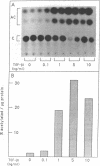
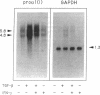
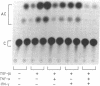
Abstract
Regulation of human type I procollagen gene expression was studied in cultured fibroblasts both at the transcriptional and posttranscriptional level. Transcriptional regulation was examined in cultures transfected with a human pro alpha 2(I) collagen promoter/reporter gene (chloramphenicol acetyltransferase) construct, while posttranscriptional regulation was assessed by parallel determinations of type I procollagen mRNA steady-state levels. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) elicited a marked, approximately 5-23-fold, enhancement of pro alpha 2(I) collagen promoter activity, which was accompanied by an elevation of type I procollagen mRNA levels. This enhancement of gene expression was suppressed by tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), as determined at mRNA steady-state level, but two distinct mechanisms were involved. TNF-alpha suppressed the pro alpha 2(I) collagen promoter activity, whereas IFN-gamma had only a minimal effect at transcriptional level. The effects of TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma were synergistic, suggesting that combination of these two factors may potentially provide pharmacologic means to counteract tissue deposition of collagen in diseases involving TGF-beta.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abergel R. P., Chu M. L., Bauer E. A., Uitto J. Regulation of collagen gene expression in cutaneous diseases with dermal fibrosis: evidence for pretranslational control. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Jun;88(6):727–731. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12470397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abergel R. P., Pizzurro D., Meeker C. A., Lask G., Matsuoka L. Y., Minor R. R., Chu M. L., Uitto J. Biochemical composition of the connective tissue in keloids and analysis of collagen metabolism in keloid fibroblast cultures. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 May;84(5):384–390. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12265471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman B., Duncan M. R. Short-term keloid treatment in vivo with human interferon alfa-2b results in a selective and persistent normalization of keloidal fibroblast collagen, glycosaminoglycan, and collagenase production in vitro. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989 Oct;21(4 Pt 1):694–702. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70239-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boast S., Su M. W., Ramirez F., Sanchez M., Avvedimento E. V. Functional analysis of cis-acting DNA sequences controlling transcription of the human type I collagen genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13351–13356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., Myers J. C., Bernard M. P., Ding J. F., Ramirez F. Cloning and characterization of five overlapping cDNAs specific for the human pro alpha 1(I) collagen chain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 11;10(19):5925–5934. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.19.5925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazio M. J., Kähäri V. M., Bashir M. M., Saitta B., Rosenbloom J., Uitto J. Regulation of elastin gene expression: evidence for functional promoter activity in the 5'-flanking region of the human gene. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Feb;94(2):191–196. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12874495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldring M. B., Krane S. M. Modulation by recombinant interleukin 1 of synthesis of types I and III collagens and associated procollagen mRNA levels in cultured human cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16724–16729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granstein R. D., Murphy G. F., Margolis R. J., Byrne M. H., Amento E. P. Gamma-interferon inhibits collagen synthesis in vivo in the mouse. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1254–1258. doi: 10.1172/JCI112945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignotz R. A., Endo T., Massagué J. Regulation of fibronectin and type I collagen mRNA levels by transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6443–6446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kähäri V. M., Heino J., Niskanen L., Fräki J., Uitto J. Eosinophilic fasciitis. Increased collagen production and type I procollagen messenger RNA levels in fibroblasts cultured from involved skin. Arch Dermatol. 1990 May;126(5):613–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kähäri V. M., Heino J., Vuorio E. Interleukin-1 increases collagen production and mRNA levels in cultured skin fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 6;929(2):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90169-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kähäri V. M., Multimäki P., Vuorio E. Elevated pro alpha 2(I) collagen mRNA levels in cultured scleroderma fibroblasts result from an increased transcription rate of the corresponding gene. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 11;215(2):331–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80172-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kähäri V. M., Sandberg M., Kalimo H., Vuorio T., Vuorio E. Identification of fibroblasts responsible for increased collagen production in localized scleroderma by in situ hybridization. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 May;90(5):664–670. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12560826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kähäri V. M., Vuorio T., Näntö-Salonen K., Vuorio E. Increased type I collagen mRNA levels in cultured scleroderma fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Feb 24;781(1-2):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Proper J. A., Goustin A. S., Shipley G. D., DiCorleto P. E., Moses H. L. Induction of c-sis mRNA and activity similar to platelet-derived growth factor by transforming growth factor beta: a proposed model for indirect mitogenesis involving autocrine activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2453–2457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy E. C., Smith E. A., Kahaleh M. B., Trojanowska M., Silver R. M. A strategy for determining the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Is transforming growth factor beta the answer? Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Jul;32(7):817–825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauviel A., Daireaux M., Rédini F., Galera P., Loyau G., Pujol J. P. Tumor necrosis factor inhibits collagen and fibronectin synthesis in human dermal fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 15;236(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80283-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J. C., Chu M. L., Faro S. H., Clark W. J., Prockop D. J., Ramirez F. Cloning a cDNA for the pro-alpha 2 chain of human type I collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3516–3520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltonen J., Kähäri L., Jaakkola S., Kähäri V. M., Varga J., Uitto J., Jimenez S. A. Evaluation of transforming growth factor beta and type I procollagen gene expression in fibrotic skin diseases by in situ hybridization. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Mar;94(3):365–371. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12874491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penttinen R. P., Kobayashi S., Bornstein P. Transforming growth factor beta increases mRNA for matrix proteins both in the presence and in the absence of changes in mRNA stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1105–1108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwaite A. E., Raghow R., Stricklin G. P., Poppleton H., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. Modulation of fibroblast functions by interleukin 1: increased steady-state accumulation of type I procollagen messenger RNAs and stimulation of other functions but not chemotaxis by human recombinant interleukin 1 alpha and beta. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):311–318. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghow R., Postlethwaite A. E., Keski-Oja J., Moses H. L., Kang A. H. Transforming growth factor-beta increases steady state levels of type I procollagen and fibronectin messenger RNAs posttranscriptionally in cultured human dermal fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1285–1288. doi: 10.1172/JCI112950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Assoian R. K., Smith J. M., Roche N. S., Wakefield L. M., Heine U. I., Liotta L. A., Falanga V., Kehrl J. H. Transforming growth factor type beta: rapid induction of fibrosis and angiogenesis in vivo and stimulation of collagen formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4167–4171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbloom J., Feldman G., Freundlich B., Jimenez S. A. Transcriptional control of human diploid fibroblast collagen synthesis by gamma-interferon. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 30;123(1):365–372. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90422-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi P., Karsenty G., Roberts A. B., Roche N. S., Sporn M. B., de Crombrugghe B. A nuclear factor 1 binding site mediates the transcriptional activation of a type I collagen promoter by transforming growth factor-beta. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):405–414. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe M., Falanga V. Growth factors. Their biology and promise in dermatologic diseases and tissue repair. Arch Dermatol. 1989 Oct;125(10):1390–1398. doi: 10.1001/archderm.125.10.1390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharffetter K., Lankat-Buttgereit B., Krieg T. Localization of collagen mRNA in normal and scleroderma skin by in-situ hybridization. Eur J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;18(1):9–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1988.tb01158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solis-Herruzo J. A., Brenner D. A., Chojkier M. Tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibits collagen gene transcription and collagen synthesis in cultured human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5841–5845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Peptide growth factors are multifunctional. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):217–219. doi: 10.1038/332217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson M. L., Krane S. M., Amento E. P., McCroskery P. A., Byrne M. Immune interferon inhibits collagen synthesis by rheumatoid synovial cells associated with decreased levels of the procollagen mRNAs. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 21;180(1):43–50. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80227-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto M., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor receptors in HeLa cells and their regulation by interferon-gamma. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5384–5388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitto J., Bauer E. A., Eisen A. Z. Scleroderma: increased biosynthesis of triple-helical type I and type III procollagens associated with unaltered expression of collagenase by skin fibroblasts in culture. J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;64(4):921–930. doi: 10.1172/JCI109558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varga J., Rosenbloom J., Jimenez S. A. Transforming growth factor beta (TGF beta) causes a persistent increase in steady-state amounts of type I and type III collagen and fibronectin mRNAs in normal human dermal fibroblasts. Biochem J. 1987 Nov 1;247(3):597–604. doi: 10.1042/bj2470597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]