Abstract
In the title compound, C13H16ClNO, the cyclohexyl ring adopts a chair conformation, with puckering parameters Q = 0.576 (3) Å, θ = 0.1 (3) and ϕ = 8 (15)°. In the crystal structure, intermolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link molecules into one-dimensional chains propagating in [010].
Related literature
For applications of N-substituted benzamides, see: Beccalli et al. (2005 ▶); Calderone et al. (2006 ▶); Vega-Noverola et al. (1989 ▶); Zhichkin et al. (2007 ▶); Lindgren et al. (2001 ▶); Olsson et al. (2002 ▶). For related crystal structures, see: Jones & Kuś (2004 ▶); Saeed et al. (2008 ▶). For puckering parameters, see: Cremer & Pople (1975 ▶). For a description of the Cambridge Structural Database, see: Allen (2002 ▶). 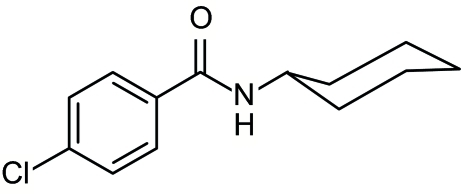
Experimental
Crystal data
C13H16ClNO
M r = 237.72
Monoclinic,

a = 14.755 (14) Å
b = 5.043 (7) Å
c = 16.818 (16) Å
β = 96.13 (6)°
V = 1244 (2) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.29 mm−1
T = 173 K
0.12 × 0.08 × 0.06 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SORTAV; Blessing, 1997 ▶) T min = 0.967, T max = 0.983
3651 measured reflections
2388 independent reflections
1497 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.034
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.051
wR(F 2) = 0.151
S = 1.06
2388 reflections
145 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3
Data collection: COLLECT (Hooft, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: DENZO (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); data reduction: SCALEPACK (Otwinowski & Minor, 1997 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809021217/lh2834sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809021217/lh2834Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯O1i | 0.88 | 2.06 | 2.901 (5) | 160 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
N-Substituted benzamides, e.g., declopramideare, are well known anticancer compounds and the mechanism of benzamide-induced apoptosis has been studied, (Olsson et al., 2002). N-substituted benzamides inhibit the activity of nuclear factor-B and nuclear factor of activated T cells (Lindgren et al., 2001). Various N-substituted benzamides exhibit potent antiemetic activity (Vega-Noverola et al., 1989), while heterocyclic benzanilide are potassium channel activators (Calderone et al., 2006). N-Alkylated 2-nitrobenzamides are intermediates in the synthesis of dibenzo[b,e][1,4]diazepines (Zhichkin et al., 2007) and N-Acyl-2-nitrobenzamides are precursors of 2,3-disubstitued 3H-quinazoline-4-ones (Beccalli et al., 2005). As part of our work on the structure of benzanilides and related compounds, in this paper, we report the crystal structure of the title compound, (I).
The molecular structure of (I) is presented in Fig. 1. The molecular dimensions in (I) are normal (CSD version 5.30; Allen, 2002). The six-membered ring adopts a chair conformation with puckering parameters: Q = 0.576 (3) Å, θ = 0.1 (3)° and φ = 8(15)° (Cremer & Pople, 1975). The structure is stabilized by hydrogen bonding (N1–H1···O1) forming chains of molecules along the b-axis (details are in Table 1). The crystal structures of closely related compounds have been reported (Saeed et al., 2008; Jones & Kuś, 2004).
Experimental
4-Chlorobenzoyl chloride (5.4 mmol) in CHCl3 was treated with cyclohexylamine (21.6 mmol) under a nitrogen atmosphere at reflux for 3 h. Upon cooling, the reaction mixture was diluted with CHCl3 and washed consecutively with aq 1 M HCl and saturated aq NaHCO3. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate and concentrated under reduced pressure. Crystallization of the residue in CHCl3 afforded the title compound (87%) as colorless needles: Anal. calcd. for C13H16ClNO,: C, 65.68; H, 6.78; N, 5.89%; found: C, 65.61; H, 6.80; N, 5.91%.
