Abstract
In the title compound, C16H16N2O5, the methoxy group is disordered with site occupancies of 0.20 (3) and 0.80 (3). The dihedral angle between the two aromatic rings is 73.7 (2)°. The crystal structure is characterized by intermolecular N—H⋯O, O—H⋯O, C—H⋯O and C—H⋯π hydrogen bonds.
Related literature
For N-substituted phenyl acetamides as intermediates in organic synthesis, see: Gowda et al. (2007 ▶); Ghosh et al. (2005 ▶). For a related structure, see: NizamMohideen et al. (2009 ▶). For hydrogen-bond motifs, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).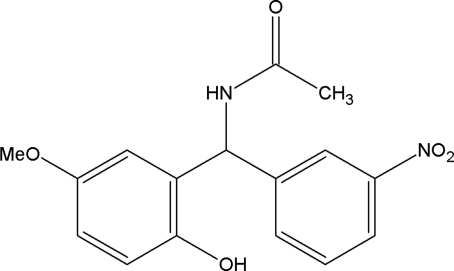
Experimental
Crystal data
C16H16N2O5
M r = 316.31
Monoclinic,

a = 15.3351 (3) Å
b = 8.1327 (2) Å
c = 14.5308 (3) Å
β = 117.387 (1)°
V = 1609.10 (6) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.10 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.32 × 0.28 × 0.25 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: none
23127 measured reflections
6121 independent reflections
3900 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.032
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.058
wR(F 2) = 0.196
S = 1.03
6121 reflections
216 parameters
1 restraint
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.41 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: APEX2 and SAINT (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT and XPREP (Bruker, 2004 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809009726/bt2901sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809009726/bt2901Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2⋯O5i | 0.82 | 1.80 | 2.617 (2) | 179 |
| N1—H1⋯O4ii | 0.86 | 2.30 | 3.159 (2) | 174 |
| C10—H10⋯O1iii | 0.93 | 2.47 | 3.320 (2) | 152 |
| C12—H12⋯O2iv | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.397 (2) | 147 |
| C14—H14⋯O4ii | 0.93 | 2.55 | 3.470 (2) | 169 |
| C8—H8⋯O5 | 0.98 | 2.30 | 2.714 (2) | 105 |
| C11—H11⋯Cg1iv | 0.93 | 2.83 | 3.680 (2) | 153 |
| C1B—H1B1⋯Cg2v | 0.96 | 2.61 | 3.531 (2) | 160 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 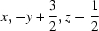 ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v)  . Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the C2-C7 and C9-C14 rings, respectively.
. Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the C2-C7 and C9-C14 rings, respectively.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr Babu Vargheese, SAIF, IIT, Madras, India, for his help in collecting the X-ray intensity data. MNM and ASP thank Dr J. Jothi Kumar, Principal of the Presidency College (Autonomous), Chennai, India, for providing the computer and internet facilities.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
N-(Substituted phenyl) acetamides are well known for their importance as intermediates in organic synthesis (Gowda et al., 2007). Depending on the types of substitution at the α, β and keto-C atoms, and the conformational flexibility of the substituent groups, a variety of β-acetamido ketones offering the possibility of intermolecular interactions can be obtained (Ghosh et al., 2005). The amide linkage [–NHC(O)-] is known to be strong enough to form and maintain protein architectures and has been utilized to create various molecular devices for a spectrum of purposes in organic chemistry. We have synthesized an amide system with an aromatic ring as a terminal group to determine how the rigid ring affects the conformational behavior. As part of our ongoing investigation of acetamide derivatives, the title compound has been prepared and its crystal structure is presented here.
The bond lenghts and angles are comparable with N-[(3-Nitro-phenyl)-(2-hydroxy-napthalen-1-yl)-methyl]-acetamide (NizamMohideen et al., 2009), a structure closely related to the title compound. The nitro group is slighty twisted out of the plane of the benzene ring, as indicated by O4—N2—C13—C14 and O3—N2—C13—C14 torsion angles of -8.6 (3) and 171.0 (2)°, respectively, and comparable with those in the previously reported structure mentioned above.
