Abstract
The title compound, C18H12N2O, crystallizes in a zwitterionic form. The dihedral angle between the planes of the benzene ring and naphthalene ring system is 13.95 (5)°. An intramolecular N—H⋯O interaction results in the formation of a planar six-membered ring, which is oriented at dihedral angles of 13.50 (4) and 4.49 (4)° with respect to the benzene ring and naphthalene ring system, respectively. In the crystal structure, intermolecular C—H⋯O and C—H⋯N interactions link the molecules into a two-dimensional network. π–π contacts between the naphthalene systems [centroid–centroid distance = 3.974 (1) Å] may further stabilize the structure.
Related literature
For the pharmacological activity of Schiff base compounds, see: Dao et al. (2000 ▶); Sriram et al. (2006 ▶). For the role played by Schiff base compounds in coordination chemistry related to magnetism, see: Chen et al. (2008 ▶); Weber et al. (2007 ▶). For related structures, see: Elmali et al. (2001 ▶); Yüce et al. (2006 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶).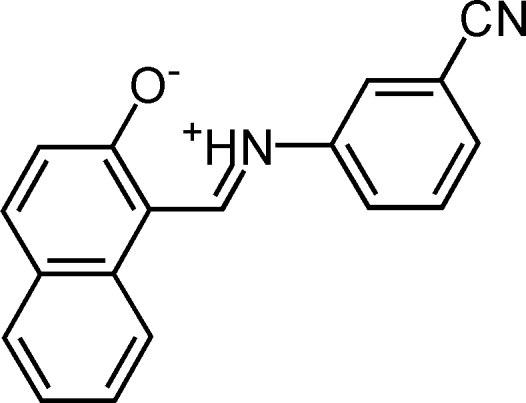
Experimental
Crystal data
C18H12N2O
M r = 272.30
Triclinic,

a = 7.8943 (16) Å
b = 9.1356 (18) Å
c = 9.4933 (19) Å
α = 83.97 (3)°
β = 84.41 (3)°
γ = 82.50 (3)°
V = 672.6 (2) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 294 K
0.20 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Rigaku SCXmini diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.976, T max = 0.983
6177 measured reflections
2628 independent reflections
1146 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.061
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.067
wR(F 2) = 0.195
S = 0.94
2628 reflections
190 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.23 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.24 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809020224/hk2700sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809020224/hk2700Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1A⋯O1 | 0.86 | 1.87 | 2.562 (3) | 136 |
| C2—H2A⋯N2i | 0.93 | 2.61 | 3.463 (3) | 152 |
| C6—H6A⋯O1ii | 0.93 | 2.57 | 3.376 (3) | 145 |
| C17—H17A⋯N2i | 0.93 | 2.62 | 3.522 (3) | 163 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Schiff base compounds have received considerable attention for many years, primarily due to various pharmacological activities, such as anticancer (Dao et al., 2000) and anti-HIV (Sriram et al., 2006) activities. In addition, Schiff base compounds play important roles in coordination chemistry related to magnetism (Weber et al., 2007) and catalysis (Chen et al., 2008). Generally, Schiff base compounds exhibit the phenol-imine and keto-amine forms. Another form of the Schiff base compounds is their zwitterionic form, and this form have been reported in the literature (Elmali, et al., 2001). We report herein the crystal structure of the title compound.
The molecule of the title compound (Fig 1) is in a zwitterionic form. The bond lengths (Allen et al., 1987) and angles are within normal ranges, and C8=N1 [1.304 (4) Å] and C10-O1 [1.287 (4) Å] bonds may be compared with the corresponding values [1.2954 (19) and 1.2946 (17) Å] in a similar zwitterionic structure (Yüce et al., 2006). Phenyl and naphthalyl rings, A (C1-C6) and B (C9-C18), are, of course, planar and the dihedral angle between them is 13.95 (5)°. Intramolecular N-H···O interaction (Table 1) results in the formation of a planar six-membered ring C (O1/N1/C8-C10/H1A), which is oriented with respect to rings A and B at dihedral angles of 13.50 (4) and 4.49 (4) °, respectively.
In the crystal structure, intramolecular N-H···O and intermolecular C-H···O and C-H···N interactions (Table 1) link the molecules into a two-dimensional network (Fig. 2), in which they may be effective in the stabilization of the structure. The π–π contact between the naphthalyl rings, Cg2—Cg2i [symmetry code: (i) -x, 1 - y, 1 - z, where Cg2 is centroid of the ring (C9-C13/C18)] may further stabilize the structure, with centroid-centroid distance of 3.974 (1) Å.