Refinement
All the H-atoms were visible in the difference Fourier maps, they were included in the refinements at geometrically idealized positions with N—H = 0.88 Å and C—H distances = 0.95 - 0.99 Å, and Uiso = 1.2 times Ueq of the atoms to which they were bonded. The final difference map was free of chemically significant features.
Figures
Fig. 1.
ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997) drawing of (I) with displacement ellipsoids plotted at 30% probability level.
Crystal data
| C13H16ClNO | F(000) = 504 |
| Mr = 237.72 | Dx = 1.269 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 3651 reflections |
| a = 14.755 (14) Å | θ = 3.9–26.0° |
| b = 5.043 (7) Å | µ = 0.29 mm−1 |
| c = 16.818 (16) Å | T = 173 K |
| β = 96.13 (6)° | Needle, colorless |
| V = 1244 (2) Å3 | 0.12 × 0.08 × 0.06 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2388 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1497 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.034 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 3.9° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SORTAV; Blessing, 1997) | h = −18→17 |
| Tmin = 0.967, Tmax = 0.983 | k = −6→4 |
| 3651 measured reflections | l = −20→20 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.051 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.151 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.06 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0665P)2 + 0.3764P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2388 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 145 parameters | Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.77571 (5) | 0.29595 (19) | 0.35603 (5) | 0.0739 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.35835 (12) | 0.8003 (3) | 0.37556 (11) | 0.0489 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.32675 (14) | 0.3654 (4) | 0.38965 (14) | 0.0491 (6) | |
| H1 | 0.3492 | 0.2036 | 0.3922 | 0.059* | |
| C1 | 0.48155 (15) | 0.4944 (5) | 0.37540 (13) | 0.0369 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.52269 (17) | 0.2853 (5) | 0.41805 (15) | 0.0462 (6) | |
| H2 | 0.4884 | 0.1813 | 0.4512 | 0.055* | |
| C3 | 0.61349 (18) | 0.2254 (6) | 0.41296 (16) | 0.0529 (7) | |
| H3 | 0.6419 | 0.0831 | 0.4431 | 0.063* | |
| C4 | 0.66205 (17) | 0.3746 (6) | 0.36373 (15) | 0.0489 (7) | |
| C5 | 0.62262 (18) | 0.5866 (6) | 0.32108 (16) | 0.0539 (7) | |
| H5 | 0.6569 | 0.6895 | 0.2876 | 0.065* | |
| C6 | 0.53255 (18) | 0.6464 (5) | 0.32789 (15) | 0.0474 (6) | |
| H6 | 0.5051 | 0.7938 | 0.2996 | 0.057* | |
| C7 | 0.38370 (16) | 0.5666 (5) | 0.38013 (13) | 0.0388 (6) | |
| C8 | 0.22970 (16) | 0.3992 (5) | 0.39603 (16) | 0.0484 (7) | |
| H8 | 0.2181 | 0.5912 | 0.4058 | 0.058* | |
| C9 | 0.20142 (17) | 0.2430 (7) | 0.46572 (16) | 0.0564 (8) | |
| H9A | 0.2371 | 0.3025 | 0.5157 | 0.068* | |
| H9B | 0.2142 | 0.0524 | 0.4582 | 0.068* | |
| C10 | 0.0997 (2) | 0.2819 (9) | 0.4724 (2) | 0.0789 (11) | |
| H10A | 0.0816 | 0.1731 | 0.5171 | 0.095* | |
| H10B | 0.0881 | 0.4702 | 0.4845 | 0.095* | |
| C11 | 0.04290 (19) | 0.2051 (7) | 0.3968 (2) | 0.0735 (10) | |
| H11A | −0.0221 | 0.2421 | 0.4022 | 0.088* | |
| H11B | 0.0494 | 0.0126 | 0.3875 | 0.088* | |
| C12 | 0.0718 (2) | 0.3567 (8) | 0.3267 (2) | 0.0819 (11) | |
| H12A | 0.0588 | 0.5476 | 0.3333 | 0.098* | |
| H12B | 0.0360 | 0.2949 | 0.2770 | 0.098* | |
| C13 | 0.1742 (2) | 0.3193 (7) | 0.31917 (18) | 0.0699 (9) | |
| H13A | 0.1864 | 0.1313 | 0.3072 | 0.084* | |
| H13B | 0.1920 | 0.4289 | 0.2746 | 0.084* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0443 (4) | 0.0948 (7) | 0.0840 (6) | 0.0035 (4) | 0.0128 (4) | −0.0220 (5) |
