Abstract
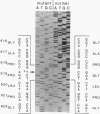
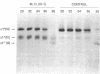
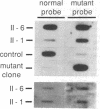
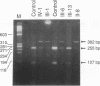
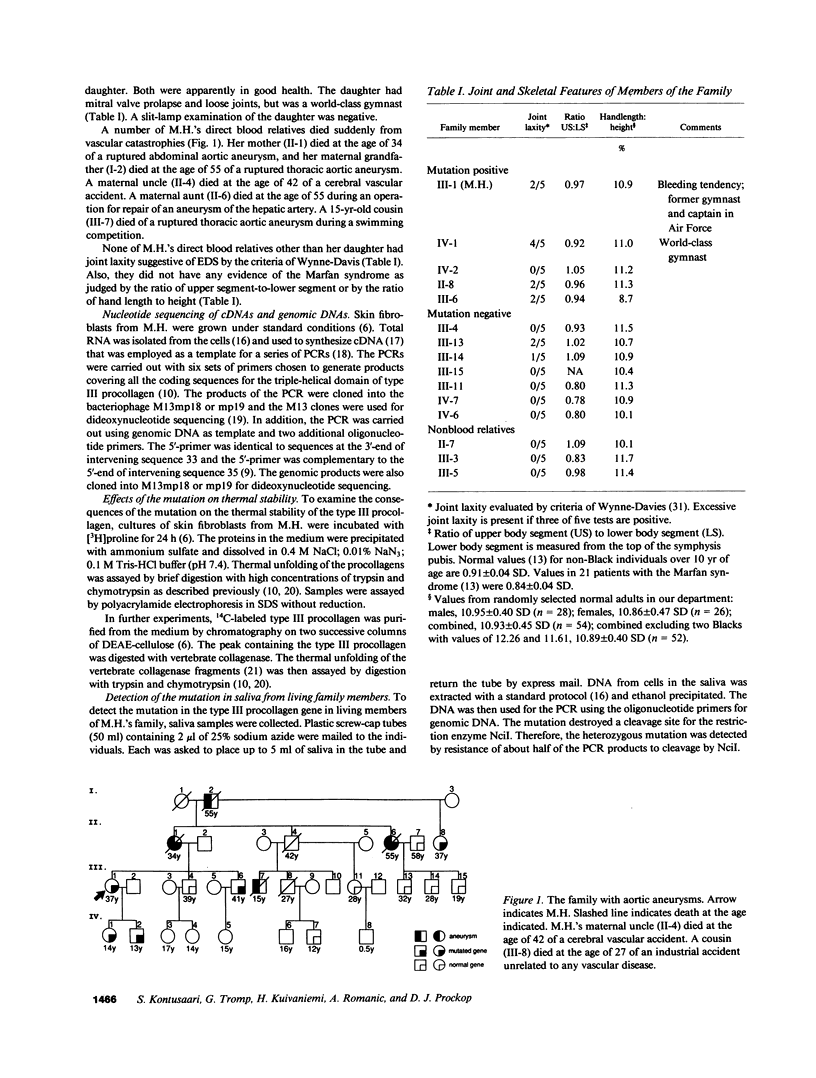
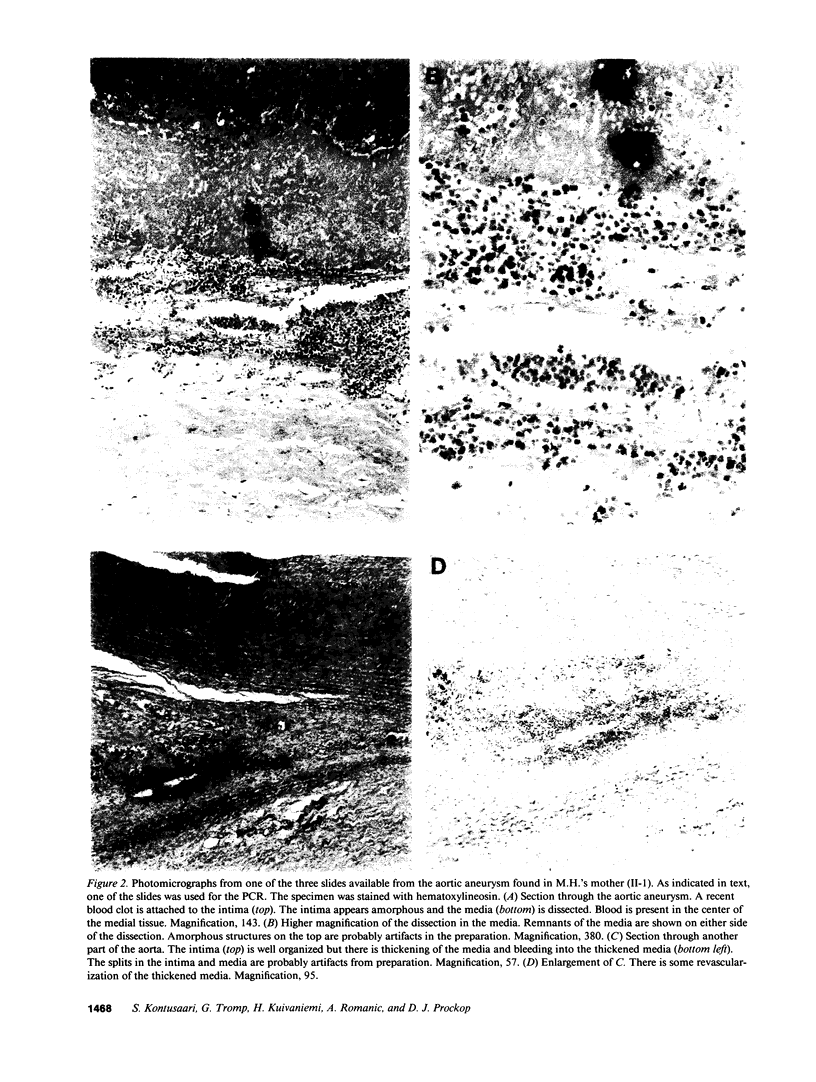
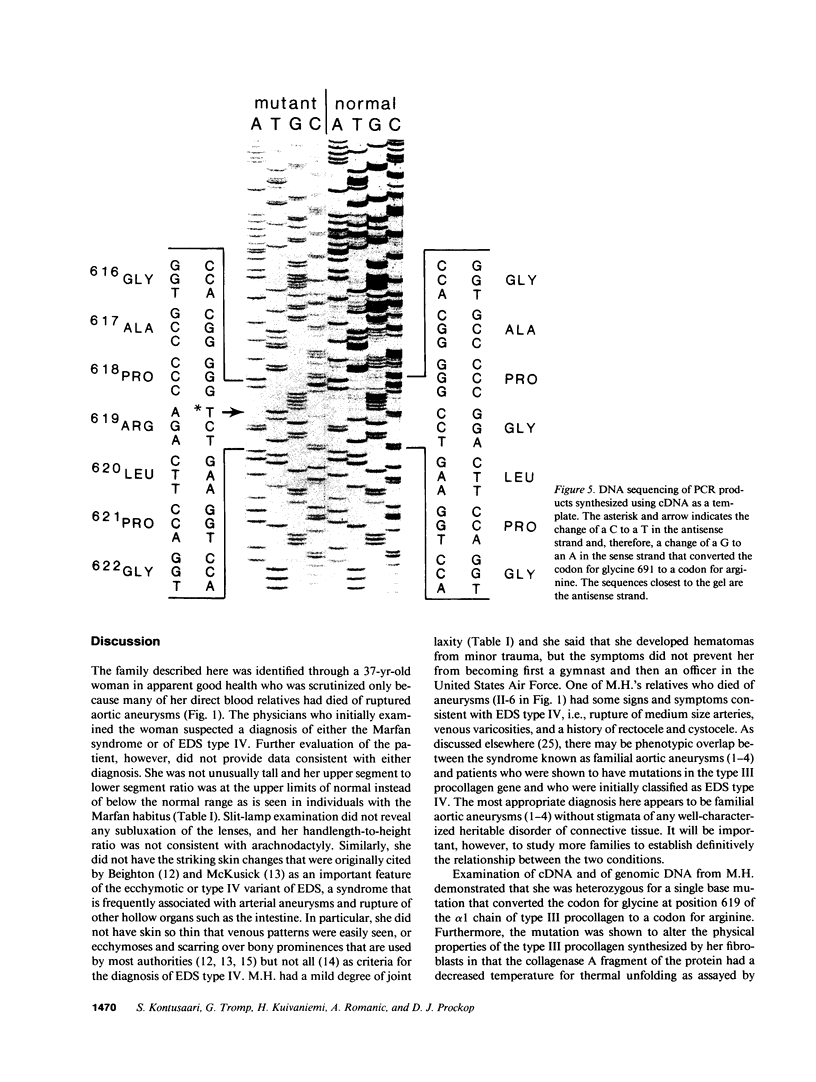
Experiments were carried out to test the hypothesis that familial aortic aneurysms, either thoracic or abdominal, are caused by mutations in the gene for type III procollagen (COL3A1) similar to mutations in the same gene that have been shown to cause rupture of aorta and other disastrous consequences in the rare genetic disorder known as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV. A family was identified through a 37-yr-old female captain in the United States Air Force who was scrutinized only because many of her direct blood relatives had died of ruptured aortic aneurysms. The woman was heterozygous for a single-base mutation that converted the codon for glycine 619 of the alpha 1(III) chain of type III procollagen to a codon for arginine. Studies on cultured skin fibroblasts demonstrated the mutation caused synthesis of type III procollagen that had a decreased temperature for thermal unfolding of the protein. The same mutation was identified in DNA extracted from pathologic specimens from her mother who had died at the age of 34 and a maternal aunt who died at the age of 55 of aortic aneurysms. Examination of DNA from samples of saliva revealed that the woman's daughter, her son, a brother, and an aunt also had the mutation. The results demonstrated that mutations in the type III procollagen gene can cause familial aortic aneurysms and that DNA tests for such mutations can identify individuals at risk for aneurysms.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ala-Kokko L., Kontusaari S., Baldwin C. T., Kuivaniemi H., Prockop D. J. Structure of cDNA clones coding for the entire prepro alpha 1 (III) chain of human type III procollagen. Differences in protein structure from type I procollagen and conservation of codon preferences. Biochem J. 1989 Jun 1;260(2):509–516. doi: 10.1042/bj2600509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson H., Norrgård O., Angquist K. A., Ekberg O., Oberg L., Bergqvist D. Ultrasonographic screening of the abdominal aorta among siblings of patients with abdominal aortic aneurysms. Br J Surg. 1989 Jun;76(6):589–591. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800760620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergqvist D., Bengtsson H. Okat antal patienter dör av bukaortaaneurysm. Okad diagnostisk skärpa krävs. Lakartidningen. 1986 Sep 10;83(37):3010–3012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruckner P., Eikenberry E. F., Prockop D. J. Formation of the triple helix of type I procollagen in cellulo. A kinetic model based on cis-trans isomerization of peptide bonds. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Sep 1;118(3):607–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05562.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. H., Holbrook K. A., Barsh G. S., Smith L. T., Bornstein P. Altered secretion of type III procollagen in a form of type IV Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Biochemical studies in cultured fibroblasts. Lab Invest. 1981 Apr;44(4):336–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collin J. Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysms. Br J Surg. 1985 Nov;72(11):851–852. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800721102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantinou C. D., Vogel B. E., Jeffrey J. J., Prockop D. J. The A and B fragments of normal type I procollagen have a similar thermal stability to proteinase digestion but are selectively destabilized by structural mutations. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Mar 2;163(2):247–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10794.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford E. S., Saleh S. A., Babb J. W., 3rd, Glaeser D. H., Vaccaro P. S., Silvers A. Infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm: factors influencing survival after operation performed over a 25-year period. Ann Surg. 1981 Jun;193(6):699–709. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198106000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling R. C., 3rd, Brewster D. C., Darling R. C., LaMuraglia G. M., Moncure A. C., Cambria R. P., Abbott W. M. Are familial abdominal aortic aneurysms different? J Vasc Surg. 1989 Jul;10(1):39–43. doi: 10.1067/mva.1989.vs0100039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Impraim C. C., Saiki R. K., Erlich H. A., Teplitz R. L. Analysis of DNA extracted from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues by enzymatic amplification and hybridization with sequence-specific oligonucleotides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Feb 13;142(3):710–716. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontusaari S., Tromp G., Kuivaniemi H., Ladda R. L., Prockop D. J. Inheritance of an RNA splicing mutation (G+ 1 IVS20) in the type III procollagen gene (COL3A1) in a family having aortic aneurysms and easy bruisability: phenotypic overlap between familial arterial aneurysms and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Jul;47(1):112–120. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuivaniemi H., Kontusaari S., Tromp G., Zhao M. J., Sabol C., Prockop D. J. Identical G+1 to A mutations in three different introns of the type III procollagen gene (COL3A1) produce different patterns of RNA splicing in three variants of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. IV. An explanation for exon skipping some mutations and not others. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):12067–12074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prockop D. J., Constantinou C. D., Dombrowski K. E., Hojima Y., Kadler K. E., Kuivaniemi H., Tromp G., Vogel B. E. Type I procollagen: the gene-protein system that harbors most of the mutations causing osteogenesis imperfecta and probably more common heritable disorders of connective tissue. Am J Med Genet. 1989 Sep;34(1):60–67. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320340112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolle C. A., Pyeritz R. E., Myers J. C., Prockop D. J. Synthesis of an altered type III procollagen in a patient with type IV Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. A structural change in the alpha 1(III) chain which makes the protein more susceptible to proteinases. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1937–1944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studencki A. B., Wallace R. B. Allele-specific hybridization using oligonucleotide probes of very high specific activity: discrimination of the human beta A- and beta S-globin genes. DNA. 1984;3(1):7–15. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Superti-Furga A., Steinmann B., Ramirez F., Byers P. H. Molecular defects of type III procollagen in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV. Hum Genet. 1989 May;82(2):104–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00284038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tromp G., Kuivaniemi H., Shikata H., Prockop D. J. A single base mutation that substitutes serine for glycine 790 of the alpha 1 (III) chain of type III procollagen exposes an arginine and causes Ehlers-Danlos syndrome IV. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1349–1352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tromp G., Kuivaniemi H., Stolle C., Pope F. M., Prockop D. J. Single base mutation in the type III procollagen gene that converts the codon for glycine 883 to aspartate in a mild variant of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome IV. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19313–19317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel B. E., Doelz R., Kadler K. E., Hojima Y., Engel J., Prockop D. J. A substitution of cysteine for glycine 748 of the alpha 1 chain produces a kink at this site in the procollagen I molecule and an altered N-proteinase cleavage site over 225 nm away. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19249–19255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wynne-Davies R. Acetabular dysplasia and familial joint laxity: two etiological factors in congenital dislocation of the hip. A review of 589 patients and their families. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1970 Nov;52(4):704–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]