Experimental
For the preparation of the title compound, 3-aminobenzonitrile (0.59 g, 5 mmol) and 2-hydroxynaphthalene-1-carbaldehyde (0.861 g, 5 mmol) were dissolved in ethanol (25 ml). The resulting mixture was heated to reflux for 6 h, and then cooled to room temperature. The solid product was collected by filtration. Crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained on slow evaporation at room temperature.
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically, with N-H = 0.86 Å (for NH) and C-H = 0.93 Å for aromatic H and constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C,N).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title molecule, with the atom-numbering scheme. Hydrogen bond is shown as dashed line.
Fig. 2.
A partial packing diagram of the title compound. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C18H12N2O | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 272.30 | F(000) = 284 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.345 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 7.8943 (16) Å | Cell parameters from 4320 reflections |
| b = 9.1356 (18) Å | θ = 3.2–27.5° |
| c = 9.4933 (19) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| α = 83.97 (3)° | T = 294 K |
| β = 84.41 (3)° | Prism, yellow |
| γ = 82.50 (3)° | 0.20 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm |
| V = 672.6 (2) Å3 |
Data collection
| Rigaku SCXmini diffractometer | 2628 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1146 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.061 |
| Detector resolution: 13.6612 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 3.2° |
| ω scans | h = −9→9 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku, 2005) | k = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.976, Tmax = 0.983 | l = −11→11 |
| 6177 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.067 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.195 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 0.94 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0919P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2628 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.016 |
| 190 parameters | Δρmax = 0.23 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.9002 (3) | 0.6505 (3) | 0.2062 (2) | 0.0608 (8) | |
| N1 | 0.7833 (3) | 0.3998 (3) | 0.2569 (3) | 0.0439 (7) | |
| H1A | 0.8270 | 0.4652 | 0.1974 | 0.053* | |
| N2 | 0.4237 (5) | −0.1364 (4) | 0.3557 (4) | 0.0852 (12) | |
| C1 | 0.7515 (4) | 0.2689 (4) | 0.2031 (3) | 0.0421 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.6494 (4) | 0.1697 (3) | 0.2774 (3) | 0.0452 (9) | |
| H2A | 0.5984 | 0.1876 | 0.3675 | 0.054* | |
| C3 | 0.6234 (4) | 0.0444 (4) | 0.2177 (4) | 0.0482 (9) | |
| C4 | 0.6973 (5) | 0.0157 (4) | 0.0832 (4) | 0.0609 (11) | |
| H4A | 0.6799 | −0.0695 | 0.0437 | 0.073* | |
| C5 | 0.7971 (5) | 0.1160 (4) | 0.0093 (4) | 0.0654 (11) | |
| H5A | 0.8467 | 0.0985 | −0.0812 | 0.079* | |
| C6 | 0.8240 (4) | 0.2410 (4) | 0.0675 (3) | 0.0514 (10) | |
| H6A | 0.8914 | 0.3077 | 0.0160 | 0.062* | |
| C7 | 0.5115 (5) | −0.0569 (4) | 0.2954 (4) | 0.0611 (11) | |
| C8 | 0.7525 (4) | 0.4310 (3) | 0.3886 (3) | 0.0408 (8) | |
| H8A | 0.7016 | 0.3630 | 0.4536 | 0.049* | |
| C9 | 0.7916 (4) | 0.5615 (3) | 0.4381 (3) | 0.0405 (8) | |
| C10 | 0.8725 (4) | 0.6662 (3) | 0.3400 (4) | 0.0433 (9) | |