The dihedral angle between the C2—C7 and C9—C14 benzene rings is 73.7 (2)°. The dihedral angle between the acetamide residue and the benzene rings (C2—C7 and C9—C14) are 70.0 (1) and 37.4 (2)°, respectively.
The intermolecular aggregation of the molecules is determined by combination of N—H···O, C—H···O, O—H···O and C—H···π hydrogen bonds (Table 1). The crystal structure is characterized by intermolecular bifurcated acceptor hydrogen bonds between the benzene and acetamide groups (Fig. 2). Atom N1 and C14 in the molecule at (x, y, z) act as a hydrogen-bond donor via atom H1 and H14 to atom O4 in the molecule at (-x, 1 - y, -z). This intermolecular hydrogen bond links the molecule into dimers with a cyclic R22(16) and R22(10) (Bernstein et al., 1995) ring system, respectively. Atom C10 in the molecule at (x, y, z) acts as a hydrogen-bond donor via atom H10 to atom O1 in the molecule at (1 - x, 1 - y, 1 - z). This intermolecular hydrogen bond links the molecule into dimers with a cyclic R22(16) ring system. The crystal structure is further stabilized by C—H···π interactions involing rings C11—H11···Cg1 (Cg1 is the centroid of the C2—C7 ring) and C1—H1a···Cg2 (where Cg2 is the centroid of the C9—C14 ring).
Experimental
A mixture of 3-nitrobenzaldehyde (10 mmol), 4-methoxyphenol (10 mmol) and iodine (0.4 mmol, 4 mol%) were mixed in acetonitrile (5 ml). To that suspension acetyl chloride (2.8 mmol, 0.2 ml) was added and the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 5 h. After the completion of the reaction (as monitored by TLC), saturated sodium thiosulfate solution (5 ml) was added. The precipitated solid was filtered and dried. The dried sample was washed with diethyl ether (2 × 10 ml) and again dried. Single crystals of the title compound suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained by slow evaporation of a solution in Ethanol.
Refinement
The C atoms of the methoxy group are disordered over two positions with refined occupancies of 0.20 (3) and 0.80 (3). The corresponding bond distances involving the disordered atoms were restrained to be equal. H atoms were positioned geometrically, with N—H = 0.86, O—H = 0.82 and C—H = 0.93, 0.98 and 0.96 Å aromatic, methylene and methyl H, respectively, and were treated as riding on their parent atoms, with Uiso(H) = xUeq(C, N), where x = 1.2 for all H atoms.
Figures
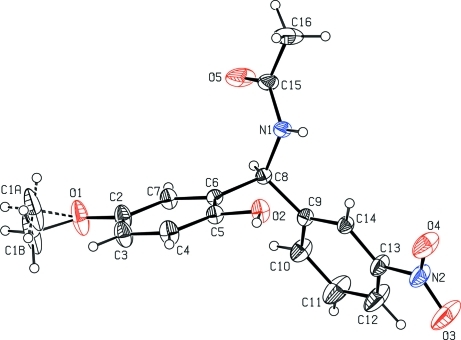
Fig. 1.
