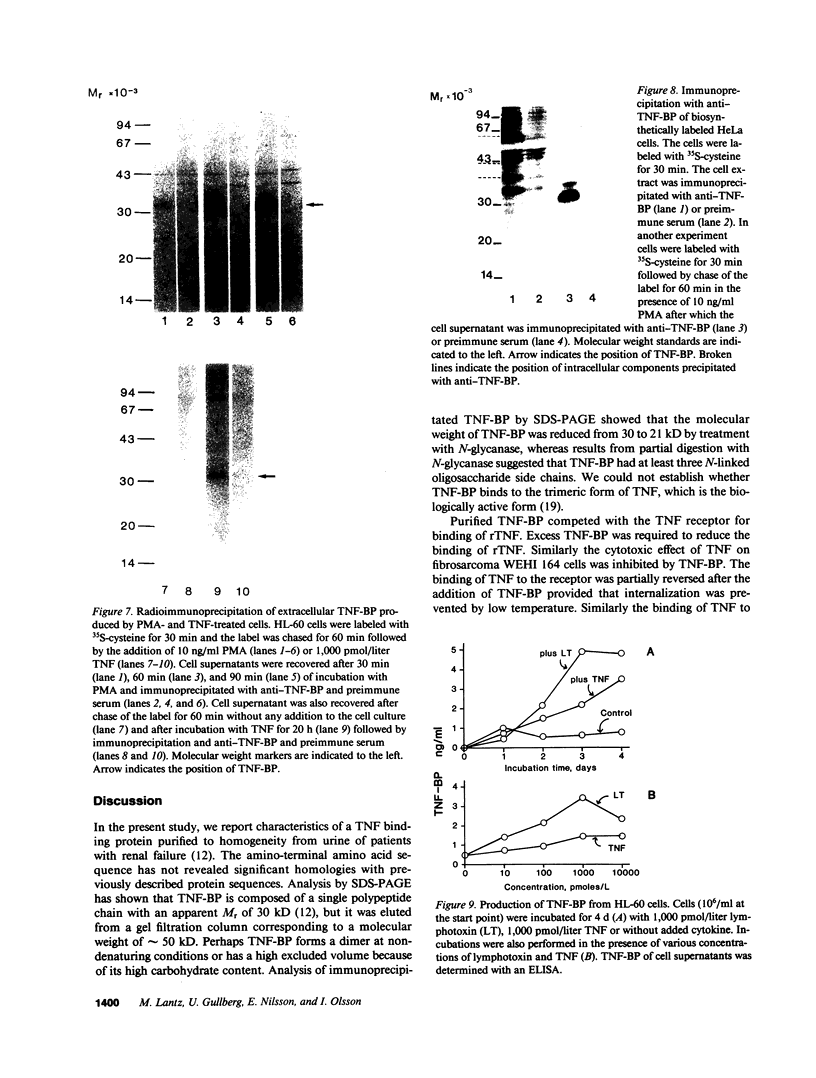
Abstract
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a pleiotropic mediator of inflammatory responses. A cysteine-rich, highly glycosylated 30-kD TNF-binding protein (TNF-BP) purified from urine may have a role in regulation because it protects in vitro against the biological effects of TNF. The cytotoxic effect of TNF on the fibrosarcoma cell line WEHI 164 was inhibited by 50% at a 10-fold excess of TNF-BP. The binding of TNF to the receptor was partially reversed after the addition of TNF-BP. Results from biosynthetic labeling of cells with 35S-cysteine followed by immunoprecipitation with anti-TNF-BP indicated that TNF-BP is formed and released at the cell surface by cleavage because no corresponding cellular polypeptide was observed. A cellular 60-kD polypeptide, which was immunoprecipitated with anti-TNF-BP, may correspond to the transmembrane TNF-receptor molecule and be the precursor of TNF-BP. Thus, TNF-BP appears to be a soluble form of a transmembrane TNF-receptor. Moreover our results demonstrate that the production of TNF-BP is increased when the TNF receptor is downregulated in cells by treatment with TNF or by activation of protein kinase C with phorbol esters. TNF-BP may be an important agent that blocks harmful effects of TNF, and, therefore, useful in clinical applications.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler B., Greenwald D., Hulmes J. D., Chang M., Pan Y. C., Mathison J., Ulevitch R., Cerami A. Identity of tumour necrosis factor and the macrophage-secreted factor cachectin. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):552–554. doi: 10.1038/316552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carswell E. A., Old L. J., Kassel R. L., Green S., Fiore N., Williamson B. An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E. Continuous growth and differentiation of human myeloid leukaemic cells in suspension culture. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):347–349. doi: 10.1038/270347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing J. R., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Ligand and protein kinase C downmodulate the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor by independent mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2890–2896. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann H., Aderka D., Rubinstein M., Rotman D., Wallach D. A tumor necrosis factor-binding protein purified to homogeneity from human urine protects cells from tumor necrosis factor toxicity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11974–11980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelmann H., Novick D., Wallach D. Two tumor necrosis factor-binding proteins purified from human urine. Evidence for immunological cross-reactivity with cell surface tumor necrosis factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1531–1536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espevik T., Nissen-Meyer J. A highly sensitive cell line, WEHI 164 clone 13, for measuring cytotoxic factor/tumor necrosis factor from human monocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Dec 4;95(1):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullberg U., Lantz M., Nilsson E., Olsson I. Characterization of the receptor for lymphotoxin; a spontaneous internalization without recycling and ligand-induced downregulation in HL-60 cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;49(2):334–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullberg U., Lantz M., Nilsson E., Peetre C., Adolf G., Olsson I. Characterization of a relationship between the T-lymphocyte derived differentiation inducing factor (DIF) and lymphotoxin: a common receptor system for DIF, lymphotoxin and tumor necrosis factor downregulated by phorbol diesters. Eur J Haematol. 1987 Sep;39(3):241–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1987.tb00765.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loetscher H., Pan Y. C., Lahm H. W., Gentz R., Brockhaus M., Tabuchi H., Lesslauer W. Molecular cloning and expression of the human 55 kd tumor necrosis factor receptor. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90815-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick D., Engelmann H., Wallach D., Rubinstein M. Soluble cytokine receptors are present in normal human urine. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1409–1414. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Tumour necrosis factor. Polypeptide mediator network. 1987 Mar 26-Apr 1Nature. 326(6111):330–331. doi: 10.1038/326330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson I., Lantz M., Nilsson E., Peetre C., Thysell H., Grubb A., Adolf G. Isolation and characterization of a tumor necrosis factor binding protein from urine. Eur J Haematol. 1989 Mar;42(3):270–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1989.tb00111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantazis P., Bonner W. M. Quantitative determination of histone modification. H2A acetylation and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4669–4675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peetre C., Gullberg U., Nilsson E., Olsson I. Effects of recombinant tumor necrosis factor on proliferation and differentiation of leukemic and normal hemopoietic cells in vitro. Relationship to cell surface receptor. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1694–1700. doi: 10.1172/JCI112764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peetre C., Thysell H., Grubb A., Olsson I. A tumor necrosis factor binding protein is present in human biological fluids. Eur J Haematol. 1988 Nov;41(5):414–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1988.tb00220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piguet P. F., Grau G. E., Allet B., Vassalli P. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin is an effector of skin and gut lesions of the acute phase of graft-vs.-host disease. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1280–1289. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin L. A., Kurman C. C., Fritz M. E., Biddison W. E., Boutin B., Yarchoan R., Nelson D. L. Soluble interleukin 2 receptors are released from activated human lymphoid cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3172–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schall T. J., Lewis M., Koller K. J., Lee A., Rice G. C., Wong G. H., Gatanaga T., Granger G. A., Lentz R., Raab H. Molecular cloning and expression of a receptor for human tumor necrosis factor. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):361–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90816-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheurich P., Ucer U., Krönke M., Pfizenmaier K. Quantification and characterization of high-affinity membrane receptors for tumor necrosis factor on human leukemic cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1986 Jul 15;38(1):127–133. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910380120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Isaaz S., Dayer J. M. A human inhibitor of tumor necrosis factor alpha. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1511–1516. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seckinger P., Isaaz S., Dayer J. M. Purification and biologic characterization of a specific tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11966–11973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry B., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor exerts endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine control of inflammatory responses. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1269–1277. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Baglioni C. The active form of tumor necrosis factor is a trimer. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):6951–6954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Kirstein M., Fiers W., Baglioni C. Species specificity of human and murine tumor necrosis factor. A comparative study of tumor necrosis factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):14871–14874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauber G. B., Aiyer R. A., Aggarwal B. B. Human tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor. Purification by immunoaffinity chromatography and initial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19098–19104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tejedor F., Ballesta J. P. Iodination of biological samples without loss of functional activity. Anal Biochem. 1982 Nov 15;127(1):143–149. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90156-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torti F. M., Dieckmann B., Beutler B., Cerami A., Ringold G. M. A macrophage factor inhibits adipocyte gene expression: an in vitro model of cachexia. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):867–869. doi: 10.1126/science.3839597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto M., Feinman R., Kohase M., Vilcek J. Characterization and affinity crosslinking of receptors for tumor necrosis factor on human cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Sep;249(2):563–568. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto M., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor-induced downregulation of its receptors in HeLa cells. J Biochem. 1987 Dec;102(6):1571–1577. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unglaub R., Maxeiner B., Thoma B., Pfizenmaier K., Scheurich P. Downregulation of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) sensitivity via modulation of TNF binding capacity by protein kinase C activators. J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1788–1797. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A., Halstensen A., Espevik T. Association between tumour necrosis factor in serum and fatal outcome in patients with meningococcal disease. Lancet. 1987 Feb 14;1(8529):355–357. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91728-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach D., Holtmann H., Engelmann H., Nophar Y. Sensitization and desensitization to lethal effects of tumor necrosis factor and IL-1. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):2994–2999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe N., Kuriyama H., Sone H., Neda H., Yamauchi N., Maeda M., Niitsu Y. Continuous internalization of tumor necrosis factor receptors in a human myosarcoma cell line. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10262–10266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]