Abstract
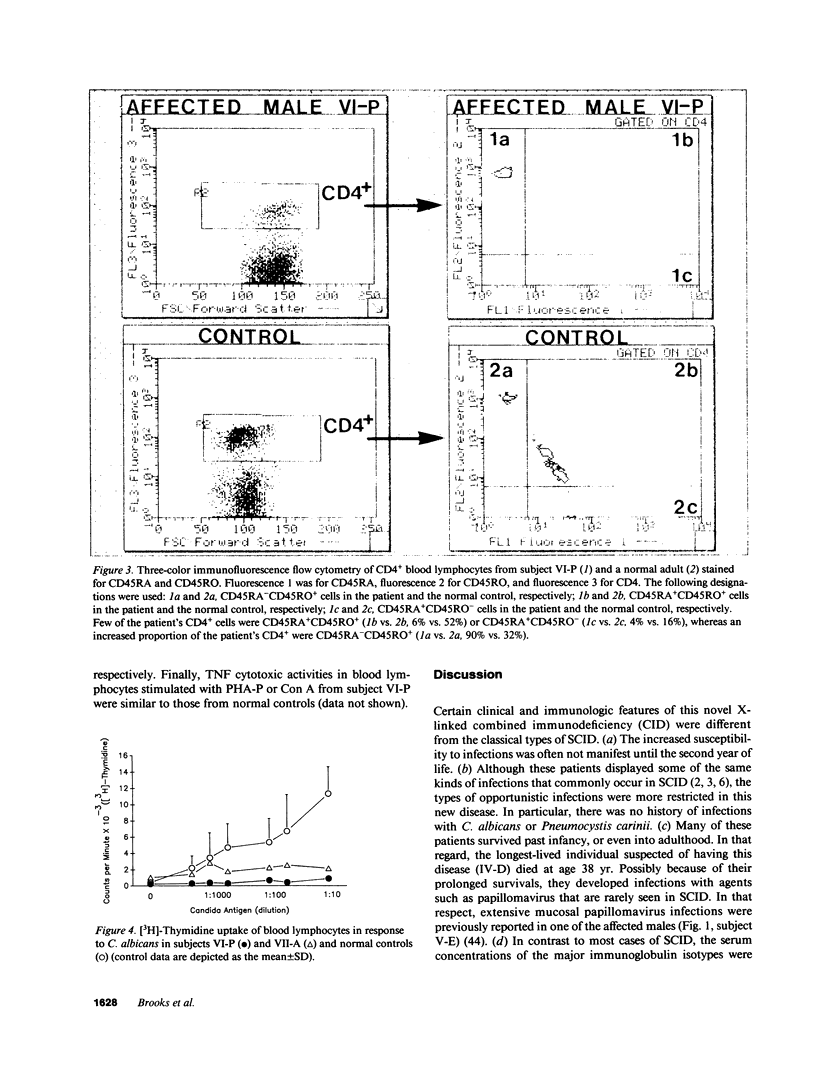
A novel X-linked combined immunodeficiency disease was found in five living males in an extended family in the United States. The age of the affected males ranged from 2.5 to 34 yr. The most prominent clinical abnormalities were a paucity of lymphoid tissue; recurrent sinusitis, otitis media, bronchitis, and pneumonia; severe varicella; and chronic papillomavirus infections. The principal immunologic features of the disorder were normal concentrations of serum immunoglobulins but restricted formation of IgG antibodies to immunogens; normal numbers of B cells and NK cells but decreased numbers of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes, particularly the CD45RA+ subpopulations; diminished proliferative responses of blood T cells to allogeneic cells, mitogens and antigens; and decreased production of IL-2 by mitogen stimulated blood lymphocytes. Thus, affected males in this family carry an abnormal gene on their X chromosome that results in a combined immunodeficiency that is distinct from previously reported disorders.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akbar A. N., Terry L., Timms A., Beverley P. C., Janossy G. Loss of CD45R and gain of UCHL1 reactivity is a feature of primed T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2171–2178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUTON O. C. Agammaglobulinemia. Pediatrics. 1952 Jun;9(6):722–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehner R. L., Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Haines J. L., Conneally P. M., Palmer C., Heerema N., Orkin S. H. DNA linkage analysis of X chromosome-linked chronic granulomatous disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3398–3401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley R. H., Schiff S. E., Sampson H. A., Schiff R. I., Markert M. L., Knutsen A. P., Hershfield M. S., Huang A. T., Mickey G. H., Ward F. E. Development of immunity in human severe primary T cell deficiency following haploidentical bone marrow stem cell transplantation. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;136(7):2398–2407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne J. A., Butler J. L., Cooper M. D. Differential activation requirements for virgin and memory T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3249–3257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. B., Grunberger T., Kochman M. A., White S. L. A microplaque reduction assay for human and mouse interferon. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Aug;21(8):1247–1253. doi: 10.1139/m75-186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clement L. T., Yamashita N., Martin A. M. The functionally distinct subpopulations of human CD4+ helper/inducer T lymphocytes defined by anti-CD45R antibodies derive sequentially from a differentiation pathway that is regulated by activation-dependent post-thymic differentiation. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1464–1470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Brown P., Pickard A. R., Buckley R. H., Miller D. S., Raskind W. H., Singer J. W., Fialkow P. J. Expression of the gene defect in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 28;315(9):564–567. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608283150907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper M. D., Chae H. P., Lowman J. T., Krivit W., Good R. A. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. An immunologic deficiency disease involving the afferent limb of immunity. Am J Med. 1968 Apr;44(4):499–513. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deans J. P., Boyd A. W., Pilarski L. M. Transitions from high to low molecular weight isoforms of CD45 (T200) involve rapid activation of alternate mRNA splicing and slow turnover of surface CD45R. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1233–1238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinauer M. C., Orkin S. H., Brown R., Jesaitis A. J., Parkos C. A. The glycoprotein encoded by the X-linked chronic granulomatous disease locus is a component of the neutrophil cytochrome b complex. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):717–720. doi: 10.1038/327717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinauer M. C., Orkin S. H. Chronic granulomatous disease. Molecular genetics. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1988 Jun;2(2):225–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Hedlund G., Sjögren H. O., Carlsson R. Two subsets of human CD4+ T helper cells differing in kinetics and capacities to produce interleukin 2 and interferon-gamma can be defined by the Leu-18 and UCHL1 monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Aug;18(8):1173–1178. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekowitz R. A., Orkin S. H., Newburger P. E. Recombinant interferon gamma augments phagocyte superoxide production and X-chronic granulomatous disease gene expression in X-linked variant chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1009–1016. doi: 10.1172/JCI113153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman S. B., Sexton F. M., Glenn J. D., Lookingbill D. P. Immunosuppression in men with bowenoid papulosis. Arch Dermatol. 