Abstract
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, C11H12N2O4, contains two crystallographically independent molecules with similar geometries. Both molecules contain an intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond. The dihedral angles between the benzene ring and the mean plane of the cyclobutane ring are 38.29 (7) and 57.04 (8)° in the two molecules, and the nitro group is twisted slightly away from the plane of the benzene ring [dihedral angles = 9.15 (12) and 9.55 (12)° in the two molecules]. In the crystal, the independent molecules are linked into dimers by O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds between their carboxyl groups, and C—H⋯O and C—H⋯π interactions are formed between dimers.
Related literature
For the biological activity of benzimidazole derivatives, see: Wright (1951 ▶); Singh et al. (2009 ▶). For details of the synthesis, see: Narendra Babu et al. (2009a
▶,b
▶); Ishida et al. (2006 ▶).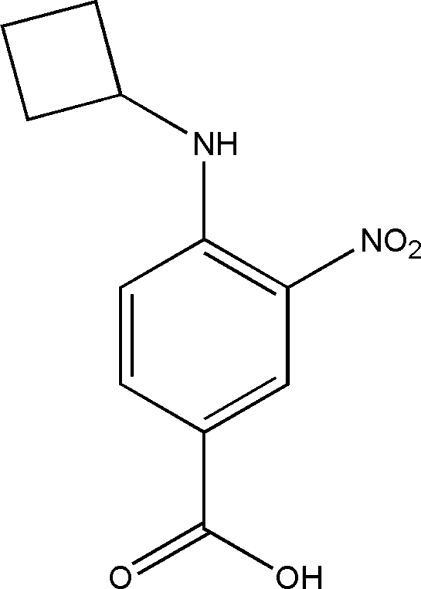
Experimental
Crystal data
C11H12N2O4
M r = 236.23
Triclinic,

a = 9.8555 (2) Å
b = 10.5308 (2) Å
c = 10.9110 (2) Å
α = 74.860 (1)°
β = 78.265 (1)°
γ = 84.826 (1)°
V = 1069.44 (4) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.11 mm−1
T = 110 K
0.37 × 0.23 × 0.21 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.960, T max = 0.976
29344 measured reflections
7670 independent reflections
6094 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.027
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.048
wR(F 2) = 0.139
S = 1.05
7670 reflections
315 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.68 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2005 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809021412/bi2372sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809021412/bi2372Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2A—H1OA⋯O1Bi | 0.81 | 1.76 | 2.5608 (13) | 166 |
| O2B—H1OB⋯O1Aii | 0.83 | 1.89 | 2.7118 (12) | 170 |
| N2A—H1NA⋯O4A | 0.89 (2) | 1.93 (2) | 2.6332 (13) | 135.3 (17) |
| N2B—H1NB⋯O4B | 0.80 (2) | 2.05 (2) | 2.6432 (13) | 130.7 (18) |
| C8B—H8BB⋯O4Aiii | 0.97 | 2.54 | 3.4613 (16) | 158 |
| C8B—H8BA⋯Cg1iv | 0.97 | 2.83 | 3.4744 (13) | 124 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii) 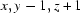 ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  . Cg1 is the centroid of the C1B–C6B benzene ring.
. Cg1 is the centroid of the C1B–C6B benzene ring.
Acknowledgments
SNNB, ASAR and HO are grateful to Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM) for funding the synthetic chemistry work under the University Research Grant (1001/PFARMASI/815026). SNNB acknowledges USM for a Postdoctoral Research Fellowship. HKF and CKQ thank USM for the Research University Golden Goose Grant (1001/PFIZIK/811012). CKQ thanks USM for a Research Fellowship.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Multi functionalized benzimidazole remains as an attractive scaffold to display essential binding moieties against many validated biological targets (Wright, 1951; Singh et al., 2009). This heterocycle is commonly accessed via nitro benzoic acid derivatives, which form a part of our current synthetic chemistry work (Narendra Babu et al., 2009a&b; Ishida et al., 2006). Recently, we have successfully synthesized the title compound, whose crystal structure is described here.
