Abstract
In the title compound, C17H18ClN3O3, the dihedral angle between the planes of the two benzene rings is 1.03 (7)°. The overall conformation of the molecule is influenced, in part, by electron delocalization and by an intramolecular bifurcated O—H⋯(O,N) hydrogen bonds. The O atoms of the nitro group, one of which serves as an H bond acceptor, are disordered over two sets of sites with refined occupancies of 0.56 (3) and 0.44 (3).
Related literature
For benzotriazoles as UV absorbers and their applications in industry, see: Ravichandran et al. (2002 ▶). N-oxides are a key type intermediates in the synthesis of benzotriazoles, see: Wen et al. (2006 ▶); Crawford (1999 ▶). For the use of green synthetic methods to obtain intermediates, see: Tanaka & Toda (2000 ▶).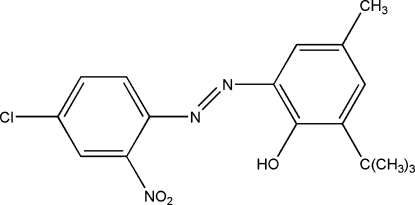
Experimental
Crystal data
C17H18ClN3O3
M r = 347.79
Monoclinic,

a = 14.578 (4) Å
b = 7.0616 (19) Å
c = 17.043 (5) Å
β = 101.233 (3)°
V = 1720.9 (8) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.24 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.31 × 0.18 × 0.16 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.930, T max = 0.963
14642 measured reflections
3927 independent reflections
2563 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.033
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.044
wR(F 2) = 0.141
S = 1.03
3927 reflections
241 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.26 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2006 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2006 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809019631/lh2824sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809019631/lh2824Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3—H3⋯O1′ | 0.82 | 2.28 | 2.933 (7) | 136 |
| O3—H3⋯O1 | 0.82 | 2.50 | 3.142 (12) | 136 |
| O3—H3⋯N2 | 0.82 | 1.84 | 2.553 (2) | 145 |
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (20662007) and the Key Laboratory Open Foundation of Food Science of the Ministry of Education, Nanchang University (NCU200407).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Benzotriazoles play an important role as a class of UV absorbers and have promising industrial applications (Ravichandran et al., 2002). N-oxides are a key type intermediates in the synthesis of benzotriazoles (Wen et al., 2006; Crawford, 1999) and the title compound is an important intermediate in the synthesis of 2-(2'-Hydroxy-3'-tert-butyl-5'-methylphenyl)-5-chloro benzotriazole (UV 326), a good ultraviolet absorber. Due to the growing awareness of environmental protection, the demand for clean and 'green' (i.e solvent free) chemical syntheses has been growing, so using these synthetic methods to form intermediates have received attention (Tanaka & Toda, 2000). Herein we report a 'green' synthetic method and the crystal structure of the title compound. In the title moleclue (Fig .1) the dihedral angle between the two benzene rings is 1.03 (7)°. The overall conformation of the molecule is influenced, in part, by electron delocalization and by intramolecular O—H···O and O—H···N hydrogen bonds.
Experimental
The title compound was synthesized via the solid phase reaction of 4-chloro-2-nitroaniline and 2-tert-butyl-4-substituted phenol at room temperature. After intensive grinding a mixture of 4-chloro-2-nitrobenzenamine 1.72 g (10 mmol), 2-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol 1.72 g (10.5 mmol), NaNO2 0.69 g (10 mmol), and KHSO4 1.36 g (10 mmol) in a mortar for 15 min at 293 K, the product was washed with hot water. A few purple crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis were obtained upon recrystallization in ethanol after several days (m. p. 445–446 K), which gave the product in 93% yield and higher than 99% purity (by HPLC).
Refinement
All H atoms were included in calculated positions with O—H = 0.82Å; C—H(methyl) = 0.96 Å, C—H(aromatic) = 0.93 Å, and Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(Cmethyl,O) and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for aromatic H atoms. The O atoms of the nitro group are disordered over two sites with refined occupancies of 0.56 (3) and 0.44 (3).