| C11 | 0.9241 (5) | 0.7903 (4) | 0.3945 (4) | 0.0576 (11) | |
| H11A | 0.9789 | 0.8582 | 0.3323 | 0.069* | |
| C12 | 0.8969 (5) | 0.8139 (4) | 0.5334 (4) | 0.0577 (10) | |
| H12A | 0.9334 | 0.8968 | 0.5645 | 0.069* | |
| C13 | 0.8122 (4) | 0.7125 (3) | 0.6335 (4) | 0.0424 (9) | |
| C14 | 0.7876 (4) | 0.7374 (4) | 0.7790 (4) | 0.0533 (10) | |
| H14A | 0.8261 | 0.8199 | 0.8091 | 0.064* | |
| C15 | 0.7077 (4) | 0.6415 (4) | 0.8761 (4) | 0.0554 (10) | |
| H15A | 0.6908 | 0.6590 | 0.9715 | 0.067* | |
| C16 | 0.6524 (4) | 0.5185 (4) | 0.8304 (4) | 0.0509 (9) | |
| H16A | 0.5981 | 0.4529 | 0.8957 | 0.061* | |
| C17 | 0.6766 (4) | 0.4920 (4) | 0.6902 (3) | 0.0483 (9) | |
| H17A | 0.6374 | 0.4087 | 0.6623 | 0.058* | |
| C18 | 0.7585 (4) | 0.5863 (3) | 0.5875 (3) | 0.0367 (8) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.083 (2) | 0.0657 (17) | 0.0347 (15) | −0.0255 (14) | 0.0047 (13) | 0.0010 (12) |
| N1 | 0.0520 (19) | 0.0430 (17) | 0.0370 (17) | −0.0146 (13) | 0.0051 (13) | −0.0025 (14) |
| N2 | 0.120 (3) | 0.064 (2) | 0.076 (3) | −0.043 (2) | 0.011 (2) | −0.010 (2) |
| C1 | 0.043 (2) | 0.044 (2) | 0.040 (2) | −0.0072 (16) | −0.0024 (16) | −0.0059 (17) |
| C2 | 0.057 (2) | 0.044 (2) | 0.035 (2) | −0.0102 (18) | 0.0011 (16) | −0.0075 (16) |
| C3 | 0.057 (2) | 0.042 (2) | 0.048 (2) | −0.0068 (18) | −0.0062 (18) | −0.0107 (17) |
| C4 | 0.079 (3) | 0.055 (2) | 0.051 (3) | −0.008 (2) | −0.004 (2) | −0.018 (2) |
| C5 | 0.083 (3) | 0.069 (3) | 0.047 (2) | −0.018 (2) | 0.010 (2) | −0.020 (2) |
| C6 | 0.053 (2) | 0.061 (2) | 0.040 (2) | −0.0129 (19) | 0.0046 (17) | −0.0033 (18) |
| C7 | 0.080 (3) | 0.051 (2) | 0.054 (3) | −0.014 (2) | −0.001 (2) | −0.011 (2) |
| C8 | 0.040 (2) | 0.044 (2) | 0.038 (2) | −0.0066 (16) | 0.0015 (15) | −0.0029 (16) |
| C9 | 0.039 (2) | 0.041 (2) | 0.041 (2) | −0.0065 (16) | −0.0007 (15) | 0.0003 (16) |
| C10 | 0.052 (2) | 0.0366 (19) | 0.042 (2) | −0.0093 (16) | −0.0054 (17) | −0.0010 (16) |
| C11 | 0.070 (3) | 0.047 (2) | 0.058 (3) | −0.0253 (19) | −0.001 (2) | 0.003 (2) |
| C12 | 0.068 (3) | 0.050 (2) | 0.060 (3) | −0.022 (2) | −0.003 (2) | −0.007 (2) |
| C13 | 0.041 (2) | 0.042 (2) | 0.046 (2) | −0.0029 (16) | −0.0066 (16) | −0.0074 (17) |
| C14 | 0.053 (2) | 0.055 (2) | 0.056 (3) | −0.0066 (19) | −0.0103 (19) | −0.020 (2) |
| C15 | 0.058 (2) | 0.064 (3) | 0.043 (2) | −0.003 (2) | 0.0004 (18) | −0.009 (2) |
| C16 | 0.057 (2) | 0.051 (2) | 0.043 (2) | −0.0085 (18) | 0.0046 (17) | −0.0013 (18) |
| C17 | 0.052 (2) | 0.045 (2) | 0.048 (2) | −0.0097 (18) | 0.0029 (17) | −0.0074 (18) |
| C18 | 0.0366 (19) | 0.0372 (19) | 0.0377 (19) | −0.0076 (15) | −0.0012 (14) | −0.0074 (15) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C10 | 1.287 (4) | C9—C10 | 1.431 (4) |
| N1—C1 | 1.409 (4) | C9—C18 | 1.453 (4) |
| N1—C8 | 1.304 (4) | C11—C10 | 1.416 (4) |
| N1—H1A | 0.8600 | C11—C12 | 1.350 (5) |
| N2—C7 | 1.142 (4) | C11—H11A | 0.9300 |
| C2—C1 | 1.384 (4) | C12—H12A | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.376 (4) | C13—C12 | 1.435 (4) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9300 | C13—C14 | 1.414 (4) |
| C4—C3 | 1.387 (5) | C13—C18 | 1.403 (4) |
| C4—C5 | 1.377 (5) | C14—H14A | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9300 | C15—C14 | 1.370 (4) |
| C5—H5A | 0.9300 | C15—C16 | 1.382 (5) |
| C6—C1 | 1.392 (4) | C15—H15A | 0.9300 |
| C6—C5 | 1.369 (5) | C16—H16A | 0.9300 |