The asymmetric unit contains two crystallographically independent molecules (Fig. 1), A and B with similar geometries. An intramolecular N–H···O hydrogen bond is formed in both independent molecules. The dihedral angle formed by the C1A–C6A benzene ring and C7A–C10A cyclobutane is 38.29 (7)° and that between the C1B–C6B benzene ring and C7B–C10B cyclobutane is 57.04 (8)°. The nitro group in each molecule is slightly twisted away from the attached benzene ring as indicated by the torsion angle O3—N1—C1—C2, being 7.97 (15)° and 7.80 (14)° in molecules A and B, respectively.
The crystal packing (Fig. 2) is consolidated by intermolecular O—H···O and C—H···O hydrogen bonds. Molecules are linked by O—H···O hydrogen bonds between their carboxylate groups to form dimers. The crystal structure is further stabilized by C—H···π (Table 1) interactions involving the C1B–C6B benzene ring (centroid Cg1) and short O4B···O4B contacts (symmetry code: 2 - x, 1 - y, 1 - z) with distance = 2.8957 (12) Å which is shorter than the sum of van der Waals radii of the O atoms.
Experimental
The title compound was obtained by refluxing ethyl 4-(cyclobutylamino)-3-nitro-benzoate (0.2 g, 0.0007 mol) and KOH (0.08 g, 0.0015 mol) in aqueous ethanol (5 ml) for 3 h. After completion of the reaction, ethanol was distilled off and the reaction mixture was diluted with water (5 ml). The aqueous layer was washed with dichloromethane (2 × 5 ml) and acidified with concentrated hydrochloric acid to afford a yellow solid. Yellow crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained after recrystallization of the crude product with hot ethyl acetate.
Refinement
H atoms bound to N and O atoms were located from difference Fourier maps. Atoms H1NA and H1NB were refined freely, while atoms H1OA and H1OB were refined as riding on the parent O atom with Uiso(H) = 1.5 Ueq(O). The remaining H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model, with C—H = 0.93–0.98 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2 or 1.5 Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound, showing 50% probability displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms. The dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds.
Fig. 2.

Packing diagram viewed along the a axis. Intermolecular interactions are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C11H12N2O4 | Z = 4 |
| Mr = 236.23 | F(000) = 496 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.467 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.8555 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 9970 reflections |