Figures
Fig. 1.
: The molecular structure of the title compound, showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids. The minor comonent of disorder is shown with open bonds and hydrogen bonds are shown with dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C17H18ClN3O3 | F(000) = 728 |
| Mr = 347.79 | Dx = 1.342 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 4044 reflections |
| a = 14.578 (4) Å | θ = 2.6–27.2° |
| b = 7.0616 (19) Å | µ = 0.24 mm−1 |
| c = 17.043 (5) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 101.233 (3)° | Block, purple |
| V = 1720.9 (8) Å3 | 0.31 × 0.18 × 0.16 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3927 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2563 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.033 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.4° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −18→18 |
| Tmin = 0.930, Tmax = 0.963 | k = −9→8 |
| 14642 measured reflections | l = −22→22 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.044 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.141 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0591P)2 + 0.5672P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3927 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 241 parameters | Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.26 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| Cl1 | 1.37753 (4) | 0.52156 (11) | 0.44085 (5) | 0.0871 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.9625 (4) | 0.559 (3) | 0.2905 (6) | 0.109 (4) | 0.56 (3) |
| O2 | 1.0758 (7) | 0.659 (2) | 0.2334 (6) | 0.115 (4) | 0.56 (3) |
| O3 | 0.81516 (9) | 0.7932 (3) | 0.36241 (8) | 0.0666 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.8703 | 0.7643 | 0.3663 | 0.100* | |
| O1' | 0.9670 (8) | 0.689 (4) | 0.2804 (4) | 0.100 (5) | 0.44 (3) |
| O2' | 1.0687 (12) | 0.545 (5) | 0.2372 (10) | 0.156 (8) | 0.44 (3) |
| N1 | 1.04252 (15) | 0.6167 (4) | 0.29115 (12) | 0.0765 (6) | |
| N2 | 0.98233 (10) | 0.7293 (2) | 0.43581 (9) | 0.0475 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.96277 (10) | 0.7767 (2) | 0.50347 (9) | 0.0468 (4) | |
| C1 | 1.10633 (13) | 0.6202 (3) | 0.36932 (12) | 0.0528 (5) | |
| C2 | 1.19824 (14) | 0.5718 (3) | 0.36947 (14) | 0.0597 (5) | |
| H2 | 1.2171 | 0.5395 | 0.3221 | 0.072* | |
| C3 | 1.26084 (14) | 0.5723 (3) | 0.44035 (15) | 0.0599 (6) | |
| C4 | 1.23301 (14) | 0.6162 (3) | 0.51114 (14) | 0.0606 (5) | |
| H4 | 1.2760 | 0.6122 | 0.5592 | 0.073* | |
| C5 | 1.14154 (13) | 0.6660 (3) | 0.51035 (12) | 0.0537 (5) | |
| H5 | 1.1233 | 0.6963 | 0.5582 | 0.064* | |
| C6 | 1.07582 (12) | 0.6716 (3) | 0.43917 (11) | 0.0468 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.87202 (12) | 0.8321 (3) | 0.50305 (10) | 0.0425 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.85301 (13) | 0.8758 (3) | 0.57888 (11) | 0.0465 (4) | |
| H8 | 0.9010 | 0.8707 | 0.6236 | 0.056* | |
| C9 | 0.76528 (13) | 0.9255 (3) | 0.58763 (10) | 0.0473 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.69528 (13) | 0.9379 (3) | 0.51815 (11) | 0.0485 (5) | |
| H10 | 0.6358 | 0.9748 | 0.5242 | 0.058* | |
| C11 | 0.70815 (12) | 0.8993 (3) | 0.44168 (10) | 0.0485 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.79931 (12) | 0.8412 (3) | 0.43353 (10) | 0.0465 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.74126 (16) | 0.9610 (4) | 0.66868 (11) | 0.0646 (6) | |
| H13A | 0.7066 | 0.8553 | 0.6831 | 0.097* | |