View of the title compound showing the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing of the title compound showing the R22(16), R22(10) and R22(16) rings. Hydrogen bonding is shown as dashed lines. H atoms not involved in the hydrogen bonding have been omitted for clarity. [Symmetry codes: (ii) -x + 1, -y + 1, -z + 1, (iii)-x, -y + 1, -z]]
Crystal data
| C16H16N2O5 | F(000) = 664 |
| Mr = 316.31 | Dx = 1.306 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 3900 reflections |
| a = 15.3351 (3) Å | θ = 2.5–25° |
| b = 8.1327 (2) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| c = 14.5308 (3) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 117.387 (1)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 1609.10 (6) Å3 | 0.32 × 0.28 × 0.25 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3900 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.032 |
| graphite | θmax = 33.2°, θmin = 2.8° |
| ω and φ scans | h = −23→23 |
| 23127 measured reflections | k = −12→11 |
| 6121 independent reflections | l = −22→22 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.058 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.196 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.1083P)2 + 0.189P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 6121 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 216 parameters | Δρmax = 0.41 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| C1A | 0.640 (2) | 0.888 (2) | 0.458 (2) | 0.117 (3) | 0.20 (3) |
| H1A1 | 0.6596 | 0.8863 | 0.4043 | 0.175* | 0.20 (3) |
| H1A2 | 0.6970 | 0.8979 | 0.5243 | 0.175* | 0.20 (3) |
| H1A3 | 0.5974 | 0.9805 | 0.4479 | 0.175* | 0.20 (3) |
| C1B | 0.6664 (8) | 0.834 (2) | 0.4528 (4) | 0.117 (3) | 0.80 (3) |
| H1B1 | 0.6854 | 0.7851 | 0.4044 | 0.175* | 0.80 (3) |
| H1B2 | 0.7218 | 0.8351 | 0.5206 | 0.175* | 0.80 (3) |
| H1B3 | 0.6444 | 0.9445 | 0.4316 | 0.175* | 0.80 (3) |
| C2 | 0.50275 (11) | 0.7283 (2) | 0.36557 (11) | 0.0484 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.48701 (12) | 0.7903 (2) | 0.27035 (12) | 0.0532 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.5369 | 0.8465 | 0.2643 | 0.064* | |
| C4 | 0.39705 (12) | 0.7686 (2) | 0.18441 (11) | 0.0477 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.3870 | 0.8102 | 0.1207 | 0.057* | |
| C5 | 0.32155 (9) | 0.68542 (15) | 0.19185 (9) | 0.0332 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.33683 (9) | 0.62281 (13) | 0.28794 (8) | 0.0278 (2) | |
| C7 | 0.42728 (10) | 0.64540 (17) | 0.37363 (9) | 0.0372 (3) | |
| H7 | 0.4377 | 0.6044 | 0.4376 | 0.045* | |
| C8 | 0.25554 (8) | 0.53368 (14) | 0.29997 (8) | 0.0279 (2) | |
| H8 | 0.2826 | 0.5052 | 0.3735 | 0.034* | |
| C9 | 0.22779 (9) | 0.37267 (14) | 0.24099 (9) | 0.0310 (2) | |
| C10 | 0.28657 (13) | 0.23670 (18) | 0.28828 (12) | 0.0516 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.3393 | 0.2477 | 0.3541 | 0.062* | |
| C11 | 0.26797 (18) | 0.0857 (2) | 0.23924 (16) | 0.0808 (7) | |
| H11 | 0.3072 | −0.0042 | 0.2728 | 0.097* | |
| C12 | 0.19121 (17) | 0.0676 (2) | 0.14040 (16) | 0.0775 (7) | |
| H12 | 0.1782 | −0.0332 | 0.1064 | 0.093* | |
| C13 | 0.13489 (12) | 0.20355 (17) | 0.09422 (12) | 0.0478 (4) | |
| C14 | 0.15003 (9) | 0.35523 (14) | 0.14216 (10) | 0.0335 (2) | |
| H14 | 0.1091 | 0.4436 | 0.1090 | 0.040* | |