| b = 10.5308 (2) Å | θ = 2.1–34.1° |
| c = 10.9110 (2) Å | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| α = 74.860 (1)° | T = 110 K |
| β = 78.265 (1)° | Block, yellow |
| γ = 84.826 (1)° | 0.37 × 0.23 × 0.21 mm |
| V = 1069.44 (4) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEXII CCD diffractometer | 7670 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 6094 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.027 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 32.5°, θmin = 2.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | h = −13→14 |
| Tmin = 0.960, Tmax = 0.976 | k = −15→15 |
| 29344 measured reflections | l = −16→16 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.048 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.139 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.079P)2 + 0.2648P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 7670 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 315 parameters | Δρmax = 0.68 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. The crystal was placed in the cold stream of an Oxford Cyrosystems Cobra open-flow nitrogen cryostat operating at 110.0 (1) K. Cosier, J. & Glazer, A. M. (1986). J. Appl. Cryst.19, 105–107. |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1A | 0.41436 (8) | 0.68803 (8) | −0.08160 (8) | 0.02153 (17) | |
| O2A | 0.24499 (9) | 0.80673 (8) | 0.01400 (9) | 0.02327 (17) | |
| H1OA | 0.2969 | 0.8671 | −0.0208 | 0.035* | |
| O3A | −0.16874 (10) | 0.63616 (9) | 0.25760 (10) | 0.0315 (2) | |
| O4A | −0.22880 (9) | 0.43744 (8) | 0.28295 (10) | 0.02693 (19) | |
| N1A | −0.14187 (9) | 0.52458 (9) | 0.24261 (9) | 0.01836 (18) | |
| N2A | −0.04041 (10) | 0.25875 (8) | 0.22307 (9) | 0.01699 (17) | |
| C1A | −0.00540 (10) | 0.49386 (10) | 0.17520 (10) | 0.01442 (17) | |
| C2A | 0.07959 (10) | 0.59982 (10) | 0.11780 (10) | 0.01488 (18) | |
| H2AA | 0.0469 | 0.6840 | 0.1240 | 0.018* | |
| C3A | 0.21236 (10) | 0.58164 (10) | 0.05150 (10) | 0.01456 (17) | |
| C4A | 0.26136 (10) | 0.45284 (10) | 0.04592 (10) | 0.01638 (18) | |
| H4AA | 0.3507 | 0.4394 | 0.0023 | 0.020* | |
| C5A | 0.17907 (11) | 0.34694 (10) | 0.10395 (10) | 0.01650 (18) | |
| H5AA | 0.2147 | 0.2629 | 0.1001 | 0.020* | |
| C6A | 0.04005 (10) | 0.36263 (9) | 0.17013 (9) | 0.01448 (17) | |
| C7A | 0.00443 (12) | 0.12158 (10) | 0.24008 (10) | 0.01755 (19) | |
| H7AA | 0.0805 | 0.1007 | 0.2885 | 0.021* | |
| C8A | 0.03497 (12) | 0.06059 (10) | 0.12218 (11) | 0.0202 (2) | |
| H8AA | −0.0060 | 0.1105 | 0.0496 | 0.024* | |
| H8AB | 0.1325 | 0.0396 | 0.0947 | 0.024* | |
| C9A | −0.04894 (13) | −0.05907 (11) | 0.20696 (11) | 0.0229 (2) | |