| O1 | 0.0535 (11) | 0.0273 (9) | 0.0662 (12) | 0.0040 (8) | 0.0080 (9) | 0.0016 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0406 (11) | 0.0278 (12) | 0.0806 (15) | 0.0040 (9) | 0.0135 (11) | 0.0015 (10) |
| C1 | 0.0413 (12) | 0.0304 (12) | 0.0393 (12) | −0.0013 (10) | 0.0055 (10) | −0.0056 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0445 (13) | 0.0408 (14) | 0.0535 (15) | 0.0020 (12) | 0.0069 (11) | 0.0053 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0475 (15) | 0.0517 (17) | 0.0589 (16) | 0.0078 (13) | 0.0025 (12) | 0.0025 (14) |
| C4 | 0.0410 (13) | 0.0589 (18) | 0.0472 (14) | −0.0017 (13) | 0.0063 (11) | −0.0165 (13) |
| C5 | 0.0550 (16) | 0.0583 (18) | 0.0510 (15) | −0.0079 (14) | 0.0183 (13) | −0.0018 (14) |
| C6 | 0.0527 (15) | 0.0415 (16) | 0.0486 (14) | −0.0019 (12) | 0.0086 (12) | 0.0051 (12) |
| C7 | 0.0462 (14) | 0.0305 (14) | 0.0399 (13) | 0.0006 (11) | 0.0058 (10) | −0.0009 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0396 (13) | 0.0292 (13) | 0.0768 (18) | 0.0047 (11) | 0.0074 (13) | −0.0048 (13) |
| C9 | 0.0407 (14) | 0.078 (2) | 0.0518 (15) | 0.0046 (14) | 0.0100 (12) | −0.0119 (14) |
| C10 | 0.0473 (16) | 0.113 (3) | 0.080 (2) | 0.0028 (18) | 0.0212 (15) | −0.016 (2) |
| C11 | 0.0400 (15) | 0.067 (2) | 0.113 (3) | −0.0003 (14) | 0.0070 (17) | −0.018 (2) |
| C12 | 0.0597 (19) | 0.088 (3) | 0.091 (2) | 0.0080 (18) | −0.0240 (17) | −0.005 (2) |
| C13 | 0.0609 (18) | 0.088 (2) | 0.0589 (17) | 0.0027 (17) | −0.0039 (14) | 0.0122 (17) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—C4 | 1.742 (3) | C8—C13 | 1.510 (4) |
| O1—C7 | 1.236 (3) | C8—H8 | 1.0000 |
| N1—C7 | 1.338 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.530 (4) |
| N1—C8 | 1.457 (3) | C9—H9A | 0.9900 |
| N1—H1 | 0.8800 | C9—H9B | 0.9900 |
| C1—C2 | 1.379 (4) | C10—C11 | 1.496 (5) |
| C1—C6 | 1.386 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9900 |
| C1—C7 | 1.499 (3) | C10—H10B | 0.9900 |
| C2—C3 | 1.385 (4) | C11—C12 | 1.505 (5) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C11—H11A | 0.9900 |
| C3—C4 | 1.375 (4) | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C12—C13 | 1.541 (4) |
| C4—C5 | 1.381 (4) | C12—H12A | 0.9900 |
| C5—C6 | 1.379 (4) | C12—H12B | 0.9900 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C13—H13A | 0.9900 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C13—H13B | 0.9900 |
| C8—C9 | 1.508 (4) | ||
| C7—N1—C8 | 123.7 (2) | C8—C9—C10 | 110.2 (2) |
| C7—N1—H1 | 118.1 | C8—C9—H9A | 109.6 |
| C8—N1—H1 | 118.1 | C10—C9—H9A | 109.6 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.1 (2) | C8—C9—H9B | 109.6 |
| C2—C1—C7 | 122.1 (2) | C10—C9—H9B | 109.6 |
| C6—C1—C7 | 118.8 (2) | H9A—C9—H9B | 108.1 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 120.6 (2) | C11—C10—C9 | 111.7 (3) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.7 | C11—C10—H10A | 109.3 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.7 | C9—C10—H10A | 109.3 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.2 (3) | C11—C10—H10B | 109.3 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.4 | C9—C10—H10B | 109.3 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.4 | H10A—C10—H10B | 107.9 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.2 (3) | C10—C11—C12 | 110.8 (3) |