| C15 | 0.16393 (11) | 0.7236 (2) | 0.35184 (10) | 0.0447 (3) | |
| C16 | 0.07682 (16) | 0.8327 (3) | 0.32137 (16) | 0.0799 (7) | |
| H16A | 0.0179 | 0.7684 | 0.2885 | 0.120* | |
| H16B | 0.0768 | 0.9151 | 0.2740 | 0.120* | |
| H16C | 0.0797 | 0.8848 | 0.3820 | 0.120* | |
| N1 | 0.17154 (8) | 0.64005 (14) | 0.27656 (8) | 0.0348 (2) | |
| H1 | 0.1263 | 0.6493 | 0.2136 | 0.042* | |
| N2 | 0.05722 (11) | 0.18961 (17) | −0.01317 (11) | 0.0577 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.58945 (9) | 0.7410 (2) | 0.45516 (10) | 0.0795 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.23072 (7) | 0.66466 (13) | 0.11020 (7) | 0.0423 (2) | |
| H2 | 0.2299 | 0.7038 | 0.0578 | 0.063* | |
| O3 | 0.05139 (15) | 0.06269 (19) | −0.06005 (12) | 0.1014 (7) | |
| O4 | 0.00217 (11) | 0.30376 (18) | −0.05160 (11) | 0.0816 (5) | |
| O5 | 0.22599 (10) | 0.7079 (2) | 0.44251 (9) | 0.0746 (5) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1A | 0.050 (3) | 0.233 (7) | 0.0560 (14) | −0.069 (5) | 0.0140 (19) | 0.011 (3) |
| C1B | 0.050 (3) | 0.233 (7) | 0.0560 (14) | −0.069 (5) | 0.0140 (19) | 0.011 (3) |
| C2 | 0.0342 (7) | 0.0719 (10) | 0.0316 (6) | −0.0132 (6) | 0.0086 (6) | 0.0049 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0426 (8) | 0.0758 (11) | 0.0417 (8) | −0.0160 (7) | 0.0199 (7) | 0.0096 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0465 (8) | 0.0653 (9) | 0.0314 (6) | −0.0103 (7) | 0.0180 (6) | 0.0115 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0347 (6) | 0.0399 (6) | 0.0226 (5) | −0.0013 (5) | 0.0111 (5) | 0.0041 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0304 (5) | 0.0314 (5) | 0.0214 (4) | 0.0003 (4) | 0.0118 (4) | 0.0018 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0344 (6) | 0.0493 (7) | 0.0238 (5) | −0.0044 (5) | 0.0100 (5) | 0.0049 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0300 (5) | 0.0332 (5) | 0.0188 (4) | −0.0004 (4) | 0.0098 (4) | 0.0001 (3) |
| C9 | 0.0334 (6) | 0.0320 (5) | 0.0252 (5) | −0.0019 (4) | 0.0116 (5) | 0.0010 (4) |
| C10 | 0.0575 (9) | 0.0393 (7) | 0.0350 (7) | 0.0069 (6) | 0.0017 (7) | 0.0016 (5) |
| C11 | 0.0947 (16) | 0.0388 (8) | 0.0589 (11) | 0.0212 (9) | −0.0076 (11) | −0.0013 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0909 (15) | 0.0358 (7) | 0.0598 (11) | 0.0108 (8) | −0.0046 (10) | −0.0117 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0477 (8) | 0.0378 (6) | 0.0380 (7) | 0.0005 (6) | 0.0026 (6) | −0.0079 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0328 (6) | 0.0327 (5) | 0.0294 (5) | 0.0003 (4) | 0.0095 (5) | −0.0018 (4) |
| C15 | 0.0397 (7) | 0.0641 (9) | 0.0296 (6) | 0.0056 (6) | 0.0154 (6) | −0.0126 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0686 (13) | 0.1103 (17) | 0.0559 (11) | 0.0371 (12) | 0.0245 (10) | −0.0197 (11) |
| N1 | 0.0314 (5) | 0.0479 (6) | 0.0216 (4) | 0.0042 (4) | 0.0092 (4) | −0.0058 (4) |
| N2 | 0.0559 (8) | 0.0492 (7) | 0.0434 (7) | 0.0002 (6) | 0.0016 (6) | −0.0162 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0415 (7) | 0.1398 (13) | 0.0397 (6) | −0.0371 (8) | 0.0038 (5) | 0.0145 (7) |
| O2 | 0.0397 (5) | 0.0583 (6) | 0.0221 (4) | −0.0068 (4) | 0.0085 (4) | 0.0098 (4) |
| O3 | 0.1210 (15) | 0.0656 (9) | 0.0623 (9) | 0.0099 (9) | −0.0052 (9) | −0.0328 (7) |