| H9AA | −0.1156 | −0.0859 | 0.1652 | 0.027* | |
| H9AB | 0.0080 | −0.1337 | 0.2436 | 0.027* | |
| C10A | −0.11338 (13) | 0.02595 (11) | 0.30201 (11) | 0.0235 (2) | |
| H10A | −0.2046 | 0.0642 | 0.2902 | 0.028* | |
| H10B | −0.1131 | −0.0179 | 0.3920 | 0.028* | |
| C11A | 0.29658 (10) | 0.69811 (10) | −0.00959 (10) | 0.01597 (18) | |
| O1B | 0.37447 (9) | 0.02069 (9) | 0.91518 (9) | 0.02540 (18) | |
| O2B | 0.55207 (10) | −0.08564 (8) | 0.81460 (9) | 0.02504 (18) | |
| H1OB | 0.5107 | −0.1537 | 0.8547 | 0.038* | |
| O3B | 0.91441 (9) | 0.17243 (8) | 0.51738 (8) | 0.02423 (18) | |
| O4B | 0.93948 (9) | 0.37738 (8) | 0.50719 (9) | 0.02599 (19) | |
| N1B | 0.87317 (9) | 0.27498 (9) | 0.54966 (9) | 0.01787 (17) | |
| N2B | 0.73342 (10) | 0.51524 (9) | 0.61428 (9) | 0.01799 (17) | |
| C1B | 0.74352 (10) | 0.27632 (10) | 0.63934 (10) | 0.01530 (18) | |
| C2B | 0.68286 (11) | 0.15493 (10) | 0.69549 (10) | 0.01604 (18) | |
| H2BA | 0.7277 | 0.0790 | 0.6762 | 0.019* | |
| C3B | 0.55681 (11) | 0.14668 (10) | 0.77957 (10) | 0.01613 (18) | |
| C4B | 0.48894 (11) | 0.26379 (10) | 0.80444 (10) | 0.01760 (19) | |
| H4BA | 0.4031 | 0.2595 | 0.8595 | 0.021* | |
| C5B | 0.54711 (11) | 0.38380 (10) | 0.74909 (10) | 0.01740 (19) | |
| H5BA | 0.4991 | 0.4591 | 0.7669 | 0.021* | |
| C6B | 0.67903 (10) | 0.39638 (10) | 0.66502 (10) | 0.01536 (18) | |
| C7B | 0.65788 (11) | 0.63794 (10) | 0.62404 (10) | 0.01690 (18) | |
| H7BA | 0.6232 | 0.6385 | 0.7147 | 0.020* | |
| C8B | 0.54323 (12) | 0.68736 (12) | 0.54265 (12) | 0.0239 (2) | |
| H8BA | 0.5534 | 0.6522 | 0.4674 | 0.029* | |
| H8BB | 0.4497 | 0.6780 | 0.5926 | 0.029* | |
| C9B | 0.59819 (13) | 0.82720 (11) | 0.51283 (13) | 0.0249 (2) | |
| H9BA | 0.6070 | 0.8749 | 0.4228 | 0.030* | |
| H9BB | 0.5483 | 0.8803 | 0.5693 | 0.030* | |
| C10B | 0.73574 (12) | 0.76364 (10) | 0.55077 (11) | 0.0208 (2) | |
| H10C | 0.8066 | 0.7525 | 0.4780 | 0.025* | |
| H10D | 0.7719 | 0.8058 | 0.6059 | 0.025* | |
| C11B | 0.49108 (11) | 0.01977 (10) | 0.83986 (10) | 0.01689 (19) | |
| H1NA | −0.124 (2) | 0.2777 (18) | 0.2638 (18) | 0.038 (5)* | |
| H1NB | 0.805 (2) | 0.5208 (18) | 0.5636 (18) | 0.035 (5)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1A | 0.0161 (3) | 0.0208 (4) | 0.0240 (4) | −0.0040 (3) | 0.0020 (3) | −0.0025 (3) |
| O2A | 0.0194 (4) | 0.0128 (3) | 0.0356 (5) | −0.0029 (3) | −0.0012 (3) | −0.0049 (3) |
| O3A | 0.0237 (4) | 0.0165 (4) | 0.0500 (6) | −0.0019 (3) | 0.0087 (4) | −0.0125 (4) |
| O4A | 0.0160 (4) | 0.0180 (4) | 0.0415 (5) | −0.0058 (3) | 0.0052 (3) | −0.0044 (3) |