| C6—H6A | 0.9300 | C17—C16 | 1.369 (4) |
| C7—C3 | 1.458 (5) | C17—C18 | 1.399 (4) |
| C8—H8A | 0.9300 | C17—H17A | 0.9300 |
| C9—C8 | 1.406 (4) | ||
| C1—N1—H1A | 117.0 | O1—C10—C9 | 122.5 (3) |
| C8—N1—C1 | 126.0 (3) | O1—C10—C11 | 119.7 (3) |
| C8—N1—H1A | 117.0 | C11—C10—C9 | 117.8 (3) |
| C2—C1—N1 | 123.1 (3) | C10—C11—H11A | 118.7 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 119.0 (3) | C12—C11—C10 | 122.6 (3) |
| C6—C1—N1 | 117.9 (3) | C12—C11—H11A | 118.7 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 120.1 | C11—C12—C13 | 120.8 (3) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.8 (3) | C11—C12—H12A | 119.6 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 120.1 | C13—C12—H12A | 119.6 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.1 (3) | C14—C13—C12 | 120.0 (3) |
| C2—C3—C7 | 119.2 (3) | C18—C13—C12 | 119.9 (3) |
| C4—C3—C7 | 119.6 (3) | C18—C13—C14 | 120.0 (3) |
| C3—C4—H4A | 120.7 | C13—C14—H14A | 119.6 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 118.6 (4) | C15—C14—C13 | 120.8 (3) |
| C5—C4—H4A | 120.7 | C15—C14—H14A | 119.6 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 119.6 | C14—C15—C16 | 119.1 (3) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.9 (4) | C14—C15—H15A | 120.5 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 119.6 | C16—C15—H15A | 120.5 |
| C1—C6—H6A | 119.7 | C15—C16—H16A | 119.6 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 120.5 (3) | C17—C16—C15 | 120.8 (3) |
| C5—C6—H6A | 119.7 | C17—C16—H16A | 119.6 |
| N2—C7—C3 | 179.7 (4) | C16—C17—C18 | 122.1 (3) |
| N1—C8—C9 | 123.9 (3) | C16—C17—H17A | 119.0 |
| N1—C8—H8A | 118.0 | C18—C17—H17A | 119.0 |
| C9—C8—H8A | 118.0 | C13—C18—C9 | 118.5 (3) |
| C8—C9—C10 | 118.8 (3) | C17—C18—C13 | 117.1 (3) |
| C8—C9—C18 | 120.7 (3) | C17—C18—C9 | 124.4 (3) |
| C10—C9—C18 | 120.4 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1A···O1 | 0.86 | 1.87 | 2.562 (3) | 136 |
| C2—H2A···N2i | 0.93 | 2.61 | 3.463 (3) | 152 |
| C6—H6A···O1ii | 0.93 | 2.57 | 3.376 (3) | 145 |
| C17—H17A···N2i | 0.93 | 2.62 | 3.522 (3) | 163 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (ii) −x+2, −y+1, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HK2700).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Chen, Z. H., Morimoto, H., Matsunaga, S. & Shibasaki, M. (2008). J. Am. Chem. Soc.130, 2170–2171. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dao, V.-T., Gaspard, C., Mayer, M., Werner, G. H., Nguyen, S. N. & Michelot, R. J. (2000). Eur. J. Med. Chem.35, 805–813. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Elmali, A., Elerman, Y. & Svoboda, I. (2001). Acta Cryst. C57, 485–486. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Rigaku (2005). CrystalClear Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sriram, D., Yogeeswari, P., Myneedu, N. S. & Saraswat, V. (2006). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.16, 2127–2129. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Weber, B., Tandon, R. & Himsl, D. (2007). Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem.633, 1159–1162.
- Yüce, S., Albayrak, Ç., Odabaşoğlu, M. & Büyükgüngör, O. (2006). Acta Cryst. C62, o389–o393. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809020224/hk2700sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809020224/hk2700Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