| O4 | 0.0698 (9) | 0.0699 (8) | 0.0517 (7) | 0.0233 (7) | −0.0179 (7) | −0.0195 (6) |
| O5 | 0.0692 (9) | 0.1152 (11) | 0.0278 (5) | 0.0295 (8) | 0.0124 (6) | −0.0204 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1A—O1 | 1.416 (4) | C9—C14 | 1.3888 (17) |
| C1A—H1A1 | 0.9600 | C9—C10 | 1.3920 (18) |
| C1A—H1A2 | 0.9600 | C10—C11 | 1.382 (2) |
| C1A—H1A3 | 0.9600 | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C1B—O1 | 1.416 (4) | C11—C12 | 1.384 (3) |
| C1B—H1B1 | 0.9600 | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C1B—H1B2 | 0.9600 | C12—C13 | 1.373 (2) |
| C1B—H1B3 | 0.9600 | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C2—O1 | 1.3714 (18) | C13—C14 | 1.3827 (18) |
| C2—C3 | 1.386 (2) | C13—N2 | 1.4685 (19) |
| C2—C7 | 1.390 (2) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.382 (2) | C15—O5 | 1.2264 (18) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C15—O5 | 1.2264 (18) |
| C4—C5 | 1.3872 (18) | C15—N1 | 1.3375 (15) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C15—C16 | 1.491 (2) |
| C5—O2 | 1.3623 (15) | C16—H16A | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.4010 (15) | C16—H16B | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.3854 (17) | C16—H16C | 0.9600 |
| C6—C8 | 1.5199 (16) | N1—H1 | 0.8600 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9300 | N2—O4 | 1.2052 (19) |
| C8—N1 | 1.4561 (15) | N2—O3 | 1.2172 (18) |
| C8—C9 | 1.5149 (16) | O2—H2 | 0.8200 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9800 | ||
| O1—C1A—H1A1 | 109.5 | C11—C10—C9 | 121.21 (14) |
| O1—C1A—H1A2 | 109.5 | C11—C10—H10 | 119.4 |
| O1—C1A—H1A3 | 109.5 | C9—C10—H10 | 119.4 |
| O1—C1B—H1B1 | 109.5 | C10—C11—C12 | 120.34 (15) |
| O1—C1B—H1B2 | 109.5 | C10—C11—H11 | 119.8 |
| H1B1—C1B—H1B2 | 109.5 | C12—C11—H11 | 119.8 |
| O1—C1B—H1B3 | 109.5 | C13—C12—C11 | 117.69 (14) |
| H1B1—C1B—H1B3 | 109.5 | C13—C12—H12 | 121.2 |
| H1B2—C1B—H1B3 | 109.5 | C11—C12—H12 | 121.2 |
| O1—C2—C3 | 124.59 (13) | C12—C13—C14 | 123.38 (14) |
| O1—C2—C7 | 115.97 (12) | C12—C13—N2 | 118.51 (13) |
| C3—C2—C7 | 119.43 (13) | C14—C13—N2 | 118.06 (12) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.91 (13) | C13—C14—C9 | 118.51 (12) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.0 | C13—C14—H14 | 120.7 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.0 | C9—C14—H14 | 120.7 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.94 (12) | O5—C15—N1 | 120.63 (13) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.5 | O5—C15—N1 | 120.63 (13) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.5 | O5—C15—C16 | 121.81 (13) |
| O2—C5—C4 | 123.24 (11) | O5—C15—C16 | 121.81 (13) |
| O2—C5—C6 | 117.27 (11) | N1—C15—C16 | 117.56 (13) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.46 (12) | C15—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 119.13 (11) | C15—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C8 | 119.67 (9) | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C8 | 121.19 (10) | C15—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C2 | 121.12 (11) | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.4 | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C2—C7—H7 | 119.4 | C15—N1—C8 | 120.75 (11) |
| N1—C8—C9 | 113.16 (10) | C15—N1—H1 | 119.6 |
| N1—C8—C6 | 111.96 (9) | C8—N1—H1 | 119.6 |