| N1A | 0.0148 (4) | 0.0143 (4) | 0.0234 (4) | −0.0015 (3) | 0.0000 (3) | −0.0027 (3) |
| N2A | 0.0180 (4) | 0.0103 (4) | 0.0205 (4) | −0.0027 (3) | −0.0002 (3) | −0.0020 (3) |
| C1A | 0.0128 (4) | 0.0122 (4) | 0.0169 (4) | −0.0012 (3) | −0.0014 (3) | −0.0021 (3) |
| C2A | 0.0150 (4) | 0.0114 (4) | 0.0173 (4) | −0.0014 (3) | −0.0031 (3) | −0.0015 (3) |
| C3A | 0.0140 (4) | 0.0120 (4) | 0.0167 (4) | −0.0026 (3) | −0.0029 (3) | −0.0011 (3) |
| C4A | 0.0141 (4) | 0.0151 (4) | 0.0194 (4) | −0.0003 (3) | −0.0025 (3) | −0.0039 (3) |
| C5A | 0.0166 (4) | 0.0123 (4) | 0.0200 (4) | 0.0002 (3) | −0.0033 (3) | −0.0032 (3) |
| C6A | 0.0164 (4) | 0.0116 (4) | 0.0149 (4) | −0.0020 (3) | −0.0036 (3) | −0.0014 (3) |
| C7A | 0.0228 (5) | 0.0102 (4) | 0.0193 (4) | −0.0021 (3) | −0.0047 (4) | −0.0019 (3) |
| C8A | 0.0239 (5) | 0.0149 (4) | 0.0215 (5) | −0.0003 (4) | −0.0036 (4) | −0.0043 (4) |
| C9A | 0.0327 (6) | 0.0137 (4) | 0.0242 (5) | −0.0039 (4) | −0.0082 (4) | −0.0049 (4) |
| C10A | 0.0311 (6) | 0.0140 (4) | 0.0233 (5) | −0.0083 (4) | 0.0007 (4) | −0.0030 (4) |
| C11A | 0.0149 (4) | 0.0140 (4) | 0.0183 (4) | −0.0026 (3) | −0.0036 (3) | −0.0018 (3) |
| O1B | 0.0196 (4) | 0.0211 (4) | 0.0306 (4) | −0.0075 (3) | 0.0025 (3) | −0.0011 (3) |
| O2B | 0.0304 (4) | 0.0145 (4) | 0.0284 (4) | −0.0049 (3) | −0.0012 (3) | −0.0040 (3) |
| O3B | 0.0265 (4) | 0.0204 (4) | 0.0240 (4) | −0.0019 (3) | 0.0033 (3) | −0.0082 (3) |
| O4B | 0.0185 (4) | 0.0176 (4) | 0.0358 (5) | −0.0053 (3) | 0.0044 (3) | −0.0016 (3) |
| N1B | 0.0166 (4) | 0.0166 (4) | 0.0183 (4) | −0.0021 (3) | −0.0013 (3) | −0.0017 (3) |
| N2B | 0.0160 (4) | 0.0133 (4) | 0.0221 (4) | −0.0024 (3) | −0.0012 (3) | −0.0011 (3) |
| C1B | 0.0137 (4) | 0.0145 (4) | 0.0164 (4) | −0.0030 (3) | −0.0017 (3) | −0.0016 (3) |
| C2B | 0.0170 (4) | 0.0133 (4) | 0.0174 (4) | −0.0025 (3) | −0.0031 (3) | −0.0025 (3) |
| C3B | 0.0164 (4) | 0.0134 (4) | 0.0177 (4) | −0.0040 (3) | −0.0029 (3) | −0.0014 (3) |
| C4B | 0.0154 (4) | 0.0164 (4) | 0.0191 (4) | −0.0025 (3) | −0.0011 (3) | −0.0022 (4) |
| C5B | 0.0157 (4) | 0.0146 (4) | 0.0200 (5) | −0.0016 (3) | −0.0015 (3) | −0.0022 (3) |
| C6B | 0.0153 (4) | 0.0134 (4) | 0.0169 (4) | −0.0020 (3) | −0.0043 (3) | −0.0015 (3) |
| C7B | 0.0185 (4) | 0.0129 (4) | 0.0186 (4) | −0.0014 (3) | −0.0043 (4) | −0.0017 (3) |
| C8B | 0.0188 (5) | 0.0209 (5) | 0.0304 (6) | −0.0031 (4) | −0.0089 (4) | 0.0008 (4) |
| C9B | 0.0241 (5) | 0.0166 (5) | 0.0308 (6) | −0.0003 (4) | −0.0080 (4) | 0.0018 (4) |
| C10B | 0.0221 (5) | 0.0131 (4) | 0.0270 (5) | −0.0038 (4) | −0.0080 (4) | −0.0011 (4) |