| C3—C4—Cl1 | 119.2 (2) | C10—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—Cl1 | 119.6 (2) | C12—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 118.8 (2) | C10—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.6 | C12—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.6 | H11A—C11—H11B | 108.1 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 121.0 (3) | C11—C12—C13 | 111.3 (3) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.5 | C11—C12—H12A | 109.4 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.5 | C13—C12—H12A | 109.4 |
| O1—C7—N1 | 122.7 (2) | C11—C12—H12B | 109.4 |
| O1—C7—C1 | 121.0 (2) | C13—C12—H12B | 109.4 |
| N1—C7—C1 | 116.3 (2) | H12A—C12—H12B | 108.0 |
| N1—C8—C9 | 110.6 (2) | C8—C13—C12 | 110.1 (3) |
| N1—C8—C13 | 110.7 (2) | C8—C13—H13A | 109.6 |
| C9—C8—C13 | 110.9 (2) | C12—C13—H13A | 109.6 |
| N1—C8—H8 | 108.2 | C8—C13—H13B | 109.6 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 108.2 | C12—C13—H13B | 109.6 |
| C13—C8—H8 | 108.2 | H13A—C13—H13B | 108.1 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.7 (4) | C6—C1—C7—O1 | −32.8 (3) |
| C7—C1—C2—C3 | −179.3 (2) | C2—C1—C7—N1 | −34.0 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.0 (4) | C6—C1—C7—N1 | 147.4 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.7 (4) | C7—N1—C8—C9 | −132.2 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—Cl1 | −178.9 (2) | C7—N1—C8—C13 | 104.5 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.6 (4) | N1—C8—C9—C10 | 179.5 (2) |
| Cl1—C4—C5—C6 | −180.0 (2) | C13—C8—C9—C10 | −57.3 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −1.2 (4) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 56.9 (4) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 1.8 (4) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −56.0 (4) |
| C7—C1—C6—C5 | −179.5 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 55.5 (4) |
| C8—N1—C7—O1 | −0.3 (4) | N1—C8—C13—C12 | −179.8 (3) |
| C8—N1—C7—C1 | 179.5 (2) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | 57.0 (3) |
| C2—C1—C7—O1 | 145.9 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | −56.1 (4) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···O1i | 0.88 | 2.06 | 2.901 (5) | 160 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y−1, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LH2834).
References
- Allen, F. H. (2002). Acta Cryst. B58, 380–388. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Beccalli, E. M., Broggini, G., Paladinoa, G. & Zonia, C. (2005). Tetrahedron, 61, 61–68.
- Blessing, R. H. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 421–426.
- Calderone, V., Fiamingo, F. L., Giorgi, I., Leonardi, M., Livi, O., Martelli, A. & Martinotti, E. (2006). Eur. J. Med. Chem.41, 761–767. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc.97, 1354–1358.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Hooft, R. (1998). COLLECT Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Jones, P. G. & Kuś, P. (2004). Acta Cryst. E60, o1299–o1300.
- Lindgren, H., Pero, R. W., Ivars, F. & Leanderson, T. (2001). Mol. Immunol.38, 267–277. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Olsson, A. R., Lindgren, H., Pero, R. W. & Leanderson, T. (2002). Br. J. Cancer, 86, 971–978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Saeed, A., Abbas, N., Hussain, S. & Flörke, U. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Vega-Noverola, A. P., Soto, J. M., Noguera, F. P., Mauri, J. M. & Spickett, G. W. R. (1989). US Patent No. 4 877 780.
- Zhichkin, P., Kesicki, E., Treiberg, J., Bourdon, L., Ronsheim, M., Ooi, H. C., White, S., Judkins, A. & Fairfax, D. (2007). Org. Lett.9, 1415–1418. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809021217/lh2834sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809021217/lh2834Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