| H13B | 0.7042 | 1.0738 | 0.6666 | 0.097* | |
| H13C | 0.7978 | 0.9763 | 0.7078 | 0.097* | |
| C14 | 0.62867 (14) | 0.9137 (4) | 0.36802 (12) | 0.0658 (6) | |
| C15 | 0.53856 (16) | 0.9904 (5) | 0.39088 (14) | 0.0868 (9) | |
| H15A | 0.5192 | 0.9069 | 0.4290 | 0.130* | |
| H15B | 0.4901 | 0.9979 | 0.3439 | 0.130* | |
| H15C | 0.5502 | 1.1142 | 0.4139 | 0.130* | |
| C16 | 0.65620 (18) | 1.0504 (5) | 0.30642 (14) | 0.0959 (10) | |
| H16A | 0.6645 | 1.1753 | 0.3290 | 0.144* | |
| H16B | 0.6077 | 1.0528 | 0.2594 | 0.144* | |
| H16C | 0.7136 | 1.0087 | 0.2924 | 0.144* | |
| C17 | 0.60711 (17) | 0.7157 (5) | 0.33203 (15) | 0.0931 (10) | |
| H17A | 0.6629 | 0.6623 | 0.3190 | 0.140* | |
| H17B | 0.5598 | 0.7250 | 0.2844 | 0.140* | |
| H17C | 0.5852 | 0.6360 | 0.3701 | 0.140* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0412 (3) | 0.1022 (5) | 0.1217 (6) | 0.0083 (3) | 0.0251 (3) | 0.0142 (4) |
| O1 | 0.052 (2) | 0.186 (11) | 0.084 (3) | −0.001 (4) | −0.001 (2) | −0.047 (5) |
| O2 | 0.105 (4) | 0.185 (9) | 0.056 (3) | −0.001 (5) | 0.016 (3) | 0.012 (4) |
| O3 | 0.0420 (7) | 0.1165 (13) | 0.0417 (7) | 0.0091 (8) | 0.0094 (6) | −0.0118 (8) |
| O1' | 0.070 (4) | 0.173 (13) | 0.055 (3) | 0.043 (5) | 0.007 (2) | −0.013 (4) |
| O2' | 0.115 (7) | 0.255 (18) | 0.091 (7) | 0.062 (10) | 0.007 (5) | −0.080 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0612 (13) | 0.1073 (17) | 0.0606 (12) | 0.0158 (13) | 0.0106 (10) | −0.0208 (12) |
| N2 | 0.0388 (8) | 0.0553 (10) | 0.0491 (9) | −0.0003 (7) | 0.0102 (7) | −0.0025 (7) |
| N3 | 0.0412 (8) | 0.0512 (9) | 0.0478 (9) | −0.0017 (7) | 0.0083 (7) | −0.0007 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0465 (11) | 0.0550 (12) | 0.0571 (12) | 0.0003 (9) | 0.0106 (9) | −0.0026 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0503 (12) | 0.0634 (14) | 0.0702 (14) | 0.0041 (10) | 0.0232 (11) | 0.0006 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0385 (10) | 0.0570 (13) | 0.0869 (16) | 0.0007 (9) | 0.0186 (11) | 0.0079 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0429 (11) | 0.0655 (13) | 0.0699 (14) | −0.0021 (9) | 0.0021 (10) | 0.0061 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0455 (11) | 0.0588 (12) | 0.0561 (12) | −0.0017 (9) | 0.0084 (9) | 0.0023 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0394 (9) | 0.0460 (10) | 0.0554 (11) | −0.0029 (8) | 0.0104 (8) | −0.0006 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0374 (9) | 0.0472 (10) | 0.0425 (9) | −0.0019 (7) | 0.0072 (7) | −0.0006 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0469 (10) | 0.0531 (11) | 0.0378 (9) | −0.0022 (8) | 0.0038 (8) | 0.0008 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0515 (11) | 0.0542 (11) | 0.0380 (9) | −0.0012 (9) | 0.0131 (8) | 0.0004 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0418 (10) | 0.0617 (12) | 0.0441 (10) | 0.0039 (8) | 0.0139 (8) | 0.0015 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0402 (10) | 0.0668 (13) | 0.0384 (9) | −0.0008 (9) | 0.0074 (7) | 0.0002 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0418 (10) | 0.0606 (12) | 0.0381 (9) | 0.0003 (8) | 0.0102 (8) | −0.0032 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0651 (13) | 0.0909 (17) | 0.0408 (10) | 0.0048 (12) | 0.0178 (10) | −0.0003 (11) |
| C14 | 0.0399 (11) | 0.115 (2) | 0.0415 (10) | 0.0116 (11) | 0.0065 (8) | −0.0021 (11) |
| C15 | 0.0470 (12) | 0.156 (3) | 0.0552 (13) | 0.0292 (15) | 0.0053 (10) | 0.0027 (15) |