| C11B | 0.0168 (4) | 0.0145 (4) | 0.0186 (4) | −0.0039 (3) | −0.0028 (3) | −0.0022 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1A—C11A | 1.2752 (13) | O1B—C11B | 1.2705 (13) |
| O2A—C11A | 1.2763 (12) | O2B—C11B | 1.2812 (13) |
| O2A—H1OA | 0.815 | O2B—H1OB | 0.829 |
| O3A—N1A | 1.2264 (12) | O3B—N1B | 1.2316 (12) |
| O4A—N1A | 1.2439 (12) | O4B—N1B | 1.2440 (12) |
| N1A—C1A | 1.4484 (13) | N1B—C1B | 1.4442 (13) |
| N2A—C6A | 1.3413 (13) | N2B—C6B | 1.3412 (13) |
| N2A—C7A | 1.4472 (13) | N2B—C7B | 1.4497 (13) |
| N2A—H1NA | 0.888 (19) | N2B—H1NB | 0.802 (19) |
| C1A—C2A | 1.3889 (14) | C1B—C2B | 1.3952 (14) |
| C1A—C6A | 1.4254 (13) | C1B—C6B | 1.4313 (14) |
| C2A—C3A | 1.3836 (14) | C2B—C3B | 1.3808 (14) |
| C2A—H2AA | 0.930 | C2B—H2BA | 0.930 |
| C3A—C4A | 1.4105 (13) | C3B—C4B | 1.4122 (14) |
| C3A—C11A | 1.4728 (14) | C3B—C11B | 1.4704 (14) |
| C4A—C5A | 1.3740 (14) | C4B—C5B | 1.3718 (14) |
| C4A—H4AA | 0.930 | C4B—H4BA | 0.930 |
| C5A—C6A | 1.4300 (14) | C5B—C6B | 1.4254 (14) |
| C5A—H5AA | 0.930 | C5B—H5BA | 0.930 |
| C7A—C10A | 1.5347 (15) | C7B—C10B | 1.5365 (15) |
| C7A—C8A | 1.5483 (15) | C7B—C8B | 1.5482 (15) |
| C7A—H7AA | 0.980 | C7B—H7BA | 0.980 |
| C8A—C9A | 1.5477 (16) | C8B—C9B | 1.5458 (17) |
| C8A—H8AA | 0.970 | C8B—H8BA | 0.970 |
| C8A—H8AB | 0.970 | C8B—H8BB | 0.970 |
| C9A—C10A | 1.5476 (16) | C9B—C10B | 1.5418 (16) |
| C9A—H9AA | 0.970 | C9B—H9BA | 0.970 |
| C9A—H9AB | 0.970 | C9B—H9BB | 0.970 |
| C10A—H10A | 0.970 | C10B—H10C | 0.970 |
| C10A—H10B | 0.970 | C10B—H10D | 0.970 |
| C11A—O2A—H1OA | 111.9 | C11B—O2B—H1OB | 114.1 |
| O3A—N1A—O4A | 121.83 (9) | O3B—N1B—O4B | 122.07 (9) |
| O3A—N1A—C1A | 119.01 (9) | O3B—N1B—C1B | 118.88 (9) |
| O4A—N1A—C1A | 119.16 (9) | O4B—N1B—C1B | 119.05 (9) |
| C6A—N2A—C7A | 126.24 (9) | C6B—N2B—C7B | 123.78 (9) |
| C6A—N2A—H1NA | 114.6 (12) | C6B—N2B—H1NB | 118.5 (13) |
| C7A—N2A—H1NA | 118.1 (12) | C7B—N2B—H1NB | 116.5 (13) |
| C2A—C1A—C6A | 121.97 (9) | C2B—C1B—C6B | 122.19 (9) |
| C2A—C1A—N1A | 115.91 (9) | C2B—C1B—N1B | 116.19 (9) |
| C6A—C1A—N1A | 122.12 (9) | C6B—C1B—N1B | 121.58 (9) |
| C3A—C2A—C1A | 120.77 (9) | C3B—C2B—C1B | 120.48 (9) |
| C3A—C2A—H2AA | 119.6 | C3B—C2B—H2BA | 119.8 |
| C1A—C2A—H2AA | 119.6 | C1B—C2B—H2BA | 119.8 |
| C2A—C3A—C4A | 118.77 (9) | C2B—C3B—C4B | 118.68 (9) |
| C2A—C3A—C11A | 118.30 (9) | C2B—C3B—C11B | 121.37 (9) |
| C4A—C3A—C11A | 122.93 (9) | C4B—C3B—C11B | 119.92 (9) |
| C5A—C4A—C3A | 121.02 (9) | C5B—C4B—C3B | 121.34 (10) |
| C5A—C4A—H4AA | 119.5 | C5B—C4B—H4BA | 119.3 |
| C3A—C4A—H4AA | 119.5 | C3B—C4B—H4BA | 119.3 |
| C4A—C5A—C6A | 121.66 (9) | C4B—C5B—C6B | 121.84 (9) |
| C4A—C5A—H5AA | 119.2 | C4B—C5B—H5BA | 119.1 |