| C9—C8—C6 | 112.27 (9) | O4—N2—O3 | 122.58 (15) |
| N1—C8—H8 | 106.3 | O4—N2—C13 | 119.06 (12) |
| C9—C8—H8 | 106.3 | O3—N2—C13 | 118.36 (14) |
| C6—C8—H8 | 106.3 | C2—O1—C1B | 118.2 (3) |
| C14—C9—C10 | 118.84 (11) | C2—O1—C1A | 111.8 (10) |
| C14—C9—C8 | 123.88 (10) | C5—O2—H2 | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 117.24 (11) | ||
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | 179.06 (19) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 1.5 (4) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | −0.4 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −0.4 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.2 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −1.3 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—O2 | 178.11 (15) | C11—C12—C13—N2 | 176.0 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.1 (2) | C12—C13—C14—C9 | 1.9 (3) |
| O2—C5—C6—C7 | −178.18 (11) | N2—C13—C14—C9 | −175.45 (14) |
| O2—C5—C6—C8 | 0.70 (17) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | −0.8 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C8 | 178.87 (12) | C8—C9—C14—C13 | 176.87 (13) |
| C5—C6—C7—C2 | −0.3 (2) | O5—C15—N1—C8 | −2.4 (2) |
| C8—C6—C7—C2 | −179.14 (13) | O5—C15—N1—C8 | −2.4 (2) |
| O1—C2—C7—C6 | −179.05 (15) | C16—C15—N1—C8 | 178.72 (17) |
| C3—C2—C7—C6 | 0.5 (2) | C9—C8—N1—C15 | 138.63 (13) |
| C7—C6—C8—N1 | 116.41 (12) | C6—C8—N1—C15 | −93.27 (14) |
| C5—C6—C8—N1 | −62.46 (13) | C12—C13—N2—O4 | 173.9 (2) |
| C7—C6—C8—C9 | −115.02 (12) | C14—C13—N2—O4 | −8.6 (3) |
| C5—C6—C8—C9 | 66.11 (14) | C12—C13—N2—O3 | −6.4 (3) |
| N1—C8—C9—C14 | 32.10 (15) | C14—C13—N2—O3 | 171.07 (19) |
| C6—C8—C9—C14 | −95.83 (14) | C3—C2—O1—C1B | 4.8 (10) |
| N1—C8—C9—C10 | −150.24 (13) | C7—C2—O1—C1B | −175.7 (9) |
| C6—C8—C9—C10 | 81.83 (14) | C3—C2—O1—C1A | 32.3 (18) |
| C14—C9—C10—C11 | −0.8 (3) | C7—C2—O1—C1A | −148.2 (18) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −178.63 (19) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2···O5i | 0.82 | 1.80 | 2.617 (2) | 179 |
| N1—H1···O4ii | 0.86 | 2.30 | 3.159 (2) | 174 |
| C10—H10···O1iii | 0.93 | 2.47 | 3.320 (2) | 152 |
| C12—H12···O2iv | 0.93 | 2.58 | 3.397 (2) | 147 |
| C14—H14···O4ii | 0.93 | 2.55 | 3.470 (2) | 169 |
| C8—H8···O5 | 0.98 | 2.30 | 2.714 (2) | 105 |
| C11—H11···Cg1iv | 0.93 | 2.83 | 3.680 (2) | 153 |
| C1B—H1B1···Cg2v | 0.96 | 2.61 | 3.531 (2) | 160 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+3/2, z−1/2; (ii) −x, −y+1, −z; (iii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (iv) x, y−1, z; (v) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BT2901).
References
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555-1573.
- Bruker (2004). APEX2, SAINT and XPREP Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Ghosh, R., Maity, S. & Chakraborty, A. (2005). Synlett, pp. 115-118.
- Gowda, B. T., Foro, S. & Fuess, H. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o3364.
- NizamMohideen, M., SubbiahPandi, A., Panneer Selvam, N. & Perumal, P. T. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o714–o715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809009726/bt2901sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809009726/bt2901Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report