1989 May;125(5):651–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flick D. A., Gifford G. E. Comparison of in vitro cell cytotoxic assays for tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Mar 30;68(1-2):167–175. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90147-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Buescher E. S., Seligmann B. E., Nath J., Gaither T., Katz P. NIH conference. Recent advances in chronic granulomatous disease. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Nov;99(5):657–674. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-5-657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand E. W., Dosch H. M. Diagnosis and classification of severe combined immunodeficiency disease. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1983;19(3):65–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman A. S., Garza C., Nichols B. L., Goldblum R. M. Immunologic factors in human milk during the first year of lactation. J Pediatr. 1982 Apr;100(4):563–567. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80753-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grierson H., Purtilo D. T. Epstein-Barr virus infections in males with the X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Apr;106(4):538–545. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-106-4-538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. G., Wilson R. W., Spillman T., Roebber M. Monoclonal antibody-based immunoenzymetric assays for quantification of human IgG and its four subclasses. J Immunoassay. 1988;9(3-4):275–296. doi: 10.1080/01971528808053217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschhorn R. Genetic deficiencies of adenosine deaminase and purine nucleoside phosphorylase: overview, genetic heterogeneity and therapy. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1983;19(3):73–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilowite N. T., Fligner C. L., Ochs H. D., Brichacek B., Harada S., Haas J. E., Purtilo D. T., Wedgwood R. J. Pulmonary angiitis with atypical lymphoreticular infiltrates in Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome: possible relationship of lymphomatoid granulomatosis and EBV infection. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Dec;41(3):479–484. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90018-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenney D., Cairns L., Remold-O'Donnell E., Peterson J., Rosen F. S., Parkman R. Morphological abnormalities in the lymphocytes of patients with the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Blood. 1986 Dec;68(6):1329–1332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killingsworth L. M., Savory J. Automated immunochemical procedures for measurement of immunoglobulins IgG, IgA, and IgM in human serum. Clin Chem. 1971 Sep;17(9):936–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan S. P., Kunkel L., Bruns G., Wedgwood R. J., Latt S., Rosen F. S. Mapping of the X-linked agammaglobulinemia locus by use of restriction fragment-length polymorphism. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):649–652. doi: 10.1172/JCI112351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Le A. M., Phillips J. H., Warner N. L., Babcock G. F. Subpopulations of human natural killer cells defined by expression of the Leu-7 (HNK-1) and Leu-11 (NK-15) antigens. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1789–1796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederman H. M., Winkelstein J. A. X-linked agammaglobulinemia: an analysis of 96 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 1985 May;64(3):145–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu L., Srour E. F., Warren D. J., Walker D., Graham C. D., Walker E. B., Jansen J., Broxmeyer H. E. Enhancement of release of granulocyte- and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factors from phytohemagglutinin-stimulated sorted subsets of human T lymphocytes by recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Synergism with recombinant human IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):201–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathé G. Virus EBV, immunodeficience, aplasie médullaire, mononucléose maligne et syndrome lymphoprolifératif B lié au sexe (XLP). Biomed Pharmacother. 1983;37(6):249–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mensink E. J., Schuurman R. K. Immunodeficiency disease genes on the X chromosome. Dis Markers. 1987 Sep;5(3):129–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mensink E. J., Thompson A., Sandkuyl L. A., Kraakman M. E., Schot J. D., Espanol T., Schuurman R. K. X-linked immunodeficiency with hyperimmunoglobulinemia M appears to be linked to the DXS42 restriction fragment length polymorphism locus. Hum Genet. 1987 May;76(1):96–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00283057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mensink E. J., Thompson A., Schot J. D., van de Greef W. M., Sandkuyl L. A., Schuurman R. K. Mapping of a gene for X-linked agammaglobulinemia and evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Hum Genet. 1986 Aug;73(4):327–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00279095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentzer S. J., Remold-O'Donnell E., Crimmins M. A., Bierer B. E., Rosen F. S., Burakoff S. J. Sialophorin, a surface sialoglycoprotein defective in the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, is involved in human T lymphocyte proliferation. J Exp Med. 1987 May 1;165(5):1383–1392. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.5.1383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkenschlager M., Terry L., Edwards R., Beverley P. C. Limiting dilution analysis of proliferative responses in human lymphocyte populations defined by the monoclonal antibody UCHL1: implications for differential CD45 expression in T cell memory formation. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Nov;18(11):1653–1661. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830181102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacocke M., Siminovitch K. A. Linkage of the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome with polymorphic DNA sequences from the human X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3430–3433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primary immunodeficiency diseases. Report of a World Health Organization scientific group. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Jul;40(1):166–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pross H. F., Baines M. G., Rubin P., Shragge P., Patterson M. S. Spontaneous human lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity against tumor target cells. IX. The quantitation of natural killer cell activity. J Clin Immunol. 1981 Jan;1(1):51–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00915477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck J. M., Nussbaum R. L., Smead D. L., Conley M. E. X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency: localization within the region Xq13.1-q21.1 by linkage and deletion analysis. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 May;44(5):724–730. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtilo D. T., Tatsumi E., Manolov G., Manolova Y., Harada S., Lipscomb H., Krueger G. Epstein-Barr virus as an etiological agent in the pathogenesis of lymphoproliferative and aproliferative diseases in immune deficient patients. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1985;27:113–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen F. S., Cooper M. D., Wedgwood R. J. The primary immunodeficiencies. (2). N Engl J Med. 1984 Aug 2;311(5):300–310. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198408023110506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd C. E., Anderson P., Morimoto C., Streuli M., Schlossman S. F. Molecular interactions, T-cell subsets and a role of the CD4/CD8:p56lck complex in human T-cell activation. Immunol Rev. 1989 Oct;111:225–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00548.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon M., Kitas G. D., Bacon P. A. Production of lymphokine mRNA by CD45R+ and CD45R- helper T cells from human peripheral blood and by human CD4+ T cell clones. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 1;143(3):907–912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon M., Kitas G. D., Gaston J. S., Bacon P. A. Interleukin-2 production and response by helper T-cell subsets in man. Immunology. 1988 Sep;65(1):81–85. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Makgoba M. W., Sharrow S. O., Stephany D., Springer T. A., Young H. A., Shaw S. Human memory T lymphocytes express increased levels of three cell adhesion molecules (LFA-3, CD2, and LFA-1) and three other molecules (UCHL1, CDw29, and Pgp-1) and have enhanced IFN-gamma production. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1401–1407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmalstieg F. C., Nelson J. A., Mills G. C., Monahan T. M., Goldman A. S., Goldblum R. M. Increased purine nucleotides in adenosine deaminase-deficient lymphocytes. J Pediatr. 1977 Jul;91(1):48–51. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)80442-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skare J. C., Grierson H. L., Sullivan J. L., Nussbaum R. L., Purtilo D. T., Sylla B. S., Lenoir G. M., Reilly D. S., White B. N., Milunsky A. Linkage analysis of seven kindreds with the X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome (XLP) confirms that the XLP locus is near DXS42 and DXS37. Hum Genet. 1989 Jul;82(4):354–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00273997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita N., Clement L. T. Phenotypic characterization of the post-thymic differentiation of human alloantigen-specific CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 1;143(5):1518–1523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabay J. M., Fontán G., Campos A., García-Rodriguez M. C., Pascual-Salcedo D., Bootello A., de la Concha E. G. Disorders of regulatory T cell function in patients with the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Apr;56(1):23–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Saint Basile G., Arveiler B., Oberlé I., Malcolm S., Levinsky R. J., Lau Y. L., Hofker M., Debre M., Fischer A., Griscelli C. Close linkage of the locus for X chromosome-linked severe combined immunodeficiency to polymorphic DNA markers in Xq11-q13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7576–7579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]