| C6A—C5A—H5AA | 119.2 | C6B—C5B—H5BA | 119.1 |
| N2A—C6A—C1A | 123.24 (9) | N2B—C6B—C5B | 120.09 (9) |
| N2A—C6A—C5A | 120.98 (9) | N2B—C6B—C1B | 124.48 (9) |
| C1A—C6A—C5A | 115.78 (9) | C5B—C6B—C1B | 115.42 (9) |
| N2A—C7A—C10A | 113.66 (9) | N2B—C7B—C10B | 115.50 (9) |
| N2A—C7A—C8A | 119.61 (9) | N2B—C7B—C8B | 118.69 (9) |
| C10A—C7A—C8A | 89.08 (8) | C10B—C7B—C8B | 88.50 (8) |
| N2A—C7A—H7AA | 110.9 | N2B—C7B—H7BA | 110.8 |
| C10A—C7A—H7AA | 110.9 | C10B—C7B—H7BA | 110.8 |
| C8A—C7A—H7AA | 110.9 | C8B—C7B—H7BA | 110.8 |
| C9A—C8A—C7A | 88.22 (8) | C9B—C8B—C7B | 87.84 (8) |
| C9A—C8A—H8AA | 113.9 | C9B—C8B—H8BA | 114.0 |
| C7A—C8A—H8AA | 113.9 | C7B—C8B—H8BA | 114.0 |
| C9A—C8A—H8AB | 113.9 | C9B—C8B—H8BB | 114.0 |
| C7A—C8A—H8AB | 113.9 | C7B—C8B—H8BB | 114.0 |
| H8AA—C8A—H8AB | 111.2 | H8BA—C8B—H8BB | 111.2 |
| C10A—C9A—C8A | 88.63 (8) | C10B—C9B—C8B | 88.40 (8) |
| C10A—C9A—H9AA | 113.9 | C10B—C9B—H9BA | 113.9 |
| C8A—C9A—H9AA | 113.9 | C8B—C9B—H9BA | 113.9 |
| C10A—C9A—H9AB | 113.9 | C10B—C9B—H9BB | 113.9 |
| C8A—C9A—H9AB | 113.9 | C8B—C9B—H9BB | 113.9 |
| H9AA—C9A—H9AB | 111.1 | H9BA—C9B—H9BB | 111.1 |
| C7A—C10A—C9A | 88.71 (9) | C7B—C10B—C9B | 88.40 (8) |
| C7A—C10A—H10A | 113.9 | C7B—C10B—H10C | 113.9 |
| C9A—C10A—H10A | 113.9 | C9B—C10B—H10C | 113.9 |
| C7A—C10A—H10B | 113.9 | C7B—C10B—H10D | 113.9 |
| C9A—C10A—H10B | 113.9 | C9B—C10B—H10D | 113.9 |
| H10A—C10A—H10B | 111.1 | H10C—C10B—H10D | 111.1 |
| O1A—C11A—O2A | 123.11 (10) | O1B—C11B—O2B | 122.99 (10) |
| O1A—C11A—C3A | 120.54 (9) | O1B—C11B—C3B | 117.51 (9) |
| O2A—C11A—C3A | 116.35 (9) | O2B—C11B—C3B | 119.49 (9) |
| O3A—N1A—C1A—C2A | −7.97 (15) | O3B—N1B—C1B—C2B | 7.80 (14) |
| O4A—N1A—C1A—C2A | 171.59 (10) | O4B—N1B—C1B—C2B | −172.39 (10) |
| O3A—N1A—C1A—C6A | 170.85 (10) | O3B—N1B—C1B—C6B | −169.99 (10) |
| O4A—N1A—C1A—C6A | −9.59 (15) | O4B—N1B—C1B—C6B | 9.82 (15) |
| C6A—C1A—C2A—C3A | 0.82 (16) | C6B—C1B—C2B—C3B | −0.32 (16) |
| N1A—C1A—C2A—C3A | 179.65 (9) | N1B—C1B—C2B—C3B | −178.10 (9) |
| C1A—C2A—C3A—C4A | −1.57 (15) | C1B—C2B—C3B—C4B | 1.83 (15) |
| C1A—C2A—C3A—C11A | 178.78 (9) | C1B—C2B—C3B—C11B | −179.98 (10) |
| C2A—C3A—C4A—C5A | 0.59 (15) | C2B—C3B—C4B—C5B | −1.38 (16) |
| C11A—C3A—C4A—C5A | −179.77 (10) | C11B—C3B—C4B—C5B | −179.61 (10) |
| C3A—C4A—C5A—C6A | 1.17 (16) | C3B—C4B—C5B—C6B | −0.62 (16) |
| C7A—N2A—C6A—C1A | −169.40 (10) | C7B—N2B—C6B—C5B | −9.26 (16) |
| C7A—N2A—C6A—C5A | 10.71 (16) | C7B—N2B—C6B—C1B | 169.59 (10) |
| C2A—C1A—C6A—N2A | −179.01 (10) | C4B—C5B—C6B—N2B | −179.01 (10) |
| N1A—C1A—C6A—N2A | 2.23 (16) | C4B—C5B—C6B—C1B | 2.04 (15) |
| C2A—C1A—C6A—C5A | 0.88 (15) | C2B—C1B—C6B—N2B | 179.51 (10) |