| C16 | 0.0679 (16) | 0.170 (3) | 0.0488 (13) | 0.0225 (18) | 0.0092 (11) | 0.0315 (16) |
| C17 | 0.0536 (14) | 0.154 (3) | 0.0663 (15) | −0.0061 (16) | −0.0019 (11) | −0.0380 (17) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—C3 | 1.737 (2) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| O1—N1 | 1.233 (8) | C9—C10 | 1.407 (3) |
| O2—N1 | 1.217 (8) | C9—C13 | 1.511 (2) |
| O3—C12 | 1.322 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.379 (2) |
| O3—H3 | 0.8200 | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| O1'—N1 | 1.195 (7) | C11—C12 | 1.423 (2) |
| O2'—N1 | 1.179 (10) | C11—C14 | 1.537 (3) |
| N1—C1 | 1.469 (3) | C13—H13A | 0.9600 |
| N2—N3 | 1.285 (2) | C13—H13B | 0.9600 |
| N2—C6 | 1.413 (2) | C13—H13C | 0.9600 |
| N3—C7 | 1.378 (2) | C14—C17 | 1.534 (4) |
| C1—C2 | 1.382 (3) | C14—C16 | 1.536 (4) |
| C1—C6 | 1.397 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.540 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.365 (3) | C15—H15A | 0.9600 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C15—H15B | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.381 (3) | C15—H15C | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.376 (3) | C16—H16A | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C16—H16B | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.392 (3) | C16—H16C | 0.9600 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C17—H17A | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.408 (2) | C17—H17B | 0.9600 |
| C7—C12 | 1.429 (3) | C17—H17C | 0.9600 |
| C8—C9 | 1.362 (3) | ||
| C12—O3—H3 | 109.5 | C9—C10—H10 | 117.5 |
| O2'—N1—O1' | 119.6 (10) | C10—C11—C12 | 116.78 (16) |
| O2—N1—O1 | 126.8 (8) | C10—C11—C14 | 122.62 (17) |
| O2'—N1—C1 | 118.1 (7) | C12—C11—C14 | 120.59 (16) |
| O1'—N1—C1 | 122.2 (5) | O3—C12—C11 | 119.79 (16) |
| O2—N1—C1 | 116.6 (5) | O3—C12—C7 | 120.99 (16) |
| O1—N1—C1 | 116.4 (6) | C11—C12—C7 | 119.20 (15) |
| N3—N2—C6 | 114.81 (15) | C9—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| N2—N3—C7 | 116.74 (15) | C9—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 122.12 (19) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—N1 | 116.10 (18) | C9—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—N1 | 121.77 (17) | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 118.8 (2) | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.6 | C17—C14—C16 | 111.1 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.6 | C17—C14—C11 | 109.2 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.94 (19) | C16—C14—C11 | 110.12 (19) |
| C2—C3—Cl1 | 119.29 (17) | C17—C14—C15 | 107.7 (2) |
| C4—C3—Cl1 | 119.75 (18) | C16—C14—C15 | 107.5 (2) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.8 (2) | C11—C14—C15 | 111.17 (17) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.1 | C14—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.1 | C14—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.11 (19) | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.4 | C14—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.4 | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 117.11 (17) | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—N2 | 122.56 (17) | C14—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—N2 | 120.32 (17) | C14—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| N3—C7—C8 | 114.70 (16) | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| N3—C7—C12 | 124.97 (16) | C14—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—C12 | 120.30 (16) | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 120.93 (17) | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.5 | C14—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.5 | C14—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 117.79 (16) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—C13 | 122.19 (17) | C14—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C13 | 120.00 (17) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 124.95 (17) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—H10 | 117.5 | ||
| C6—N2—N3—C7 | −179.36 (15) | N2—N3—C7—C8 | 177.70 (16) |
| O2'—N1—C1—C2 | 12 (2) | N2—N3—C7—C12 | −0.3 (3) |
| O1'—N1—C1—C2 | −165.3 (16) | N3—C7—C8—C9 | −177.44 (18) |
| O2—N1—C1—C2 | −32.9 (10) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | 0.7 (3) |
| O1—N1—C1—C2 | 142.5 (11) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −2.1 (3) |
| O2'—N1—C1—C6 | −168 (2) | C7—C8—C9—C13 | 176.00 (19) |
| O1'—N1—C1—C6 | 14.0 (16) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 1.5 (3) |
| O2—N1—C1—C6 | 146.4 (10) | C13—C9—C10—C11 | −176.6 (2) |
| O1—N1—C1—C6 | −38.2 (11) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.6 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.7 (3) | C9—C10—C11—C14 | 179.5 (2) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −179.9 (2) | C10—C11—C12—O3 | 176.69 (19) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.4 (3) | C14—C11—C12—O3 | −2.2 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—Cl1 | −177.30 (16) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | −2.0 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −2.0 (3) | C14—C11—C12—C7 | 179.05 (19) |
| Cl1—C3—C4—C5 | 176.67 (17) | N3—C7—C12—O3 | 0.7 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.5 (3) | C8—C7—C12—O3 | −177.22 (18) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 1.5 (3) | N3—C7—C12—C11 | 179.40 (18) |
| C4—C5—C6—N2 | −177.41 (19) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | 1.5 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −2.1 (3) | C10—C11—C14—C17 | −114.1 (2) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | 178.6 (2) | C12—C11—C14—C17 | 64.7 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—N2 | 176.80 (19) | C10—C11—C14—C16 | 123.6 (2) |
| N1—C1—C6—N2 | −2.5 (3) | C12—C11—C14—C16 | −57.5 (3) |
| N3—N2—C6—C5 | 0.2 (3) | C10—C11—C14—C15 | 4.6 (3) |
| N3—N2—C6—C1 | −178.68 (17) | C12—C11—C14—C15 | −176.6 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O3—H3···O1' | 0.82 | 2.28 | 2.933 (7) | 136 |
| O3—H3···O1 | 0.82 | 2.50 | 3.142 (12) | 136 |
| O3—H3···N2 | 0.82 | 1.84 | 2.553 (2) | 145 |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LH2824).
References
- Bruker (2006). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Crawford, J. C. (1999). Prog. Polym. Sci 24, 7–43.
- Ravichandran, R., Suhadolnik, J., Wood, M. G., Debeillis, A., Detlefsen, R. E., Iyengar, R. & Wolf, J. P. (2002). US Patent No. 6 458 872.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K. & Toda, F. (2000). Chem. Rev.100, 1025–1074. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.-L., Chen, Y.-H., Hu, H.-W., Zhou, X.-Y. & Liu, C.-B. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o4702–o4703.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809019631/lh2824sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809019631/lh2824Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