| N1A—C1A—C6A—C5A | −177.88 (9) | N1B—C1B—C6B—N2B | −2.83 (16) |
| C4A—C5A—C6A—N2A | 178.03 (10) | C2B—C1B—C6B—C5B | −1.59 (15) |
| C4A—C5A—C6A—C1A | −1.86 (15) | N1B—C1B—C6B—C5B | 176.07 (9) |
| C6A—N2A—C7A—C10A | −179.08 (10) | C6B—N2B—C7B—C10B | −175.71 (10) |
| C6A—N2A—C7A—C8A | −75.85 (14) | C6B—N2B—C7B—C8B | −72.54 (14) |
| N2A—C7A—C8A—C9A | −134.34 (10) | N2B—C7B—C8B—C9B | −138.08 (10) |
| C10A—C7A—C8A—C9A | −17.43 (9) | C10B—C7B—C8B—C9B | −19.62 (9) |
| C7A—C8A—C9A—C10A | 17.28 (9) | C7B—C8B—C9B—C10B | 19.55 (9) |
| N2A—C7A—C10A—C9A | 139.60 (9) | N2B—C7B—C10B—C9B | 140.96 (10) |
| C8A—C7A—C10A—C9A | 17.42 (8) | C8B—C7B—C10B—C9B | 19.66 (9) |
| C8A—C9A—C10A—C7A | −17.43 (9) | C8B—C9B—C10B—C7B | −19.70 (9) |
| C2A—C3A—C11A—O1A | −173.48 (10) | C2B—C3B—C11B—O1B | −179.36 (10) |
| C4A—C3A—C11A—O1A | 6.87 (16) | C4B—C3B—C11B—O1B | −1.19 (15) |
| C2A—C3A—C11A—O2A | 6.58 (14) | C2B—C3B—C11B—O2B | 0.37 (16) |
| C4A—C3A—C11A—O2A | −173.06 (10) | C4B—C3B—C11B—O2B | 178.54 (10) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2A—H1OA···O1Bi | 0.81 | 1.76 | 2.5608 (13) | 166 |
| O2B—H1OB···O1Aii | 0.83 | 1.89 | 2.7118 (12) | 170 |
| N2A—H1NA···O4A | 0.89 (2) | 1.93 (2) | 2.6332 (13) | 135.3 (17) |
| N2B—H1NB···O4B | 0.80 (2) | 2.05 (2) | 2.6432 (13) | 130.7 (18) |
| C8B—H8BB···O4Aiii | 0.97 | 2.54 | 3.4613 (16) | 158 |
| C8B—H8BA···Cg1iv | 0.97 | 2.83 | 3.4744 (13) | 124 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y+1, z−1; (ii) x, y−1, z+1; (iii) −x, −y+1, −z+1; (iv) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BI2372).
References
- Bruker (2005). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Ishida, T., Suzuki, T., Hirashima, S., Mizutani, K., Yoshida, A., Ando, I., Ikeda, S., Adachi, T. & Hashimoto, H. (2006). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.16, 1859–1863. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Narendra Babu, S. N., Abdul Rahim, A. S., Abd Hamid, S., Quah, C. K. & Fun, H.-K. (2009a). Acta Cryst. E65, o1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Narendra Babu, S. N., Abdul Rahim, A. S., Osman, H., Jebas, S. R. & Fun, H.-K. (2009b). Acta Cryst. E65, o1122–o1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Singh, S., Bharti, N. & Mohapatra, P. P. (2009). Chem. Rev.109, 1900–1947. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wright, J. B. (1951). Chem. Rev.48, 397–541. [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809021412/bi2372sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809021412/bi2372Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



